-
109articlesSort byLatested
 High-risk neuroblastoma stage 4 (NBS4): multi-target inhibitors for c-Src kinases (Csk) and retinoic acid (RA) signalling pathwaysOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This paper investigates two possible treatment targets for neuroblastoma (NB) stage 4 (NBS4), c-Src kinase (Csk) and retinoic acid (RA) signalling pathways as potential candidates for a mult...Amgad Gerges, Una CanningPublished: May 09, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008109
High-risk neuroblastoma stage 4 (NBS4): multi-target inhibitors for c-Src kinases (Csk) and retinoic acid (RA) signalling pathwaysOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This paper investigates two possible treatment targets for neuroblastoma (NB) stage 4 (NBS4), c-Src kinase (Csk) and retinoic acid (RA) signalling pathways as potential candidates for a mult...Amgad Gerges, Una CanningPublished: May 09, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008109 Combinatorial and fragment-based in silico design of PI3K-alpha natural hybrid antagonists for breast cancer therapeuticsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)-alpha isoform is found upregulated in 30–40% of breast cancer. Currently, there are limited selective and specific drugs that target PI3K-alpha, and no...Navya Aggarwal ... Banashree BondhopadhyayPublished: April 29, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008108
Combinatorial and fragment-based in silico design of PI3K-alpha natural hybrid antagonists for breast cancer therapeuticsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)-alpha isoform is found upregulated in 30–40% of breast cancer. Currently, there are limited selective and specific drugs that target PI3K-alpha, and no...Navya Aggarwal ... Banashree BondhopadhyayPublished: April 29, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008108 Synthesis and antitumoral activity of novel biaryl hydroxy-triazole and fluorene-triazole hybridsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of selective and potent antitumor agents remains a significant challenge. This study aimed to synthesize and evaluate biaryl hydroxy-1,2,3-triazoles and 9H-fluorene-1,2,3-tri...David Chafi Zeitune ... Camilla Djenne BuarquePublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008107
Synthesis and antitumoral activity of novel biaryl hydroxy-triazole and fluorene-triazole hybridsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of selective and potent antitumor agents remains a significant challenge. This study aimed to synthesize and evaluate biaryl hydroxy-1,2,3-triazoles and 9H-fluorene-1,2,3-tri...David Chafi Zeitune ... Camilla Djenne BuarquePublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008107 Natural products targeting cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic approachOpen AccessReviewCancer remains the second leading cause of death globally, posing an ongoing threat to public health. A hallmark of cancer cells is their capacity to invade adjacent tissues and evolve into malignan...Julia K. Opara ... Shrikant AnantPublished: April 18, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008106
Natural products targeting cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic approachOpen AccessReviewCancer remains the second leading cause of death globally, posing an ongoing threat to public health. A hallmark of cancer cells is their capacity to invade adjacent tissues and evolve into malignan...Julia K. Opara ... Shrikant AnantPublished: April 18, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008106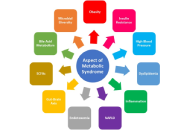 A narrative review on the role of gut microbiome, dietary strategies, and supplements in managing metabolic syndromeOpen AccessReviewMetabolic syndrome is a complex, multifactorial disorder, with emerging research emphasizing the significant role of gut health in its prevention and management. Recent studies suggest that dietary ...Sunil Chopra ... Ramendra Pati PandeyPublished: April 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008105
A narrative review on the role of gut microbiome, dietary strategies, and supplements in managing metabolic syndromeOpen AccessReviewMetabolic syndrome is a complex, multifactorial disorder, with emerging research emphasizing the significant role of gut health in its prevention and management. Recent studies suggest that dietary ...Sunil Chopra ... Ramendra Pati PandeyPublished: April 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008105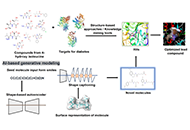 Revolutionizing diabetes treatment: computational insights into 4-hydroxy isoleucine derivatives and advanced molecular screening for antidiabetic compoundsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to computationally identify and optimize 4-hydroxy isoleucine (4HILe) derivatives from fenugreek as multitarget antidiabetic agents against α-glucosidase, α-amylase, and a...Lakshmi Mounika Kelam ... M. Elizabeth SobhiaPublished: April 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008104
Revolutionizing diabetes treatment: computational insights into 4-hydroxy isoleucine derivatives and advanced molecular screening for antidiabetic compoundsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to computationally identify and optimize 4-hydroxy isoleucine (4HILe) derivatives from fenugreek as multitarget antidiabetic agents against α-glucosidase, α-amylase, and a...Lakshmi Mounika Kelam ... M. Elizabeth SobhiaPublished: April 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008104 Folic acid conjugated with serum albumin for nano- and submicron delivery systems for applications in therapy and diagnosticsOpen AccessReviewFolic acid (FA) residue is a well-known and widely spread targeting ligand, or biovector, used as a component in engineering artificial nanosized and submicron particles (NSPs) to target various cel...Maria G. Gorobets ... Anna V. BychkovaPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008101
Folic acid conjugated with serum albumin for nano- and submicron delivery systems for applications in therapy and diagnosticsOpen AccessReviewFolic acid (FA) residue is a well-known and widely spread targeting ligand, or biovector, used as a component in engineering artificial nanosized and submicron particles (NSPs) to target various cel...Maria G. Gorobets ... Anna V. BychkovaPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008101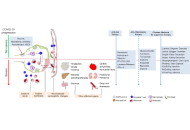 Novel progression on clinical therapy of COVID-19: Western and Traditional Chinese MedicinesOpen AccessReviewSevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel coronavirus that causes a global epidemic named COVID-19. It still continues to plague humans with severe complications and un...Yongjia Xiong ... Feiyue XingPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008102
Novel progression on clinical therapy of COVID-19: Western and Traditional Chinese MedicinesOpen AccessReviewSevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel coronavirus that causes a global epidemic named COVID-19. It still continues to plague humans with severe complications and un...Yongjia Xiong ... Feiyue XingPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008102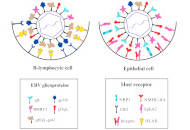 The use of peptides for deciphering the mechanism of EBV, HPV, and HCV invasion of human cellsOpen AccessReviewEpstein-Barr virus (EBV), human papillomavirus (HPV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are significant human pathogens associated with various diseases, employing complex molecular mechanisms for cellula...Daniela Perdomo-Joven ... Mauricio Urquiza-MartinezPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008103
The use of peptides for deciphering the mechanism of EBV, HPV, and HCV invasion of human cellsOpen AccessReviewEpstein-Barr virus (EBV), human papillomavirus (HPV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are significant human pathogens associated with various diseases, employing complex molecular mechanisms for cellula...Daniela Perdomo-Joven ... Mauricio Urquiza-MartinezPublished: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008103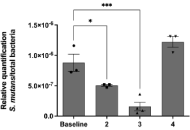 Efficacy of propolis varnish in reducing Streptococcus mutans countsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate the efficacy of experimental propolis varnish containing 15% green propolis in reducing Streptococcus mutans (SM) from saliva and dental biofilms. Methods: Patients aged 8...Mariana Passos De Luca ... Vagner Rodrigues SantosPublished: March 20, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100899
Efficacy of propolis varnish in reducing Streptococcus mutans countsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To evaluate the efficacy of experimental propolis varnish containing 15% green propolis in reducing Streptococcus mutans (SM) from saliva and dental biofilms. Methods: Patients aged 8...Mariana Passos De Luca ... Vagner Rodrigues SantosPublished: March 20, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100899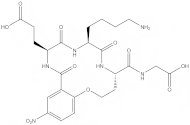 Dimeric dipeptide mimetics of neurotrophins as molecular tools and potential neuroprotective drugsOpen AccessReviewProteins from the neurotrophin family perform trophic and regulatory functions in the nervous and other body systems. Understanding the mechanisms of neurotrophin action is crucial not only for the ...Tatiana Gudasheva ... Vladimir DorofeevPublished: March 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008100
Dimeric dipeptide mimetics of neurotrophins as molecular tools and potential neuroprotective drugsOpen AccessReviewProteins from the neurotrophin family perform trophic and regulatory functions in the nervous and other body systems. Understanding the mechanisms of neurotrophin action is crucial not only for the ...Tatiana Gudasheva ... Vladimir DorofeevPublished: March 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.1008100 Multidrug resistance and major facilitator superfamily antimicrobial efflux pumps of the ESKAPEE pathogen Staphylococcus aureusOpen AccessReviewMultiple drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacterial pathogens are causative agents of serious infectious disease and are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality rates. Of particular ...Ebenezer Aborah ... Manuel F. VarelaPublished: March 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100897
Multidrug resistance and major facilitator superfamily antimicrobial efflux pumps of the ESKAPEE pathogen Staphylococcus aureusOpen AccessReviewMultiple drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacterial pathogens are causative agents of serious infectious disease and are responsible for significant morbidity and mortality rates. Of particular ...Ebenezer Aborah ... Manuel F. VarelaPublished: March 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100897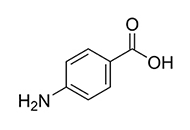 Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic prospects of 4-aminobenzoic acid in neuropsychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review of neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory pathways, and antioxidant defenseOpen AccessReview4-Aminobenzoic acid (PABA, para-aminobenzoic acid) exhibits multifaceted therapeutic potential in neuropsychiatric disorders through its roles in neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory actio...Siyu Chen ... Yangyang LiuPublished: March 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100898
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic prospects of 4-aminobenzoic acid in neuropsychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review of neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory pathways, and antioxidant defenseOpen AccessReview4-Aminobenzoic acid (PABA, para-aminobenzoic acid) exhibits multifaceted therapeutic potential in neuropsychiatric disorders through its roles in neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory actio...Siyu Chen ... Yangyang LiuPublished: March 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100898 Retraction: Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studiesOpen AccessRetractionJuan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria TuttolomondoPublished: March 17, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100896
