Authors must cite relevant literature to support any statements in their manuscripts that rely on external sources of information. All references must be closely related to the content of the article, and all cited data must be traceable to their original sources.
Journal Policies
Aims and Scope
Exploration of Drug Science is a peer-reviewed, open access online journal, covering all this process from the first idea in the laboratory to the drug already in the market. Drug Science is a multi-vector scientific activity with a great impact on society. Thus, apart from the scientific fact, the discovery of a new drug can save many lives or restore or improve social health and wellbeing. The journal considers the following topics:
★ Therapeutics strategies
★ Target discovery and validation
★ Medicinal chemistry
★ Computational chemistry, cheminformatics, and bioinformatics
★ High-throughput synthesis and screening; related technologies
★ Omics
★ Pharmacology
★ Toxicology
★ Preclinical research
★ Chemical entities, biologics, biologic treatments
★ Orphan drugs
★ Vaccines
★ Drug repurposing
★ Drug resistance
★ Drug delivery, including nanotechnologies
★ Clinical phases
★ Industry analysis and market studies
★ Patents and intellectual property
★ Pharmacoeconomics
More information is available at Aims and Scope.
Open Access
Exploration of Drug Science is an open access journal and all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
Copyright and License to Publish
Journal articles are published under the CC BY license. Authors retain the copyright and full publishing rights without restrictions and agree to make their original works completely available and free to use, copy and/or redistribute in all formats without permission, as long as the authors and the original source are properly cited. A copyright statement is published on full text files including HTML, PDF and XML.
Authors are required to sign a License to Publish agreement before formal publication of an article. This grants Open Exploration the right to publish the article and associated supplementary materials in Exploration of Drug Science under the CC BY license.
Permission for use of copyrighted materials (Figures or Tables) from other sources in the work, including re-published, adapted, modified, or partial tables from the internet, must be obtained. It is authors’ responsibility to acquire such permission, to follow any citation instruction requested by third-party rights holders, and to cover any supplementary charges. For more details, please refer to License to Publish.
Peer Review
The journal adopts a single-blind peer review model meaning that reviewers’ identities are kept concealed from authors, but authors’ identities are known to reviewers. All accepted articles (except for some Editorials released by the Editors) will have undergone a rigorous and thorough review process to evaluate their novelty, scientific content, academic integrity, etc. For more information on Peer Review, please refer to Editorial Policies.
Article Processing Charge
The journal does not charge APC from authors before January 31, 2028, during which time the APC is wholly financed by Open Exploration. From February 1, 2028, the journal charges an APC fee of $2,000 per article (excluding tax). Detailed information of APC waivers and discounts can be found at Article Processing Charges.
Archive
To ensure long-term digital preservation, all published articles will be archived on the Portico platform. Authors are also encouraged to deposit their articles in PubMed Central/Europe PMC, and other appropriate archives. It is the authors’ responsibility to ensure that any Institutional or funders requirements for archiving are met.
Preprint Policy
The journal allows authors to post preprints of the Original Version, Accepted Manuscript, and Version of Record, on preprint servers, authors’ or institutional websites, and open communications between researchers whether on community preprint servers or preprint commenting platforms. Readers should visit Sherpa Romeo to view our preprint policy. For detailed information on our preprint policy, please refer to Editorial Policies.
Cover Letter
A cover letter is welcomed to be submitted accompanying each manuscript. We suggest authors include the following contents in a cover letter:
★ The title and type of the manuscript;
★ A brief summary of the background and content of the work, and an explanation of why it warrants publication in the journal (e.g., novelty, importance etc);
★ Whether the article should be considered as part of a Special Issue;
★ A statement that this paper has not been submitted or published elsewhere;
★ A statement will be required if there are other cases need to be explained, for example, if the manuscript or part of it has been posted on preprints, conference, etc. Please find more cases at Duplicate Publication policy.
Publication Ethics
Research Ethics
For any study involving human subjects, authors should provide a statement to state that the study is approved by an institutional ethics. Written informed consent to participate should be obtained from all participants.
For manuscripts involving privacy issues (e.g., including individuals’ details in images or videos), authors must obtain the consent to publication from the participants. Authors need to provide a statement to attest that they have obtained such consent.
Any research involving animals should be approved by an animal care and use committee and conducted according to the approved protocol and acceptable research standards for animal experimentation. An ethical statement should be included at the end of the manuscript stating that the study was approved by an animal care and use committee.
For details on how to prepare such statements, please refer to the Declarations part in Structure of Manuscripts.
More specific information of Research Ethics can be found in the Editorial Policies of the journal.
Registration of Clinical Trials
The journal requires that all clinical trials should be registered in a public trials registry (WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) or in ClinicalTrials.gov) at or before the time of first patient enrollment. The trial registration number should be listed at the end of the Abstract. Secondary data analyses of primary (parent) clinical trials should not be registered as separate clinical trials, but instead should reference the trial registration number of the primary trial. Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors should provide a statement to disclose any potential or existing conflict of interest. The corresponding author must ensure that all authors have been asked to disclose any conflict of interest.
Manuscripts submitted by the editorial board members are handled separately by other editors, and the concerned editor is not involved in the decision-making or the review process.
All sources of funding should be declared, including the role of the study sponsor(s) in the study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
Authorship
The journal endorses the authorship criteria defined by ICMJE. Individuals who fulfill the following criteria can be defined as authors.
Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; AND
Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; AND
Final approval of the version to be published; AND
Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Author Contributions statement should be provided to specify the contribution of each author. The journal adopts the CRediT Taxonomy to describe each author’s individual contributions to the work. More information is available at Structure of Manuscripts.
Other individuals who have participated in the generation of the research paper but do not meet the criteria for authorship should be listed in the Acknowledgments section with a brief description of their contributions. Minors who have been involved in a piece of research (for example, children using technology) are typically acknowledged as they cannot be fully accountable for all aspects of the research.
Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
AI and AI-assisted Technologies in Scientific Writing:
For AI-assisted work, author(s) should not list AI and AI-assisted technologies as an author or co-author, nor cite AI as an author. AI and AI-assisted technologies cannot replace the tasks of researchers, such as developing scientific insights, analyzing and interpreting data, drawing scientific graphs, or drawing scientific conclusions. Author(s) should primarily use AI technologies to improve the readability and language. The use of AI to directly attribute references to cited text is strongly discouraged. When using AI for literature searches, authors should carefully verify any references provided, as they may be inaccurate or fabricated.
Author(s) are ultimately responsible and accountable for the originality, accuracy, and integrity of the article, and should disclose the use of AI and AI-assisted technology in the writing process in the Declarations section at the end of the manuscript by following the instructions below:
AI-Assisted Work Statement: During the preparation of this work, author(s) used the [name tool/service] for [reason]. After using the tool/service, author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take(s) full responsibility for the content of the publication.
This declaration does not apply to the use of basic tools for checking grammar, spelling, references etc. If there is nothing to disclose, there is no need to add a statement.
Note: A violation of this policy will be considered as scientific misconduct. The journal deals with any scientific misconduct on a case-by-case basis according to the guidance by COPE, WAME and ICMJE.
Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is not acceptable and includes, but is not limited to, copying or reusing text, ideas, images or data from other sources without clear attribution, and goes against the principle of academic publishing. Reuse of parts of text from an author’s previous research publication without clear attribution is a form of self-plagiarism.
The journal uses iThenticate to screen submitted content for originality before publication. Any issues detected by the software will be addressed by a follow-up investigation in line with COPE Guidelines and if plagiarism is detected the manuscript may be rejected, corrected or retracted, as appropriate. In some cases, the journal may inform the authors’ institutions about the case. We expect that the editors and peer reviewers will inform the journal about any concerns related to plagiarism at any stage of peer-review, publication, or post-publication. We also encourage readers to report suspicious plagiarism after publication. For more information on plagiarism and how we handle it, please refer to Editorial Policies.
Duplicate Publication
The journal considers only original content meaning that articles must not have been previously published or submitted for publication, including in a language other than English. If related materials are under consideration or in press elsewhere, the authors should point this out in their cover letter.
If authors have used their own previously published work, or work that is currently under review, as the basis for a submitted manuscript, they must cite the previous articles and indicate how their submitted manuscript differs from their previous work. Reuse of the authors’ own figures or substantial amounts of wording may require permission from the copyright holder and the authors are responsible for obtaining this.
Several exceptions do not constitute duplicate publication if justified and made clear in the cover letter. Please find such exceptions at Editorial Policies.
If a manuscript is published and later found to be redundant, the editor should refer to the COPE Flowcharts and work with the publisher to retract the duplicate paper.
