Editor's Picks
Open Access
Original Article
A real-world clustering analysis reveals heterogeneous response patterns to biologic therapy in severe asthma
Aim:
Despite the revolutionary impact of biologics (Bx) on severe asthma management, predicting individual treatment responses remains challenging. We aimed to characterize the heterogeneous nature of clinical status and disease activity in patients with severe asthma after biologic therapies through a comprehensive evaluation of real-world clinical outcomes.
Methods:
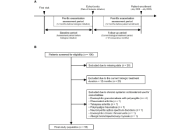
In this retrospective, multicenter study of 53 patients with severe asthma who received biologic therapies, hierarchical clustering analysis was performed based on three key parameters during treatment: exacerbation, maintenance oral corticosteroid (mOCS) dose, and lung function. Canonical correlation analysis and multinomial logistic regression were used to identify predictors of response patterns.
Results:
Clustering analysis revealed three distinct control groups: well-controlled (n = 23), moderately controlled (n = 22), and poorly controlled (n = 8). Well-controlled patients exhibited minimal exacerbations, no oral corticosteroid (OCS) use, and optimal or stabilized lung function. Moderately controlled patients showed minimal exacerbations and no mOCS use but variable lung function improvements. Poorly controlled patients exhibited persistent exacerbations, mOCS dependence, or both with limited lung function improvement. Baseline forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) %predicted (percent predicted FEV1) values and blood eosinophil counts independently differentiated well-controlled from moderately controlled patients, whereas baseline mOCS use distinguished moderately controlled from poorly controlled patients.
Conclusions:
Our findings reveal distinct patterns of disease control following biologic therapy in severe asthma, with baseline lung function, eosinophilic inflammation, and OCS use as key predictive factors. These results support the need for personalized treatment approaches in severe asthma management.
Open Access
Review
Maternal RSV vaccination to protect infants: current evidence and future directions
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) burden among infants. Maternal vaccination is a promising preventive strategy, conferring passive immunity through transplacental antibody transfer. The current narrative review was conducted to summarize the current evidence of efficacy and safety of maternal RSV vaccination and assess the practical barriers to its implementation. This review was based on a structured literature search of PubMed/MEDLINE and Google Scholar to identify peer-reviewed studies published between January 2022 and March 2025 using terms such as “maternal RSV vaccine”, “efficacy”, “safety”, “pregnancy”, “Abrysvo”, and “hesitancy”. The review included 5 clinical trials evaluating maternal RSV vaccines and 17 observational and survey studies assessing vaccine acceptance across diverse settings. The bivalent RSVpreF vaccine (Abrysvo) is the only licensed maternal RSV vaccine as of May 2025. In the MATISSE phase 3 trial (n = 7,358), the vaccine demonstrated 81.8% efficacy against medically attended RSV-LRTI at 90 days and 69.4% at 180 days, with 57.1% efficacy against severe RSV-LRTI. No major safety concerns were identified; adverse events and preterm birth rates were comparable between groups. In contrast, trials of GSK’s RSVPreF3-Mat vaccine revealed higher rates of preterm birth (6.8% vs. 4.9%) and a numerical imbalance in infant deaths (0.4% vs. 0.2%), prompting early termination. Across 17 studies (n = 14,959), RSV vaccine acceptance ranged from 39% (France) to 87% (Netherlands), with safety concerns and cultural context influencing attitudes. This review highlights that maternal RSV vaccination with RSVpreF offers effective infant protection with an acceptable safety profile. Future research should focus on long-term infant outcomes, comparative effectiveness in diverse settings, and next-generation vaccines. Implementation will require public trust, cultural sensitivity, and equitable global access.

Open Access
Review
Pathogenesis and management of atopic dermatitis: insights into epidermal barrier dysfunction and immune mechanisms
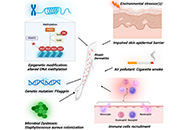
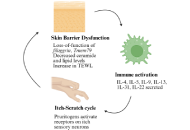
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by a compromised epidermal barrier and heightened immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, often associated with filaggrin (FLG) gene mutations. Genetic factors like FLG mutations and environmental influences, including microbial exposure and pollutants, contribute to the disease’s progression, leading to itchy, inflamed skin. AD frequently coexists with allergic conditions, severely affecting the quality of life. The disease’s pathogenesis involves complex interactions between genetic predispositions, immune responses, and environmental triggers. Despite advances, the development of effective treatments remains challenging due to an incomplete understanding of how FLG mutations influence immune pathways and the variability in AD presentation. Current biomarkers are insufficient to fully capture disease complexity or predict therapeutic responses, highlighting the need for novel biomarkers and personalized approaches. Emerging therapies such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy, stem cell therapy, and regenerative medicine show promise in addressing AD’s root causes. This review explores key aspects of AD pathogenesis, focusing on epidermal barrier dysfunction, immune mechanisms, and the need for innovative therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Articles
Latest
Most Viewed
Most Downloaded
Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
Real-life effectiveness of mepolizumab on remission and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in severe eosinophilic asthma
Mariye Doğru ... Abdulkadir Basturk
Published: February 09, 2026 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2026;4:1009109
This article belongs to the special issue Update on Chronic Rhinosinusitis

