Editor's Picks
Open Access
Review
A novel therapeutic strategy of obesity from the perspective of SPMs
The global prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)—the most common metabolic disorders—has reached epidemic proportions over the past half-century, with obesity being a key driver of insulin resistance and T2DM development. These disorders are characterized by metaflammation (chronic low-grade inflammation across multiple metabolic organs like adipose tissue, liver, muscle, and the gut), which disrupts metabolic homeostasis, exacerbates insulin resistance, impairs insulin secretion, and links to other comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases. A major advance in understanding inflammation resolution is the identification of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), a family of lipid mediators including resolvins, lipoxins, protectins, and maresins. Derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g., EPA, DHA), SPMs actively regulate inflammation resolution by constraining pro-inflammatory cell infiltration (e.g., neutrophils), promoting anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization (M2), enhancing efferocytosis (clearance of apoptotic cells), and preserving tissue barrier integrity—without inducing immunosuppression. This review summarizes evidence from human and animal studies on obesity-related metaflammation in metabolic tissues and the role of SPMs in resolving this inflammation. It details SPM mechanisms (e.g., maintaining adipose tissue homeostasis, improving insulin sensitivity, alleviating hepatic steatosis) and highlights their dysregulation in obesity (e.g., impaired biosynthesis, reduced receptor expression) as a critical driver of metabolic dysfunction. Finally, the review discusses the therapeutic potential of SPM-targeted strategies (e.g., ω-3 PUFA supplementation, SPM receptor activation) for alleviating obesity, T2DM, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MAFLD), and other metabolic disorders, along with future research directions in this field.
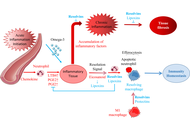
Open Access
Review
Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual incretin agonists on adipocyte type and size
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and dual incretin agonists have demonstrated significant potential in improving adipose tissue function beyond their established effects on appetite suppression and weight loss. These agents not only reduce overall fat mass but also induce favorable changes in fat distribution and adipose tissue quality. Notably, they enhance brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity and promote the browning of white adipose tissue (WAT), thereby increasing energy expenditure. They are associated with reductions in adipocyte size, particularly within visceral fat depots, alongside improvements in metabolic health markers. The aim of this publication is to provide a literature review on the effects of GLP-1RAs and dual incretin agonists on adipocyte type and size, adipose tissue functional remodeling, and their implications for obesity management. These findings highlight the capacity of incretin-based therapies to modulate adipose tissue biology, offering metabolic benefits that extend beyond weight reduction.
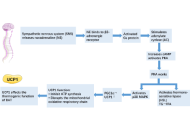
Open Access
Original Article
Waist-to-height ratio as a novel marker of metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Aim:
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is associated with chronic conditions, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disorders. New markers are needed for the early detection and successful treatment of MetS, especially in patients with T2DM. The serum uric acid-to-creatinine ratio (UCR) and waist-to-height ratio (WHR) are novel markers in various chronic metabolic disorders. We aimed to compare WHR, UCR, and other metabolic and laboratory markers in T2DM patients with and without MetS.
Methods:
Patients with T2DM who visited the outpatient clinics of our institution were enrolled in the study. Total diabetic subjects were 239 of which 180 were in MetS group while 59 were in without MetS group. Data from both study groups were compared.
Results:
The serum UCR in the MetS and control groups was 6.3 ± 2.1 and 5.8 ± 1.6, respectively (p = 0.04). The WHR in the MetS and control groups was 0.65 (0.47–0.87) and 0.62 (0.35–0.84), respectively (p < 0.001). Significant positive correlations were observed between UCR and triglycerides (r = 0.17, p = 0.009), waist circumference (r = 0.13, p = 0.046), hip circumference (r = 0.18, p = 0.006), BMI (r = 0.2, p = 0.002), and GFR (r = 0.4, p < 0.001). Similarly, significant positive correlations were noted between WHR and systolic blood pressure (r = 0.12, p = 0.049), weight (r = 0.5, p < 0.001), BMI (r = 0.7, p < 0.001), and UCR (r = 0.12, p = 0.047). In the ROC analysis, the sensitivity and specificity of WHR (when higher than 0.64) in detecting MetS were 72% and 54%, respectively (AUC: 0.69, p < 0.001, 95% CI: 0.61–0.77).
Conclusions:
We propose that WHR and UCR could be valuable tools for the early detection of MetS in patients with T2DM. The ease and low cost of evaluating WHR and UCR make them practical markers for monitoring and diagnosing MetS.
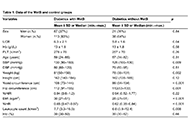
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
Fat deposits and their relationship with type 2 diabetes in patients with metabolic syndrome
Ivonne G. Narváez-Ortiz ... Alberto Maceda-Serrano
Published: March 09, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101462
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
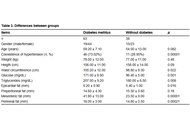
Open Access
Review
Innovative regenerative genetic and nano therapies for diabetes and metabolic disease
Maria-Kalliopi Spanorriga ... Konstantinos Tsioufis
Published: March 08, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101461
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Strategies for Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders: Current and Future Directions
Open Access
Review
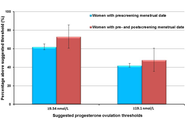
Progesterone for reproductive vitality and women’s healthy ageing
Jerilynn C. Prior, Virginia J. Vitzthum
Published: February 25, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101460
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Open Access
Original Article
Normal triglyceride levels are positively associated with plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes diagnosis in Chinese adults
Yutang Wang ... Guang Yang
Published: February 12, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101459
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

