-
73articlesSort byLatested
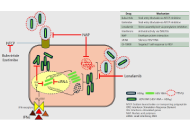 Pharmacotherapy of hepatitis D: the current and the futureOpen AccessReviewHepatitis D virus (HDV), a satellite virus requiring hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for propagation, is a hepatotropic virus implicated in acute and chronic viral hepatitis, with an accentuated...George Sarin Zacharia, Anu JacobPublished: May 08, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100573
Pharmacotherapy of hepatitis D: the current and the futureOpen AccessReviewHepatitis D virus (HDV), a satellite virus requiring hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for propagation, is a hepatotropic virus implicated in acute and chronic viral hepatitis, with an accentuated...George Sarin Zacharia, Anu JacobPublished: May 08, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100573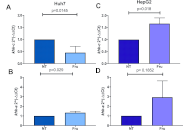 Fructose induces metabolic reprogramming in liver cancer cells, promoting aggressiveness and chemotherapy resistanceOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Fructose is a highly lipogenic compound related to the onset of steatosis, its progression to steatohepatitis, and the eventual initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). One of the cance...Lisette Chávez-Rodríguez ... Luis E. Gomez-QuirozPublished: April 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100572
Fructose induces metabolic reprogramming in liver cancer cells, promoting aggressiveness and chemotherapy resistanceOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Fructose is a highly lipogenic compound related to the onset of steatosis, its progression to steatohepatitis, and the eventual initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). One of the cance...Lisette Chávez-Rodríguez ... Luis E. Gomez-QuirozPublished: April 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100572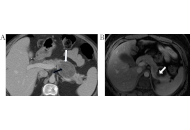 Molecular insights into pancreatic cysts: navigating diagnosis and precision managementOpen AccessPerspectivePancreatic cystic lesions are frequently found incidentally on cross-sectional imaging and are broadly classified into mucinous and non-mucinous cysts. While some exhibit benign behavior, others hav...Rudy El Asmar ... Samer AlMasriPublished: April 13, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100571
Molecular insights into pancreatic cysts: navigating diagnosis and precision managementOpen AccessPerspectivePancreatic cystic lesions are frequently found incidentally on cross-sectional imaging and are broadly classified into mucinous and non-mucinous cysts. While some exhibit benign behavior, others hav...Rudy El Asmar ... Samer AlMasriPublished: April 13, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100571 Debugging surgical guidelines for acute diverticulitisOpen AccessPerspectiveDiverticular disease of the colon is a very important digestive disease and its management depends on the characteristics of the disease and the patient and the resources available. There are benefi...Valter Nilton FelixPublished: April 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100570
Debugging surgical guidelines for acute diverticulitisOpen AccessPerspectiveDiverticular disease of the colon is a very important digestive disease and its management depends on the characteristics of the disease and the patient and the resources available. There are benefi...Valter Nilton FelixPublished: April 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100570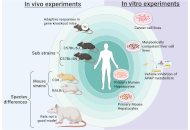 The multiple mechanisms and modes of cell death after acetaminophen overdoseOpen AccessReviewAcetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury and acute liver failure is a significant clinical problem worldwide; in addition, APAP overdoses in animals or in cell culture are used as popular models to...Hartmut Jaeschke, Anup RamachandranPublished: April 07, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100569
The multiple mechanisms and modes of cell death after acetaminophen overdoseOpen AccessReviewAcetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury and acute liver failure is a significant clinical problem worldwide; in addition, APAP overdoses in animals or in cell culture are used as popular models to...Hartmut Jaeschke, Anup RamachandranPublished: April 07, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100569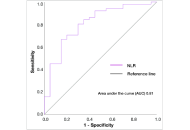 Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a multi-institutional retrospective real-world studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Selecting patients for immunotherapy in metastatic gastric cancer (mGC) in second and subsequent lines remains challenging. The aim of our study is to assess the feasibility of anti-programm...Anastasia Rays ... Аlexey TryakinPublished: March 27, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100568
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a multi-institutional retrospective real-world studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Selecting patients for immunotherapy in metastatic gastric cancer (mGC) in second and subsequent lines remains challenging. The aim of our study is to assess the feasibility of anti-programm...Anastasia Rays ... Аlexey TryakinPublished: March 27, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100568 Helicobacter pylori infection in the pathophysiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and its complicationsOpen AccessLetter to the EditorJannis Kountouras ... Maria Tzitiridou-ChatzopoulouPublished: March 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100567
Helicobacter pylori infection in the pathophysiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and its complicationsOpen AccessLetter to the EditorJannis Kountouras ... Maria Tzitiridou-ChatzopoulouPublished: March 20, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100567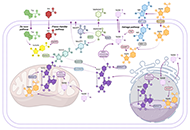 Mitochondrial dysfunction in PBMC: a potential sensor for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and therapeutic insight for NAD+-increasing strategiesOpen AccessReviewThe epidemic of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is increasingly growing worldwide. Thus, there is an urgent need for novel, non-invasive, and reliable biomarkers to ...Julia Niño-Narvión ... Josep JulvePublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100566
Mitochondrial dysfunction in PBMC: a potential sensor for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and therapeutic insight for NAD+-increasing strategiesOpen AccessReviewThe epidemic of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is increasingly growing worldwide. Thus, there is an urgent need for novel, non-invasive, and reliable biomarkers to ...Julia Niño-Narvión ... Josep JulvePublished: February 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100566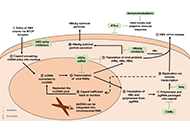 Hepatitis B virus induced cirrhosis and hepatocarcinoma: pathogenesis and therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major risk factor of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. Pathogenesis of HBV-induced cirrhosis and HCC involves viral factors and virus-tri...Juntian Yao ... Youhua XiePublished: February 21, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100565
Hepatitis B virus induced cirrhosis and hepatocarcinoma: pathogenesis and therapeuticsOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major risk factor of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. Pathogenesis of HBV-induced cirrhosis and HCC involves viral factors and virus-tri...Juntian Yao ... Youhua XiePublished: February 21, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100565 Current efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancer and potential biomarkersOpen AccessReviewMicrosatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors have a high mutational load (particularly frame-shift mutations) that creates numerous neoantigens that are presented to major histocompa...Mariam Rojas ... Joan MaurelPublished: February 18, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100564
