Editor's Picks
Open Access
Review
Understanding liver and digestive diseases: a paved road to improve diagnosis, management, and treatment
Digestive diseases comprise a diverse range of illnesses, which are prevalent worldwide and represent an important health issue. This is particularly relevant for the impact of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) due to its close association with the obesity pandemic, contributing to the escalation of MASLD as the most common form of chronic liver disease, and the main cause of liver cancer. Not only does MASLD reflect the deterioration of liver health, but it also has far-reaching consequences for the development of extrahepatic digestive diseases. Along with the progression of liver and digestive diseases to liver, colorectal and pancreatic cancer, the onset of inflammation in diseases of the digestive tract, drug-induced liver injury, and cholestasis, drives and contributes to the rise of these diseases in the future, which merit the attention of clinical and translational research to increase our understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms underlying these disorders in order to improve the diagnosis, management, and treatment. With this goal in mind, the current collaborative review gathers experts in a wide range of liver and digestive diseases to provide an up-to-date overview of the mechanisms of disease and identify novel strategies for the improvement of these important health issues.
Open Access
Review
Diverticulitis—new evidence to share with patients
Diverticulitis is one of the most common gastrointestinal causes of hospitalization in Western society. While previously characterized as a disease of older patients, new literature highlights an increasing incidence among the younger population. Over the past few decades, the understanding of etiology and management of diverticulitis has changed drastically. New data refute past beliefs while promoting other novel recommendations to mitigate incidence and subsequent complications. Data now confirms the safety and possible protective benefit of particulate food, while highlighting evidence-based approaches for the use of diagnostic imaging and antibiotics. We recognize modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors that are commonly seen throughout the literature and play a significant role in the management and prevention of diverticulitis. Emerging evidence also links chronic inflammation with subsequent microbial dysbiosis and alterations in the neuroendocrine system, leading to visceral hypersensitivity and perturbation of the gut-brain axis. This review provides a comprehensive update on acute uncomplicated diverticulitis according to the most recent evidence-based literature, encompassing the risks, diagnostic modalities, and management treatment regimens.

Open Access
Review
Pediatric cirrhosis: special consideration for its diagnosis and management
Pediatric cirrhosis differs significantly from adult liver disease in terms of etiology, progression, and management. The unique physiological, nutritional, and developmental needs of children require specialized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. This review underscores the distinct challenges in diagnosing and managing pediatric cirrhosis, focusing on its complications, management, and outcomes. Unlike adults, where cirrhosis often results from viral hepatitis or alcohol use, pediatric cases are predominantly cholestatic, with biliary atresia being the most common cause. Complications mainly involve portal hypertension and impaired liver function, leading to malnutrition and neurodevelopmental delay. Nutritional management is complex and requires increased caloric and protein intake, supplementation with fat-soluble vitamins, and the use of medium-chain triglycerides. Although hepatocellular carcinoma is rare in children, it remains a severe complication with a higher incidence in certain genetic and metabolic disorders. Surveillance is challenging due to diagnostic limitations and the lack of standardized pediatric screening protocols. Treatment is further complicated by constraints related to size and developmental stage, particularly in the management of portal hypertension. Pediatric cirrhosis requires an individualized multidisciplinary approach to address the interplay between growth, nutrition, and liver function. Early diagnosis, nutritional optimization, malignancy surveillance, and timely referral for liver transplantation are crucial. Ongoing research on pediatric-specific therapies and outcomes is essential for improving prognosis and quality of life.

Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Case Report
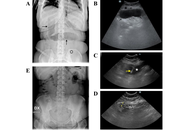
Role of ultrasound in the detection and management of complications of swallowable intragastric balloons for obesity: a report of two cases
Giampiero Francica, Cristiano Giardiello
Published: March 05, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005114
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Case Report
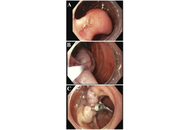
Duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma: a rare case report
Chloe Lahoud ... Jean M. Chalhoub
Published: March 05, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005113
Open Access
Review
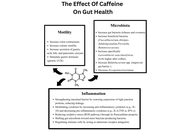
The impact of caffeine in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature
Mohamed Ahmed Mohamed ... Faith Bishop
Published: February 26, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005112
This article belongs to the special issue Inflammatory Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Open Access
Case Report
A unique association between herpes simplex esophagitis and eosinophilic esophagitis: a case report
Sahil Sabharwal ... Terryl Ortego
Published: February 13, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005111
Open Access
Review
Understanding liver and digestive diseases: a paved road to improve diagnosis, management, and treatment
Ina Bergheim ... Jose C Fernandez-Checa
Published: February 09, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005110

