Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and Cannabinoids
Guest Editors
Dr. Staci Gruber E-Mail
Director, Cognitive and Clinical Neuroimaging Core; Director, Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND), McLean Hospital; Associate Professor of Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Belmont, USA
Dr. M. Kathryn Dahlgren E-Mail
Assistant Neuroscientist, Cognitive and Clinical Neuroimaging Core, Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND), McLean Hospital; Instructor in Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Belmont, USA
Dr. Kelly Sagar E-Mail
Assistant Neuroscientist, Cognitive and Clinical Neuroimaging Core, Marijuana Investigations for Neuroscientific Discovery (MIND), McLean Hospital; Instructor in Psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Belmont, USA
About the Special lssue
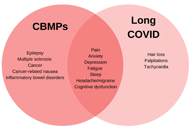
Cannabis has been used medicinally across countless cultures for thousands of years, and a recent cultural shift re-embracing plant-based medicine has resulted in growing efforts to legalize cannabis and cannabinoid-based products. Although decades of research have focused on potential harms related to recreational cannabis use, particularly in younger populations, a paucity of empirically sound data exists regarding the impact of cannabinoids when used for medical purposes. As increasing numbers of patients turn to cannabinoids as an alternative or adjunctive treatment, additional studies specifically examining the risks and benefits of medical cannabis use and cannabinoid-based treatments are clearly warranted. Although the term “cannabis” is often used to describe anything from the plant Cannabis sativa L, this term represents an extremely diverse array of constituents and compounds. Accordingly, given the unique effects associated with individual cannabinoids or combinations of cannabinoids and other constituents, it is critical that cannabinoid-based treatments being evaluated are well-characterized in terms of their source, composition, dose, and route of administration.
Investigators are invited to submit original research, reviews, meta-analyses, commentaries, or perspectives for this special issue of Exploration of Medicine entitled “Beyond Weed: Clinical Applications of Cannabis and Cannabinoids.” This issue will be focused on assessing potential clinical applications of cannabinoids for a range of medical conditions and symptoms, including but not limited to pain, inflammation, cancer, neurological disorders, psychiatric disorders, and sleep disturbance. Manuscripts examining clinical outcomes, safety, dosing, efficacy, expectancy effects, and other topics relevant to clinical applications of cannabinoid-based treatments will be considered. This collection of articles will add critically important, unbiased scientific evidence to the literature, which can ultimately play a key role in informing public health policies and guiding clinical care decisions related to the use of cannabis and cannabinoids for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: Cannabis, cannabinoids, medical marijuana, treatment, clinical outcomes, safety, public health
Published Articles