237 results in Exploration of Immunology
Latest
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Review
Postbiotics as promising oral vaccine adjuvants
Roya Abedi Soleimani ... Aziz Homayouni Rad
Published: February 13, 2026 Explor Immunol. 2026;6:1003237
Open Access
Review
Pneumococcal live attenuated vaccine: strategies, challenges and future perspectives
Marina Yusoff ... Malik Amonov
Published: January 26, 2026 Explor Immunol. 2026;6:1003236
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Vaccines development for Emerging, Acute, and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Open Access
Review
Role of pulsed radiofrequency on the immunological system in chronic pain patients: a narrative review
Felice Occhigrossi ... Giustino Varrassi
Published: January 12, 2026 Explor Immunol. 2026;6:1003235
Open Access
Review
Flagellin fusion proteins as self-adjuvanting vaccines for viral infections and cancer
Clett Erridge
Published: January 05, 2026 Explor Immunol. 2026;6:1003234
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Vaccines development for Emerging, Acute, and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Open Access
Original Article
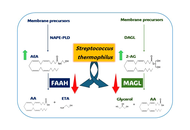
The anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential of the probiotic Streptococcus thermophilus via inhibition of endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes: a preliminary in vitro study
Serena Altamura ... Benedetta Cinque
Published: December 30, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003233
This article belongs to the special issue Immunology and Pain
Open Access
Review
Advancements in therapeutic strategies and drug development for inflammatory bowel diseases
Yu Zhou, Fang Shen
Published: December 23, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003232
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Cellular and Molecular Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases
Open Access
Original Article
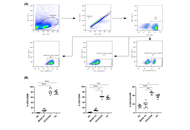
MAGE-A3-specific memory T cell induction from healthy donors: a functional in vitro evaluation
Gaurang Telang ... Rajshri Singh
Published: December 18, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003231
Open Access
Original Article
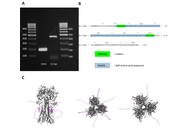
Recombinant influenza A/H1N1pdm09 vaccine expressing streptococcal surface epitope for dual protection
Yulia Desheva ... Irina Isakova-Sivak
Published: November 28, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003230
This article belongs to the special issue Old and New Paradigms in Viral Vaccinology
Open Access
Review
HLA-KIRs interactions in modulating natural killer cell responses against viral hepatitis: a concise review
Ata Shirizadeh ... Ghasem Solgi
Published: November 23, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003229
This article belongs to the special issue Immunogenetics of Chronic Illnesses
Open Access
Systematic Review
Immune evasion mechanisms and cutting-edge therapeutic strategies of PD-L1 pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma: an umbrella review
Neha Kannan ... Giuseppe Minervini
Published: November 17, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003228
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Immune Checkpoint Molecules in Cancer and Hematological Malignancies
Open Access
Review
Probing and enhancing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: insights from single-cell technologies and genetic reprogramming
Chaitanya Kumar ... Veeraraghavan Vishnu Priya
Published: November 17, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003227
This article belongs to the special issue Advances and Novel Insights into Immunoinformatics

Open Access
Review
Phenotypic and functional alterations of innate lymphoid cells in hematological malignancies: potential clinical application
Mario Di Gioacchino ... Alessandro Allegra
Published: November 17, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003226
Open Access
Editorial
The discovery of Regulatory T Cells: a long journey toward immune balance and Nobel Prize
Anna Calabrò, Calogero Caruso
Published: November 06, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003225
Open Access
Review
Cancer immunotherapy and cardiovascular side-effects: from treatment modalities to the use of the preventive effect of antihypertensive drugs
Fakher Rahim ... Issenova Balday
Published: October 28, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003224
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Immune Checkpoint Molecules in Cancer and Hematological Malignancies
Open Access
Review
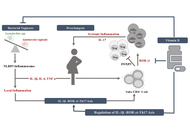
Translating the vaginal microbial landscape: a connecting link between bacterial vaginosis and preeclampsia
Devanshi Gajjar, Sriram Seshadri
Published: October 24, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003223
Open Access
Review
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: insights from molecular pathogenesis to targeted therapies
Fatima K. Alduraibi ... Peter C. Chien
Published: October 24, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003222
Open Access
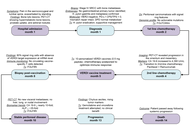
Case Report
Personalized peptide vaccines induce predicted T cell responses against signet ring cell carcinoma—a case report
Julianna Lisziewicz ... Bartolome Garcia Perez
Published: October 13, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003221
Open Access
Review
Role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in breast cancer and hematological malignancies
Qing Bao ... Hailin Tang
Published: September 29, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003220
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Immune Checkpoint Molecules in Cancer and Hematological Malignancies
Open Access
Review
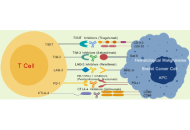
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: overcoming diagnostic obstacles and exploring pharmacotherapeutic approaches
Priya Komre ... Debarshi Kar Mahapatra
Published: September 29, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003219
Open Access
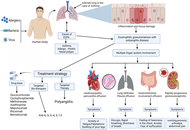
Mini Review
Skin aging and immunosenescence
Natasa Strbo ... Alessia Paganelli
Published: September 29, 2025 Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003218
This article belongs to the special issue Immunosenescence: Mechanisms and Its Impact
Journal Information
 Previous
Previous