Retraction: Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studiesOpen AccessRetractionJuan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria TuttolomondoPublished: March 17, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100896 Prediction of drug exposure in hepatic impairment: a comparison between minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic (mPBPK) and whole body PBPK modelsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The objective of this study was to develop a minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic (mPBPK) model to predict area under the curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of drug...Iftekhar MahmoodPublished: February 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100894
Prediction of drug exposure in hepatic impairment: a comparison between minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic (mPBPK) and whole body PBPK modelsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The objective of this study was to develop a minimal physiologically based pharmacokinetic (mPBPK) model to predict area under the curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of drug...Iftekhar MahmoodPublished: February 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100894 Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study evaluates the efficacy of amino-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) in the controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate (DexaP), aiming to enhance therapeutic o...Juan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria TuttolomondoPublished: February 28, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100895
Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study evaluates the efficacy of amino-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) in the controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate (DexaP), aiming to enhance therapeutic o...Juan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria TuttolomondoPublished: February 28, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100895 Unlocking the therapeutic potential of protein kinase inhibitors in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disordersOpen AccessReviewProtein phosphorylation is a fundamental regulatory mechanism governing a broad spectrum of cellular processes. In the nervous system, it is critical for modulating neurotransmitter release, synapti...Angela Asir R V ... Izhak MichaelevskiPublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100892
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of protein kinase inhibitors in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disordersOpen AccessReviewProtein phosphorylation is a fundamental regulatory mechanism governing a broad spectrum of cellular processes. In the nervous system, it is critical for modulating neurotransmitter release, synapti...Angela Asir R V ... Izhak MichaelevskiPublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100892 Critical review on nutritional, bioactive and medicinal potential of Bunium persicumOpen AccessReviewBunium persicum Boiss. Fedtsch., a highly valued spice crop from the Apiaceae family, is renowned for its rich phytochemical profile, including compounds such as cuminaldehyde, α-terpinene-7-al, γ...Prachi Bhatt ... Mamta BaunthiyalPublished: February 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100893
Critical review on nutritional, bioactive and medicinal potential of Bunium persicumOpen AccessReviewBunium persicum Boiss. Fedtsch., a highly valued spice crop from the Apiaceae family, is renowned for its rich phytochemical profile, including compounds such as cuminaldehyde, α-terpinene-7-al, γ...Prachi Bhatt ... Mamta BaunthiyalPublished: February 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100893 Behind anticancer molecules: lactoferricin dimeric peptides with fast, selective, persistent and broad-spectrum cytotoxic effectOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To identify peptides derived from bovine lactoferricin (LfcinB) as potential therapeutics for colon cancer treatment. We systematically modified dimeric peptides to enhance their selectivity...Karen Johanna Cárdenas-Martínez ... Javier Eduardo García-CastañedaPublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100891
Behind anticancer molecules: lactoferricin dimeric peptides with fast, selective, persistent and broad-spectrum cytotoxic effectOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To identify peptides derived from bovine lactoferricin (LfcinB) as potential therapeutics for colon cancer treatment. We systematically modified dimeric peptides to enhance their selectivity...Karen Johanna Cárdenas-Martínez ... Javier Eduardo García-CastañedaPublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100891 Ischemic stroke and post-stroke depression: the role of agomelatineOpen AccessReviewIschemic stroke (IS) is a leading cause of death globally. IS occurs due to a blockage of cerebral arteries, leading to neuronal injury, tissue death, and brain infarcts. This induces lack of oxygen...Aamna Arshad ... Bibek GiriPublished: February 25, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100890
Ischemic stroke and post-stroke depression: the role of agomelatineOpen AccessReviewIschemic stroke (IS) is a leading cause of death globally. IS occurs due to a blockage of cerebral arteries, leading to neuronal injury, tissue death, and brain infarcts. This induces lack of oxygen...Aamna Arshad ... Bibek GiriPublished: February 25, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100890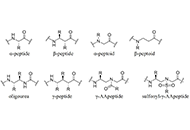 Recent exploration of γ-AApeptide based antimicrobial peptide mimics as potential therapeutics towards drug-resistant bacteriaOpen AccessCommentaryOver the last 60 years, only four new classes of antibiotics have been introduced, while the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has risen. This underscores the urgent need for new antibacterial therapeutics. This commentary leverages the recent exploration of γ-substituted-N-acylated-N-aminoethyl amino acid peptides (γ-AApeptides) to mimic the structures and function of natural antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), highlighting the promise and limitations for developing a new, effective treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacteria....Jarais Fontaine, Jianfeng CaiPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100888
Recent exploration of γ-AApeptide based antimicrobial peptide mimics as potential therapeutics towards drug-resistant bacteriaOpen AccessCommentaryOver the last 60 years, only four new classes of antibiotics have been introduced, while the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has risen. This underscores the urgent need for new antibacterial therapeutics. This commentary leverages the recent exploration of γ-substituted-N-acylated-N-aminoethyl amino acid peptides (γ-AApeptides) to mimic the structures and function of natural antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), highlighting the promise and limitations for developing a new, effective treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacteria....Jarais Fontaine, Jianfeng CaiPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100888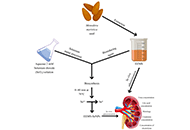 Control of diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats using ethanolic extract of Monodora myristica seeds and its biosynthesized selenium nanoparticlesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This research utilizes the ethanolic extract from seeds of Monodora myristica and its biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy (DN) in male Wis...Babalola Ola Yusuf ... Rasheed Bolaji IbrahimPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100889
Control of diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats using ethanolic extract of Monodora myristica seeds and its biosynthesized selenium nanoparticlesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This research utilizes the ethanolic extract from seeds of Monodora myristica and its biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy (DN) in male Wis...Babalola Ola Yusuf ... Rasheed Bolaji IbrahimPublished: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100889 Combating antibiotic resistance: mechanisms, challenges, and innovative approaches in antibacterial drug developmentOpen AccessReviewAntibiotic resistance is a significant threat to public health and drug development, driven largely by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in medical and agricultural settings. As bacteria adapt t...Aiswarya M. Rajesh ... Rambabu DandelaPublished: January 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100887
Combating antibiotic resistance: mechanisms, challenges, and innovative approaches in antibacterial drug developmentOpen AccessReviewAntibiotic resistance is a significant threat to public health and drug development, driven largely by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in medical and agricultural settings. As bacteria adapt t...Aiswarya M. Rajesh ... Rambabu DandelaPublished: January 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100887 Lutein and inflammation: a comprehensive review of its mechanisms of actionOpen AccessReviewLutein, a natural dihydroxy carotenoid and a member of the non-vitamin A carotenoids family, is abundant in yellow-colored fruits and green leafy vegetables such as spinach and lettuce. As the secon...Paradentavida Prathyusha ... Edakkadath R. SindhuPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100885
Lutein and inflammation: a comprehensive review of its mechanisms of actionOpen AccessReviewLutein, a natural dihydroxy carotenoid and a member of the non-vitamin A carotenoids family, is abundant in yellow-colored fruits and green leafy vegetables such as spinach and lettuce. As the secon...Paradentavida Prathyusha ... Edakkadath R. SindhuPublished: January 25, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100885 Lysozyme-based spray for treatment of radiotherapy-induced oral mucositisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this study was to examine the effectiveness and safety of lysozyme-based spray in the treatment of oral mucositis in patients undergoing head and neck radiotherapy. Methods: ...Zdenka Gojković ... Una GlamočlijaPublished: January 24, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100886
Lysozyme-based spray for treatment of radiotherapy-induced oral mucositisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this study was to examine the effectiveness and safety of lysozyme-based spray in the treatment of oral mucositis in patients undergoing head and neck radiotherapy. Methods: ...Zdenka Gojković ... Una GlamočlijaPublished: January 24, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100886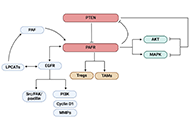 Impact of the crosstalk between the PTEN and PAFR as well as PAFR and EGFR pathways in cancerOpen AccessMini ReviewThe integration between the tumor-suppressive and oncogenic signaling pathways controls various cellular activities of cancer cells, including cell growth and apoptosis. While the activation of onco...Anita Thyagarajan ... Ravi P. SahuPublished: January 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100883
Impact of the crosstalk between the PTEN and PAFR as well as PAFR and EGFR pathways in cancerOpen AccessMini ReviewThe integration between the tumor-suppressive and oncogenic signaling pathways controls various cellular activities of cancer cells, including cell growth and apoptosis. While the activation of onco...Anita Thyagarajan ... Ravi P. SahuPublished: January 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100883 Advantages of using biofilms to obtain high-value molecules by microbial biotransformationsOpen AccessMini ReviewMicrobial biotransformations are valuable tools from “green chemistry” and involve converting parental molecules into new daughter ones with unique physical, chemical, or pharmacological propert...Nicoly Subtil de Oliveira ... Edvaldo Antonio Ribeiro RosaPublished: January 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100884
Advantages of using biofilms to obtain high-value molecules by microbial biotransformationsOpen AccessMini ReviewMicrobial biotransformations are valuable tools from “green chemistry” and involve converting parental molecules into new daughter ones with unique physical, chemical, or pharmacological propert...Nicoly Subtil de Oliveira ... Edvaldo Antonio Ribeiro RosaPublished: January 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100884 Phenylalanine-derived β-lactam TRPM8 antagonists: revisiting configuration and new benzoyl derivativesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To expand the understanding of the structure-activity relationship within a family of amino acid-derived β-lactam TRPM8 (transient receptor potential melastatin channel, subtype 8) antagoni...Cristina Martín-Escura ... Rosario González-MuñizPublished: January 13, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100882
