112 results in Exploration of Digestive Diseases
Latest
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Review
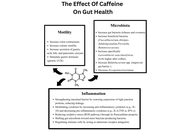
The impact of caffeine in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of the literature
Mohamed Ahmed Mohamed ... Faith Bishop
Published: February 26, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005112
This article belongs to the special issue Inflammatory Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Open Access
Case Report
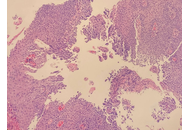
A unique association between herpes simplex esophagitis and eosinophilic esophagitis: a case report
Sahil Sabharwal ... Terryl Ortego
Published: February 13, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005111
Open Access
Review
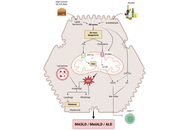
Understanding liver and digestive diseases: a paved road to improve diagnosis, management, and treatment
Ina Bergheim ... Jose C Fernandez-Checa
Published: February 09, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005110
Open Access
Review
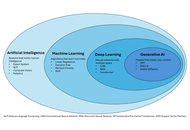
Artificial intelligence in the interventional management of liver disease: a narrative review from foundational concepts to clinical applications
Hyeon Yu
Published: January 18, 2026 Explor Dig Dis. 2026;5:1005109
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Original Article
GDF11 induces chemosensitization in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing drug-efflux transporters
Natanael German-Ramirez ... Luis E. Gomez-Quiroz
Published: December 30, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005108
Open Access
Review
Diverticulitis—new evidence to share with patients
Nicholas B. D’Alessandro ... David A. Johnson
Published: December 24, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005107
This article belongs to the special issue Diverticulitis: Pathomechanism, Diagnosis and Treatment

Open Access
Review
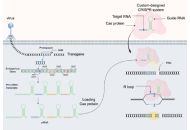
CRISPR genome editing advances against gastric cancer
Mengmeng Zhang ... Xianguang Yang
Published: December 09, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005106
Open Access
Review
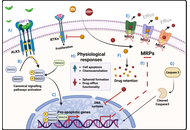
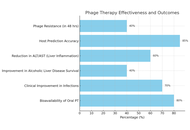
The therapeutic potential of bacteriophage therapy in liver cirrhosis: a comprehensive review of current evidence
Sarala Gudla ... Srijamya
Published: December 08, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005105
This article belongs to the special issue Gut Microbiota towards Personalized Medicine in Metabolic Disease
Open Access
Review
Pediatric cirrhosis: special consideration for its diagnosis and management
Guillermo Alejandro Costaguta, Fernando Álvarez
Published: December 07, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005104
This article belongs to the special issue Cirrhosis and Its Complications

Open Access
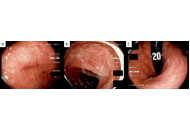
Case Report
Ixekizumab-associated severe Crohn’s in a patient without definitive immune-mediated inflammatory disease: case report and evidence-informed guidance for non-IBD clinicians
Taylor L. Spiewak ... Anish Patel
Published: December 01, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005103
Open Access
Editorial
Surveillance for cholangiocarcinoma in PSC: MRI, ERCP, both—or neither?
Vincenzo Giorgio Mirante
Published: November 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005102
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Review
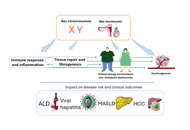
Sex differences in alcohol-related liver disease, viral hepatitis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma
Amedeo Lonardo, Ayako Suzuki
Published: November 26, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005101
Open Access
Review
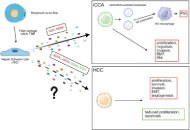
Neurotrophic signaling in liver cancers: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets
Lorenzo Mainardi ... Chiara Raggi
Published: November 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:1005100
This article belongs to the special issue Fibrosis and Hepatobiliary Cancer
Open Access
Perspective
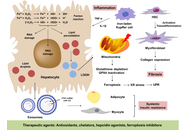
From spark to wildfire: how hyperferritinemia fans the flames of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Ralf Weiskirchen
Published: October 28, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100599
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification
Open Access
Review
Recent advances in Helicobacter pylori diagnosis, treatment, and management: a comprehensive review
Surbhi Dumra, Abhishek Ray
Published: October 21, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100598
This article belongs to the special issue Helicobacter Pylori and Infection: Genomics, Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Microbiota, Cancer, Prevention and Therapeutics

Open Access
Review
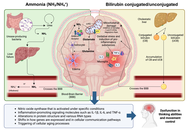
How the gut-liver axis shapes hepatic encephalopathy: mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives
Arnulfo E. Morales-Galicia ... Nahum Méndez-Sánchez
Published: October 14, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100597
Open Access
Original Article
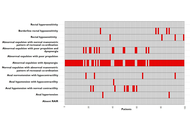
Multiple abnormalities of anorectal physiology co-exist with dyssynergia in patients with functional defecatory disorder—an observational study based on the London classification
Stephan Benny ... Noble Varghese Mathews
Published: October 11, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100596
Open Access
Review
Precision prevention of liver cancer based on risk factors
Jian-Guo Chen
Published: September 29, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100595
This article belongs to the special issue Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer

Open Access
Original Article
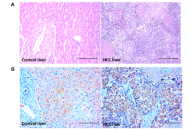
Elevated circulating pregnane X receptor as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma
Balasubramaniyan Vairappan ... Biju Pottakkat
Published: September 25, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100594
This article belongs to the special issue Prevention, Screening and Diagnosis for Primary Liver Cancer
Open Access
Review
Insights of hepatitis A virus disease burden in Indian subcontinent: why urbanized localities are vulnerable to disease outbreaks?
Zahid Hussain ... Vivek Patel
Published: September 24, 2025 Explor Dig Dis. 2025;4:100593
This article belongs to the special issue Viral Hepatitis

Journal Information
 Previous
Previous