Innovative Strategies to Target Triple-negative Breast Cancer
Guest Editors
Dr. Laura Cerchia E-Mail
Institute of Experimental Endocrinology and Oncology, Naples (Napoli), Italy
Research Keywords: RNA aptamer; SELEX technology; targeted therapy; targeted drug delivery; cancer theranostics; cancer cell biology and signaling; TNBC
Dr. Simona Camorani E-Mail
Institute of Experimental Endocrinology and Oncology, Naples (Napoli), Italy
Research Keywords: Triple-negative breast cancer; RNA aptamers; cell-SELEX technology; cancer cell biology and signaling; targeted therapy; targeted delivery system; chemotherapy resistance; cancer immunotherapy
About the Special lssue
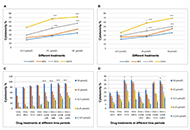
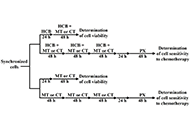
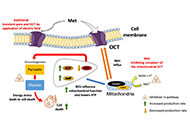
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents approximately 15-20% of all diagnosed breast cancers, has a distinctly aggressive nature, high risk for recurrence and poor prognosis. TNBC lacks expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), thus TNBC patients are not eligible for hormone or anti-HER2 therapies. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is the standard of care for many TNBC patients but about 30-50% develop resistance. While the overall mortality for breast cancer has recently declined, management of TNBC is still challenging because of its high biological/clinical heterogeneity and the limited targeted therapies that are available for restricted groups of patients. These include: 1) PARP inhibitors (Olaparib or Talazoparib) for BRCA-mutated patients; 2) anti-PD-L1 (Atezolizumab) or anti-PD-1 (Pembrolizumab) monoclonal antibodies, in combination with chemotherapy, for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic PD-L1-positive TNBC and 3) the antibody-drug conjugate (Sacituzumab govitecan), recently approved for patients with metastatic TNBC expressing anti-trophoblast cell-surface antigen.
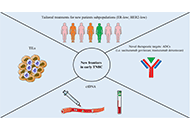
TNBC has an urgent therapeutic need. This Special Issue invites original research articles and timely reviews on all aspects regarding innovative strategies to target triple-negative breast cancer, highlighting problems, solutions and future directions in the development of new therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Molecular heterogeneity; tumor microenvironment; novel targets; active cancer targeting; mechanisms of drug resistance; immunotherapy and combination treatments; antibody-based therapeutics; aptamer-based targeted therapies
Published Articles