Phenylalanine-derived β-lactam TRPM8 antagonists: revisiting configuration and new benzoyl derivativesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: To expand the understanding of the structure-activity relationship within a family of amino acid-derived β-lactam TRPM8 (transient receptor potential melastatin channel, subtype 8) antagoni...Cristina Martín-Escura ... Rosario González-MuñizPublished: January 13, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100882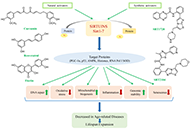 Sirtuin activators as an anti-aging intervention for longevityOpen AccessReviewSirtuins are a family of NAD+-dependent class III histone deacetylases that regulate histones and other proteins. The mammalian sirtuins comprise seven members that have a role in energy metabolism,...Puja Sah ... Donkupar SyiemPublished: January 12, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100881
Sirtuin activators as an anti-aging intervention for longevityOpen AccessReviewSirtuins are a family of NAD+-dependent class III histone deacetylases that regulate histones and other proteins. The mammalian sirtuins comprise seven members that have a role in energy metabolism,...Puja Sah ... Donkupar SyiemPublished: January 12, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100881 What are biopharmaceuticals?Open AccessReviewThroughout history, biopharmaceuticals have been essential in addressing health crises and enhancing human well-being. With advancements in genetic engineering, biotechnology, and bioinformatics, th...Abhay H. Pande ... J. AnakhaPublished: January 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100880
What are biopharmaceuticals?Open AccessReviewThroughout history, biopharmaceuticals have been essential in addressing health crises and enhancing human well-being. With advancements in genetic engineering, biotechnology, and bioinformatics, th...Abhay H. Pande ... J. AnakhaPublished: January 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2025.100880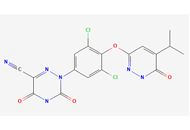 FDA’s approval of resmetirom (Rezdiffra): a breakthrough in MASH managementOpen AccessShort CommunicationThe FDA’s approval of resmetirom (Rezdiffra) marks a significant breakthrough in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and fibrosis, conditions linked to non-alcoholic f...Muhammad Mazhar Azam ... Bibek GiriPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00078
FDA’s approval of resmetirom (Rezdiffra): a breakthrough in MASH managementOpen AccessShort CommunicationThe FDA’s approval of resmetirom (Rezdiffra) marks a significant breakthrough in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and fibrosis, conditions linked to non-alcoholic f...Muhammad Mazhar Azam ... Bibek GiriPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00078 Correction: Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-beingOpen AccessCorrectionLeonel Pereira ... Ana ValadoPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00079
Correction: Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-beingOpen AccessCorrectionLeonel Pereira ... Ana ValadoPublished: December 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00079 FDA-approved kinase inhibitors: a promising therapeutic avenue for traumatic brain injuryOpen AccessReviewTraumatic brain injury (TBI) is a complex disease that leads to significant mortality and disability worldwide each year. TBI disrupts the normal activity of kinases and molecular signaling pathways...Dezhu Gao ... Weiming LiuPublished: December 2, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00077
FDA-approved kinase inhibitors: a promising therapeutic avenue for traumatic brain injuryOpen AccessReviewTraumatic brain injury (TBI) is a complex disease that leads to significant mortality and disability worldwide each year. TBI disrupts the normal activity of kinases and molecular signaling pathways...Dezhu Gao ... Weiming LiuPublished: December 2, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00077 Technetium-99m-labeled peptides and their applications in radio imaging: advancements in Latin American researchOpen AccessReviewA very new and highly specialized category of radiotracers that is still growing is radiolabeled peptides. Radiolabeled peptides, or radiopeptides, are powerful elements for diagnostic imaging and r...Vaezeh Fathi Vavsari, Saeed BalalaiePublished: November 20, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00075
Technetium-99m-labeled peptides and their applications in radio imaging: advancements in Latin American researchOpen AccessReviewA very new and highly specialized category of radiotracers that is still growing is radiolabeled peptides. Radiolabeled peptides, or radiopeptides, are powerful elements for diagnostic imaging and r...Vaezeh Fathi Vavsari, Saeed BalalaiePublished: November 20, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00075 Potential use of peptides mimicking CRAC/CARC domains as antivirulence therapies to inhibit RTX toxins activitiesOpen AccessReviewIn recent years, research efforts have increased to develop new therapeutics aimed at combating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. These efforts focus on inhibiting the virulence factors bac...Vanesa HerlaxPublished: November 20, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00076
Potential use of peptides mimicking CRAC/CARC domains as antivirulence therapies to inhibit RTX toxins activitiesOpen AccessReviewIn recent years, research efforts have increased to develop new therapeutics aimed at combating antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. These efforts focus on inhibiting the virulence factors bac...Vanesa HerlaxPublished: November 20, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00076 Bio-mimetic strategies to re-activate apoptotic cell death for cancer treatmentsOpen AccessReviewApoptosis is a crucial process to maintain the correct balance between healthy cells and committed-to-death cells in every tissue. The internal (or mitochondrial) and external (or death receptor) pa...Andrea Venerando ... Rossella De MarcoPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00074
Bio-mimetic strategies to re-activate apoptotic cell death for cancer treatmentsOpen AccessReviewApoptosis is a crucial process to maintain the correct balance between healthy cells and committed-to-death cells in every tissue. The internal (or mitochondrial) and external (or death receptor) pa...Andrea Venerando ... Rossella De MarcoPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00074 Unlocking nature’s pharmacy: an in-depth exploration of phytochemicals as potential sources of anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory moleculesOpen AccessReviewPhytochemicals, the bioactive compounds derived from plants, play a significant role in modulating pathways leading to cancer and inflammation, rendering themselves promising candidates for therapeu...Shifana C. Sadiq ... Ruby John AntoPublished: October 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00073
Unlocking nature’s pharmacy: an in-depth exploration of phytochemicals as potential sources of anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory moleculesOpen AccessReviewPhytochemicals, the bioactive compounds derived from plants, play a significant role in modulating pathways leading to cancer and inflammation, rendering themselves promising candidates for therapeu...Shifana C. Sadiq ... Ruby John AntoPublished: October 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00073 Lactoferrin: a secret weapon in the war against pathogenic bacteriaOpen AccessMini ReviewThe excessive use of antibiotics to treat bacterial infectious diseases in all living beings has caused a global epidemic of bacterial resistance to antibiotics, leading to the emergence of multidru...Lucero Ruiz-Mazón ... Mireya de la GarzaPublished: October 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00072
Lactoferrin: a secret weapon in the war against pathogenic bacteriaOpen AccessMini ReviewThe excessive use of antibiotics to treat bacterial infectious diseases in all living beings has caused a global epidemic of bacterial resistance to antibiotics, leading to the emergence of multidru...Lucero Ruiz-Mazón ... Mireya de la GarzaPublished: October 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00072 Bicyclic peptide-enhanced covalent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CL proteaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Develop technology to apply bicyclic peptides for discovering covalent inhibitors of proteases and use this technology to create bicyclic peptide—warhead conjugates for targeting the sever...Qian Wang ... Shiyu ChenPublished: October 17, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00071
Bicyclic peptide-enhanced covalent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CL proteaseOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Develop technology to apply bicyclic peptides for discovering covalent inhibitors of proteases and use this technology to create bicyclic peptide—warhead conjugates for targeting the sever...Qian Wang ... Shiyu ChenPublished: October 17, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00071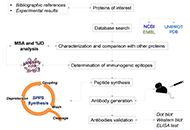 Synthetic peptides as valuable and versatile tools for research: our 20 year journey in ChileOpen AccessReviewAccording to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), peptides are small proteins with a size between 2 and 50 amino acids residues. They are ubiquitous across the evolutionary...Constanza Cárdenas ... Fanny GuzmánPublished: October 15, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00070
Synthetic peptides as valuable and versatile tools for research: our 20 year journey in ChileOpen AccessReviewAccording to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), peptides are small proteins with a size between 2 and 50 amino acids residues. They are ubiquitous across the evolutionary...Constanza Cárdenas ... Fanny GuzmánPublished: October 15, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00070 Foundational contributions of Svetlana Mojsov to the GLP-1 fieldOpen AccessPerspectiveBiochemist Svetlana Mojsov, both as a graduate student at The Rockefeller University under the mentorship of Bruce Merrifield during the 1970s, and as an independent investigator at the Massachusett...George Barany, Michael J. BaranyPublished: October 3, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00069
Foundational contributions of Svetlana Mojsov to the GLP-1 fieldOpen AccessPerspectiveBiochemist Svetlana Mojsov, both as a graduate student at The Rockefeller University under the mentorship of Bruce Merrifield during the 1970s, and as an independent investigator at the Massachusett...George Barany, Michael J. BaranyPublished: October 3, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00069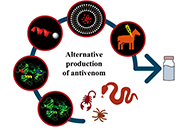 21st century Latin American synthetic peptides for their application in antivenom productionOpen AccessReviewEnvenomation caused by snakes, scorpions, and spiders represents a serious public health problem in Latin America. The antivenoms used for its treatment are produced by immunizing horses repeatedly ...Jésica A. Rodríguez ... Silvia A. CamperiPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00066
21st century Latin American synthetic peptides for their application in antivenom productionOpen AccessReviewEnvenomation caused by snakes, scorpions, and spiders represents a serious public health problem in Latin America. The antivenoms used for its treatment are produced by immunizing horses repeatedly ...Jésica A. Rodríguez ... Silvia A. CamperiPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00066 Effect of combined oral contraceptives on menstrual migraine frequency and severity: a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewMigraine, a commonly occurring neurological disorder, disproportionately affects women during their reproductive years, and its symptoms are often intensified by hormonal fluctuations. This narrativ...Yethindra Vityala ... Krishna Chaitanya MeduriPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00067