Open Access
Original Article
Prevalence and factors associated with work-related asthma among carpenters in Parakou, northern Benin
Mariano Efio ... Gildas Agodokpessi
Published: February 02, 2026 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2026;4:1009108

Open Access
Review
Climate-driven changes in pollen dynamics: increased loads and earlier, longer exposure
Jean-Pierre Besancenot, Laurent Mascarell
Published: January 29, 2026 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2026;4:1009107
This article belongs to the special issue Climate Change, Allergy, and Immunotherapy

Open Access
Commentary
Diagnosing cow’s milk allergy with the EATERS-X allergy-focused clinical history
Melvin Lee Qiyu ... Mich Erlewyn-Lajeunesse
Published: January 22, 2026 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2026;4:1009106
This article belongs to the special issue Practical Issues in Pediatric Allergy

Open Access
Mini Review
Atopic dermatitis: a mini review on pathology and treatment modalities
Amrita Sahu ... Somasundaram Arumugam
Published: January 07, 2026 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2026;4:1009105
This article belongs to the special issue Atopic Dermatitis – Pathology and Treatment Modalities
Open Access
Systematic Review
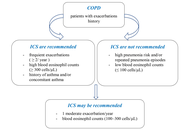
Ensuring patient safety: a closer look at glucocorticoid therapy in COPD and asthma
Alexandru Corlateanu, Cristina Toma
Published: December 22, 2025 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2025;3:1009104
This article belongs to the special issue The Era of Biologics in Allergy
Open Access
Review
Current approach to moisturizer and emollient utilization in atopic dermatitis: a review
Serap Maden
Published: August 27, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:441–449
This article belongs to the special issue Atopic Dermatitis – Pathology and Treatment modalities
Open Access
Review
A mini-update on chronic rhinosinusitis
Sepideh Darougar ... Pantea Bozorg Savoji
Published: September 19, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:473–484
This article belongs to the special issue Update on Chronic RhinoSinusitis

Open Access
Review
Maternal RSV vaccination to protect infants: current evidence and future directions
Malik Sallam ... Mohammed Sallam
Published: July 30, 2025 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2025;3:100988
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma, Allergies, and Respiratory Infections in Pediatric Age

Open Access
Review
Pathogenesis and management of atopic dermatitis: insights into epidermal barrier dysfunction and immune mechanisms
Antara Baidya, Ulaganathan Mabalirajan
Published: February 07, 2025 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2025;3:100973
This article belongs to the special issue Atopic Dermatitis – Pathology and Treatment modalities

Open Access
Review
Multiple chemical sensitivity: a review of its pathophysiology
Cătălina Elena Lavric ... Frédéric de Blay
Published: July 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:350–362
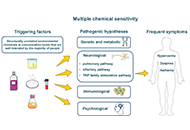
Open Access
Review
Management of asthma using probiotics
Amar P. Garg ... Bajeerao Patil
Published: February 20, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:9–32
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors

Open Access
Review
Pathogenesis and management of atopic dermatitis: insights into epidermal barrier dysfunction and immune mechanisms
Antara Baidya, Ulaganathan Mabalirajan
Published: February 07, 2025 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2025;3:100973
This article belongs to the special issue Atopic Dermatitis – Pathology and Treatment modalities

Open Access
Review
Current approach to moisturizer and emollient utilization in atopic dermatitis: a review
Serap Maden
Published: August 27, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:441–449
This article belongs to the special issue Atopic Dermatitis – Pathology and Treatment modalities

Open Access
Review
A mini-update on chronic rhinosinusitis
Sepideh Darougar ... Pantea Bozorg Savoji
Published: September 19, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:473–484
This article belongs to the special issue Update on Chronic RhinoSinusitis

