Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology
Guest Editors
About the Special lssue
Recently, precision oncology has seen raised interest, thanks to the huge advances in technologies and knowledge of both the human body and cancer disease.
Precision Oncology requires the molecular profiling of tumors to identify targetable alterations, and is rapidly developing and has entered the mainstream of clinical practice.
In this context, precision oncology represents an opportunity to provide far more tailored treatments, taking into consideration that particular attributes and characteristics are unique for patients.
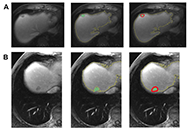
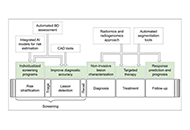
In the fields of imaging, that involve both radiology and radiation oncology, the corresponding concept is represented by the image-guided precision medicine, defined as the use of any form of medical imaging to plan, perform, and evaluate procedures and interventions.
The cross-sectional digital imaging modalities magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) are the most commonly used modalities of image-guided therapy. These procedures are also supported by ultrasound, angiography, surgical navigation equipment, tracking tools, and integration software.
At the same time, recent developments in radiotherapy with the incorporation of intensity-modulated radiotherapy, molecular imaging-guided radiotherapy, adaptive radiotherapy, and proton therapy have always included image-guided approaches in the clinical workflow.
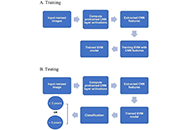
Last (but not least), artificial intelligence can also be included in this context, as a method that is reshaping the existing scenario of precision oncology, aiming at integrating the large amount of data derived from multi-omics analyses with current advances in high-performance computing and groundbreaking deep-learning strategies.
For this Special Issue, we welcome basic translational and clinical research papers, cancer biomarkers, professional opinions, and reviews in the broad field of Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology in the following categories: CNS; Head and neck; Breast; Hematology; Upper GI (oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver); Lung; Gynaecological (endometrium, cervix, vagina, vulva); Lower GI (colon, rectum, anus); Non-prostate urology; Prostate; Sarcoma; Skin cancer/malignant melanoma; Palliation; Pediatric tumours and Elderly oncology.
Keywords: Precision oncology; artificial intelligence; radiomics; radiotherapy; radiology; precision medicine
Published Articles