Open Access
Review
Artificial intelligence in the interventional management of liver disease: a narrative review from foundational concepts to clinical applications
Hyeon Yu
Published: January 18, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005109
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Review
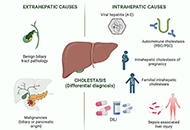
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and management
Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-Cortés
Published: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:202–222
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Open Access
Review
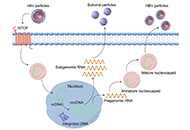
Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccines
Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang Yang
Published: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:443–458
This article belongs to the special issue Viral Hepatitis
Open Access
Review
Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?
Finn Jung ... Ina Bergheim
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:118–132
Open Access
Review
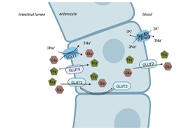
Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative review
Anja Baumann ... Ina Bergheim
Published: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:51–71
Open Access
Review
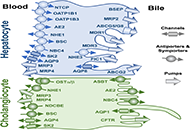
Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasis
Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. Marin
Published: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:97–117
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Open Access
Review
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradication
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:107–142
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics
Open Access
Review
Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccines
Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang Yang
Published: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:443–458
This article belongs to the special issue Viral Hepatitis

Open Access
Review
Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasis
Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. Marin
Published: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:97–117
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS

Open Access
Review
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and management
Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-Cortés
Published: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:202–222
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS

Open Access
Review
Ascites in cirrhotic patients: a comprehensive review
Paul Carrier ... Laure Elkrief
Published: August 26, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:362–381
This article belongs to the special issue Cirrhosis and Its Complications
Open Access
Review
Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative review
Anja Baumann ... Ina Bergheim
Published: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:51–71

Open Access
Review
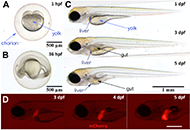
Zebrafish as a model for drug induced liver injury: state of the art and beyond
Gulcin Cakan-Akdogan ... Ozlen Konu
Published: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:44–55
This article belongs to the special issue Drug-induced Liver Injury: From Bench to Clinical Application
Open Access
Review
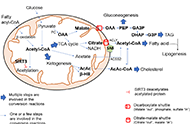
The central role of mitochondrial metabolism in hepatic steatosis
Sanda Win ... Filbert Win Min Aung
Published: February 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:42–68
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Open Access
Review
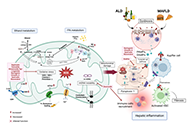
Mitochondrial ROS, a trigger for mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammasome activation and a therapeutic target in liver diseases
Hala Saeed Jaara, Sandra Torres
Published: December 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:474–503
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Open Access
Review
Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic implications
Zongmei Wu ... Han Moshage
Published: July 13, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. 2022;1:4–20
Open Access
Editorial
Extra-hepatic cancers in metabolic fatty liver syndromes
Amedeo Lonardo
Published: February 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:11–17
Open Access
Review
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradication
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:107–142
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics

Open Access
Review
Impact of mitochondrial lipid alterations on liver disease mechanisms and progression
Laura Fàbrega ... Carmen Garcia-Ruiz
Published: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. 2024;3:382–413
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer
Guest Editor: Prof. Raghu Sinha
Submission Deadline: September 01, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Inflammatory Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Guest Editor: Prof. Simona Gurzu
Submission Deadline: January 31, 2026
Published Articles: 1
Endoscopic Evaluation in Liver Diseases
Guest Editor: Prof. Cosmas Rinaldi A. Lesmana
Submission Deadline: January 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Nuclear Receptors and the Digestive Tract: from Molecular Physiology to Clinics via Pharmacology
Guest Editors: Prof. Amedeo Lonardo; Prof. Ralf Weiskirchen
Submission Deadline: November 30, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Gastrointestinal Cancer
Guest Editor: Prof. Nahum Mendez-Sanchez
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer
Guest Editor: Prof. Jian-Guo Chen
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 2
Gut Microbiota towards Personalized Medicine in Metabolic Disease
Guest Editors: Prof. Raquel Soares; Dr. Carla Luís
Submission Deadline: February 28, 2026
Published Articles: 3

The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Management of Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Guest Editor: Dr. Alfredo Caturano
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 2

Diverticulitis: Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment
Guest Editor: Prof. Roberto Cirocchi
Submission Deadline: January 15, 2026
Published Articles: 4
Immunotherapy for Cancer of Digestive System
Guest Editor: Prof. Evgeny Imyanitov
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 2
Gastrointestinal Diseases, Cholesterol, Oxysterols, and Bile Acids
Guest Editor: Prof. Oren Tirosh
Submission Deadline: January 31, 2026
Published Articles: 1
Viral Hepatitis
Guest Editors: Dr. Jinsheng Guo; Prof. Youhua Xie
Submission Deadline: February 28, 2026
Published Articles: 5
Cirrhosis and Its Complications
Guest Editor: Prof. Jean Francois D. Cadranel
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 6
Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics
Guest Editor: Prof. Tzi-Bun Ng
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 6

Latest Updates in the Endoscopic, Surgical and Medical Treatment of Resectable and Advanced Gastrointestinal Cancers
Guest Editor: Dr. Michele Ghidini
Submission Deadline: October 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Guest Editor: Prof. Amedeo Lonardo
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 8

Fibrosis and Hepatobiliary Cancer
Guest Editors: Prof. Fabio Marra; Prof. Chiara Raggi
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 4

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics
















 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