Misconduct
The journal endorses the summary of misconduct provided by WAME. Misconduct includes, but is not limited to: Falsification of data, Plagiarism, Improprieties of authorship, Misappropriation of the ideas of others, Violation of generally accepted research practices, Material failure to comply with legislative and regulatory requirements affecting research, Inappropriate behavior in relation to misconduct, Duplicate publication, Lack of declaration.The journal adopts iThenticate to detect possible plagiarism, which ensures the originality of submitted content. We encourage all reviewers to report potential misconduct of the manuscripts they reviewed. We also encourage all the readers to contact us to report potential misconduct related to published content. Open Exploration deals with all allegations of potential misconduct severely based on the COPE Flowcharts. Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
Citation
Authors are required to cite relevant and closely related literature for all statements derived from external sources of information, and to ensure that all cited data are traceable to their original sources. Please refer to Editorial Policies for further information.
Citation manipulation may exist when articles are found to contain references that do not contribute to the scholarly content of the article and have been included solely as a mechanism of increasing citations. Please refer to the COPE document to identify Citation Manipulation and legitimate self-citation. Citation manipulation will result in the article being rejected, and the journal may report the case to authors’ institutions.
Corrections and Retractions
Corrections will be published where honest errors are detected. Retraction will be published when seriously flawed or erroneous content or data are detected, such that the findings and conclusions are unreliable. Unreliable content or data may result from honest error, naive mistakes, or research misconduct.
More guidelines about when and how to publish Corrections/Retractions, please refer to Editorial Policies.
Appeals and Complaints
Authors have the right to appeal editorial decisions or review reports during the editorial process. Please contact the editorial office at edsjournal@explorationpub.com to submit your appeals. Complaints on editorial process or publication ethics should be delivered to the editorial office, and will be handled by the Editor who responsible for the journal. If the editor is involved in your complaints, please contact the publisher at info@explorationpub.com. For complaints about publication ethics, we will follow guidelines published by COPE.
Types and Templates of Manuscripts
The journal publishes Original Article, Review, Meta-Analysis, Systematic Review, Short Communication, Case Report, Protocol, Commentary, Perspective, Editorial, and Letter to the Editor.
Read more details about manuscript types and the specific requirements of each type in the following table.
If you have an article that requires more words/tables/figures/references than the recommendation below, please contact the editors at edsjournal@explorationpub.com before submission.
Article Type | Definition | Abstract | Keywords | Main Text | Word Count (main text) | Table/Figure Number | Reference Number | Note |
Original Article
| An Original Article should report scientifically sound experiments from original research, providing novel concepts and information in certain areas. It must describe significant and origial observations. | Structured abstract including Aim, Methods, Results, and Conclusions. ≤ 300 words
|
3-8
| Structured main text including Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results, and Discussion. | N/A | N/A | N/A | Supplementary Information is advisable. |
Review | A review should describe an overview of recent progress in important fields of research, providing an appreciation of the significance of the work, and an outlook into potential future directions. | Unstructured abstract. ≤ 300 words | 3-8 | Structured main text with unfixed section titles. An “Introduction” section at the beginning, several sections with unfixed titles in the middle part, and a “Conclusions” section at the end would be preferred. | ≥ 3000 words | N/A | N/A | If your review is a concise summary of a specific relevant research topic or field, of 3000 words or less, please submit it as a Mini-Review. |
Systemic Review | A systematic review should present a detailed investigation of previous research on a given topic that uses clearly defined search parameters and methods to identify, categorize, analyze, and report aggregated evidence on a specific topic. | Structured abstract including Background, Methods, Results, and Discussion. ≤ 300 words | 3-8 | Structured main text including Introduction, Materials and methods, Results, and Discussion. | N/A | N/A | N/A | It is strongly encouraged to follow the PRISMA to improve the reporting of a systematic review and provide the PRISMA flow diagram as part of the main text or Supplementary Materials. |
Meta-Analysis | A meta-analysis should involve a comprehensive and exhaustive review of relevant literature specific to a topic or research question, and it should employ statistical methods to quantitatively synthesize the results of pooled studies. | Structured abstract including Background, Methods, Results, and Discussion. ≤ 300 words | 3-8 | Structured main text including Introduction, Materials and methods, Results, and Discussion. | N/A | N/A | N/A | It is strongly encouraged to follow the PRISMA to improve the reporting of a meta-analysis and provide the PRISMA flow diagram as part of the main text or Supplementary Materials. |
Short Communication | A short communication should present groundbreaking preliminary results, a particular aspect of a problem, or a new finding that is expected to have a significant impact. The short communication should be more straightforward and concise. | Unstructured abstract. ≤ 200 words | 3-8 | N/A | ≤ 2000 words | ≤ 6 | ≤ 30 | |
Case Report | Case reports should contribute to the advancement of drug knowledge, and do not accept reports on topics that have been fully described or where other similar cases have been published. Only rare cases are generally accepted. Case reports should describe in detail the patient's signs, symptoms, diagnosis, course of treatment, and outcome. Special care should be taken when submitting a case report to ensure that proper consent to publish has been obtained from the patient in the paper. | Unstructured abstract. ≤ 300 words | 3-8 | Structured main text including Introduction, Timeline, Narrative, Diagnostics, Patient perspective, Discussion, Conclusions. | N/A | N/A | N/A | It is strongly encouraged to follow the CARE guidelines to improve the quality of reporting. Authors may use the CARE-writer online application to organize and write a case report. The completed CARE checklist should be provided as a supplementary file. |
Protocol | A protocol should provide a detailed step-by-step description of a method. It should be proven to be robust and reproducible. The protocol should report planned or ongoing research studies. | Unstructured abstract. ≤ 300 words | 3-8 | Structured main text including Introduction, Materials, Procedure, and Expected results. | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
Commentary | Commentary articles are opinions and analyses on issues of interest to readers, discussing recently published or forthcoming articles or experiments, and addressing specific issues within a subject area rather than the field as a whole. | Unstructured abstract (optional). ≤ 250 words | 3-8 (optional) | N/A | ≤ 3000 words | ≤ 3 | ≤ 30 | |
Perspective | Perspective articles should highlight important ideas from recent exciting research and emerging topics of general interest, provide a focused (rather than comprehensive) overview, to propose and support new hypotheses, or to discuss the implications of newly implemented innovations, and may include raw data and personal opinions. | Unstructured abstract. ≤ 250 words | 3-8 | N/A | ≤ 3000 words | ≤ 3 | ≤ 30 | Long Perspectives should be no more than 6000 words. |
Editorial | Editorial articles are compelling opinions on topics of broad interest and can be considered as the journal's voice, publishing articles such as inaugural articles/annual summaries/thematic introductions/introductions to new journals/concluding a special issue/reporting on a pressing topic, etc., and do not contain unpublished or original data. | Not required. | Not required. | N/A | ≤ 1000 words | N/A | N/A | Only written by the Editorial Board and Guest Editors. |
Letter to the Editor | Letter to the Editor is a substantive reanalysis of an article published in our journal, a short report related to the content of previous issues. | Unstructured abstract (optional). ≤ 250 words | 3-8 (optional) | N/A | ≤ 1000 words | ≤ 3 | ≤ 10 |
[updated on September 11, 2025]
Structure of Manuscripts
The structure varies according to the type of manuscript. Please refer to requirements in Types and Templates of Manuscripts.
Title
The title should be no more than 20 words, no more than 150 characters in total, including spaces.
The title should be specific and relevant, and provide an overall view of the paper’s significance rather than detailed contents.
The title should avoid use of jargon, uncommon abbreviations, and excessive punctuation.
Author and Affiliations
Authors’ forename and surname should be listed. The initials of middle names can be added.
The complete address information should be listed as the following format: Dept/Program/Center, Institution, City, State, Post Code, Country; E-mail Address.
One author should be designated as the corresponding author.
Authors are strongly encouraged to provide their ORCID if any, especially the corresponding author.
Dual first/last authorship is allowed. Authors should indicate dual authorship with a superscript “†”, like “Forename Surname1†, Forename Surname2†”.
Please check authors’ names carefully, as any change to authorship is not allowed after manuscript acceptance.
Check out more information about Authorship at Editorial Policies.
Abstract and Keywords
Abstract
This section usually describes the main objective(s) of the study, explains how the study was done, and the main findings.
The abstract should follow the specific requirements for word count and structure detailed in Types and Templates of Manuscripts.
Acronyms and abbreviations must be defined the first time they appear in the abstract. Abbreviations should only be used if the abbreviated term appears three or more times in the abstract (except commonly-used ones).
The abstract should not include any citation or footnote.
The registration number of clinical trials should be listed at the end of the abstract if appropriate.
Keywords
Three to eight keywords should be provided where required (see Types and Templates of Manuscripts).
Keywords should be closely related to the topic of the paper, but not too broad or specific to the field.
Non-standard abbreviations should be kept to a minimum.