Current efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancer and potential biomarkersOpen AccessReviewMicrosatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors have a high mutational load (particularly frame-shift mutations) that creates numerous neoantigens that are presented to major histocompa...Mariam Rojas ... Joan MaurelPublished: February 18, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100564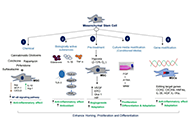 Mesenchymal stem cell and exosome-based therapy for liver diseases: can it overcome conventional therapeutic inconsistencies?Open AccessReviewLiver inflammation, injury, and hepatic cell death are caused by external agents (viruses, bacteria, drugs, alcohol, etc.) along with the genetic susceptibility of an individual. Persistent activati...Zahid HussainPublished: January 15, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100563
Mesenchymal stem cell and exosome-based therapy for liver diseases: can it overcome conventional therapeutic inconsistencies?Open AccessReviewLiver inflammation, injury, and hepatic cell death are caused by external agents (viruses, bacteria, drugs, alcohol, etc.) along with the genetic susceptibility of an individual. Persistent activati...Zahid HussainPublished: January 15, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2025.100563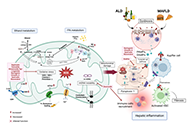 Mitochondrial ROS, a trigger for mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammasome activation and a therapeutic target in liver diseasesOpen AccessReviewMitochondria are essential organelles responsible for intracellular energy production and play crucial roles in cellular metabolism, inflammation, and apoptosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are pr...Hala Saeed Jaara, Sandra TorresPublished: December 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00062
Mitochondrial ROS, a trigger for mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammasome activation and a therapeutic target in liver diseasesOpen AccessReviewMitochondria are essential organelles responsible for intracellular energy production and play crucial roles in cellular metabolism, inflammation, and apoptosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are pr...Hala Saeed Jaara, Sandra TorresPublished: December 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00062 An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the...Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00061
An overview of pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewSteatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of this disease has remained poor until the past decade. Despite extensive research, our ability to comprehend the...Shahid Habib, Andrew JohnsonPublished: November 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00061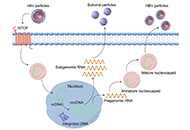 Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccinesOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 262 million people worldwide, leading to over 820,000 deaths annually. The reason HBV has been a persistent issue for decades is that it is a non-cytopathic...Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang YangPublished: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00060
Hepatitis B virus: modes of transmission, immune pathogenesis, and research progress on therapeutic vaccinesOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B virus (HBV) infection affects 262 million people worldwide, leading to over 820,000 deaths annually. The reason HBV has been a persistent issue for decades is that it is a non-cytopathic...Chunzheng Li ... Xianguang YangPublished: October 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00060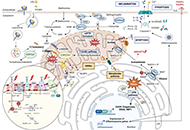 Impact of mitochondrial lipid alterations on liver disease mechanisms and progressionOpen AccessReviewLipids are intricate biomolecules responsible for the building up of biological membranes. Besides this structural function, they also display crucial roles in signaling, acting as second messengers...Laura Fàbrega ... Carmen Garcia-RuizPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00057
Impact of mitochondrial lipid alterations on liver disease mechanisms and progressionOpen AccessReviewLipids are intricate biomolecules responsible for the building up of biological membranes. Besides this structural function, they also display crucial roles in signaling, acting as second messengers...Laura Fàbrega ... Carmen Garcia-RuizPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00057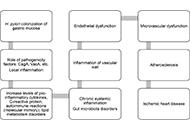 Helicobacter pylori infection and metabolic syndromeOpen AccessReviewThe formation of metabolic changes is based on many factors. In particular, the infectious theory of the development of metabolic “breakdowns” has not lost its relevance. In this regard, many sc...Natalia V. Baryshnikova ... Alexander N. SuvorovPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00058
Helicobacter pylori infection and metabolic syndromeOpen AccessReviewThe formation of metabolic changes is based on many factors. In particular, the infectious theory of the development of metabolic “breakdowns” has not lost its relevance. In this regard, many sc...Natalia V. Baryshnikova ... Alexander N. SuvorovPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00058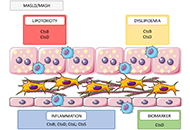 Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise...Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00059
Searching for novel cellular targets for MASLD and HCC within the humble lysosomal cathepsinsOpen AccessReviewMetabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its pathological version, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), are becoming the main leading causes of chronic liver dise...Alejandro del Castillo-Cruz ... Anna MolesPublished: September 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00059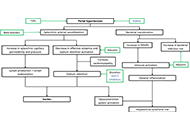 Ascites in cirrhotic patients: a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewAscites is a frequent complication in patients with cirrhosis, associated with a bad prognosis. Ascites is associated with severe complications, such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and kidney ...Paul Carrier ... Laure ElkriefPublished: August 26, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00056
Ascites in cirrhotic patients: a comprehensive reviewOpen AccessReviewAscites is a frequent complication in patients with cirrhosis, associated with a bad prognosis. Ascites is associated with severe complications, such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and kidney ...Paul Carrier ... Laure ElkriefPublished: August 26, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00056 Liver and spleen stiffness measurement in the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewOne of the primary complications of cirrhosis and portal hypertension is the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is among the most common malignancies worldwide. There is limited ava...Anna Fichera, Mirella FraquelliPublished: August 21, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00055
Liver and spleen stiffness measurement in the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver diseaseOpen AccessReviewOne of the primary complications of cirrhosis and portal hypertension is the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is among the most common malignancies worldwide. There is limited ava...Anna Fichera, Mirella FraquelliPublished: August 21, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00055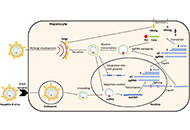 The impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) splicing on HBV replication and disease progressionOpen AccessReviewChronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease caused by persistent infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a global health problem affecting almost 300 million people worldwide, resulting in up to 1 million d...Laura C. McCoullough ... Peter A. RevillPublished: August 07, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00054
The impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) splicing on HBV replication and disease progressionOpen AccessReviewChronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease caused by persistent infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a global health problem affecting almost 300 million people worldwide, resulting in up to 1 million d...Laura C. McCoullough ... Peter A. RevillPublished: August 07, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00054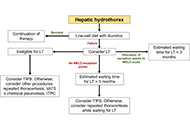 Pulmonary complications of advanced chronic liver diseases: an updated reviewOpen AccessReviewPatients with advanced chronic liver disease can develop specific pulmonary complications related or unrelated to pre-existing lung disease. The three major pulmonary complications in this patient p...Thierry Thevenot ... Hilary M. DuBrockPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00053
