Editor's Picks
Open Access
Review
Dysbiosis and colorectal cancer: conducive factors, biological and molecular role, and therapeutic prospectives
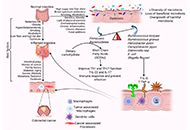
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. Emerging evidence highlights the significant role of gut microbiota dysbiosis, characterized by a reduction in beneficial bacteria and an increase in pro-inflammatory and pro-carcinogenic bacteria, in CRC pathogenesis. Both genetic and environmental factors, including diet, antibiotic use, physical activity, aging, and obesity, contribute to this microbial imbalance. Dysbiosis promotes chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation, which facilitates tumor initiation and progression. This review examines the intricate interactions between gut microbiota, immune modulation, and CRC development. It explores current and emerging therapeutic strategies that target the microbiome to enhance treatment efficacy, discusses interventions aimed at restoring healthy microbiota in CRC patients, and outlines future directions for microbiome-based therapies to improve clinical outcomes.
Open Access
Review
Biliary tract cancers: advances in diagnostic and management
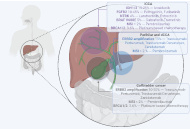
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are aggressive malignancies associated with poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Advances in precision oncology, notably the identification of recurrent molecular alterations such as fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutations, ERBB2 amplifications, and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (BRAF) V600E mutations, have introduced new therapeutic avenues and modest survival benefits for patients with advanced disease. However, the practical implementation of targeted therapies remains hampered by challenges in tumor tissue acquisition and molecular testing, highlighting the need for alternative genomic profiling strategies. This comprehensive review examines the role of liquid biopsy as a non-invasive strategy for molecular profiling in BTCs, with a focus on the clinical applications of plasma and bile-derived circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). We synthesized findings from recent clinical studies evaluating mutation detection rates, concordance between liquid biopsy and tissue-based assays, and the comparative performance of plasma versus bile ctDNA. Liquid biopsy demonstrates high rates of mutation detection and good concordance with tissue analyses. Bile-derived ctDNA, owing to its proximity to the tumor, consistently shows higher sensitivity and mutant allele frequencies (MAFs) than plasma ctDNA. Nevertheless, challenges remain, including lower sensitivity for detecting structural alterations (e.g., gene fusions), variability in ctDNA yield depending on disease status, and a lack of assay standardization across platforms. Liquid biopsy, particularly through bile ctDNA analysis, emerges as a promising adjunct to tissue biopsy for molecular profiling in BTCs. It offers opportunities for earlier, less invasive, and more personalized treatment decisions. Future directions should aim at developing tumor-informed liquid biopsy strategies that increase precision, reduce costs, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. Prospective studies are needed to confirm its clinical utility and survival impact.
Open Access
Perspective
Future perspectives: targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy
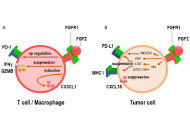
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) plays a critical role in the progression of various cancers through its involvement in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. More recently, FGFR1 has been implicated in the mechanisms of immune evasion, particularly its role in resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab. Targeting FGFR1 with monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy to enhance ICI efficacy by altering the tumor microenvironment and countering immune suppression. Preclinical studies demonstrate that combining FGFR1 inhibitors, such as the novel monoclonal antibody OM-RCA-01, with ICIs significantly improves antitumor activity, enhancing T cell responses and cytokine production. This article explores the role of FGFR1 in cancer biology, its contribution to immunotherapy resistance, and the therapeutic potential of targeting FGFR1 to enhance the efficacy of ICIs.
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Systematic Review
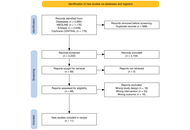
Comparison of weekly docetaxel regimens in prostate cancer: a systematic review and frequentist network meta-analysis
Shree Rath ... Amar Lal
Published: February 27, 2026 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2026;7:1002360
Open Access
Mini Review
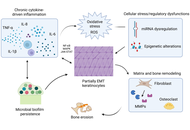
Benign, persistent, and invasive: mechanistic and translational approaches to middle‑ear cholesteatoma
Pinelopi Samara ... Ioannis Athanasopoulos
Published: February 24, 2026 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2026;7:1002359
Open Access
Review
Glioblastoma pathophysiology: roles of aging driven changes in STAT3 interactions with NF-κB dimer components in the modulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway and night-time inflammation resolution
George Anderson
Published: February 13, 2026 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2026;7:1002358

Open Access
Perspective
Application of explainable artificial intelligence integrating with electronic health record in oncology
Yuhan Yang, Xici Liu
Published: February 04, 2026 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2026;7:1002357
Open Access
Editorial
The critical need for robust decision support in the era of precision cancer therapeutics
Maurie Markman
Published: January 22, 2026 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2026;7:1002356
Open Access
Review
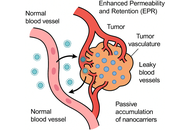
Next-generation nanocarriers for precision antitumor therapy: from passive targeting to intelligent response
Dilpreet Singh, Akshay Kumar
Published: December 28, 2025 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025;6:1002355
Open Access
Review
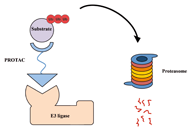
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100
Open Access
Review
Early-stage triple negative breast cancer: the therapeutic role of immunotherapy and the prognostic value of pathological complete response
Pierluigi De Santis ... Palma Fedele
Published: February 28, 2024 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5:232–250
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Open Access
Review
Steroid utility, immunotherapy, and brain tumor management: an update on conflicting therapies
Matthew Goldman ... Stephan Quintin
Published: October 31, 2022 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3:659–675
Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)
Open Access
Review
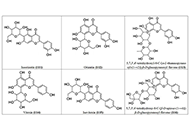
Nigerian medicinal plants with potential anticancer activity—a review
Mansurah A. Abdulazeez ... Amos A. Fatokun
Published: December 09, 2024 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5:1393–1434
Open Access
Review
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Perspective
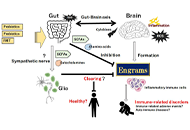
Encouraging probiotics for the prevention and treatment of immune-related adverse events in novel immunotherapies against malignant glioma
Sayuri Yoshikawa ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: December 27, 2022 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3:817–827
This article belongs to the special issue Theranostic Frontiers in Neuro-Oncology
Open Access
Perspective
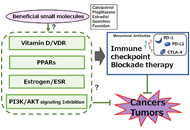
Potential tactics with vitamin D and certain phytochemicals for enhancing the effectiveness of immune-checkpoint blockade therapies
Ai Tsuji ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:460–473
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Immunotherapy and Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Perspective
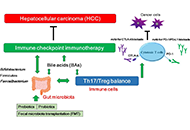
Potential tactics with certain gut microbiota for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Sayuri Yoshikawa ... Satoru Matsuda
Published: August 24, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:556–568
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Immunotherapy and Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100

Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
Current strategies for the design of PROTAC linkers: a critical review
Robert I. Troup ... Matthias G. J. Baud
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:273–312
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
The impact of tumour pH on cancer progression: strategies for clinical intervention
Carol Ward ... Simon P Langdon
Published: April 28, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:71–100

Open Access
Review
Diagnostic value of liquid biopsy in the era of precision medicine: 10 years of clinical evidence in cancer
Vincenza Caputo ... Stefania Napolitano
Published: February 28, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:102–138
This article belongs to the special issue The Implementation of Liquid Biopsy in Clinical Practice for Different Solid Tumor
Open Access
Review
Novel approaches for the rational design of PROTAC linkers
Almaz Zagidullin ... Emil Bulatov
Published: October 30, 2020 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2020;1:381–390
This article belongs to the special issue Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)

Open Access
Review
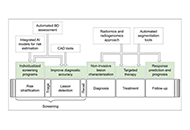
Artificial intelligence in breast cancer imaging: risk stratification, lesion detection and classification, treatment planning and prognosis—a narrative review
Maurizio Cè ... Michaela Cellina
Published: December 27, 2022 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3:795–816
This article belongs to the special issue Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology
Open Access
Review
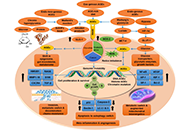
AGEs and RAGE: metabolic and molecular signatures of the glycation-inflammation axis in malignant or metastatic cancers
Gowri Palanissami, Solomon F.D. Paul
Published: September 28, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:812–849
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Emerging Innovation in Surgical and Medical Approaches on the Horizon for Urogenital Malignancies
Guest Editors: Dr. Makito Miyake; Dr. Yuki Oda
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0
Precision Oncology: Molecular Classification, Efficacy Prediction, and Treatment Decision-Making
Guest Editors: Prof. Pier Paolo Piccaluga; Dr. Jones Gyamfi
Submission Deadline: August 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Novel Precision Medicine Approaches to Brain Tumors (Primary and Metastatic)
Guest Editors: Prof. Patricia Tai; Mr. Omar Alqaisi
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Breaking Boundaries in Breast Cancer Care: Emerging Controversies and Innovation in Surgical and Medical Approaches
Guest Editor: Dr. Armando Orlandi
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Cancer Vaccines: From Basic Innovations to Clinical Translation
Guest Editor: Prof. Panagiotis J Vlachostergios
Submission Deadline: February 28, 2026
Published Articles: 2

Artificial Intelligence Technology in Tumor Radiotherapy
Guest Editor: Prof. Tuan D. Pham
Submission Deadline: September 30, 2025
Published Articles: 0

Liquid Biopsy: Has Already Changed the Clinical Decision-Making in Solid Tumors Treatment?
Guest Editor: Dr. Giulia Martini
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4
Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers in Cancer: Towards the Precision Medicine Era
Guest Editors: Prof. Luca Falzone; Dr. Antonio Rizzo; Dr. Stefano Marletta; Dr. Graziana Spoto
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 5

Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in Cancer
Guest Editor: Prof. Javier Reguera
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Potential of Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer Research and Treatment
Guest Editors: Prof. Francesco Bertoni; Dr. Luciano Cascione
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Novel Biomarkers in the Immunotherapy Era
Guest Editors: Dr. Carminia Maria Della Corte; Dr. Floriana Morgillo; Dr. Caterina De Rosa
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 2
Comprehensive Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors
Guest Editor: Dr. Michela Valeria Rita Starace
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 4

Advances in Cancer Genomics and Therapeutic Targets
Guest Editor: Prof. Apostolos Zaravinos
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2025
Published Articles: 3

Molecular Mechanisms and Intervention Options in Metastatic Spread of Cancer
Guest Editor: Dr. Katrin Sak
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 3

Use of Different Radiation Treatment Modalities in Cancer Therapy: The Role of Inflammation and Immune Response
Guest Editor: Prof. Alexandros Georgakilas
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 3

Mechanisms of Targeted Therapy Resistance and Reversal Strategies
Guest Editor: Prof. Pier Paolo Piccaluga
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2024
Published Articles: 3

Cancer Epigenetics: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Strategies
Guest Editor: Prof. Mingzhou Guo
Submission Deadline: February 01, 2025
Published Articles: 2

Posttranslational Modifications in Health and Disease
Guest Editor: Prof. Oliver Krämer
Submission Deadline: March 01, 2026
Published Articles: 4

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics












































 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