Main Body
The main text may consist of distinct sections according to the category of manuscript. For instance, an Original Article should comprise: Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results and Discussion, whereas a review, the main text may comprise several sections with unfixed section titles. Templates are provided in the Types and Templates of Manuscripts to guide authors.
Introduction
Good introductions explain these points clearly and cohesively:
★ Relevant background that puts the study into context (a brief review of key literature);
★ Purpose of the work and its significance.
Materials and Methods
Materials and Methods should be sufficiently detailed so that they can be understood precisely by readers and reviewers, and to enable other researchers to fully replicate the study. This section should include:
★ Design and setting of the study;
★ Characteristics of participants or description of materials;
★ Clear description of all processes, interventions and comparisons;
★ Type of statistical analysis used, including a power calculation if appropriate.
Please make sure you are aware that:
★ Statistical terms, abbreviations, and all symbols used should be defined clearly;
★ Generic drug names should generally be used;
★ When proprietary brands are used in research, include the brand names in parentheses;
★ All clinical trials must be registered in a public trials registry at or before the time of first patient enrollment and the registration number must be listed at the end of the abstract;
★ Protocol documents for clinical trials, observational studies, and other non-laboratory investigations may be uploaded as supplementary materials.
More detailed information about clinical trials, please refer to Editorial Policies.
Results
Results should be presented in a logical order to support the main conclusions of the study.
Results of statistical analysis should be included either as text or as tables or figures if appropriate.
Do not repeat data already shown in figures and tables, in text sections. Authors should emphasize and summarize only the most important observations.
Data on all primary and secondary outcomes identified in the section Materials and Methods should also be provided.
Extra or supplementary materials and technical details can be placed in supplementary documents.
Discussion
This section should cover the key findings of the work.
Discussion should point out the potential short-comings and limitations on their interpretations.
Future research directions may also be mentioned.
Abbreviations
In general, terms should not be abbreviated unless they are used repeatedly (at least 3 times) and the abbreviation is helpful to the reader. The use of abbreviations should meet the following requirements:
★ Commonly-used abbreviations, such as DNA, RNA, ATP, etc., can be used directly without definition;
★ Non-standard abbreviations should be defined at first use in manuscripts with their abbreviations in parentheses;
★ Non-standard abbreviations should be avoided in titles, abstracts and keywords;
★ Non-standard abbreviations in tables and figures should be explained in the footnote or caption accordingly.
This section should list and define all non-standard abbreviations.
For example, FBS: fetal bovine serum HGF: hepatocyte growth factor.
Declarations
Acknowledgments (Optional)
Acknowledge anyone who is not an author, but contributed to the paper, including intellectual assistance, technical help (writing services), or special equipment or materials.
Author Contributions
The contributions of each author should be described. The journal adopts the CRediT Taxonomy to describe each author’s individual contributions to the work. The corresponding author(s) is responsible for providing the contributions of all authors at submission. We expect that all authors will have reviewed, discussed, and agreed to their individual contributions ahead of this time. Contributions will be published with the final article, and they should accurately reflect contributions to the work. The roles are not intended to define what constitutes authorship.
Use initials of Forename and Surname when mentioning an author in this section. If the initials are the same, spell the different forename or surname. For example, John A. Smith: JA Smith, John A. Smart: JA Smart; John A. Smith: John AS, James A. Smith: James AS.
An example of an Authors’ Contribution statement using CRediT with degree of contribution:
“AB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. CDE: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. FG: Validation, Writing-review & editing, Supervision. All authors read and approved the submitted version.”
Contributor Role | Role Definition |
Conceptualization | Ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims. |
Data Curation | Management activities to annotate (produce metadata), scrub data and maintain research data (including software code, where it is necessary for interpreting the data itself) for initial use and later reuse. |
Formal Analysis | Application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data. |
Funding Acquisition | Acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication. |
Investigation | Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. |
Methodology | Development or design of methodology; creation of models. |
Project Administration | Management and coordination responsibility for the research activity planning and execution. |
Resources | Provision of study materials, reagents, materials, patients, laboratory samples, animals, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools. |
Software | Programming, software development; designing computer programs; implementation of the computer code and supporting algorithms; testing of existing code components. |
Supervision | Oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution, including mentorship external to the core team. |
Validation | Verification, whether as a part of the activity or separate, of the overall replication/reproducibility of results/experiments and other research outputs. |
Visualization | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/data presentation. |
Writing – Original Draft | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation). |
Writing – Review & Editing | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary or revision – including pre- or post-publication stages. |
Conflicts of Interest
Authors must declare any personal, professional or financial relationships which could potentially be construed as a conflict of interest. If authors are unsure whether conflicts of interest exist, please refer to Conflicts of Interest in Editorial Policies.
If there are no conflicts of interest, authors should state “The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.”.
Ethical Approval
Manuscripts involving human research must be approved by the specific ethics committee and comply with the Declaration of Helsinki. Authors should state that the article has obtained the consent from the participants and detail the information of ethics committee, including the name and the reference number if any.
Manuscripts involving animals research must be approved by an animal care and use committee. Authors should state that the article has been approved by certain committee and detail its information.
If a manuscript does not involve such issues, please state “Not applicable.” in this section.
More information is available at Editorial Policies.
Consent to Participate
The informed consent to participate in the study should be obtained from the participants, or their parents or legal guardians for children under 16. Such documents do not require a submission, but they must be available if requested. Authors should state “Informed consent to participate in the study was obtained from all participants.”.
If a manuscript does not involve such issue, please state “Not applicable.” in this section.
Consent to Publication
Authors must obtain the consent for publication from the participants in cases where manuscripts involve the privacy issues, like showing an individual’s details (images or videos). Such documents are not required at submission, but they must be available if requested. Authors should state “Informed consent to publication was obtained from relevant participants.”.
If a manuscript does not involve such issue, please state “Not applicable.” in this section.
Availability of Data and Materials
Authors are encouraged to provide details on how to access data sets supporting their findings where appropriate, such as links to publicly archived datasets.
Examples of appropriate public repositories are included as suggestions.
DNA/RNA Sequence: Genbank, Genome, BankIt, Sequence Read Archive (SRA), European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ).
Protein Sequence: Uniprot Knowledgebase (UniprotKB).
Genetic polymorphisms: dbSNP, the Database of Genomic Variants Archive (DGVa), or the Database of Genomic Structural Variation (dbVAR).
Sequencing Data/Microarray Data: NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) or ArrayExpress.
Structures of Macromolecules: Worldwide Protein Data Bank, Protein Data Bank in Europe, EMDataBank.
Structures of Small Molecules: Cambridge Structural Database (CSD), PubChem.
Examples for how to write this statement:
★ Datasets are in a publicly accessible repository:
The datasets [GENERATED/ANALYZED] for this study can be found in the [NAME OF REPOSITORY] [LINK].
★ Datasets are available on request:
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
★ All relevant data is contained within the manuscript:
All datasets [GENERATED/ANALYZED] for this study are included in the manuscript and the supplementary files.
★ The datasets request access:
The datasets for this manuscript are not publicly available because: [VALID REASON]. Requests for accessing the datasets should be directed to [NAME, EMAIL].
★ Data has been obtained from a third party:
The data analyzed in this study was obtained from [SOURCE]. Requests for access to these datasets should be directed to [NAME, EMAIL].
★ No datasets were generated for this study:
Not applicable.
It is not always possible to share research data publicly, for instance when individual privacy could be compromised. Authors who cannot share their data should state that the data will not be shared and explain why.
Funding
All sources of funding should be declared by naming financially supporting bodies followed by any associated grant numbers in square brackets. Authors must describe the role of the study sponsor(s) in the study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication, if any. If not, authors should state “The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.”.
If a manuscript does not involve any funding, please state “Not applicable.” in this section.
Copyright
A declaration “© The Author(s) YEAR.” will be added to each article.
References
In-Text Citations
References should be listed in the order in which they appear in the text. The reference number should be in square brackets in the text.
Do not include references in the abstract.
Make sure the parts of the manuscript are in the correct order before ordering the citations.
References List
The reference list must be accurate, with correct information, fully cited, and arranged in ascending order.
List the first six authors, followed by et al.
Abbreviations of journals should be provided on the basis of Index Medicus.
The endnote style of the journal can be downloaded at here.