Pulmonary complications of advanced chronic liver diseases: an updated reviewOpen AccessReviewPatients with advanced chronic liver disease can develop specific pulmonary complications related or unrelated to pre-existing lung disease. The three major pulmonary complications in this patient p...Thierry Thevenot ... Hilary M. DuBrockPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00053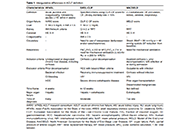 Acute decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failureOpen AccessReviewAcute decompensation is defined as the development of ascites, bleeding due to portal hypertension, jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy in the presence of known or unknown chronic liver disease. Acu...Sencan AcarPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00052
Acute decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failureOpen AccessReviewAcute decompensation is defined as the development of ascites, bleeding due to portal hypertension, jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy in the presence of known or unknown chronic liver disease. Acu...Sencan AcarPublished: July 24, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00052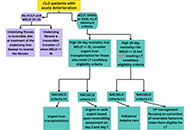 Liver transplantation consideration and evaluation: a life-saving treatment in acute-on-chronic liver failureOpen AccessReviewWith the rising prevalence of chronic liver disease worldwide, the incidence and prevalence of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) are increasing and attribute to higher morbidity, mortality, and ...Andrew Johnson, Shahid HabibPublished: July 23, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00051
Liver transplantation consideration and evaluation: a life-saving treatment in acute-on-chronic liver failureOpen AccessReviewWith the rising prevalence of chronic liver disease worldwide, the incidence and prevalence of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) are increasing and attribute to higher morbidity, mortality, and ...Andrew Johnson, Shahid HabibPublished: July 23, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00051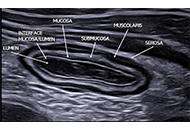 Transabdominal Gastro-Intestinal UltraSound (GIUS): a visual approach to intestinal pathologyOpen AccessPerspectiveTransabdominal ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic approach for evaluating the gastrointestinal tract and related disorders. This dynamic examination provides real-time visualization of the digestiv...Cristina Felicani ... Pietro AndreonePublished: July 05, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00050
Transabdominal Gastro-Intestinal UltraSound (GIUS): a visual approach to intestinal pathologyOpen AccessPerspectiveTransabdominal ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic approach for evaluating the gastrointestinal tract and related disorders. This dynamic examination provides real-time visualization of the digestiv...Cristina Felicani ... Pietro AndreonePublished: July 05, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00050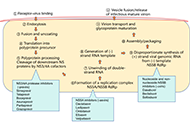 Key points for the management of hepatitis C in the era of pan-genotypic direct-acting antiviral therapyOpen AccessReviewHepatitis C viral infections present a significant global health challenge, carrying substantial economic implications. These infections manifest in various clinical forms, including acute and chron...Hao Xiong, Jinsheng GuoPublished: June 18, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00049
Key points for the management of hepatitis C in the era of pan-genotypic direct-acting antiviral therapyOpen AccessReviewHepatitis C viral infections present a significant global health challenge, carrying substantial economic implications. These infections manifest in various clinical forms, including acute and chron...Hao Xiong, Jinsheng GuoPublished: June 18, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00049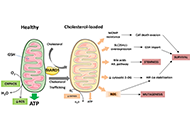 Role of cholesterol homeostasis in MASH-driven hepatocellular carcinoma: not just a neutral fatOpen AccessReviewHepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer and its death rate is rising faster than that of any other cancer, while we still lack effective treatments. The increasing inc...Vicent RibasPublished: June 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00048
Role of cholesterol homeostasis in MASH-driven hepatocellular carcinoma: not just a neutral fatOpen AccessReviewHepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer and its death rate is rising faster than that of any other cancer, while we still lack effective treatments. The increasing inc...Vicent RibasPublished: June 14, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00048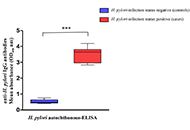 Development and evaluation of an in-house ELISA based on autochthonous antigens for detecting IgG anti-Helicobacter pylori in Cuban adultsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to develop and evaluate an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on autochthonous antigens to detect immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against Helicobacte...Rosabel Corrales ... Rafael LlanesPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00047
Development and evaluation of an in-house ELISA based on autochthonous antigens for detecting IgG anti-Helicobacter pylori in Cuban adultsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to develop and evaluate an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on autochthonous antigens to detect immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against Helicobacte...Rosabel Corrales ... Rafael LlanesPublished: May 31, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00047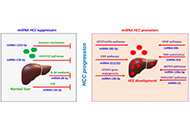 Deciphering the cross-talk between miRNA and tight junctions in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewThe most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) causes a lower survival rate even after systemic treatment. Previous studies have shown evidence that various molecular and epi...Siva Bala Subramaniyan, Balasubramaniyan VairappanPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00045
Deciphering the cross-talk between miRNA and tight junctions in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewThe most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) causes a lower survival rate even after systemic treatment. Previous studies have shown evidence that various molecular and epi...Siva Bala Subramaniyan, Balasubramaniyan VairappanPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00045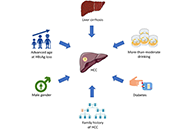 Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance after HBsAg seroclearanceOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance is considered the functional cure and the optimal treatment endpoint for chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Patients with CHB who cleared HBsAg generally ha...Jimmy Che-To Lai ... Terry Cheuk-Fung YipPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00046
Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance after HBsAg seroclearanceOpen AccessReviewHepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance is considered the functional cure and the optimal treatment endpoint for chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Patients with CHB who cleared HBsAg generally ha...Jimmy Che-To Lai ... Terry Cheuk-Fung YipPublished: May 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00046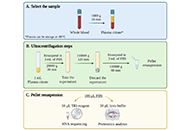 Optimization of protocols for blood-derived extracellular vesicles for studies in liver diseasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have gained significant attention for their diagnostic and therapeutic potential in various diseases, including liver disorders. This study focuses on optimizing...Magnolia Martínez-Aguilar ... Han MoshagePublished: April 28, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00044