Effect of combined oral contraceptives on menstrual migraine frequency and severity: a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewMigraine, a commonly occurring neurological disorder, disproportionately affects women during their reproductive years, and its symptoms are often intensified by hormonal fluctuations. This narrativ...Yethindra Vityala ... Krishna Chaitanya MeduriPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00067 Prediction of absolute bioavailability of medicines in children: based on predicted pediatric clearance from adultsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The objective of this study was to evaluate the predictive performance of a proposed method to predict absolute bioavailability of medicines in children (infants to adolescents). Method...Iftekhar MahmoodPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00068
Prediction of absolute bioavailability of medicines in children: based on predicted pediatric clearance from adultsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The objective of this study was to evaluate the predictive performance of a proposed method to predict absolute bioavailability of medicines in children (infants to adolescents). Method...Iftekhar MahmoodPublished: September 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00068 Hybrid peptides inspired by the RWQWRWQWR sequence inhibit cervical cancer cells growth in vitroOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this research was to generate new peptide molecules with cytotoxic activity against cervical cancer that can become effective in mitigating the impact of the disease and preventin...Natalia Ardila-Chantré ... Javier Eduardo García-CastañedaPublished: September 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00064
Hybrid peptides inspired by the RWQWRWQWR sequence inhibit cervical cancer cells growth in vitroOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this research was to generate new peptide molecules with cytotoxic activity against cervical cancer that can become effective in mitigating the impact of the disease and preventin...Natalia Ardila-Chantré ... Javier Eduardo García-CastañedaPublished: September 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00064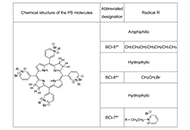 Properties of new polycationic bacteriochlorin photosensitizers: cytotoxicity and interaction with biofilmsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Biofilms of pathogenic bacteria are phenotypically resistant to antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents, host immune systems, and adverse environmental conditions, and are responsible for...Irina Tiganova ... Yulia RomanovaPublished: September 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00065
Properties of new polycationic bacteriochlorin photosensitizers: cytotoxicity and interaction with biofilmsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Biofilms of pathogenic bacteria are phenotypically resistant to antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents, host immune systems, and adverse environmental conditions, and are responsible for...Irina Tiganova ... Yulia RomanovaPublished: September 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00065 Psoralidin: emerging biological activities of therapeutic benefits and its potential utility in cervical cancerOpen AccessReviewCervical cancer (CaCx) is the fourth most prevalent cancer in women contributing to 341,831 annual deaths globally in 2020. Owing to its high mortality rate, the identification of novel inhibitors p...Tanya Tripathi ... Alok Chandra BhartiPublished: September 24, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00063
Psoralidin: emerging biological activities of therapeutic benefits and its potential utility in cervical cancerOpen AccessReviewCervical cancer (CaCx) is the fourth most prevalent cancer in women contributing to 341,831 annual deaths globally in 2020. Owing to its high mortality rate, the identification of novel inhibitors p...Tanya Tripathi ... Alok Chandra BhartiPublished: September 24, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00063 Clinical utility of combined contrast-enhanced ultrasound and intracavitary contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the percutaneous treatment of pyogenic liver abscessOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the utility of the combined use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and intracavitary CEUS (IC-CEUS) with diluted SonoVue in the management of percutaneous tr...Giampiero FrancicaPublished: September 13, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00061
Clinical utility of combined contrast-enhanced ultrasound and intracavitary contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the percutaneous treatment of pyogenic liver abscessOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the utility of the combined use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and intracavitary CEUS (IC-CEUS) with diluted SonoVue in the management of percutaneous tr...Giampiero FrancicaPublished: September 13, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00061 Multi-target and natural product-based multi-drug approach for anti-VEGF resistance in glioblastomaOpen AccessReviewGlioblastoma (GBM) remains a formidable challenge in neuro-oncology due to its aggressive nature and propensity for therapeutic resistance. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies, ...Sasikumar Jalajakumari Soumya ... Perumana R. SudhakaranPublished: September 13, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00062
Multi-target and natural product-based multi-drug approach for anti-VEGF resistance in glioblastomaOpen AccessReviewGlioblastoma (GBM) remains a formidable challenge in neuro-oncology due to its aggressive nature and propensity for therapeutic resistance. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies, ...Sasikumar Jalajakumari Soumya ... Perumana R. SudhakaranPublished: September 13, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00062 A review of leishmaniasis: current knowledge and future directions of heterocyclic moleculesOpen AccessReviewLeishmanial diseases, caused by various species of the protozoan parasite Leishmania, continue to pose a significant global health challenge. Medicinal drugs have been at the forefront of combating ...Tejaswini Masne ... Deepali BansodePublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00059
A review of leishmaniasis: current knowledge and future directions of heterocyclic moleculesOpen AccessReviewLeishmanial diseases, caused by various species of the protozoan parasite Leishmania, continue to pose a significant global health challenge. Medicinal drugs have been at the forefront of combating ...Tejaswini Masne ... Deepali BansodePublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00059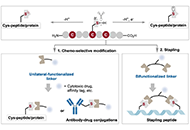 Chemo-selective modification of cysteine residue: synthesis and application in the discovery of potential drug candidatesOpen AccessReviewChemo-select modification of peptides, targeting a handful of the most reactive proteinogenic amino acids (AAs), is gradually utilized to address the medical needs of peptide drugs and biopharmaceut...Yanyan Liao, Xuefeng JiangPublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00060
Chemo-selective modification of cysteine residue: synthesis and application in the discovery of potential drug candidatesOpen AccessReviewChemo-select modification of peptides, targeting a handful of the most reactive proteinogenic amino acids (AAs), is gradually utilized to address the medical needs of peptide drugs and biopharmaceut...Yanyan Liao, Xuefeng JiangPublished: September 06, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00060 A review of the effects of pharmaceutical pollutants on humans and aquatic ecosystemOpen AccessReviewThe presence of high-quality water is essential not only for human survival but also for the well-being of plants and animals. This research aimed to examine studies investigating the occurrence of ...Jaya Vinny Eapen ... Jayesh AntonyPublished: August 28, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00058
A review of the effects of pharmaceutical pollutants on humans and aquatic ecosystemOpen AccessReviewThe presence of high-quality water is essential not only for human survival but also for the well-being of plants and animals. This research aimed to examine studies investigating the occurrence of ...Jaya Vinny Eapen ... Jayesh AntonyPublished: August 28, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00058 Biological activities of extracts of some plants which utilized in coldsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, antioxidant activities and antibacterial activities of acetone and chloroform extracts obtained from Rosa canina, Echinacea purpurea, Althaea officinalis and...Sinem AydinPublished: August 22, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00057
Biological activities of extracts of some plants which utilized in coldsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In this study, antioxidant activities and antibacterial activities of acetone and chloroform extracts obtained from Rosa canina, Echinacea purpurea, Althaea officinalis and...Sinem AydinPublished: August 22, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00057 Decoding vascular aging: implications for atherosclerosis progression and clinical interventionOpen AccessReviewAge-related pathologies, particularly cardiovascular disorders, pose a significant global health concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts an increase in advanced mortality by 2030 unles...Silumbwe Ceaser Wankumbu ... Ming XuPublished: August 02, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00056
Decoding vascular aging: implications for atherosclerosis progression and clinical interventionOpen AccessReviewAge-related pathologies, particularly cardiovascular disorders, pose a significant global health concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts an increase in advanced mortality by 2030 unles...Silumbwe Ceaser Wankumbu ... Ming XuPublished: August 02, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00056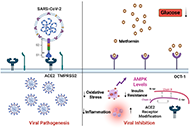 Metformin in COVID-19: a magical role beyond the hyperglycemiaOpen AccessReviewCoronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as an aggressive viral infection in the last few years. Initially reported in the Wuhan area of the People’s Republic of China, it soon emerged acro...Gaurav Kumar Chaubey ... Manoj RajePublished: July 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00055
Metformin in COVID-19: a magical role beyond the hyperglycemiaOpen AccessReviewCoronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as an aggressive viral infection in the last few years. Initially reported in the Wuhan area of the People’s Republic of China, it soon emerged acro...Gaurav Kumar Chaubey ... Manoj RajePublished: July 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00055 From canonical to unique: extension of a lipophilicity scale of amino acids to non-standard residuesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The lipophilicity of amino acids plays a crucial role in delineating their physicochemical properties, offering insights into solubility, binding affinity, and bioavailability, properties th...Antonio Viayna ... William J. ZamoraPublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00053
From canonical to unique: extension of a lipophilicity scale of amino acids to non-standard residuesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The lipophilicity of amino acids plays a crucial role in delineating their physicochemical properties, offering insights into solubility, binding affinity, and bioavailability, properties th...Antonio Viayna ... William J. ZamoraPublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00053 Natural products as anticancer agents and enhancing their efficacy by a mechanism-based precision approachOpen AccessReviewTraditional medicines and their active ingredients and some natural products and derived analogs have been used for treating multiple diseases including cancer. Among these compounds cytotoxic agent...Stephen SafePublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00054
Natural products as anticancer agents and enhancing their efficacy by a mechanism-based precision approachOpen AccessReviewTraditional medicines and their active ingredients and some natural products and derived analogs have been used for treating multiple diseases including cancer. Among these compounds cytotoxic agent...Stephen SafePublished: July 30, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00054 Enhanced breast cancer cell targeting: RGD integrin ligand potentiates RWQWRWQWR’s cytotoxicity and inhibits migrationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Evaluate the selective cytotoxic effect of the palindromic sequence RWQWRWQWR and its analogues obtained by replacement of L-amino acids by D-amino acids or the functionalization by adding t...Andrea Barragán-Cárdenas ... Javier García-CastañedaPublished: July 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00052