Open Access
Review
New therapeutic approaches with biological drugs for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Alejandra Carrón-Herrero ... Giovanni Paoletti
Published: June 08, 2023 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2023;1:31–48
This article belongs to the special issue The Era of Biologics in Allergy
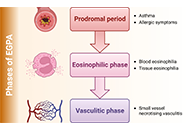
Open Access
Review
Multiple chemical sensitivity: a review of its pathophysiology
Cătălina Elena Lavric ... Frédéric de Blay
Published: July 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:350–362

Open Access
Review
Update on the diagnosis of severe asthma in children and adolescents
Alberto Vidal
Published: January 10, 2025 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2025;3:100965
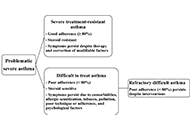
Open Access
Review
Exploring the therapeutic potential of algae derived food and diet factors in allergy and inflammation
Leonel Pereira, Ana Valado
Published: April 23, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:127–147
This article belongs to the special issue The Different Faces of Food Allergy

Open Access
Review
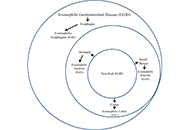
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases: current perspectives on pathogenesis and management
Georgia Papaiakovou ... Nikoletta Rovina
Published: June 07, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:205–218
Open Access
Review
Multiple chemical sensitivity: a review of its pathophysiology
Cătălina Elena Lavric ... Frédéric de Blay
Published: July 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:350–362

Open Access
Mini Review
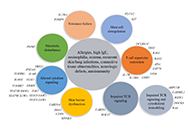
Food allergy as one of the faces of primary immunodeficiency
Polina Kostova ... Guergana Petrova
Published: February 29, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:65–75
This article belongs to the special issue The Different Faces of Food Allergy
Open Access
Review
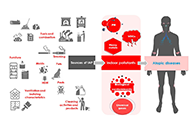
Indoor air pollution and atopic diseases: a comprehensive framework
Erminia Ridolo ... Francesca Nicoletta
Published: May 31, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:170–185
Open Access
Review
The impact of occupational exposures on chronic rhinosinusitis: a scoping review
Aurelia S. Monk ... Adam J. Kimple
Published: July 19, 2024 Explor Asthma Allergy. 2024;2:301–318
This article belongs to the special issue Environment, Infectious Diseases, and Allergy
Special Issues
Ongoing Special lssues
Completed Special lssues
Allergic Asthma - New Insights
Guest Editors: Prof. Bernard Ryffel; Dr. Peter Cook; Prof. Dieudonnée Togbe
Submission Deadline: May 31, 2026
Published Articles: 0

The Complex Interactions Between Lifestyles and Asthma
Guest Editor: Dr. Manlio Milanese
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 0

Allergy and Asthma in the Digital Age
Guest Editors: Prof. Juan Carlos Ivancevich; Prof. Ivan Cherrez-Ojeda
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2025
Published Articles: 1

Bridging Experimental and Translational Allergology
Guest Editors: Prof. Torsten Zuberbier; Dr. Katarina Stevanovic
Submission Deadline: April 30, 2026
Published Articles: 1

Climate Change, Allergy, and Immunotherapy
Guest Editor: Dr. Laurent Mascarell
Submission Deadline: December 31, 2026
Published Articles: 4

Practical Issues in Pediatric Allergy
Guest Editors: Prof. Nelson A. Rosario Filho; Prof. Herberto J. Chong Neto
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2026
Published Articles: 1

Asthma, Allergies, and Respiratory Infections in Pediatric Age
Guest Editors: Prof. Michele Miraglia del Giudice; Dr. Cristiana Indolfi; Dr. Angela Klain; Dr. Giulio Dinardo
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 4
Beyond Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
Guest Editor: Dr. Eleonora Nucera
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 2
Environment, Infectious Diseases, and Allergy
Guest Editor: Prof. Vincenzo Patella
Submission Deadline: July 31, 2026
Published Articles: 1

Innate Immune Mechanisms in Allergic Diseases
Guest Editors: Prof. Uday Kishore; Dr. Ahmad Al Aiyan; Dr. Ann Mary Joseph
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 1

Airway Epithelial Cells in Asthma
Guest Editor: Prof. Garry M. Walsh
Submission Deadline: June 30, 2026
Published Articles: 1
Update on Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Guest Editor: Prof. Ludger Klimek
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 6

Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors
Guest Editor: Prof. Pasquale Caponnetto
Submission Deadline: March 31, 2026
Published Articles: 5

Journal Information
Journal Indexing
Journal Metrics

















 Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys
Title: Unravelling the interplaybetween #Harmattan wind andbaroreflex functions: implicationon environmental health andcardiovascular #pathophys