Optimization of protocols for blood-derived extracellular vesicles for studies in liver diseasesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have gained significant attention for their diagnostic and therapeutic potential in various diseases, including liver disorders. This study focuses on optimizing...Magnolia Martínez-Aguilar ... Han MoshagePublished: April 28, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00044 Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradicationOpen AccessReviewIt is generally accepted that eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection may reduce the risk of the development of gastric cancer. Recommendations for global generalized tests and trea...Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro VoumvourakiPublished: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00043
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: a critical approach to who really needs eradicationOpen AccessReviewIt is generally accepted that eradication of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection may reduce the risk of the development of gastric cancer. Recommendations for global generalized tests and trea...Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro VoumvourakiPublished: April 16, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00043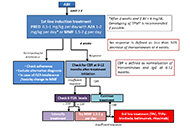 Second- and third-line treatment agents in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH): Where do we stand?Open AccessReviewAutoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver disease of unknown aetiology that can lead to end stage liver disease if left without treatment. Corticosteroids with or without azathioprine (AZA) are ...Pinelopi Arvaniti ... Maria-Carlota LondoñoPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00042
Second- and third-line treatment agents in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH): Where do we stand?Open AccessReviewAutoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver disease of unknown aetiology that can lead to end stage liver disease if left without treatment. Corticosteroids with or without azathioprine (AZA) are ...Pinelopi Arvaniti ... Maria-Carlota LondoñoPublished: April 10, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00042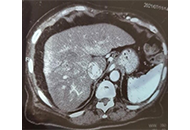 Remarkable alpha-fetoprotein elevation and pseudo-infarction of cirrhotic liver: case reportOpen AccessCase ReportThis is a case of remarkable alpha-fetoprotein in a female patient with known cryptogenic liver cirrhosis. Both ultrasound and triphasic computed tomography (CT) abdomen cannot diagnose or exclude h...Maged Tharwat Elghannam ... Mohammed Darwish ELTalkawyPublished: March 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00041
Remarkable alpha-fetoprotein elevation and pseudo-infarction of cirrhotic liver: case reportOpen AccessCase ReportThis is a case of remarkable alpha-fetoprotein in a female patient with known cryptogenic liver cirrhosis. Both ultrasound and triphasic computed tomography (CT) abdomen cannot diagnose or exclude h...Maged Tharwat Elghannam ... Mohammed Darwish ELTalkawyPublished: March 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00041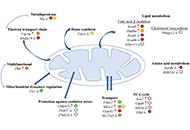 Liver metastatic colonization by invasive cancer cells: a review of potential biomarkers with mitochondrial involvementOpen AccessReviewThe liver, characterized by a unique metabolic and immunosuppressive environment, is also the organ to which invasive malignant cells of many different cancer types most frequently metastasize. The ...Daniel L. PouliquenPublished: March 22, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00040
Liver metastatic colonization by invasive cancer cells: a review of potential biomarkers with mitochondrial involvementOpen AccessReviewThe liver, characterized by a unique metabolic and immunosuppressive environment, is also the organ to which invasive malignant cells of many different cancer types most frequently metastasize. The ...Daniel L. PouliquenPublished: March 22, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00040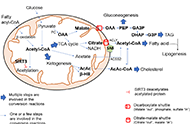 The central role of mitochondrial metabolism in hepatic steatosisOpen AccessReviewMitochondria are present in all mammalian cells except matured red blood cells. Mitochondria consist of several metabolic pathways for glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and bioenergetic pathways fo...Sanda Win ... Filbert Win Min AungPublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00039
The central role of mitochondrial metabolism in hepatic steatosisOpen AccessReviewMitochondria are present in all mammalian cells except matured red blood cells. Mitochondria consist of several metabolic pathways for glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and bioenergetic pathways fo...Sanda Win ... Filbert Win Min AungPublished: February 29, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00039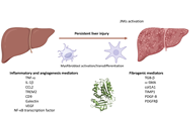 SERPINB3 in fibrogenic chronic liver diseases and primary liver cancersOpen AccessReviewChronic liver diseases (CLDs), which are typically characterized by fibrogenic progression towards liver cirrhosis and related complications eventually leading to organ failure and can also lead to ...Patrizia Pontisso, Maurizio ParolaPublished: February 28, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00038
SERPINB3 in fibrogenic chronic liver diseases and primary liver cancersOpen AccessReviewChronic liver diseases (CLDs), which are typically characterized by fibrogenic progression towards liver cirrhosis and related complications eventually leading to organ failure and can also lead to ...Patrizia Pontisso, Maurizio ParolaPublished: February 28, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00038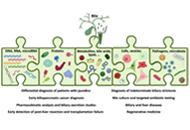 Bile as a liquid biopsy matrix: potential applications and limitationsOpen AccessReviewHunting for tumoral material in body fluids, traditionally in blood, the so-called liquid biopsy is set to revolutionize the diagnosis and management of oncological patients. However, other biofluid...Maria Arechederra ... Carmen BerasainPublished: February 04, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00037
Bile as a liquid biopsy matrix: potential applications and limitationsOpen AccessReviewHunting for tumoral material in body fluids, traditionally in blood, the so-called liquid biopsy is set to revolutionize the diagnosis and management of oncological patients. However, other biofluid...Maria Arechederra ... Carmen BerasainPublished: February 04, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00037 Precision medicine in chemotherapy: Is there room for advancement in colorectal cancer?Open AccessEditorialMichele GhidiniPublished: January 18, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00036
Precision medicine in chemotherapy: Is there room for advancement in colorectal cancer?Open AccessEditorialMichele GhidiniPublished: January 18, 2024 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00036 Correction: Familial achalasia isolated or syndromic: about 18 familiesOpen AccessCorrectionEditorial OfficePublished: January 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00035
Correction: Familial achalasia isolated or syndromic: about 18 familiesOpen AccessCorrectionEditorial OfficePublished: January 11, 2024 Explor Dig Dis DOI: 10.37349/edd.2024.00035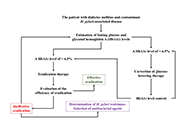 The significance of chronic hyperglycemia for the reduced efficacy of eradication therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and for Helicobacter pylori survivalOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to determine the significance of chronic hyperglycemia for the reduced efficacy of eradication therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and Helicobacter pylor...Luiza Gilmanovna Bektemirova ... Vasiliy Ivanovich ReshetnyakPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00033
The significance of chronic hyperglycemia for the reduced efficacy of eradication therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and for Helicobacter pylori survivalOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aims to determine the significance of chronic hyperglycemia for the reduced efficacy of eradication therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and Helicobacter pylor...Luiza Gilmanovna Bektemirova ... Vasiliy Ivanovich ReshetnyakPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00033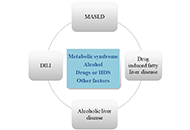 Deciphering the liver enigma: distinguishing drug-induced liver injury and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease—a comprehensive narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewDrug-induced liver injury (DILI) poses a complex and heterogeneous clinical challenge, which often resembles non-drug related acute or chronic liver diseases, such as metabolic dysfunction-associate...Miren García-Cortés ... Alberto García-GarcíaPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00034