The journal adopts the references outlined by U.S. National Library of Medicine. Examples are shown below. For other types, please refer to U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Source | Example |
Standard journal article | Rose ME, Huerbin MB, Melick J, Marion DW, Palmer AM, Schiding JK, et al. Regulation of interstitial excitatory amino acid concentrations after cortical contusion injury. Brain Res. 2002;935:40-6. |
Halpern SD, Ubel PA, Caplan AL. Solid-organ transplantation in HIV-infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:284-7. | |
Organization as author | Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Hypertension, insulin, and proinsulin in participants with impaired glucose tolerance. Hypertension. 2002;40:679-86. |
Both personal authors and organization as author | Vallancien G, Emberton M, Harving N, van Moorselaar RJ; Alf-One Study Group. Sexual dysfunction in 1,274 European men suffering from lower urinary tract symptoms. J Urol. 2003;169:2257-61. |
Article not in English | Ellingsen AE, Wilhelmsen I. Sykdomsangst blant medisin- og jusstudenter. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2002;122:785-7. Norwegian. |
Volume with supplement | Geraud G, Spierings EL, Keywood C. Tolerability and safety of frovatriptan with short- and long-term use for treatment of migraine and in comparison with sumatriptan. Headache. 2002;42 Suppl 2:S93-9. |
Article published electronically ahead of the print version | Yu WM, Hawley TS, Hawley RG, Qu CK. Immortalization of yolk sac-derived precursor cells. Blood. 2002;[Epub ahead of print]. |
Forthcoming | Tian D, Araki H, Stahl E, Bergelson J, Kreitman M. Signature of balancing selection in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Forthcoming 2002. |
Preprints | Alvarez R. Near optimal neural network estimator for spectral x-ray photon counting data with pileup. arXiv:1702.01006v1 [Preprint]. 2017 [cited 2017 Feb 9]: [11 p.]. Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.01006 |
Books | Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Kobayashi GS, Pfaller MA. Medical microbiology. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2002. |
Gilstrap LC 3rd, Cunningham FG, VanDorsten JP, editors. Operative obstetrics. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2002. | |
Breedlove GK, Schorfheide AM. Adolescent pregnancy. 2nd ed. Wieczorek RR, editor. White Plains (NY): March of Dimes Education Services; 2001. | |
Chapter in a book | Meltzer PS, Kallioniemi A, Trent JM. Chromosome alterations in human solid tumors. In: Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, editors. The genetic basis of human cancer. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2002. p. 93-113. |
Conference paper | Christensen S, Oppacher F. An analysis of Koza’s computational effort statistic for genetic programming. In: Foster JA, Lutton E, Miller J, Ryan C, Tettamanzi AG, editors. Genetic programming. EuroGP 2002: Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Genetic Programming; 2002 Apr 3-5; Kinsdale, Ireland. Berlin: Springer; 2002. pp. 182-91. |
Homepage/Web site | eatright.org [Internet]. Chicago: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics; c2016 [cited 2016 Dec 27]. Available from: https://www.eatright.org/ |
Supplementary Materials (Optional)
Accompanying the manuscripts, the additional data and information must be uploaded as supplementary materials. These contents can be accessed by certain links instead of direct presentation in the text. Authors should make sure that:
★ All files must be submitted separately and named clearly (e.g., Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Video 1);
★ The file formats are acceptable as follows: data sheet (word, excel, csv, cdx, fasta, pdf or zip files), presentation (powerpoint, pdf or zip files), image (cdx, eps, jpeg, pdf, png or tiff), table (word, excel, csv), audio (mp3, wav or wma) or video (avi, flv, mov, mp4 or wmv);
★ All information of the materials must be clearly displayed;
★ Supplementary figures and tables should comply with the requirements of figures and tables in the main text;
★ The video and audio should meet the requirements in Multimedia Files;
★ Supplementary materials should be cited in the main text in numeric order (e.g., Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Table 2).
Figures
Figures submitted to Exploration of Drug Science should not be published elsewhere (unless you have obtained the copyright permission, and mentioned and/or cited it in the figure legend with a clear note). As Exploration of Drug Science adopts a single-column layout, please submit figures at the size you wish to display, and ensure that all the information can be clearly identified. To avoid potential major changes after manuscript’s acceptance, please read the following guidelines and requirements.
File Format
For high-quality presentation of figures, acceptable file formats include bmp, jpg, png, tif, eps, pdf, psd; ChemDraw (.cdx) for chemical structures; figures created in Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Adobe Illustrator, etc. should be editable, such as column charts, bar charts, line charts, pie charts, etc.
Image Resolution
In order to best represent your scientific work, authors are recommended to upload figures that are clear enough when submitting their manuscripts. Authors are strongly recommended to provide figures of high resolution: a minimum resolution of 300 dpi for multi-color images, 500 dpi for mono-color images, and 1000 dpi for line graphics. If there are subfigures, please make sure each subfigure also meets the resolution requirements. In order to ensure the legibility of the article, figures that do not present the information clearly and accurately may need to be re-provided.
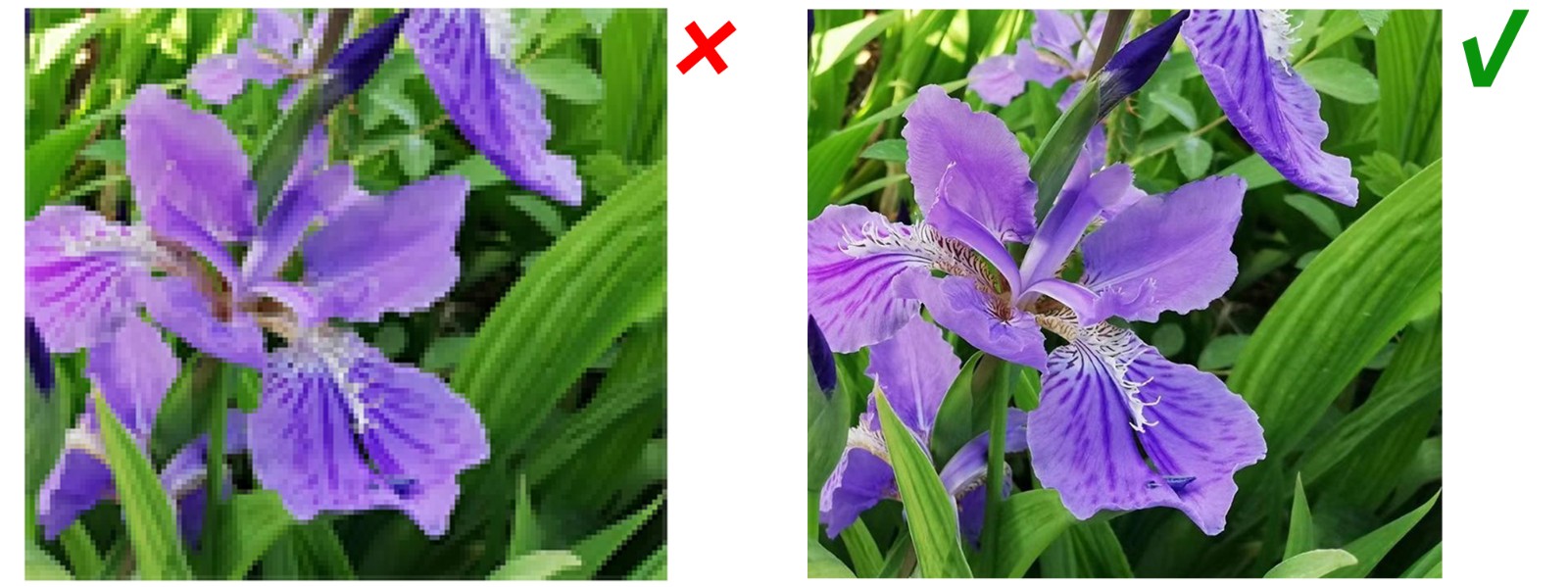

Image Size
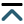
For a good layout, we suggest that you submit figures at the desired size to fit a single-column layout. Figures ranging from 2/3 of a page to a full page (115–170 mm width) are optimal.
