Cytokines and Skin Diseases
Guest Editor
Dr. Masutaka Furue E-Mail
Emeritus professor, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
Research Keywords: Atopic dermatitis, aryl hydrocarbon receptor, antioxidant, melanoma, skin disease, dioxin
About the Special lssue
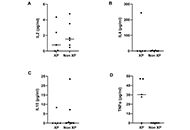
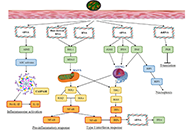
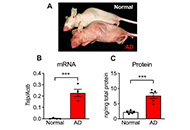
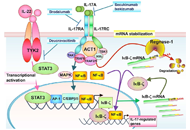
The skin is the outermost organ of body. To maintain the homeostatic stability and sustainability of interface between internal and external atmosphere, the skin is equipped with specialized surface barrier and immune surveillance systems. Like other organs, cytokines are indispensable tools for communication in these skin systems. Recent advancement in skin immunology reveals that dysregulation of skin-associated cytokine-tissue interaction causes various inflammatory skin diseases. One of the clear evidence is psoriasis vs IL-23/IL-17A and TNF-α axes, which is verified by an excellent therapeutic efficacy of biologics against IL-23, IL-17A and TNF-α in psoriasis. Such pathogenic implication is now accumulating in other skin diseases, for example, atopic dermatitis and IL-4/IL-13 axis, pruritus and IL-31 axis, and hidradenitis suppurativa and TNF-α axis. In this special issue, we would like to welcome original and review articles which deal with interaction between cytokines and skin diseases.
Keywords: Cytokines, skin immunology, skin diseases
Published Articles