Deciphering the liver enigma: distinguishing drug-induced liver injury and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease—a comprehensive narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewDrug-induced liver injury (DILI) poses a complex and heterogeneous clinical challenge, which often resembles non-drug related acute or chronic liver diseases, such as metabolic dysfunction-associate...Miren García-Cortés ... Alberto García-GarcíaPublished: December 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00034 Impact of the direct acting antivirals on chronic hepatitis C prevalence on the Swiss organ transplantation list: a retrospective analysisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In Switzerland, the first access to interferon-free direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) for hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment was in 2014. This study aimed to analyze the effects of DAAs on the ...Luis Falcato ... Franz ImmerPublished: December 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00032
Impact of the direct acting antivirals on chronic hepatitis C prevalence on the Swiss organ transplantation list: a retrospective analysisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: In Switzerland, the first access to interferon-free direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) for hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment was in 2014. This study aimed to analyze the effects of DAAs on the ...Luis Falcato ... Franz ImmerPublished: December 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00032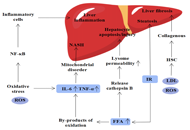 Therapeutic targets for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and their roles in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewMetabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases. Over time, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of MASLD. It has...Chenyu Wei ... Xianguang YangPublished: December 13, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00031
Therapeutic targets for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and their roles in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewMetabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is one of the most common chronic liver diseases. Over time, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of MASLD. It has...Chenyu Wei ... Xianguang YangPublished: December 13, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00031 Familial achalasia isolated or syndromic: about 18 familiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Familial achalasia (FA) is a very rare condition. This work aims to evaluate its prevalence, characterize its clinical profile in a large series, and assess the efficacy and safety of pneuma...Amar Tebaibia ... Nadia OumniaPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00030
Familial achalasia isolated or syndromic: about 18 familiesOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Familial achalasia (FA) is a very rare condition. This work aims to evaluate its prevalence, characterize its clinical profile in a large series, and assess the efficacy and safety of pneuma...Amar Tebaibia ... Nadia OumniaPublished: October 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00030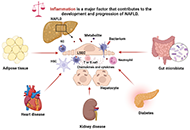 Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessReviewNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, with a progressive form of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It may progress to advanced liver diseases,...Chunye Zhang ... Ming YangPublished: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00029
Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessReviewNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, with a progressive form of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It may progress to advanced liver diseases,...Chunye Zhang ... Ming YangPublished: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00029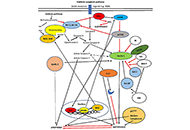 Interplay of autophagy, apoptosis, and senescence in primary biliary cholangitisOpen AccessReviewThe pathogenesis of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is particularly complicated as both intrinsic and extrinsic factors are implicated. Several forms of cellular death, both programmable and non-p...Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro VoumvourakiPublished: October 16, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00028
Interplay of autophagy, apoptosis, and senescence in primary biliary cholangitisOpen AccessReviewThe pathogenesis of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is particularly complicated as both intrinsic and extrinsic factors are implicated. Several forms of cellular death, both programmable and non-p...Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro VoumvourakiPublished: October 16, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00028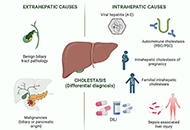 Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and managementOpen AccessReviewDrug-induced liver injury (DILI) is an adverse reaction to drugs and other xenobiotics that can have serious consequences and jeopardise progress in pharmacological therapy. While DILI is predominan...Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-CortésPublished: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00027
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and managementOpen AccessReviewDrug-induced liver injury (DILI) is an adverse reaction to drugs and other xenobiotics that can have serious consequences and jeopardise progress in pharmacological therapy. While DILI is predominan...Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-CortésPublished: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00027 Human liver stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles modulate long non-coding RNA expression profile in an in vivo model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modifications in long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) expression are associated with inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. It has been recently demonstrated that human liver stem cell...Giulia Chiabotto ... Stefania BrunoPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00025
Human liver stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles modulate long non-coding RNA expression profile in an in vivo model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitisOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Modifications in long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) expression are associated with inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. It has been recently demonstrated that human liver stem cell...Giulia Chiabotto ... Stefania BrunoPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00025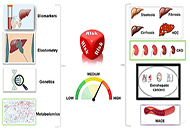 Principles of risk stratification in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A narrative review emphasizing non-invasive strategiesOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an umbrella definition that describes the ectopic deposition of fat within the liver that occurs in the absence of inciting factors other than the metabol...Amedeo LonardoPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00026
Principles of risk stratification in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A narrative review emphasizing non-invasive strategiesOpen AccessReviewNonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an umbrella definition that describes the ectopic deposition of fat within the liver that occurs in the absence of inciting factors other than the metabol...Amedeo LonardoPublished: August 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00026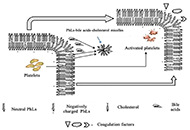 Pathophysiology of biochemical signs of primary biliary cholangitisOpen AccessReviewPrimary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a rare chronic autoimmune cholestatic liver disease, affecting mostly females. With PBС develops chronic cholang...Vasiliy Ivanovich Reshetnyak, Igor Veniaminovich MaevPublished: August 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00024