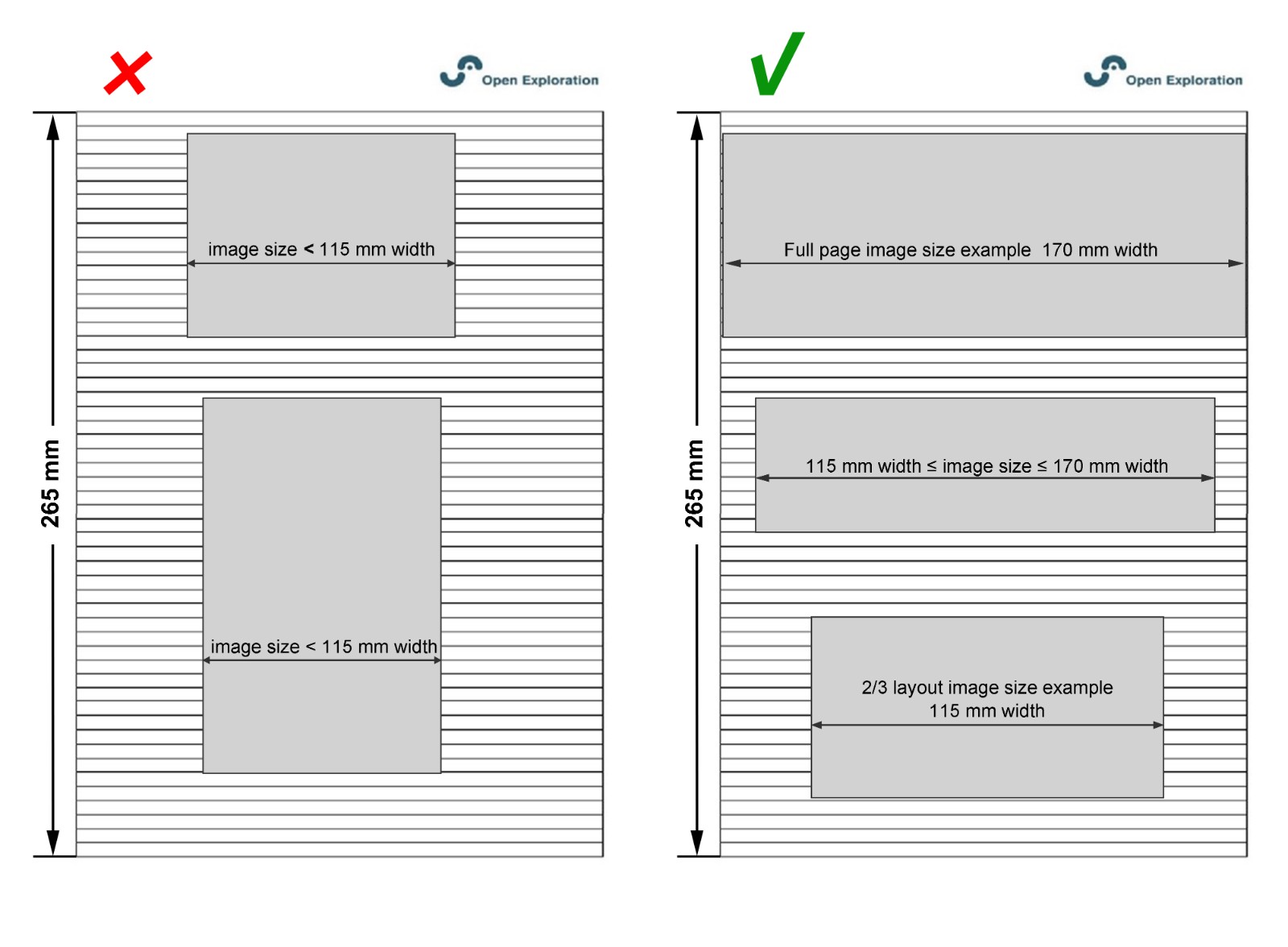
Figure Font and Size
Font should be legible, preferably in Helvetica, Arial, or Times New Roman with a size of 8–10 pt. All editable figures in the same article should unify the font and avoid shadows, outlines, etc.
Visual Effect
Font Display
The fonts in a subfigure (horizontal and vertical axis titles, scales, etc.) should be unified; Try not to use white fonts (except for halftone figures). Please avoid light fonts for content that needs to be emphasized, and try to replace them with dark colors.
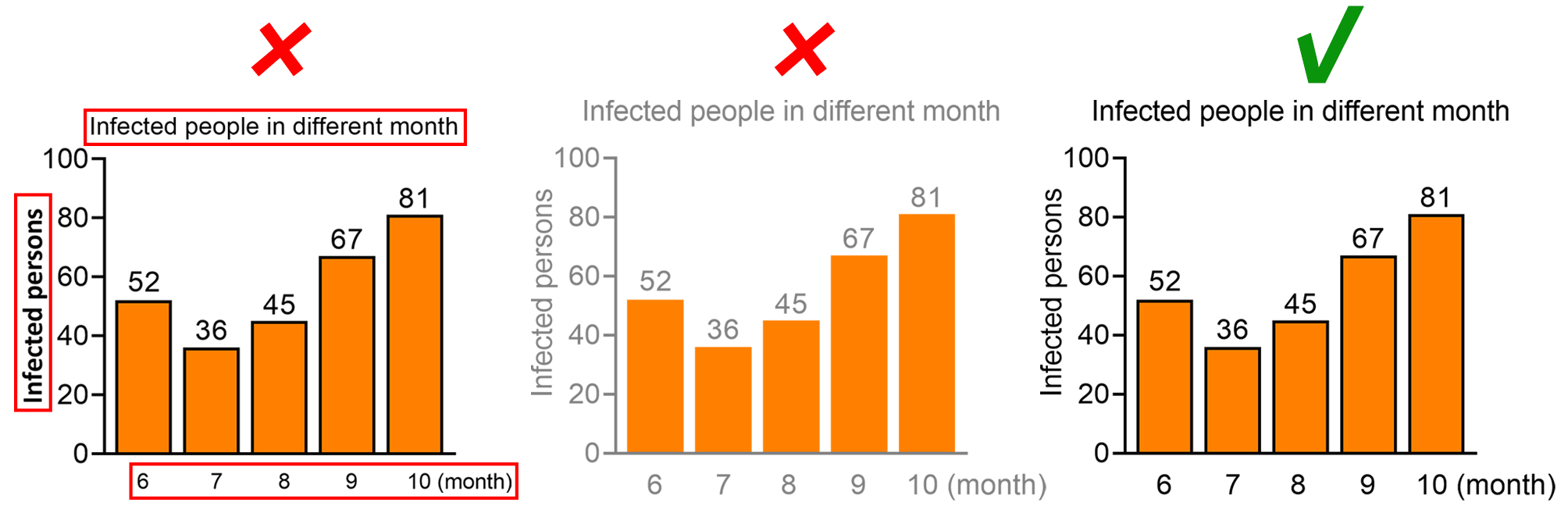
The text in the figure should not cover the content of the figure, nor should it overflow the figure causing the text to be incompletely displayed.
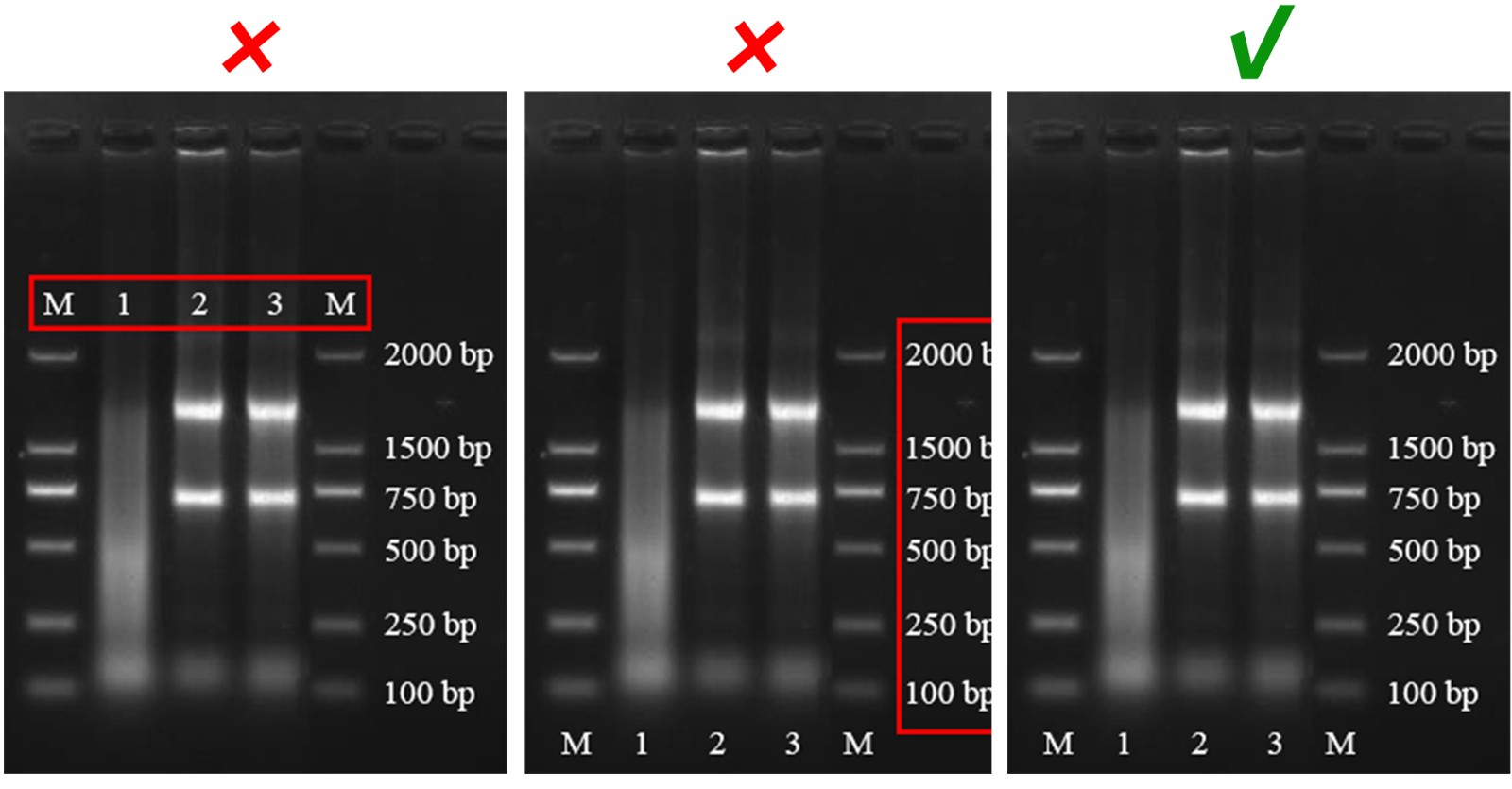
Figure Background
In order to ensure the presentation of the information in the figure, it is best to use white, light, or low-saturation colors for the background, rather than dark colors that cannot highlight the message of the article.