Enhanced breast cancer cell targeting: RGD integrin ligand potentiates RWQWRWQWR’s cytotoxicity and inhibits migrationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Evaluate the selective cytotoxic effect of the palindromic sequence RWQWRWQWR and its analogues obtained by replacement of L-amino acids by D-amino acids or the functionalization by adding t...Andrea Barragán-Cárdenas ... Javier García-CastañedaPublished: July 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00052 Plants and fungi metabolites as novel autophagy inducers and senescence inhibitorsOpen AccessPerspectivePremature aging can be partially explained by inefficient autophagy (the process of cellular self-digestion that recycles intracellular components) and premature senescence (cease of cellular divisi...Rivka OfirPublished: July 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00051
Plants and fungi metabolites as novel autophagy inducers and senescence inhibitorsOpen AccessPerspectivePremature aging can be partially explained by inefficient autophagy (the process of cellular self-digestion that recycles intracellular components) and premature senescence (cease of cellular divisi...Rivka OfirPublished: July 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00051 Mechanism of the blood-brain barrier modulation by cadherin peptidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study was aimed at finding the binding site on the human E-cadherin for Ala-Asp-Thr Cyclic 5 (ADTC5), ADTC7, and ADTC9 peptides as blood-brain barrier modulator (BBBM) for determining t...Elinaz Farokhi ... Teruna J. SiahaanPublished: June 26, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00049
Mechanism of the blood-brain barrier modulation by cadherin peptidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study was aimed at finding the binding site on the human E-cadherin for Ala-Asp-Thr Cyclic 5 (ADTC5), ADTC7, and ADTC9 peptides as blood-brain barrier modulator (BBBM) for determining t...Elinaz Farokhi ... Teruna J. SiahaanPublished: June 26, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00049 Harnessing the immunomodulatory potential of natural products in precision medicine—a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewTraditional medicine systems worldwide utilize natural products (NPs), including plant-derived compounds, minerals, and organisms, harnessing their healing potential. NPs offer a rich source of pote...Maya G. Pillai, Helen AntonyPublished: June 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00050
Harnessing the immunomodulatory potential of natural products in precision medicine—a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewTraditional medicine systems worldwide utilize natural products (NPs), including plant-derived compounds, minerals, and organisms, harnessing their healing potential. NPs offer a rich source of pote...Maya G. Pillai, Helen AntonyPublished: June 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00050 Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-beingOpen AccessReviewIn recent times, there has been a revolutionary surge in antioxidant research, with a focus on harnessing microalgae to enhance wellness and extend human longevity. Microalgae, a diverse group of un...Leonel Pereira ... Ana ValadoPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00048
Antioxidants from microalgae and their potential impact on human well-beingOpen AccessReviewIn recent times, there has been a revolutionary surge in antioxidant research, with a focus on harnessing microalgae to enhance wellness and extend human longevity. Microalgae, a diverse group of un...Leonel Pereira ... Ana ValadoPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00048 Pain management for the neurosurgical patient in spinal procedures: overview of historic and new modalitiesOpen AccessMini ReviewThe potent pain-relieving properties of opioids come at a steep price. Their addictive nature and side effects raise critical concerns in managing pain after surgical spine procedures. Postoperative...Ashley M. Carter ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: May 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00046
Pain management for the neurosurgical patient in spinal procedures: overview of historic and new modalitiesOpen AccessMini ReviewThe potent pain-relieving properties of opioids come at a steep price. Their addictive nature and side effects raise critical concerns in managing pain after surgical spine procedures. Postoperative...Ashley M. Carter ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: May 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00046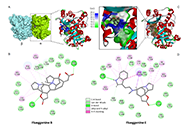 Interaction of norsecurinine-type monomeric and dimeric alkaloids with α-tubulin: a molecular docking studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: New microtubule-targeting agents are needed to improve cancer treatment. The recent characterization of the anticancer alkaloid securinine as a tubulin-binding agent prompted us to explore t...Gérard Vergoten, Christian BaillyPublished: May 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00047
Interaction of norsecurinine-type monomeric and dimeric alkaloids with α-tubulin: a molecular docking studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: New microtubule-targeting agents are needed to improve cancer treatment. The recent characterization of the anticancer alkaloid securinine as a tubulin-binding agent prompted us to explore t...Gérard Vergoten, Christian BaillyPublished: May 21, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00047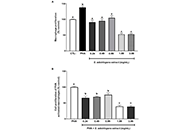 Stryphnodendron adstringens have a modulatory effect on inflammatory cytokines markers of in vitro activated macrophagesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The purpose of this study is to conduct a comprehensive investigation into the modulatory effects of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.; S. adstringens), a Brazilian wound-healing plant, on ...Ivana Beatrice Mânica da Cruz ... Fernanda BarbisanPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00045
Stryphnodendron adstringens have a modulatory effect on inflammatory cytokines markers of in vitro activated macrophagesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The purpose of this study is to conduct a comprehensive investigation into the modulatory effects of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.; S. adstringens), a Brazilian wound-healing plant, on ...Ivana Beatrice Mânica da Cruz ... Fernanda BarbisanPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00045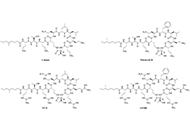 Lipopeptide adjuvants for antibiotics and vaccines: the future step in the fight against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant pathogensOpen AccessReviewWith the surge of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, the need for a larger arsenal of effective antibiotics and vaccines has drastically increased in the past decades. Antibiotics like vaccines can ...Chloé O. Sebilleau, Steven J. SucheckPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00043
Lipopeptide adjuvants for antibiotics and vaccines: the future step in the fight against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant pathogensOpen AccessReviewWith the surge of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, the need for a larger arsenal of effective antibiotics and vaccines has drastically increased in the past decades. Antibiotics like vaccines can ...Chloé O. Sebilleau, Steven J. SucheckPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00043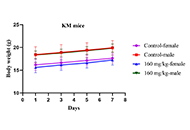 Subacute toxicity of isoliquiritigenin-zein phosphatidylcholine nanoparticles on biochemical, hematological, and histopathological parameters in Sprague-Dawley ratsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) is a natural flavonoid found in many natural plants, which exhibits numerous pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, and antiv...Ke Yang ... Jianping ChenPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00044
Subacute toxicity of isoliquiritigenin-zein phosphatidylcholine nanoparticles on biochemical, hematological, and histopathological parameters in Sprague-Dawley ratsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Isoliquiritigenin (ISL) is a natural flavonoid found in many natural plants, which exhibits numerous pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, and antiv...Ke Yang ... Jianping ChenPublished: April 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00044 Daropeptide natural productsOpen AccessPerspectiveCyclophane-containing peptides comprise an important group of macrocyclic peptides with unique structural properties and pharmaceutical relevance. Darobactin A is a ribosomally synthesized and post-...Suze Ma ... Qi ZhangPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00042
Daropeptide natural productsOpen AccessPerspectiveCyclophane-containing peptides comprise an important group of macrocyclic peptides with unique structural properties and pharmaceutical relevance. Darobactin A is a ribosomally synthesized and post-...Suze Ma ... Qi ZhangPublished: April 19, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00042 Stapled peptides: targeting protein-protein interactions in drug developmentOpen AccessReviewProtein-protein interactions (PPIs) impersonate a significant role in many biological processes and are potential therapeutic targets in numerous human diseases. Stapled peptides, as the most promis...Qian Zhang ... Chunqiu ZhangPublished: April 18, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00041
Stapled peptides: targeting protein-protein interactions in drug developmentOpen AccessReviewProtein-protein interactions (PPIs) impersonate a significant role in many biological processes and are potential therapeutic targets in numerous human diseases. Stapled peptides, as the most promis...Qian Zhang ... Chunqiu ZhangPublished: April 18, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00041 Clinical studies with drugs and biologics aimed at slowing or reversing normal aging processes—emerging results and future perspectivesOpen AccessPerspectiveFive families of investigational products are in clinical investigation to slow or reverse normal aging processes [longevity candidates, mesenchymal stem cells, senolytics drugs, sirtuin activators,...Ricardo P. GarayPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00040
Clinical studies with drugs and biologics aimed at slowing or reversing normal aging processes—emerging results and future perspectivesOpen AccessPerspectiveFive families of investigational products are in clinical investigation to slow or reverse normal aging processes [longevity candidates, mesenchymal stem cells, senolytics drugs, sirtuin activators,...Ricardo P. GarayPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00040 Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonists for the treatment of obesity and diabetes mellitusOpen AccessReviewPharmaceutical interventions play a vital role in managing various conditions, including weight-related issues such as obesity. In this context, lifestyle changes are often challenging to maintain, ...Alexander C. Martins ... Fernando AlbericioPublished: April 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00039
Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide agonists for the treatment of obesity and diabetes mellitusOpen AccessReviewPharmaceutical interventions play a vital role in managing various conditions, including weight-related issues such as obesity. In this context, lifestyle changes are often challenging to maintain, ...Alexander C. Martins ... Fernando AlbericioPublished: April 03, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00039 Influenza A virus hemagglutinin: from classical fusion inhibitors to proteolysis targeting chimera-based strategies in antiviral drug discoveryOpen AccessReviewThe influenza virus glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA) participates in critical steps of the attachment of viral particles to the host cell membrane receptor and membrane fusion. Due to its crucial inv...Francisco Javier Hermoso-Pinilla ... Francisco Javier LuquePublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00037