Pathophysiology of biochemical signs of primary biliary cholangitisOpen AccessReviewPrimary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a rare chronic autoimmune cholestatic liver disease, affecting mostly females. With PBС develops chronic cholang...Vasiliy Ivanovich Reshetnyak, Igor Veniaminovich MaevPublished: August 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00024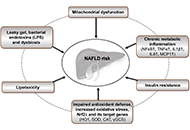 Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—What are the proposed mechanisms?Open AccessReviewA high consumption of ultra-processed food (UPF) is a hallmark of Western diets that has been related to increased risk of non-communicable diseases. As an underlying mechanism, UPF may promote non-...Franziska A. Hägele ... Anja Bosy-WestphalPublished: August 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00023
Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—What are the proposed mechanisms?Open AccessReviewA high consumption of ultra-processed food (UPF) is a hallmark of Western diets that has been related to increased risk of non-communicable diseases. As an underlying mechanism, UPF may promote non-...Franziska A. Hägele ... Anja Bosy-WestphalPublished: August 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00023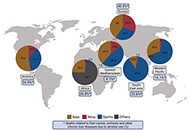 Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?Open AccessReviewExcessive alcohol intake is still among the leading causes of chronic liver diseases. Epidemiological studies suggest that per capita consumption of alcohol from various alcohol beverages e.g., beer...Finn Jung ... Ina BergheimPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00022
Alcohol-related liver disease: also a question of what you drink?Open AccessReviewExcessive alcohol intake is still among the leading causes of chronic liver diseases. Epidemiological studies suggest that per capita consumption of alcohol from various alcohol beverages e.g., beer...Finn Jung ... Ina BergheimPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00022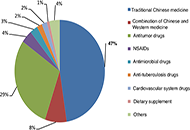 An analysis on the clinical features and risk factors associated with the prognosis of patients with drug-induced liver injuryOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This is a Chinese population-based study aimed to determine the causes and clinical features of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) from traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) and current Western m...Qian Wei ... Jinsheng GuoPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00021
An analysis on the clinical features and risk factors associated with the prognosis of patients with drug-induced liver injuryOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This is a Chinese population-based study aimed to determine the causes and clinical features of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) from traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) and current Western m...Qian Wei ... Jinsheng GuoPublished: June 30, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00021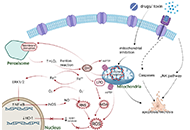 Role of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug-induced liver injuryOpen AccessReviewThe pathogenesis of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is still in an early stage of research. However, investigators have shown that both oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress play a...Hanghang Wu ... Francisco Javier CuberoPublished: June 28, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00020
Role of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in drug-induced liver injuryOpen AccessReviewThe pathogenesis of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is still in an early stage of research. However, investigators have shown that both oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress play a...Hanghang Wu ... Francisco Javier CuberoPublished: June 28, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00020 Liver injury related to Japanese herbal medicines: clinical features and diagnosisOpen AccessReviewThe word “Kampo medicine” means the traditional Japanese herbal medicine. Even “natural herb” can cause drug-induced liver injury (DILI). In this review, the characteristics of Kampo medicin...Naoki MantaniPublished: June 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00019
Liver injury related to Japanese herbal medicines: clinical features and diagnosisOpen AccessReviewThe word “Kampo medicine” means the traditional Japanese herbal medicine. Even “natural herb” can cause drug-induced liver injury (DILI). In this review, the characteristics of Kampo medicin...Naoki MantaniPublished: June 27, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00019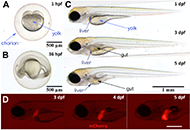 Zebrafish as a model for drug induced liver injury: state of the art and beyondOpen AccessReviewZebrafish as a preclinical drug induced liver injury (DILI) model provides multiple advantages ranging from ease of breeding and maintenance, availability of different strains and transgenic fish am...Gulcin Cakan-Akdogan ... Ozlen KonuPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00017
Zebrafish as a model for drug induced liver injury: state of the art and beyondOpen AccessReviewZebrafish as a preclinical drug induced liver injury (DILI) model provides multiple advantages ranging from ease of breeding and maintenance, availability of different strains and transgenic fish am...Gulcin Cakan-Akdogan ... Ozlen KonuPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00017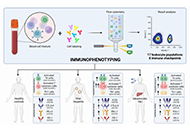 Immunophenotyping to improve the mechanistic understanding of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: clinical implications and future directionsOpen AccessReviewThe late event onset of a fraction of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases and the link observed by genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of certain human leucocyte antigen (HLA) a...Alejandro Cueto-Sánchez ... Marina Villanueva-PazPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00018
Immunophenotyping to improve the mechanistic understanding of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: clinical implications and future directionsOpen AccessReviewThe late event onset of a fraction of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (DILI) cases and the link observed by genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of certain human leucocyte antigen (HLA) a...Alejandro Cueto-Sánchez ... Marina Villanueva-PazPublished: April 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00018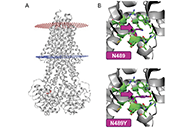 Diagnostic workup of suspected hereditary cholestasis in adults: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportHereditary cholestasis comprises a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes of varying severity. Severe forms such as progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) mostly affect children with di...Carola Dröge ... Verena KeitelPublished: April 21, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00016
Diagnostic workup of suspected hereditary cholestasis in adults: a case reportOpen AccessCase ReportHereditary cholestasis comprises a broad spectrum of clinical phenotypes of varying severity. Severe forms such as progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) mostly affect children with di...Carola Dröge ... Verena KeitelPublished: April 21, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00016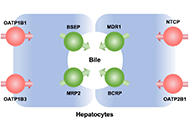 Monitoring the hepatobiliary function using image techniques and labeled cholephilic compoundsOpen AccessReviewEvaluation of the hepatobiliary function is critical for the clinicians, not only for the diagnosis of a large variety of liver diseases but also in the follow-up and management of some patients, for instance, those with different degrees of cholestasis suffering from a drug-induced liver injury (DILI) or scheduled for liver resection. Currently, the determination of global liver function mainly relies on laboratory tests, clinical scores, and data from images obtained with ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance. Nuclear medicine scanning, displaying either planar or three-dimensional spatial distribution of liver function, is enhanced when using hepatotropic tracers based on classical radioisotopes such as technetium-99m (99mTc) and with higher resolution using metabolized probes such as those based on monosaccharide derivatives labeled with 18F. Other cholephilic compounds, and hence selectively secreted into bile, have been proposed to visualize the correct function of the liver parenchyma and the associated secretory machinery. This review aims to summarize the state-of-the-art regarding the techniques and chemical probes available to monitor liver and gallbladder function, in some cases based on imaging techniques reflecting the dynamic of labeled cholephilic compounds....Beatriz Sanchez de Blas ... Marta R. RomeroPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00015
