The Sepsis induced Immune Conundrum
Guest Editor
Dr. Didier Payen E-Mail
Emeritus Professor at University Paris 7, Paris, France
Research Keywords: Sepsis, immune response, ARDS, emodynamic monitoring, cardiovascular physiology, acute kidney injury, brain injury
About the Special lssue
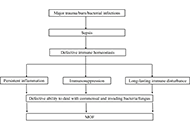
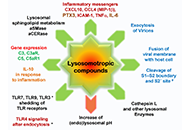
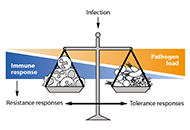
Sepsis syndrome was born many years ago to link infection and observed organ failures. It was refined along time according to the comprehensive involved mechanisms, the technological advances in supportive therapies & the input of translational biological research. Professionals are now facing new septic challenges, in patients with more complex underlying diseases or co-morbidity. This is unfortunately well illustrated in the present time by the pandemia related to SARS-Cov-2 infection. Focused on immunology, this proposed issue will cover the evolution of the recently modified definition of sepsis, the impact on epidemiology, particularly for severe sepsis and septic shock, which have the worse outcome. During the last decades, the concepts have evolved from clinical symptoms to the characterization and kinetics of inflammatory components, which will be updated in this issue. Since inflammation processes also relate to coagulation activation, immune stimulation, and cellular metabolism pathways changes, the complexity is ever increasing. Such aspects have to be further studied at the basic scientific level and clarified for the clinician in order to provide reliable tools for diagnosis, pronostic evaluation and treatment monitoring. The time-to-time changes observed in cellular and humoral immunity, with immune monitoring or characterization of septic patients are providing new knowledge in understanding the stratification of sepsis. As an example, an induced-acute immunodepression syndrome observed after initial stimulation brings new strategies for treating patients along the hospitalization. The actual pandemic development illustrates the role of the host response in the clinical presentation and outcome, facing almost a stable virus as an infective agent, for which only immune strategies could succeed to control the process, as acquired immunity after infection recovery or vaccination, in absence of efficient anti SARS-CoV-2.
The explosive research activity during the COVID-19 had improved mechanistic knowledge on inflammation related to the SARS-CoV-2, which will be discussed in the context of sepsis. Therapeutic targets to modulate acute inflammation related to the infection have been identified with ongoing trials on agents that modified the immune response, as corticosteroids or "boosters" of immunity. This approach will allow to adapt the treatment according to the immune status of each patient. Consequently, it becomes essential to develop innovativeimmune and inflammation biomarkers to be monitored as it will be discussed in this special issue. Such a precision medicine approach particularly focused on the immune and inflammatory components will be of great benefit for management of sepsis in the future.
We eagerly expect submitted contributions.
Let's enjoy the completion of such exciting and ambitious project.
Keywords: Sepsis syndrome, SARS-COV-2, immune response, inflammation
Published Articles