Figure Cropping
To ensure clarity of the figures, each figure should be tightly cropped to minimize the margins of the figure.
Color Tone
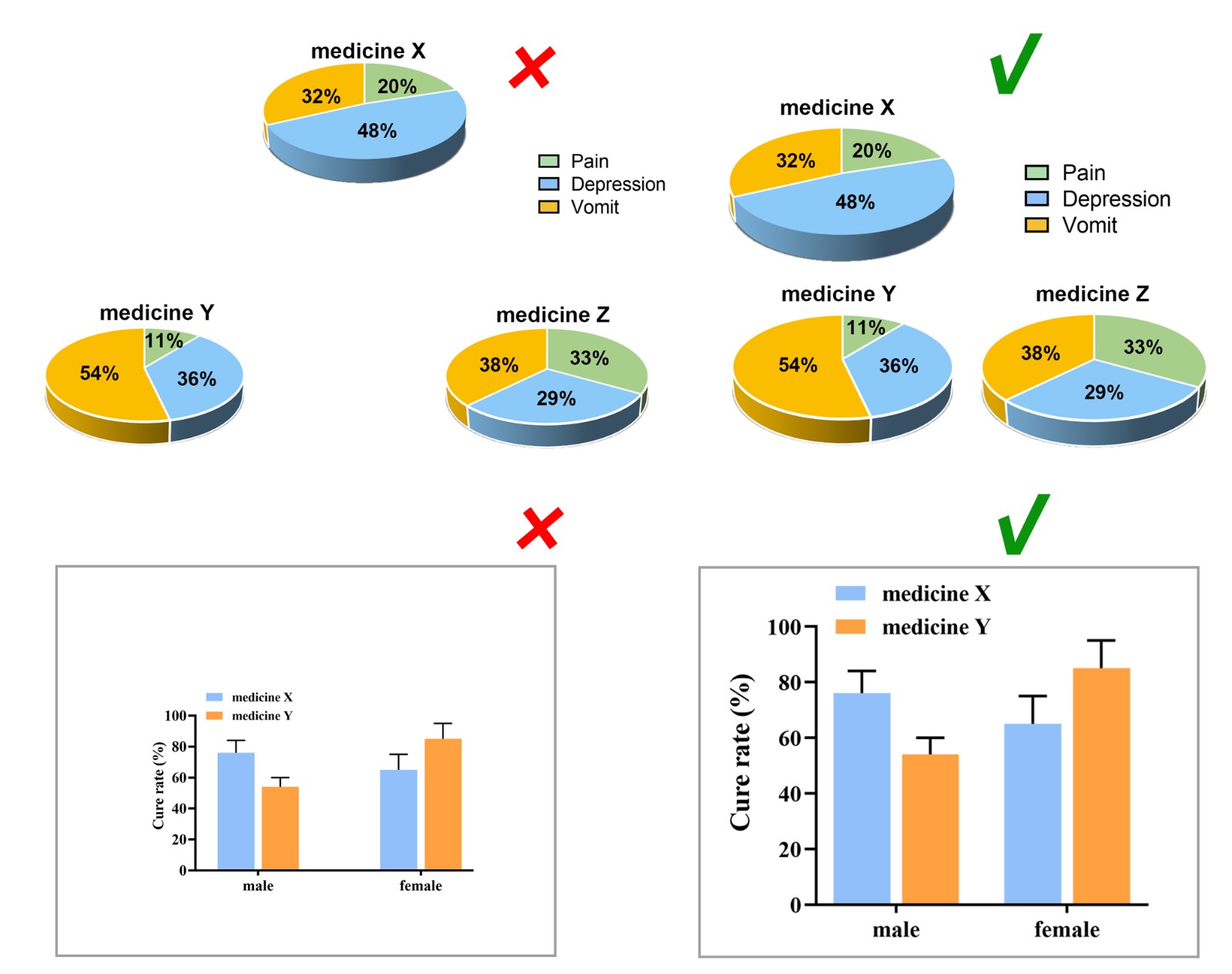
Considering the reading needs of color-blind people, please try to choose colors that can be easily recognized by people with different color visions. For example, blue-orange or blue-red are considered friendly to color-blind people, while red-green or green-brown should be avoided. However, red-green is very common in the life sciences, especially in color fluorescent images, magenta-green is recommended in your original image.
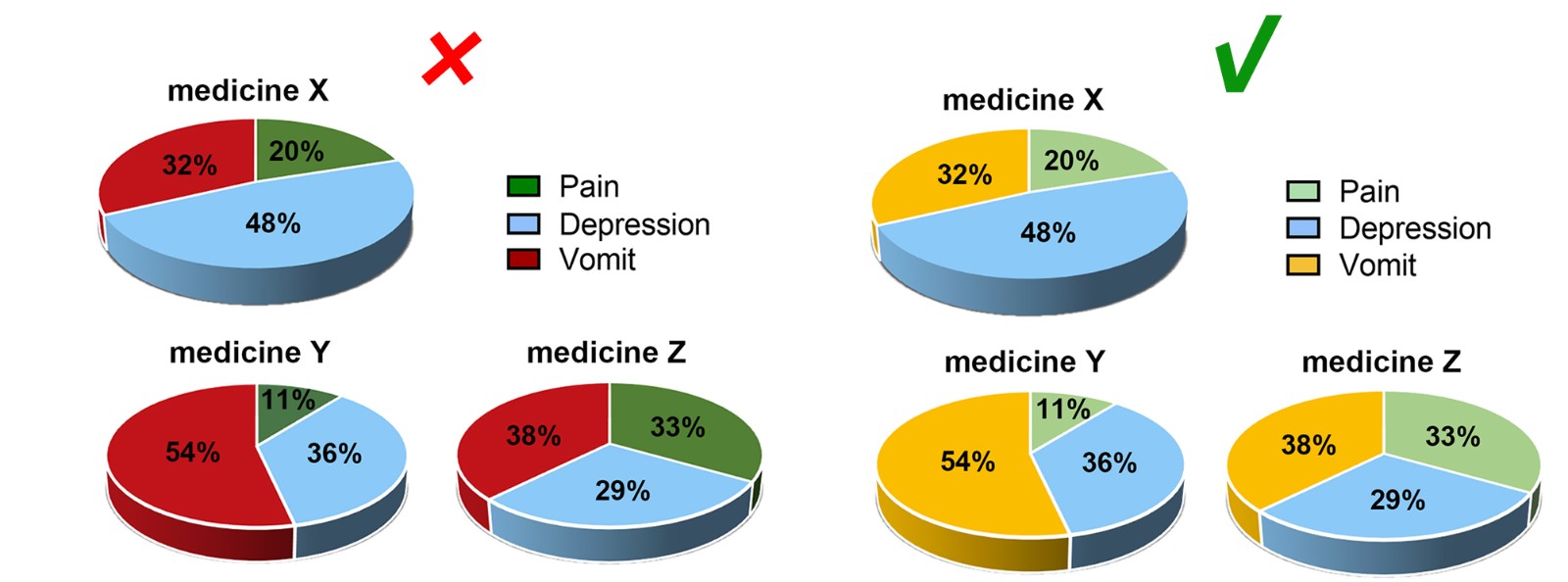
Contrast
Use high contrast. Although people with color vision disabilities have difficulties in perceiving color tones, they commonly perceive contrast well. Light and dark contrasts can be used to make figure information more accessible.
Data Display
When presenting data, different shapes, patterns, lines, and texture fillings can be used. Labels, arrows, annotations, or other indicators can be added to the figure to help readers better understand the data.
Figure Elements
Labels, numbers, letters, arrows, and symbols used in the figure should be clearly displayed, and should contrast with the background; they must be explained in the figure legend.