Monitoring the hepatobiliary function using image techniques and labeled cholephilic compoundsOpen AccessReviewEvaluation of the hepatobiliary function is critical for the clinicians, not only for the diagnosis of a large variety of liver diseases but also in the follow-up and management of some patients, for instance, those with different degrees of cholestasis suffering from a drug-induced liver injury (DILI) or scheduled for liver resection. Currently, the determination of global liver function mainly relies on laboratory tests, clinical scores, and data from images obtained with ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance. Nuclear medicine scanning, displaying either planar or three-dimensional spatial distribution of liver function, is enhanced when using hepatotropic tracers based on classical radioisotopes such as technetium-99m (99mTc) and with higher resolution using metabolized probes such as those based on monosaccharide derivatives labeled with 18F. Other cholephilic compounds, and hence selectively secreted into bile, have been proposed to visualize the correct function of the liver parenchyma and the associated secretory machinery. This review aims to summarize the state-of-the-art regarding the techniques and chemical probes available to monitor liver and gallbladder function, in some cases based on imaging techniques reflecting the dynamic of labeled cholephilic compounds....Beatriz Sanchez de Blas ... Marta R. RomeroPublished: February 28, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00015 Extra-hepatic cancers in metabolic fatty liver syndromesOpen AccessEditorialAmedeo LonardoPublished: February 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00014
Extra-hepatic cancers in metabolic fatty liver syndromesOpen AccessEditorialAmedeo LonardoPublished: February 24, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00014 Lysosomal hydrolases, from waste-bags effectors to essential multipurpose enzymes in liver fibrosisOpen AccessReviewLysosomal hydrolases were once considered effectors of the waste disposal system of the cell, the endo-lysosomal system. However, they are now recognized as highly selective enzymes, which can modul...María Fernández-Fernández ... Anna MolesPublished: February 22, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00013
Lysosomal hydrolases, from waste-bags effectors to essential multipurpose enzymes in liver fibrosisOpen AccessReviewLysosomal hydrolases were once considered effectors of the waste disposal system of the cell, the endo-lysosomal system. However, they are now recognized as highly selective enzymes, which can modul...María Fernández-Fernández ... Anna MolesPublished: February 22, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2023.00013 The bile acid receptor TGR5 and cholestasisOpen AccessReviewMetabolic zonation in the liver carries out the maintenance of organ and body homeostasis. Hypoxia is an inherent physiological feature of the liver and contributes to the zonal properties of the he...Grégory Merlen ... Thierry TordjmannPublished: December 30, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00011
The bile acid receptor TGR5 and cholestasisOpen AccessReviewMetabolic zonation in the liver carries out the maintenance of organ and body homeostasis. Hypoxia is an inherent physiological feature of the liver and contributes to the zonal properties of the he...Grégory Merlen ... Thierry TordjmannPublished: December 30, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00011 Hypoxia signaling and cholesterol/steroidogenic acute regulatory protein 1 axis: interplay and role in alcohol and non-alcohol-related liver diseasesOpen AccessPerspectiveMetabolic zonation in the liver carries out the maintenance of organ and body homeostasis. Hypoxia is an inherent physiological feature of the liver and contributes to the zonal properties of the he...Sandra Torres ... Carmen Garcia-RuizPublished: December 30, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00012
Hypoxia signaling and cholesterol/steroidogenic acute regulatory protein 1 axis: interplay and role in alcohol and non-alcohol-related liver diseasesOpen AccessPerspectiveMetabolic zonation in the liver carries out the maintenance of organ and body homeostasis. Hypoxia is an inherent physiological feature of the liver and contributes to the zonal properties of the he...Sandra Torres ... Carmen Garcia-RuizPublished: December 30, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00012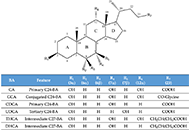 Cholestasis associated to inborn errors in bile acid synthesisOpen AccessReviewSeveral metabolic pathways are involved in the biotransformation of C27 neutral cholesterol to C24 primary bile acids (BAs), mainly cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), which are then conjugated with glycine or taurine. This process can start with the modification of the steroid ring or the shortening of the side chain and involves enzymes present in different subcellular compartments. Inborn errors affecting the biogenesis of organelles, such as peroxisomes, or the expression or function of specific enzymes of these convergent routes result in: i) the lack of mature C24-BAs, with the subsequent impairment in digestion and absorption of dietary fat and liposoluble vitamins, such as vitamin K, which may account for a deficient hepatic synthesis of several coagulation factors; ii) the accumulation of intermediate metabolites, which may affect hepatocyte physiology, causing cholestasis as a commonly shared alteration besides other deleterious hepatic events; and iii) extrahepatic clinical manifestations due to accumulation of toxic metabolites in other territories, such as the nervous system, causing neurological disorders. In general, diseases whose primary alteration is a genetic defect in BA synthesis are diagnosed in children or young individuals with a very low incidence. The symptomatology can markedly vary among individuals, ranging from mild to severe conditions. Oral therapy, based on the enrichment of the BA pool with natural C24-BAs, such as CA, CDCA, glyco-CA, or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), depending on the exact deficiency causing the disease, may be beneficial in preventing life-threatening situations. In contrast, in other cases, a liver transplant is the only option for these patients. This review describes the updated information on the genetic and molecular bases of these diseases and the current approaches to achieve a selective diagnosis and specific treatment....Ricardo Espinosa-Escudero ... Maria J. MontePublished: December 7, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00010
