Exploring NAFLD/NASH
Guest Editors
Dr. Amedeo Lonardo E-Mail
Director of Simple Operating Unit, Ospedale Civile di Baggiovara, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Modena, Modena, Italy
Research Keywords: NAFLD, NASH, cirrhosis, HCC
Dr. Giovanni Targher E-Mail
Section of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
Research Keywords: Role of NAFLD in cardiovascular morbidity/mortality, role of NAFLD in microvascular complications of diabetes
About the Special lssue
Exploration of Medicine (EM) is a novel peer-reviewed, open access, online journal. It publishes articles that provide substantial and novel insights into medicine spanning molecular and cell biology through research of all human diseases. The journal adopts a single-blind peer review. Those authors who publish for EM hold the copyright of their works, make their original works completely available and free to use as long as the authors and the original source are properly cited.
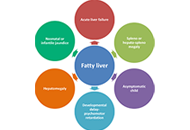
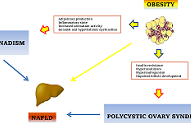
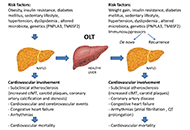
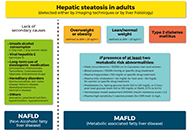
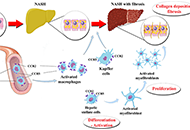
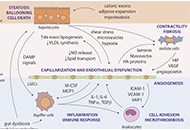
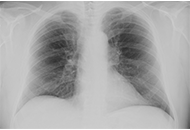
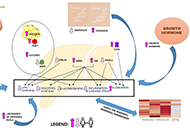
EM has charged Dr. Lonardo and Professor Targher to edit a special issue dedicated to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Why has this topic been chosen? NAFLD defines a spectrum of hepatic (steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH], cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma) and extra-hepatic manifestations (nephro-cardio-metabolic diseases and extra-hepatic cancers) that occur in individuals free of any competing causes of hepatic steatosis (e.g., alcohol, virus, drugs and others) but who often have concurrent dysmetabolic features. NAFLD is the most common chronic liver disease worldwide, causes considerable health care expenses, requests a heavy toll in terms of morbidity and premature mortality and has, therefore, gained considerable scientific interest. Areas of ongoing research include epidemiological features and risk factors, (molecular) pathogenesis, (non-invasive) diagnosis, government of the patients fluxes from primary to specialist care as well as management of this burdensome liver disease with lifestyle modifications and innovative drugs that are being evaluated.
In order to provide a virtual forum for exchange of ideas and data in Academic as well as in Translational and Clinical research, Dr. Lindsay Farrer, the Editor-in-Chief of EM, has invited Doctors Lonardo and Targher to edit this single-topic issue.
Keywords: NAFLD, NASH, HCC, cirrhosis
Published Articles