Angiotensins—A Century of Progress
Guest Editors
Dr. Carlos M. Ferrario E-Mail
Professor, General Surgery, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, USA
Research Keywords: Biochemical physiology of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system, neurohormonal regulation of blood pressure, essential hypertension and its mechanisms
Dr. Leanne Groban E-Mail
Professor, Anesthesiology, Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, USA
Research Keywords: Sex differences in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease, aging and diastolic dysfunction, women’s heart health, diabetes and menopause
About the Special lssue
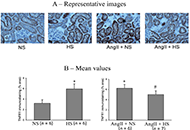
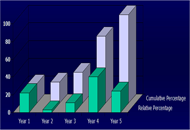
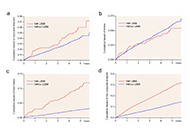
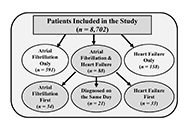
“The history of hypertension is both long and short”, so it was stated in the Preface to Angiotensin, Angiotensin, a book edited by Irvine H Page and F. Merlin Bumpus in 1974. Sixty-six years of continuous progress since the research of Skeggs et al. (PMCID: PMC2136385) isolation of angiotensin, the importance of this hormone, a product of the humoral system conceptualized as the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) are pillars sustaining the development and applicability of medicines having a definitive impact in human disease, above and beyond their applicability to the treatment of diseases of the heart and the blood vessels. The multiplicity of the actions of the peptide hormones expressed within the RAAS continues to shed new light into human biology, tissue homeostasis, and the development of chronic non-communicable diseases. To celebrate these accomplishments and provide a forward look to RAAS participation in human disease, this special issue will highlight the major contributions to the understanding of the functions of angiotensins not only within and beyond its applicability to control of tissue perfusion, organ metabolic processes, inflammation, innate immunity, and fetal programming. And this issue welcomes diverse types of articles, including Original Article, Review, Meta-analysis, Systematic Review, Case Report, and Commentary.
The Editors believe that this special issue of Exploration of Medicine will allow the scientific community to reflect how far we have advanced in the frontiers of knowledge, where accepted knowledge of the system may need revision, and target the new frontiers of discovery in reaching ultimate knowledge of how hormones act to both regulate and dysregulate body homeostasis.
Keywords: Angiotensins, renin, angiotensinogen, heart diseases, vascular diseases, stroke, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, pregnancy, fetal programming, age-related mobility/disability, sepsis, surgery/anesthesia-related hypotension, sex differences
Published Articles