Cholestasis associated to inborn errors in bile acid synthesisOpen AccessReviewSeveral metabolic pathways are involved in the biotransformation of C27 neutral cholesterol to C24 primary bile acids (BAs), mainly cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), which are then conjugated with glycine or taurine. This process can start with the modification of the steroid ring or the shortening of the side chain and involves enzymes present in different subcellular compartments. Inborn errors affecting the biogenesis of organelles, such as peroxisomes, or the expression or function of specific enzymes of these convergent routes result in: i) the lack of mature C24-BAs, with the subsequent impairment in digestion and absorption of dietary fat and liposoluble vitamins, such as vitamin K, which may account for a deficient hepatic synthesis of several coagulation factors; ii) the accumulation of intermediate metabolites, which may affect hepatocyte physiology, causing cholestasis as a commonly shared alteration besides other deleterious hepatic events; and iii) extrahepatic clinical manifestations due to accumulation of toxic metabolites in other territories, such as the nervous system, causing neurological disorders. In general, diseases whose primary alteration is a genetic defect in BA synthesis are diagnosed in children or young individuals with a very low incidence. The symptomatology can markedly vary among individuals, ranging from mild to severe conditions. Oral therapy, based on the enrichment of the BA pool with natural C24-BAs, such as CA, CDCA, glyco-CA, or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), depending on the exact deficiency causing the disease, may be beneficial in preventing life-threatening situations. In contrast, in other cases, a liver transplant is the only option for these patients. This review describes the updated information on the genetic and molecular bases of these diseases and the current approaches to achieve a selective diagnosis and specific treatment....Ricardo Espinosa-Escudero ... Maria J. MontePublished: December 7, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00010 Probiotic human alcohol dehydrogenase-4 expressing bacteria protects from diet-induced obesity and metabolic impairment: a new concept of disease preventionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Probiotic bacteria consumption for improving human health and for disease prevention is still controversial. There is a need to develop functional probiotic bacteria with proven efficacy for...Rajnish Prakash Singh ... Zvi HayoukaPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00009
Probiotic human alcohol dehydrogenase-4 expressing bacteria protects from diet-induced obesity and metabolic impairment: a new concept of disease preventionOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Probiotic bacteria consumption for improving human health and for disease prevention is still controversial. There is a need to develop functional probiotic bacteria with proven efficacy for...Rajnish Prakash Singh ... Zvi HayoukaPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00009 Caspase-2 in liver disease and hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewCaspases are key factors in the regulation of the apoptotic and/or inflammatory responses, both crucial in the pathogenesis of diverse diseases. Caspase-2 is the most evolutionary conserved albeit f...Amaya Lopez-Pascual ... Maite G. Fernández-BarrenaPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00007
Caspase-2 in liver disease and hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewCaspases are key factors in the regulation of the apoptotic and/or inflammatory responses, both crucial in the pathogenesis of diverse diseases. Caspase-2 is the most evolutionary conserved albeit f...Amaya Lopez-Pascual ... Maite G. Fernández-BarrenaPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00007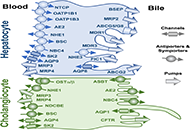 Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasisOpen AccessReviewNormal hepatobiliary function depends on an adequate bile flow from the liver through the biliary tree to the gallbladder, where bile is stored and concentrated, and from the gallbladder to the duod...Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. MarinPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00008
Etiopathogenesis and pathophysiology of cholestasisOpen AccessReviewNormal hepatobiliary function depends on an adequate bile flow from the liver through the biliary tree to the gallbladder, where bile is stored and concentrated, and from the gallbladder to the duod...Maitane Asensio ... Jose J. G. MarinPublished: October 31, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00008 The intermicrovillar adhesion complex in gut barrier function and inflammationOpen AccessPerspectiveThe surface of intestinal epithelial cells is covered by the brush border, which consists of densely packed cellular extrusions called microvilli. Until recently, microvilli have not been known to b...Bernadette Mödl ... Robert EferlPublished: October 11, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00006
The intermicrovillar adhesion complex in gut barrier function and inflammationOpen AccessPerspectiveThe surface of intestinal epithelial cells is covered by the brush border, which consists of densely packed cellular extrusions called microvilli. Until recently, microvilli have not been known to b...Bernadette Mödl ... Robert EferlPublished: October 11, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00006 Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewWorldwide the number of individuals being overweight or obese has dramatically increased during the last decades, which is also associated with a similar dramatic increase of individuals afflicted w...Anja Baumann ... Ina BergheimPublished: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00005
Fructose, a trigger of metabolic diseases?—a narrative reviewOpen AccessReviewWorldwide the number of individuals being overweight or obese has dramatically increased during the last decades, which is also associated with a similar dramatic increase of individuals afflicted w...Anja Baumann ... Ina BergheimPublished: August 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00005 The hepatocyte growth factor induces an anti-inflammatory and repairing response in the cholestasis-induced colon damageOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cholestasis remains a partially characterized disease. Evidence has been gained that it is a systemic disease that begins in the liver but significantly impacts other organs and systems such...Jocelyn López-Ramirez ... Leticia Bucio-OrtizPublished: August 11, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00004
The hepatocyte growth factor induces an anti-inflammatory and repairing response in the cholestasis-induced colon damageOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Cholestasis remains a partially characterized disease. Evidence has been gained that it is a systemic disease that begins in the liver but significantly impacts other organs and systems such...Jocelyn López-Ramirez ... Leticia Bucio-OrtizPublished: August 11, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00004 Tumor immune microenvironment modulation by cholesterol in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewHepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is considered one of the most aggressive tumors worldwide. The consumption of lipid-enriched diets, mainly high cholesterol, induces oxidative stress and chronic infla...Alejandro Escobedo-Calvario ... María Concepción Gutiérrez-RuízPublished: July 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00003
Tumor immune microenvironment modulation by cholesterol in hepatocellular carcinomaOpen AccessReviewHepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is considered one of the most aggressive tumors worldwide. The consumption of lipid-enriched diets, mainly high cholesterol, induces oxidative stress and chronic infla...Alejandro Escobedo-Calvario ... María Concepción Gutiérrez-RuízPublished: July 29, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00003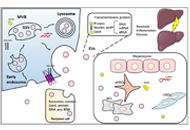 Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic implicationsOpen AccessReviewThe prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is increasing rapidly worldwide due to the obesity epidemic. Advanced stages of the MAFLD, such as non-alcoholic steato...Zongmei Wu ... Han MoshagePublished: July 13, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00002
Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic implicationsOpen AccessReviewThe prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is increasing rapidly worldwide due to the obesity epidemic. Advanced stages of the MAFLD, such as non-alcoholic steato...Zongmei Wu ... Han MoshagePublished: July 13, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00002 Exploration of Digestive Diseases, where discovery and communication meetOpen AccessEditorialJose C. Fernandez-ChecaPublished: July 01, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00001
Exploration of Digestive Diseases, where discovery and communication meetOpen AccessEditorialJose C. Fernandez-ChecaPublished: July 01, 2022 Explor Dig Dis. DOI: 10.37349/edd.2022.00001 -