Influenza A virus hemagglutinin: from classical fusion inhibitors to proteolysis targeting chimera-based strategies in antiviral drug discoveryOpen AccessReviewThe influenza virus glycoprotein hemagglutinin (HA) participates in critical steps of the attachment of viral particles to the host cell membrane receptor and membrane fusion. Due to its crucial inv...Francisco Javier Hermoso-Pinilla ... Francisco Javier LuquePublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00037 Mini-review on the antimicrobial potential of actinobacteria associated with seagrassesOpen AccessMini ReviewThe search for novel therapeutic agents to combat the crisis of antimicrobial resistance has spanned from terrestrial to unique, marine environments. Currently, most of the drugs available for usage...Galana Siro, Atanas PipitePublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00038
Mini-review on the antimicrobial potential of actinobacteria associated with seagrassesOpen AccessMini ReviewThe search for novel therapeutic agents to combat the crisis of antimicrobial resistance has spanned from terrestrial to unique, marine environments. Currently, most of the drugs available for usage...Galana Siro, Atanas PipitePublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00038 Seaweed: a sustainable solution for greening drug manufacturing in the pursuit of sustainable healthcareOpen AccessReviewThe environmental impact of drug manufacturing raises concerns about sustainability in healthcare. To address this, exploring alternative approaches to drug production is crucial. This review focuse...Leonel Pereira, João CotasPublished: February 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00036
Seaweed: a sustainable solution for greening drug manufacturing in the pursuit of sustainable healthcareOpen AccessReviewThe environmental impact of drug manufacturing raises concerns about sustainability in healthcare. To address this, exploring alternative approaches to drug production is crucial. This review focuse...Leonel Pereira, João CotasPublished: February 27, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00036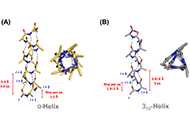 Revisiting 310-helices: biological relevance, mimetics and applicationsOpen AccessReview310-Helices represent the third most abundant secondary structure proteins. Although understandably overshadowed by α-helices for decades, the 310-helix structure is slowly regaining certain releva...Diego Núñez-VillanuevaPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00034
Revisiting 310-helices: biological relevance, mimetics and applicationsOpen AccessReview310-Helices represent the third most abundant secondary structure proteins. Although understandably overshadowed by α-helices for decades, the 310-helix structure is slowly regaining certain releva...Diego Núñez-VillanuevaPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00034 Effect of the size of nucleic acid delivery systems on their fate in cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewNucleic acid therapeutics are emerging as a promising class of medicines, offering unique therapeutic options for cancer at the gene level. However, the druggability of nucleic acid therapeutics is ...Mengyun Ye ... Dandan ZhuPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00035
Effect of the size of nucleic acid delivery systems on their fate in cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewNucleic acid therapeutics are emerging as a promising class of medicines, offering unique therapeutic options for cancer at the gene level. However, the druggability of nucleic acid therapeutics is ...Mengyun Ye ... Dandan ZhuPublished: February 01, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00035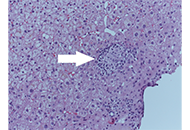 Histological diagnosis of primary biliary cholangitis in one patient without cholestasis alterations: a case report that escaped guidelinesOpen AccessCase ReportPrimary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is an autoimmune cholangiopathy that affects mainly women and, if untreated, can evolve into biliary cirrhosis. Its prevalence varies worldwide, depending on race, ...Matteo Biagi ... Pietro AndreonePublished: January 22, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00033
Histological diagnosis of primary biliary cholangitis in one patient without cholestasis alterations: a case report that escaped guidelinesOpen AccessCase ReportPrimary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is an autoimmune cholangiopathy that affects mainly women and, if untreated, can evolve into biliary cirrhosis. Its prevalence varies worldwide, depending on race, ...Matteo Biagi ... Pietro AndreonePublished: January 22, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2024.00033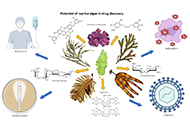 Harnessing the power of seaweed: unveiling the potential of marine algae in drug discoveryOpen AccessReviewSeaweeds, also known as marine algae, have gained attention as a promising source of bioactive compounds with potential applications in drug discovery. This review explores the emerging field of sea...Leonel Pereira, Ana ValadoPublished: December 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00032
Harnessing the power of seaweed: unveiling the potential of marine algae in drug discoveryOpen AccessReviewSeaweeds, also known as marine algae, have gained attention as a promising source of bioactive compounds with potential applications in drug discovery. This review explores the emerging field of sea...Leonel Pereira, Ana ValadoPublished: December 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00032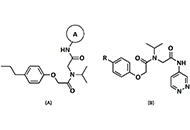 Rational design of novel phenol ether derivatives as non-covalent proteasome inhibitors through 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and ADMET predictionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The purpose of this paper is to use different structures and ligand-based drug design methods properly to provide theoretical guidance for the design of novel non-covalent proteasome inhibit...Miao Yuan ... Ping ChengPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00029
Rational design of novel phenol ether derivatives as non-covalent proteasome inhibitors through 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and ADMET predictionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The purpose of this paper is to use different structures and ligand-based drug design methods properly to provide theoretical guidance for the design of novel non-covalent proteasome inhibit...Miao Yuan ... Ping ChengPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00029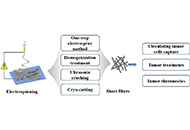 Electrospun short fibers: a new platform for cancer nanomedicine applicationsOpen AccessReviewWith the continuous development of nanomaterials, nanofibers prepared by electrospinning have gradually occupied people’s vision because of their unique advantages, such as crisscross network and ...Yifan Huang ... Xiangyang ShiPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00030
Electrospun short fibers: a new platform for cancer nanomedicine applicationsOpen AccessReviewWith the continuous development of nanomaterials, nanofibers prepared by electrospinning have gradually occupied people’s vision because of their unique advantages, such as crisscross network and ...Yifan Huang ... Xiangyang ShiPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00030 Reactivation of latent hepatitis B infection during immunosuppressive therapy with guselkumab for plaque psoriasis: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportReactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV; RHBV) is a significant concern during immunosuppressive therapy, as it can lead to severe hepatitis and liver failure. The article reports a case of RHBV duri...Elena Franchi ... Pietro AndreonePublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00031
Reactivation of latent hepatitis B infection during immunosuppressive therapy with guselkumab for plaque psoriasis: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportReactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV; RHBV) is a significant concern during immunosuppressive therapy, as it can lead to severe hepatitis and liver failure. The article reports a case of RHBV duri...Elena Franchi ... Pietro AndreonePublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00031 Hybrid azole-based conjugates as upcoming anticancer and antimicrobial agentsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study discloses the synthesis and the antimicrobial and anticancer activities of four molecules of structural basis saccharin-thiadiazolyl (4), saccharin-pyridyl (6, 8), and tetrazole-t...Luís M. T. Frija ... Patrícia RijoPublished: November 23, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00028
Hybrid azole-based conjugates as upcoming anticancer and antimicrobial agentsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study discloses the synthesis and the antimicrobial and anticancer activities of four molecules of structural basis saccharin-thiadiazolyl (4), saccharin-pyridyl (6, 8), and tetrazole-t...Luís M. T. Frija ... Patrícia RijoPublished: November 23, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00028 Insights into the binding selectivity of harzianoic acids A and B to tetraspanin CD81Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Harzianoic acids A and B (Hz-A/B) are two rare cyclobutene-containing sesquiterpenes isolated from a marine strain of the sponge-associated fungus Trichoderma harzianum. They display anticancer and antiviral effects, reducing the entry of hepatitis C virus (HCV) into hepatocarcinoma cells. The large extracellular loop (LEL) of the tetraspanin protein CD81 represents a molecular target for both Hz-A and Hz-B. Methods: The interaction of Hz-A/B with CD81 has been modeled, using structures of the cholesterol-bound full-length protein and a truncated protein corresponding to the LEL portion. The models mimicked the closed and open conformations of the LEL. Results: The best ligand Hz-B can form stable complexes with the open LEL structure, whereas binding to the closed form is drastically reduced. Key H-bonds between the acid groups of Hz-B and the CD81-LEL domain stabilize the ligand-protein complex. A comparison of the interaction with the homologous tetraspanin CD9, which also presents a dynamic open/closed equilibrium, underlined the marked selectivity of Hz-A/B for CD81 over CD9. The cyclobutane-containing monoterpene grandisol, an insect pheromone, has been identified as a fragment that could be modulated to improve its modest interaction with CD81-LEL. Conclusions: The modeling docking analysis suggests that Hz-B is a robust CD81 binder, better interacting with the LEL portion of CD81 compared to CD9-LEL. The docking study paves the way to the design of small molecules targeting CD81. The study has implications for a better understanding of CD81 binding properties and the regulation of its activities....Gérard Vergoten, Christian BaillyPublished: November 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00027
Insights into the binding selectivity of harzianoic acids A and B to tetraspanin CD81Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Harzianoic acids A and B (Hz-A/B) are two rare cyclobutene-containing sesquiterpenes isolated from a marine strain of the sponge-associated fungus Trichoderma harzianum. They display anticancer and antiviral effects, reducing the entry of hepatitis C virus (HCV) into hepatocarcinoma cells. The large extracellular loop (LEL) of the tetraspanin protein CD81 represents a molecular target for both Hz-A and Hz-B. Methods: The interaction of Hz-A/B with CD81 has been modeled, using structures of the cholesterol-bound full-length protein and a truncated protein corresponding to the LEL portion. The models mimicked the closed and open conformations of the LEL. Results: The best ligand Hz-B can form stable complexes with the open LEL structure, whereas binding to the closed form is drastically reduced. Key H-bonds between the acid groups of Hz-B and the CD81-LEL domain stabilize the ligand-protein complex. A comparison of the interaction with the homologous tetraspanin CD9, which also presents a dynamic open/closed equilibrium, underlined the marked selectivity of Hz-A/B for CD81 over CD9. The cyclobutane-containing monoterpene grandisol, an insect pheromone, has been identified as a fragment that could be modulated to improve its modest interaction with CD81-LEL. Conclusions: The modeling docking analysis suggests that Hz-B is a robust CD81 binder, better interacting with the LEL portion of CD81 compared to CD9-LEL. The docking study paves the way to the design of small molecules targeting CD81. The study has implications for a better understanding of CD81 binding properties and the regulation of its activities....Gérard Vergoten, Christian BaillyPublished: November 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00027 Creation and interpretation of machine learning models for aqueous solubility predictionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Solubility prediction is an essential factor in rational drug design and many models have been developed with machine learning (ML) methods to enhance the predictive ability. However, most o...Minyi Su, Enric HerreroPublished: October 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00026
