Editor's Picks
Open Access
Editorial
Who is the Editor-in-Chief of a scientific journal: supreme judge or mailman?
The editor-in-chief plays a vital role in ensuring a journal’s scientific integrity and quality. Their primary responsibilities include managing the peer-review process, selecting qualified reviewers, and making final decisions on manuscript acceptance, revision, or rejection. In cases of scientific misconduct, conflicts of interest, authorship disputes, or ethical concerns, the editor has the ultimate authority.
An editor’s vision for the journal shapes which manuscripts are reviewed and accepted, influencing the journal’s academic direction. While the role offers benefits such as scientific prestige, greater research visibility, and financial compensation, it also entails significant ethical responsibilities. Academic editor malpractice refers to any actions that violate ethical standards or compromises the integrity of the peer-review process.
Editors typically serve five-year terms, often with the possibility of renewal, and are frequently evaluated based on the journal’s impact factor trend. However, their role extends beyond editorial duties—they act as gatekeepers, literary agents, accountants, mediators, and judges, navigating the complex relationships among authors, reviewers, and publishers.
Editors of major journals hold an extraordinary amount of power within the publication process. They act as an umpire to judge the scientific research that is being published. Like an umpire, they must know about the sport and rules of play, but they themselves should never be in the competition. The problem is that this ideal is not always met. Whether the subject is the efficacy of an antihypertensive drug, the value of a new costly biomarker, or the origin of a pandemic, editors often make decisions for multi-parametric—and also extra-scientific—reasons. On this basis, some papers are published while others are declined, and the stream of scientific evidence can be polluted.
In summary, the editor-in-chief is a cornerstone of academic publishing, ensuring that scientific quality and integrity are upheld while balancing multiple responsibilities.

Open Access
Systematic Review
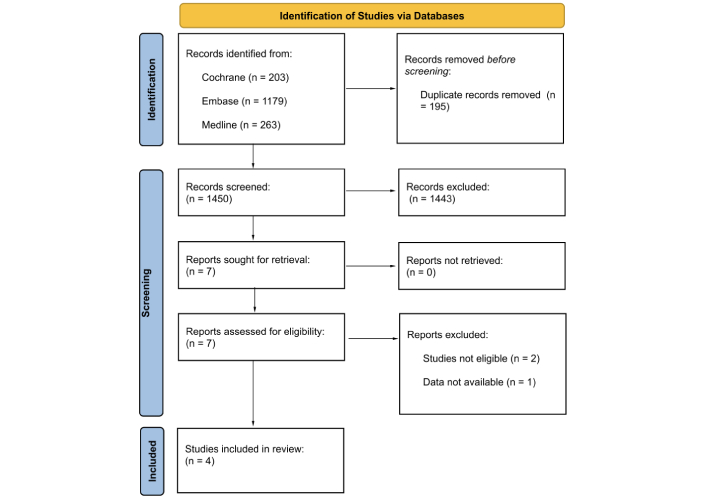
Long-term cardiovascular sequelae of COVID-19 in patients with pre-existing heart failure: a systematic review
Background:
Patients with pre-existing heart failure (HF) are particularly vulnerable to adverse outcomes following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Understanding of the long-term cardiovascular sequelae of COVID-19 in this high-risk group is essential to improve post-infection management and outcomes.
Methods:
A systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Embase was conducted to identify peer-reviewed studies published between 2020 and 2025. Eligible studies included adults with a confirmed diagnosis of HF prior to COVID-19 infection and reported cardiovascular outcomes assessed at least 12 weeks after the acute phase. Data were extracted on patient demographics, HF subtype, cardiovascular outcomes, quality of life (QoL), and management approaches.
Results:
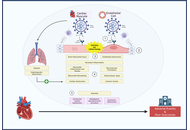
Forty-five studies met the inclusion criteria, encompassing heterogeneous but predominantly high-income country populations across multiple regions and HF phenotypes. COVID-19 was associated with increased HF symptoms, hospital readmissions 28% [95% confidence interval (CI) 24–32%] at 12 months, and mortality 18% (95% CI 15–22%) at ≥ 12 months. Patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) had a 1.4-fold greater readmission risk than HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Mechanistic data implicated persistent myocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and autonomic dysregulation. Functional capacity declined, with a mean 68-meter reduction in six-minute walk distance (6MWD). Vaccination was associated with a ~40% reduction in mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Discussion:
COVID-19 is associated with a sustained cardiovascular burden in individuals with HF, underscoring the importance of long-term surveillance, optimization of guideline-directed medical therapy, and structured rehabilitation. Standardized, prospective studies are needed to elucidate causal mechanisms and refine post-COVID management strategies.
Open Access
Case Report
EKOS failure with INARI salvage in massive pulmonary embolism: a literature review and case report
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular mortality and presents a significant challenge in acute care settings. EkoSonic Endovascular System (EKOS) (ultrasound assisted catheter directed thrombolysis) and suction thrombectomy have emerged as key treatment options for high and intermediate risk PE. EKOS delivers localized fibrinolytic therapy, whereas thrombectomy provides definitive clot removal using devices such as the FlowTriever System (Inari Medical). However, the optimal treatment strategy, particularly in recurrent PE, remains uncertain. We report a case requiring escalation of therapy from EKOS to suction thrombectomy due to recurrent PE and worsening hemodynamic status despite initial thrombolysis. The patient was initially treated with EKOS for a saddle PE but was rehospitalized with syncope and persistent right ventricular (RV) strain. Given the inadequate response to thrombolysis, suction thrombectomy was performed, leading to marked improvement in RV function and overall clinical status. This case underscores the importance of individualized management and timely escalation when initial therapy is insufficient. Assessment of therapeutic success should include not only symptomatic relief but also resolution of clot burden and RV recovery. A focused literature review comparing EKOS and suction thrombectomy suggests that while both modalities are viable, suction thrombectomy may offer faster hemodynamic improvement in select patients. However, available data remains limited, highlighting the need for further comparative studies. Overall, this case and review support a tailored, multidisciplinary approach to PE management, emphasizing shared decision making and early escalation in patients with clinical deterioration despite initial intervention.

Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Review
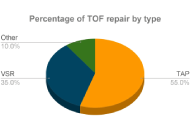
Comparison of transannular patch and valve-sparing repair techniques in tetralogy of Fallot
Jui Rajendra Gaikwad ... Lester Thomas D Costa
Published: March 08, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:1012100
Open Access
Commentary
Author’s Reply: The Editor’s role, again
Eugenio Picano
Published: March 08, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101299

Open Access
Letter to the Editor
The Editor-in-Chief should be a virtuous friend of the scientific and broader community
Timothy Daly, Jaime A. Teixeira da Silva
Published: March 02, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101298

Open Access
Case Report
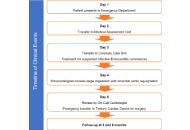
Challenges in diagnosing infective endocarditis in the context of recent COVID-19 infection: A case report
Erum Ahmad ... Azeem S. Sheikh
Published: February 27, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101297
Open Access
Case Report
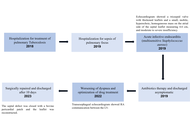
Gerbode defect secondary to tricuspid valve endocarditis: a case report
Roberto Ramos Barbosa ... Luiz Fernando Machado Barbosa
Published: February 12, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101296
Open Access
Review
Autonomic dysfunction and resting heart rate abnormalities as early cardiovascular signals in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): a focused review
Afra Wasama Islam ... Harsahaj Singh Wilkhoo
Published: February 12, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101295