Open Access
Commentary
Treating obesity with GLP-1 RAs: does sex matter? A commentary on the meta-analysis by Yang et al. (J Diabetes 2025;17(3):e70063)
Ralf Weiskirchen, Amedeo Lonardo
Published: February 02, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101458
Open Access
Review
Impaired cytokines in diabetes and diabetic foot ulcers: mechanisms and prospects
Arbab Alam ... Vikrant Rai
Published: January 21, 2026 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2026;3:101457
This article belongs to the special issue Role of Dysregulated Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Metabolic Disease
Open Access
Commentary
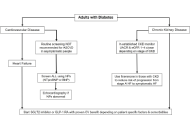
Updates from the 2025 American Diabetes Association guidelines on standards of medical care in diabetes
Dipti Tiwari ... Tar Choon Aw
Published: April 15, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101428
Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Review
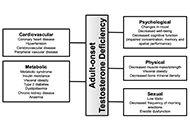
Adult-onset testosterone deficiency: the usefulness of hormone replacement in reducing mortality in men with this common age-related condition
Amar Mann ... Sudarshan Ramachandran
Published: June 28, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:83–100
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Open Access
Review
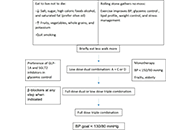
A brief approach to hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yilmaz Gunes
Published: February 04, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101422
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
Open Access
Review
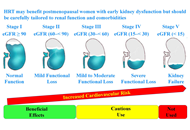
Optimizing hormone replacement therapy for postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes: a review
Butheinah A. Al-Sharafi, Samih A. Odhaib
Published: April 28, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101430
This article belongs to the special issue Metabolic Syndrome in Menopause
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26

Open Access
Commentary
Updates from the 2025 American Diabetes Association guidelines on standards of medical care in diabetes
Dipti Tiwari ... Tar Choon Aw
Published: April 15, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101428

Open Access
Case Report
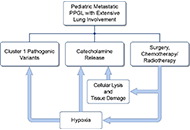
A case series of three patients with extensive lung metastatic pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: evaluation, treatment challenges, and outcomes
Kailah M. Charles ... Karel Pacak
Published: November 15, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:218–233
Open Access
Case Report
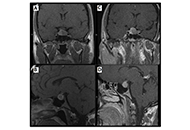
Patient diagnosed with acromegaly and pituitary apoplexy after breast carcinoma treatment: challenges in diagnosis and management
Ignacio Jiménez Hernando, Laura González Fernández
Published: November 26, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:234–243
Open Access
Review
Healthy adipose tissue after menopause: contribution of balanced diet and physical exercise
Bruno Vecchiatto ... Fabiana S. Evangelista
Published: March 13, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101424
This article belongs to the special issue Metabolic Syndrome in Menopause
Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Original Article
Waist-to-height ratio as a novel marker of metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Elif Basaran, Gulali Aktas
Published: January 10, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101421
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

Open Access
Review
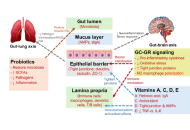
Synergistic glucocorticoids, vitamins, and microbiome strategies for gut protection in critical illness
Gianfranco Umberto Meduri
Published: May 14, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101432
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos ... Stefan R. Bornstein
Published: April 01, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:16–26

Open Access
Commentary
The 2024 American Diabetes Association guidelines on Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes: key takeaways for laboratory
Dipti Tiwari, Tar Choon Aw
Published: July 23, 2024 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2024;1:158–166

Open Access
Review
Glucocorticoid receptor alpha: origins and functions of the master regulator of homeostatic corrections in health and critical illness
Gianfranco Umberto Meduri
Published: March 28, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101426

Open Access
Commentary
Updates from the 2025 American Diabetes Association guidelines on standards of medical care in diabetes
Dipti Tiwari ... Tar Choon Aw
Published: April 15, 2025 Explor Endocr Metab Dis. 2025;2:101428

Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Innovative Strategies for Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders: Current and Future Directions
Guest Editors: Dawood Khan; Victor Gault
Submission Deadline: May 20, 2026
Published Articles: 4

Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions
Guest Editor: Gulali Aktas
Submission Deadline: May 20, 2026
Published Articles: 8
Role of Dysregulated Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Metabolic Disease
Guest Editor: Alister C. Ward
Submission Deadline: May 27, 2026
Published Articles: 1
Oxidative Stress and Diabetes – Remedies through Functional Food
Guest Editor: Viduranga Y. Waisundara
Submission Deadline: May 27, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Metabolic Syndrome in Menopause
Guest Editor: Tzong-Shyuan Lee
Submission Deadline: May 27, 2026
Published Articles: 3
The Impact of Digitalization To Improve Nutrition and Self-Management in Patients With Diabetes
Guest Editor: Peter Schwarz
Submission Deadline: May 27, 2026
Published Articles: 1

The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging
Guest Editor: Marijn Speeckaert
Submission Deadline: May 27, 2026
Published Articles: 5

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics














 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