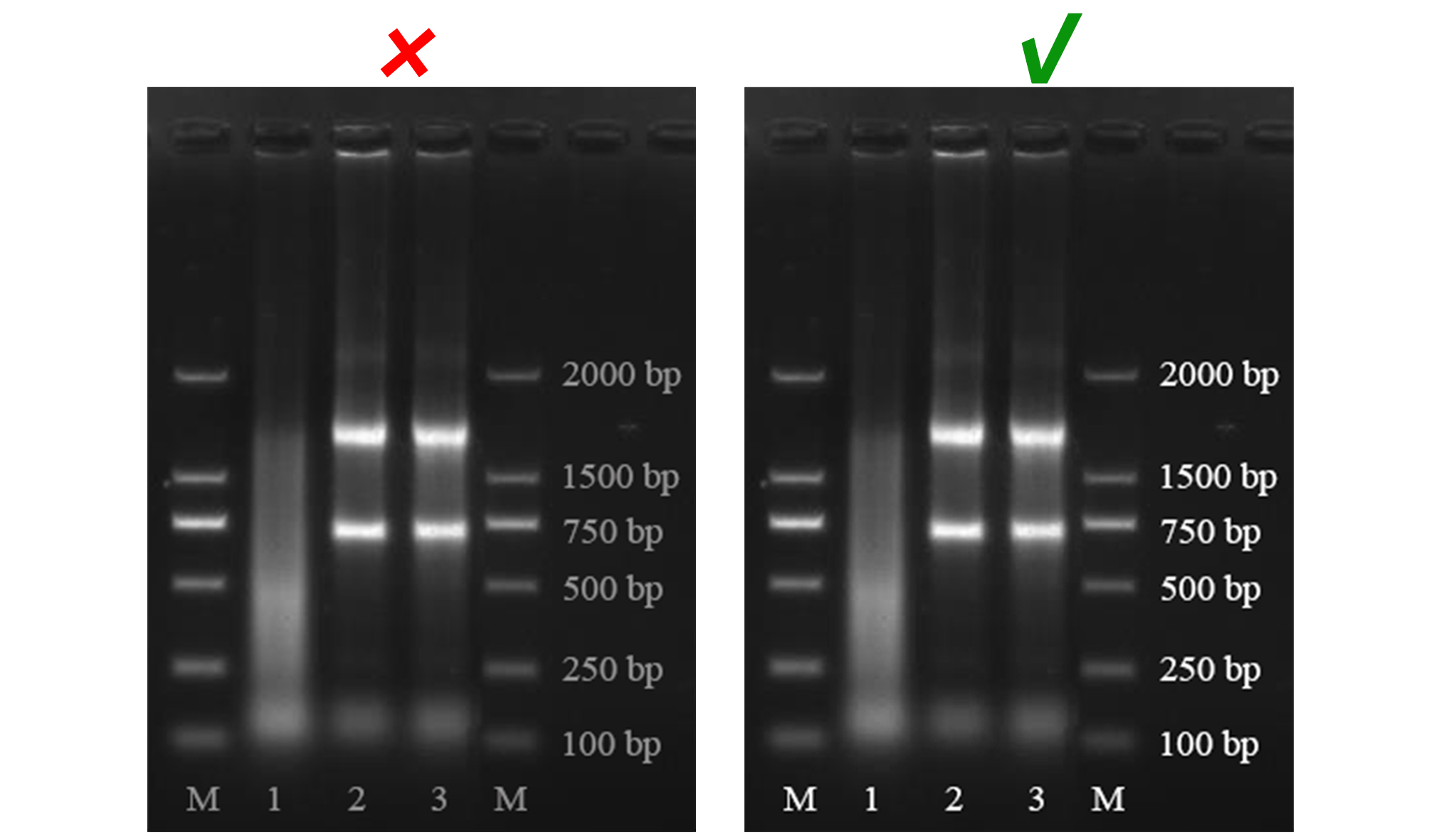
Non-standard abbreviations should be also explained with their full names in the figure legend.
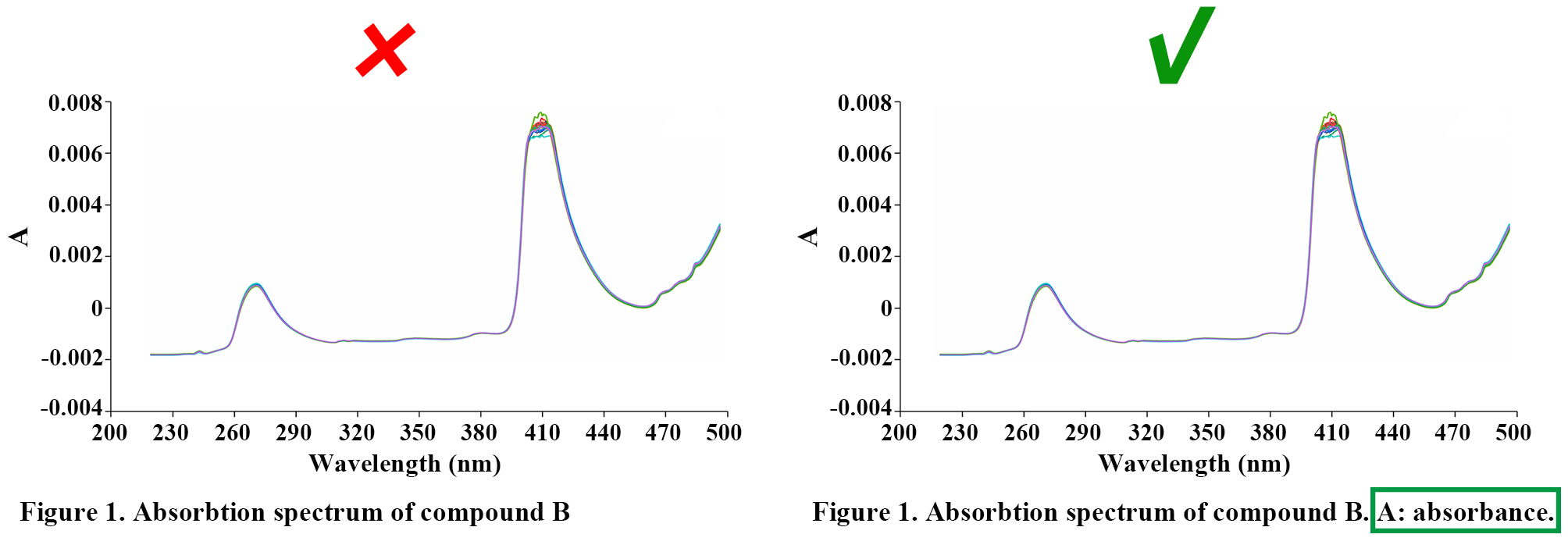
Splitting and Naming of Subfigure
Subfigures are recommended to be merged into one file according to the size and the style as expected for publication, and its size should meet the requirements in “Image size”.
Each subfigure should be labeled with capital letters A, B, C, etc. which are placed in the upper left corner, without obscuring the content of the figure, if applicable. The subfigures are expected to be separated by a distance instead of nearing together. In a side-by-side/up-and-down layout, the symbol number should be aligned horizontally/vertically, and the distance between the label and the subfigure should be consistent.