Open Access
Review
Why and when should be lipoprotein(a) level measured?
Miłosz Broncel, Marlena Broncel
Published: December 29, 2023 Explor Cardiol. 2023;1:180–192
This article belongs to the special issue Common cardiovascular target for a wide gamut of contemporary health problems – thrombotic and arrhythmic sides of an inflammatory coin
Open Access
Review
Comparison of short-term and long-term effects of peroral L-carnitine intake: clinical implications of elevated TMAO levels in cardiovascular complications
Harsahaj Singh Wilkhoo ... Adnan Akhtar Shaikh
Published: February 10, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101250
Open Access
Review
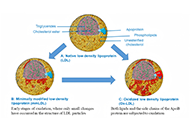
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins and their contribution to atherosclerosis
Abdullatif Taha Babakr
Published: January 17, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101246
This article belongs to the special issue Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Aging
Open Access
Review
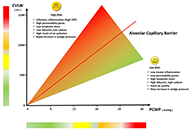
B-lines by lung ultrasound in cardiology
Marco Antonio Rodrigues Torres, Natália Moraes de Quevedo
Published: November 14, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:265–279
This article belongs to the special issue Multimodality Imaging in Ischemic Heart Disease
Open Access
Editorial
Who is the author: genuine, honorary, ghost, gold, and fake authors?
Eugenio Picano
Published: May 13, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:88–96
Open Access
Review
Mitral valve prolapse—arrhythmic faces of the valve disease
Maria Możdżan ... Karina Wierzbowska-Drabik
Published: October 31, 2023 Explor Cardiol. 2023;1:72–87
This article belongs to the special issue Common cardiovascular target for a wide gamut of contemporary health problems – thrombotic and arrhythmic sides of an inflammatory coin
Open Access
Review
Diagnostic modalities for ischemic heart disease: evaluating the role of stress echocardiography, cardiac CT, and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in guiding coronary angiography
Marco Fabio Costantino ... Luisiana Stolfi
Published: January 13, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101243
This article belongs to the special issue Multimodality Imaging in Ischemic Heart Disease
Open Access
Review
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins and their contribution to atherosclerosis
Abdullatif Taha Babakr
Published: January 17, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101246
This article belongs to the special issue Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Aging

Open Access
Review
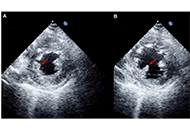
Echocardiographic Management of papillary muscle rupture during acute myocardial infarction
Paolo G. Pino ... Federico Nardi
Published: January 10, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101242
Open Access
Editorial
Who is a reviewer? The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly phenotypes
Eugenio Picano
Published: January 23, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101248
Open Access
Review
Comparison of short-term and long-term effects of peroral L-carnitine intake: clinical implications of elevated TMAO levels in cardiovascular complications
Harsahaj Singh Wilkhoo ... Adnan Akhtar Shaikh
Published: February 10, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101250

Open Access
Original Article
Heart rate variability in soccer players and the application of unsupervised machine learning
Wollner Materko ... Carlos Alberto Machado de Oliveira Figueira
Published: January 10, 2025 Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101241
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Exercise Cardiology: from Molecules to Humans
Open Access
Review
Laboratory markers of metabolic syndrome
Filipa Morgado ... Leonel Pereira
Published: June 24, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:114–133
This article belongs to the special issue Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Aging
Open Access
Review
Noninvasive identification and therapeutic implications of supernormal left ventricular contractile phenotype
Yi Wang, Lixue Yin
Published: June 17, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:97–113
Open Access
Editorial
Who is the author: genuine, honorary, ghost, gold, and fake authors?
Eugenio Picano
Published: May 13, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:88–96

Open Access
Review
Toxic metals in pregnancy and congenital heart defects. Insights and new perspectives for a technology-driven reduction in food sources
Francesca Gorini, Alessandro Tonacci
Published: November 13, 2023 Explor Cardiol. 2023;1:114–140
This article belongs to the special issue Environmental Cardiology

Open Access
Review
Epigenetic mechanisms linking pregnancy complications to cardiovascular disease in offspring
Kazim Raza Talpur ... Muhammad Waleed Abdullah
Published: November 07, 2024 Explor Cardiol. 2024;2:241–252
This article belongs to the special issue Cardiovascular Risk for Mothers and Offspring Resulting from Complicated Pregnancy
Open Access
Systematic Review
Long-term cardiovascular sequelae of COVID-19 in patients with pre-existing heart failure: a systematic review
Razieh Parizad ... Bishav Mohan
Published: January 04, 2026 Explor Cardiol. 2026;4:101284

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Heart–Brain Interactions: Clinical-Psychological Perspectives on Cardiovascular Function
Guest Editors: Pasquale Caponnetto; Graziella Chiara Prezzavento
Submission Deadline: August 15, 2026
Published Articles: 0
The Effect of Sexual Dysfunctions, Peripheral Artery Disease, and Patient Education on the Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes
Guest Editors: Carmine Gazzaruso; Adriana Coppola
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2026
Published Articles: 1
Exploring Exercise Cardiology: from Molecules to Humans
Guest Editor: Paulo Gentil
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2026
Published Articles: 3

Cardiovascular Risk for Mothers and Offspring Resulting from Complicated Pregnancy
Guest Editor: Ilona Hromadnikova
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 3
Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Aging
Guest Editor: Andrea Borghini
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2026
Published Articles: 5
Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics

















 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