Creation and interpretation of machine learning models for aqueous solubility predictionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Solubility prediction is an essential factor in rational drug design and many models have been developed with machine learning (ML) methods to enhance the predictive ability. However, most o...Minyi Su, Enric HerreroPublished: October 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00026 Therapeutic proteins immunogenicity: a peptide point of viewOpen AccessReviewProtein therapeutics are extensively used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, but a subset of patients appears to be refractory to these treatments, mainly due to the development of an immune r...Feliciana Real-Fernandez ... Paolo RoveroPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00025
Therapeutic proteins immunogenicity: a peptide point of viewOpen AccessReviewProtein therapeutics are extensively used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, but a subset of patients appears to be refractory to these treatments, mainly due to the development of an immune r...Feliciana Real-Fernandez ... Paolo RoveroPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00025 Phytochemicals for mitigating the COVID-19 crisis: evidence from pre-clinical and clinical studiesOpen AccessReviewThe outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in December 2019 quickly escalated to pandemic levels and had a severe impact on public health. There are 761 m...Atri Das ... Shantanabha DasPublished: October 24, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00024
Phytochemicals for mitigating the COVID-19 crisis: evidence from pre-clinical and clinical studiesOpen AccessReviewThe outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in December 2019 quickly escalated to pandemic levels and had a severe impact on public health. There are 761 m...Atri Das ... Shantanabha DasPublished: October 24, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00024 Late-stage diversification strategy for the synthesis of peptide acids and amides using hydrazidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modification of the C-terminus of a peptide to improve its properties, particularly after constructing the peptide chain, has great promise in the development of peptide therapeutics. This s...Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei SatoPublished: October 09, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00023
Late-stage diversification strategy for the synthesis of peptide acids and amides using hydrazidesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modification of the C-terminus of a peptide to improve its properties, particularly after constructing the peptide chain, has great promise in the development of peptide therapeutics. This s...Shoko Tanaka ... Kohei SatoPublished: October 09, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00023 Grade IV oral mucositis treatment with Brazilian green propolis mucoadherent gelOpen AccessCase ReportGreen propolis is collected by Apis mellifera from the flowers and buds of Baccharis dracunculifolia. It has several chemical compounds that confer anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, healing, and ant...Diogo Alvarenga Silva ... Vagner Rodrigues SantosPublished: October 9, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00022
Grade IV oral mucositis treatment with Brazilian green propolis mucoadherent gelOpen AccessCase ReportGreen propolis is collected by Apis mellifera from the flowers and buds of Baccharis dracunculifolia. It has several chemical compounds that confer anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, healing, and ant...Diogo Alvarenga Silva ... Vagner Rodrigues SantosPublished: October 9, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00022 Electrochemical properties of hydroxyapatite immobilization material for potential cytosensor fabricationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The biorecognition unit of an electrochemical biosensor requires molecules that are immobilised to serve as a bridge between the recognition unit and the transducing surface. Unique material...Dennis Adusei ... Elvis K. TiburuPublished: September 21, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00021
Electrochemical properties of hydroxyapatite immobilization material for potential cytosensor fabricationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The biorecognition unit of an electrochemical biosensor requires molecules that are immobilised to serve as a bridge between the recognition unit and the transducing surface. Unique material...Dennis Adusei ... Elvis K. TiburuPublished: September 21, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00021 Could flavonoid aglycones prevent the absorption of flavonoid glycosides by inhibiting sodium-dependent glucose transporter-1 in the small intestine?Open AccessCommentaryFlavonoids present a large group of natural polyphenols with numerous important health benefits for preventing and treating a diverse variety of pathological conditions. However, the actual therapeu...Katrin SakPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00019
Could flavonoid aglycones prevent the absorption of flavonoid glycosides by inhibiting sodium-dependent glucose transporter-1 in the small intestine?Open AccessCommentaryFlavonoids present a large group of natural polyphenols with numerous important health benefits for preventing and treating a diverse variety of pathological conditions. However, the actual therapeu...Katrin SakPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00019 Single or multiple treatments with lusutrombopag in subjects with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease needing an invasive procedureOpen AccessCase ReportThrombocytopenia is one of the most frequent implications of liver cirrhosis. This condition, when present in the severe form [platelet count (PLT) less than 50 × 109/L] correlates, with an increas...Davide Scalabrini ... Pietro AndreonePublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00020
Single or multiple treatments with lusutrombopag in subjects with thrombocytopenia and chronic liver disease needing an invasive procedureOpen AccessCase ReportThrombocytopenia is one of the most frequent implications of liver cirrhosis. This condition, when present in the severe form [platelet count (PLT) less than 50 × 109/L] correlates, with an increas...Davide Scalabrini ... Pietro AndreonePublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00020 In silico study about β-amyloid’s role in Alzheimer’s disease and glaucoma and prediction of its interactions with glaucoma related proteinsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The significance of β-amyloid protein as a key player in neuro-degenerative disorders viz. Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) has been extensively researched and reporte...Nancy MauryaPublished: August 29, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00018
In silico study about β-amyloid’s role in Alzheimer’s disease and glaucoma and prediction of its interactions with glaucoma related proteinsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The significance of β-amyloid protein as a key player in neuro-degenerative disorders viz. Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) has been extensively researched and reporte...Nancy MauryaPublished: August 29, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00018 The protective role of GLP-1 in neuro-ophthalmologyOpen AccessReviewDespite recent advancements in the field of neuro-ophthalmology, the rising rates of neurological and ophthalmological conditions, mismatches between supply and demand of clinicians, and an aging po...Sohum Sheth ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00015
The protective role of GLP-1 in neuro-ophthalmologyOpen AccessReviewDespite recent advancements in the field of neuro-ophthalmology, the rising rates of neurological and ophthalmological conditions, mismatches between supply and demand of clinicians, and an aging po...Sohum Sheth ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00015 Iron depletion in “metabolic fatty liver syndromes”: a strong biological rationale with disappointing liver outcomesOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), its more rapidly progressive steatohepatitic variant [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, (NASH)], and the recently defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty...Amedeo LonardoPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00016
Iron depletion in “metabolic fatty liver syndromes”: a strong biological rationale with disappointing liver outcomesOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), its more rapidly progressive steatohepatitic variant [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, (NASH)], and the recently defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty...Amedeo LonardoPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00016 Natural compounds from medicinal plants against COVID-19Open AccessReviewThe severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), known to cause the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), was declared a pandemic in early 2020. During the past time, several infecti...Anton Kolodnitsky ... Vladimir PoroikovPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00017
Natural compounds from medicinal plants against COVID-19Open AccessReviewThe severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), known to cause the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), was declared a pandemic in early 2020. During the past time, several infecti...Anton Kolodnitsky ... Vladimir PoroikovPublished: August 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00017 Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinicOpen AccessReviewBacterial infections constitute one of the major cases of primary medical incidences worldwide. Historically, the fight against bacterial infections in humans has been an ongoing battle, due to the ...Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-RomeroPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00013
Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinicOpen AccessReviewBacterial infections constitute one of the major cases of primary medical incidences worldwide. Historically, the fight against bacterial infections in humans has been an ongoing battle, due to the ...Miguel García-Castro ... Juan Manuel López-RomeroPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00013 A dextrorotatory residues-incorporated bioactive dodecapeptide against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coliOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to report an engineered peptide zp39 with favorable bioactivity against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli, EHEC). Its antibacterial mechanisms and application in a ...Ping Zeng ... Lanhua YiPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00014
A dextrorotatory residues-incorporated bioactive dodecapeptide against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coliOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to report an engineered peptide zp39 with favorable bioactivity against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli, EHEC). Its antibacterial mechanisms and application in a ...Ping Zeng ... Lanhua YiPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00014 Identification of an inter-cysteine loop potentially involved in the activity of Opisthorchis viverrini-granulin-1Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Identification of small bioactive regions in proteins and peptides can be useful information in drug design studies. The current study has shown that an inter-cysteine loop of the N-terminal...Rozita Takjoo ... Norelle L. DalyPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00012