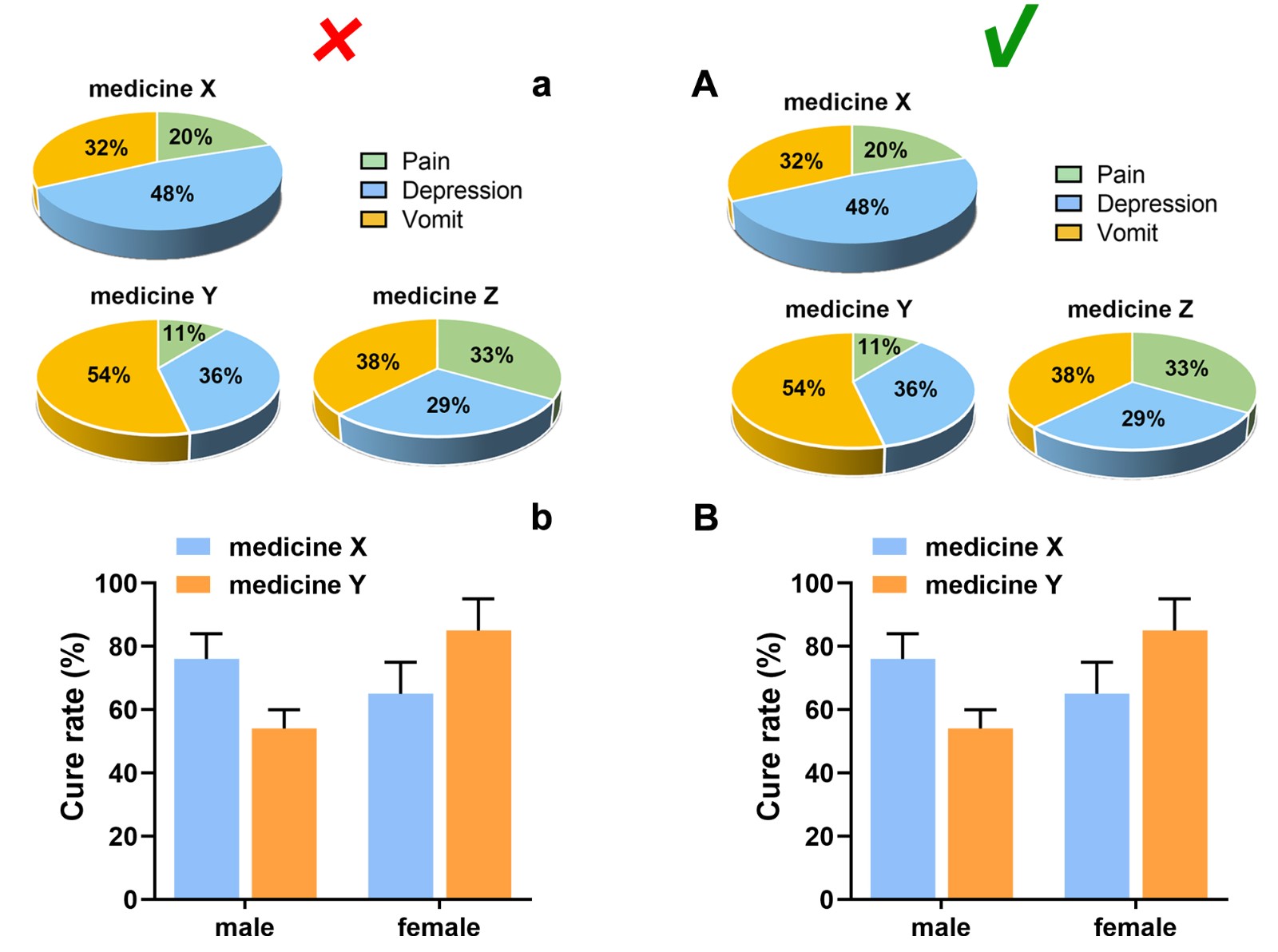
Submission of Figures
All figures should be uploaded separately in the submission. In addition, to facilitate the review of the manuscript, all figures and tables should be also placed in the main text, behind the paragraph in which they are first cited, and numbered in the order.
Modification and Adjustment of Figures
Changes in brightness, contrast or color balance, and improving resolution are acceptable as long as they do not obscure or eliminate any information in the original figures. Any feature in a figure that is selectively enhanced, blurred, removed, or added may be considered an abuse of scientific ethics and will be dealt with accordingly.
Color Mode
Images should be saved in RGB color mode.
Photomicrograph
The scale in photomicrographs should be directly clearly presented in the figure. It should be clearly contrasted to the background color. The magnification (if any) and staining method should be provided in the figure or figure legend.
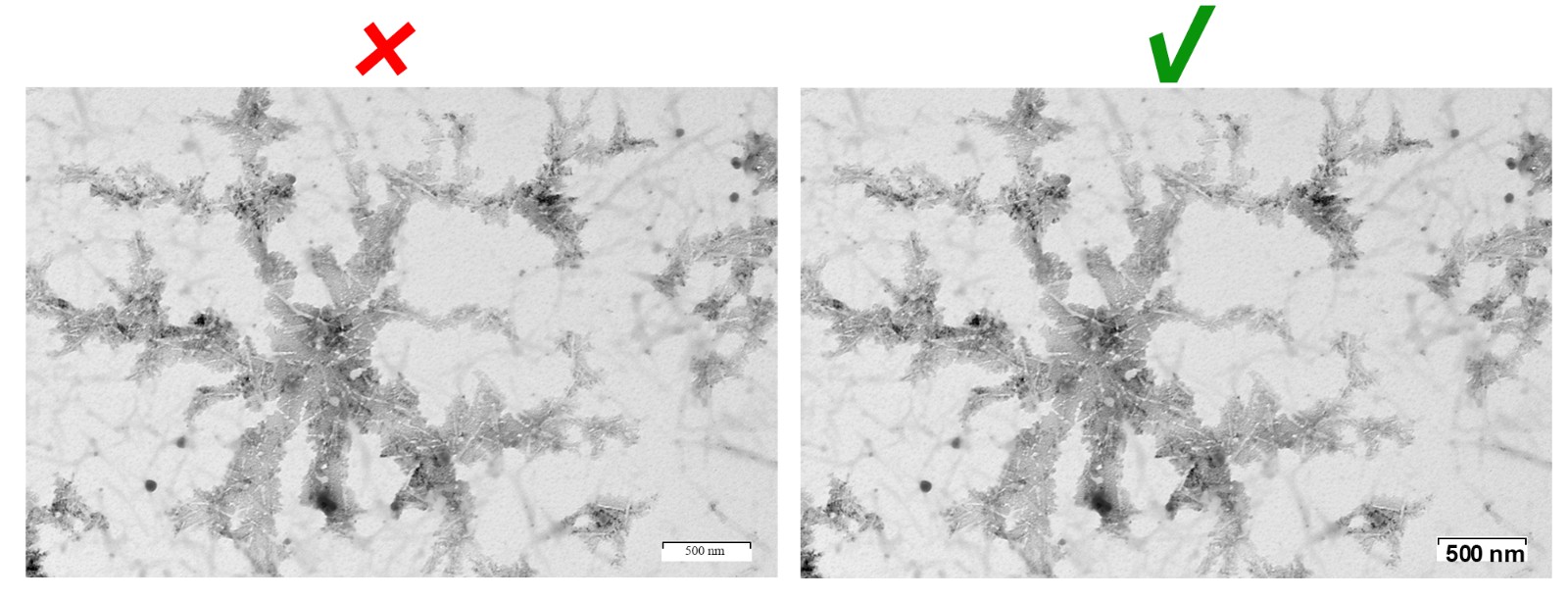
[updated on March 1, 2024]
Tables
Tables should be in Word format; picture formats and other non-editable versions are not acceptable.
The table should be placed after the paragraph where it first appears in numeric order (e.g., Table 1, Table 2); the title should be placed above the table, and the footnote should be placed below the table.
Where statistics are included, the specific methodology of the statistics needs to be written in the footnote. For statistical significance, use P < 0.05 or P < 0.01, preferably with a specific P value. If there is no significant difference (i.e., P > 0.05), it can be omitted; please note that P values are capitalized and italicized.
Labels, numbers, letters, arrows, and symbols used in the table must be clearly displayed and explained in the footnote. Non-standard abbreviations should be explained in the footnote. Descriptive information should be explained in the footnote.
For larger datasets or tables that extend beyond the width of the page, we may, after consulting with you, upload the table as an additional file or add a link to it.
[updated on March 1, 2024]
Other Formatting Requirements
Prepare manuscripts in DOC or DOCX files which should not be locked or protected.
The original figure files must be individually submitted accompanying submission in the same order as they appear in the manuscript.
Language
Manuscripts must be written in English. Make sure the English language is comprehensible to readers. If English is not your first language, please ask native speakers for help to proofread your article.
Multimedia Files (Optional)
The journal supports multimedia files which meet the following requirements:
Multimedia File | Audio | Video |
Format | mp3, wav, wma | mp4 (preferred), mov, avi, rm, wmv |
Duration | < 3 min | < 3 min |
Language | English | Any language with English subtitles (English preferred) |
Size | < 300 MB | < 300 MB |
Quality | High quality, clearly played | High quality, clearly played (language and subtitles) |
Italics
Generally, the following contents should be italic:
★ t test, F test, U test;
★ related coefficient as r;
★ sample number as n;
★ probability as P;
★ names of genes;
★ names of bacteria;
★ biology species in Latin.
Numerals
Use words for numbers appearing at the beginning of sentences.
Use words for numbers one to nine, e.g., five patients.
Use numerals for numbers ten or above, e.g., 16 years old; insert a comma to separate thousands groups, e.g., 123,456,789.
Equations
Equations should be editable. Picture format is unacceptable.
Use the Microsoft Equation Editor or the MathType for equations.
Units
Use International System of Units (SI). All other units should be converted to SI Units whenever possible.
Include a space between the number and the unit (e.g., 78 kg).
Submission Online
All the manuscripts should be submitted online in ARES system https://eds.aressystem.com/. Queries should be directed to the editorial office at edsjournal@explorationpub.com. The submitting author, generally the corresponding author, must ensure that all the eligible authors have been included in the author list and all authors read and approved the submitted version.