Identification of an inter-cysteine loop potentially involved in the activity of Opisthorchis viverrini-granulin-1Open AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Identification of small bioactive regions in proteins and peptides can be useful information in drug design studies. The current study has shown that an inter-cysteine loop of the N-terminal...Rozita Takjoo ... Norelle L. DalyPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00012 Nature-inspired and medicinally relevant short peptidesOpen AccessReviewPeptides constitute an important component of Nature’s pharmacy and they play a significant role in several signaling pathways acting as natural biological messengers. While nature has mastered th...Maria G. Ciulla ... Kamal KumarPublished: June 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00011
Nature-inspired and medicinally relevant short peptidesOpen AccessReviewPeptides constitute an important component of Nature’s pharmacy and they play a significant role in several signaling pathways acting as natural biological messengers. While nature has mastered th...Maria G. Ciulla ... Kamal KumarPublished: June 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00011 Heterogeneous graph convolutional neural network for protein-ligand scoringOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Drug discovery is a long process, often taking decades of research endeavors. It is still an active area of research in both academic and industrial sectors with efforts on reducing time and...Kevin Crampon ... Luiz Angelo SteffenelPublished: April 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00010
Heterogeneous graph convolutional neural network for protein-ligand scoringOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Drug discovery is a long process, often taking decades of research endeavors. It is still an active area of research in both academic and industrial sectors with efforts on reducing time and...Kevin Crampon ... Luiz Angelo SteffenelPublished: April 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00010 Focused ultrasound for treatment of peripheral brain tumorsOpen AccessReviewMalignant brain tumors are the leading cause of cancer-related death in children and remain a significant cause of morbidity and mortality throughout all demographics. Central nervous system (CNS) t...Phillip Mitchell Johansen ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00009
Focused ultrasound for treatment of peripheral brain tumorsOpen AccessReviewMalignant brain tumors are the leading cause of cancer-related death in children and remain a significant cause of morbidity and mortality throughout all demographics. Central nervous system (CNS) t...Phillip Mitchell Johansen ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00009 Nano theranostics involved in bladder cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a complex disease with multiple clinical manifestations and treatment challenges, and current standard-of-care therapies remain limited and unfavorable. Theranostics, the inte...Kunpeng Liu ... Qingsong YuPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00008
Nano theranostics involved in bladder cancer treatmentOpen AccessReviewBladder cancer (BC) is a complex disease with multiple clinical manifestations and treatment challenges, and current standard-of-care therapies remain limited and unfavorable. Theranostics, the inte...Kunpeng Liu ... Qingsong YuPublished: April 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00008 Machine learning for drug scienceOpen AccessEditorialWalter F. de Azevedo Jr.Published: April 16, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00007
Machine learning for drug scienceOpen AccessEditorialWalter F. de Azevedo Jr.Published: April 16, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00007 Levistolide A and periplogenin inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivoOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In the present study, the natural products levistolide A (LA) and periplogenin (PPG) were studied for their growth inhibitory effects on the development of gastric cancer cells in vitro and, ...Jia Li Guo ... Ji Zhong ZhaoPublished: March 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00006
Levistolide A and periplogenin inhibit the growth of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivoOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In the present study, the natural products levistolide A (LA) and periplogenin (PPG) were studied for their growth inhibitory effects on the development of gastric cancer cells in vitro and, ...Jia Li Guo ... Ji Zhong ZhaoPublished: March 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00006 Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain for retrieving and archiving augmented reality surgical navigation dataOpen AccessSystematic ReviewAim: Conventional techniques to share and archive spinal imaging data raise issues with trust and security, with novel approaches being more greatly considered. Ethereum smart contracts present o...Sai Batchu ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00005
Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain for retrieving and archiving augmented reality surgical navigation dataOpen AccessSystematic ReviewAim: Conventional techniques to share and archive spinal imaging data raise issues with trust and security, with novel approaches being more greatly considered. Ethereum smart contracts present o...Sai Batchu ... Brandon Lucke-WoldPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00005 Surface functionalized mesoporous polydopamine nanocomposites for killing tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic treatmentOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of a collaborative strategy with improved efficacy holds great promise in tumor treatment. This study aims to develop an effective collaborative strategy based on functionalized mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) nanocomposites for killing tumor cells. Methods: MPDA nanoparticles were synthesized and functionalized with camptothecin (CPT) payload and manganese dioxide (MnO2) coating to construct MPDA-CPT-MnO2 nanocomposites. Results: When uptaken by tumor cells, the nanocomposites can degrade to produce O2, release CPT, and generate manganese (Mn2+) under the stimulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and acid. The released CPT and Mn2+ can act as chemotherapeutic drug and Fenton-like agent, respectively. Abundant reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated in 4T1 tumor cells through an Mn2+-mediated Fenton-like reaction. After that, the generated Mn4+ can react with glutathione (GSH) through redox reaction to produce Mn2+ and deplete GSH, disrupting the reducing capacity and benefiting the production of ROS in tumor cells. Under laser irradiation, the nanocomposites can generate hyperthermia to promote the production of ROS. Conclusions: The developed MPDA-CPT-MnO2 nanocomposites can kill tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic therapy (CDT)....Yi Ouyang ... Hui LiuPublished: February 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00003
Surface functionalized mesoporous polydopamine nanocomposites for killing tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic treatmentOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The development of a collaborative strategy with improved efficacy holds great promise in tumor treatment. This study aims to develop an effective collaborative strategy based on functionalized mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA) nanocomposites for killing tumor cells. Methods: MPDA nanoparticles were synthesized and functionalized with camptothecin (CPT) payload and manganese dioxide (MnO2) coating to construct MPDA-CPT-MnO2 nanocomposites. Results: When uptaken by tumor cells, the nanocomposites can degrade to produce O2, release CPT, and generate manganese (Mn2+) under the stimulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and acid. The released CPT and Mn2+ can act as chemotherapeutic drug and Fenton-like agent, respectively. Abundant reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated in 4T1 tumor cells through an Mn2+-mediated Fenton-like reaction. After that, the generated Mn4+ can react with glutathione (GSH) through redox reaction to produce Mn2+ and deplete GSH, disrupting the reducing capacity and benefiting the production of ROS in tumor cells. Under laser irradiation, the nanocomposites can generate hyperthermia to promote the production of ROS. Conclusions: The developed MPDA-CPT-MnO2 nanocomposites can kill tumor cells through collaborative chemo/photothermal/chemodynamic therapy (CDT)....Yi Ouyang ... Hui LiuPublished: February 27, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00003 Essential functions, syntheses and detection of sialyl Lewis X on glycoproteinsOpen AccessReviewIt is widely acknowledged that sialyl Lewis X (sLeX), the composition and linkage of which are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) α2-3 galactose (Gal) β1-4 [fucose (Fuc) α1-3] N-acetylglucosamine, is usually attached to the cell surface. It presents as a terminal structure on either glycoproteins or glycolipids and has been demonstrated to be related to various biological processes, such as fertilization and selectin binding. Due to the vital role of sLeX, its synthesis as well as its determination approaches have attracted considerable attention from many researchers. In this review, the focus is sLeX on glycoproteins. The biological importance of sLeX in fertilization and development, immunity, cancers, and other aspects will be first introduced. Then the chemical and enzymatic synthesis of sLeX including the contributions from more than 15 international research groups will be described, followed by a brief view of the sLeX detection focusing on monosaccharides and linkages. This review is valuable for those readers who are interested in the chemistry and biology of sLeX....Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen LiPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00004
Essential functions, syntheses and detection of sialyl Lewis X on glycoproteinsOpen AccessReviewIt is widely acknowledged that sialyl Lewis X (sLeX), the composition and linkage of which are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) α2-3 galactose (Gal) β1-4 [fucose (Fuc) α1-3] N-acetylglucosamine, is usually attached to the cell surface. It presents as a terminal structure on either glycoproteins or glycolipids and has been demonstrated to be related to various biological processes, such as fertilization and selectin binding. Due to the vital role of sLeX, its synthesis as well as its determination approaches have attracted considerable attention from many researchers. In this review, the focus is sLeX on glycoproteins. The biological importance of sLeX in fertilization and development, immunity, cancers, and other aspects will be first introduced. Then the chemical and enzymatic synthesis of sLeX including the contributions from more than 15 international research groups will be described, followed by a brief view of the sLeX detection focusing on monosaccharides and linkages. This review is valuable for those readers who are interested in the chemistry and biology of sLeX....Qiushi Chen ... Xuechen LiPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00004 Convenient estimation of oxytetracycline and polymyxin B by a novel high-performance liquid chromatography method: development and validationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this research work was to develop a validated reversed-phase (RP)-high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for simultaneous estimation of oxytetracycline (OXY) and pol...Tanu Chaudhary ... Dilpreet SinghPublished: February 24, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00002
Convenient estimation of oxytetracycline and polymyxin B by a novel high-performance liquid chromatography method: development and validationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The aim of this research work was to develop a validated reversed-phase (RP)-high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for simultaneous estimation of oxytetracycline (OXY) and pol...Tanu Chaudhary ... Dilpreet SinghPublished: February 24, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2023.00002 Drug discovery: a multifactorial ecosystemOpen AccessEditorialFernando AlbericioPublished: January 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2022.00001
Drug discovery: a multifactorial ecosystemOpen AccessEditorialFernando AlbericioPublished: January 01, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. DOI: 10.37349/eds.2022.00001 -