-
323 results in Exploration of MedicineSort byLatest
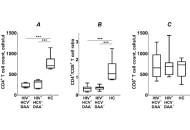 Assessment of CD4+ T cell recovery after direct-acting antiviral hepatitis C treatment in HIV/HCV coinfected immunological nonresponders to ARTOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study investigated the effects of successful hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) on CD4+ T cell recovery in HIV/HCV coinfected immunological non-respo [...] Read more.Violetta Vlasova ... Konstantin ShmagelPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001323
Assessment of CD4+ T cell recovery after direct-acting antiviral hepatitis C treatment in HIV/HCV coinfected immunological nonresponders to ARTOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study investigated the effects of successful hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) on CD4+ T cell recovery in HIV/HCV coinfected immunological non-respo [...] Read more.Violetta Vlasova ... Konstantin ShmagelPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001323
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001323
This article belongs to the special issue Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era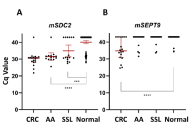 Analysis of SDC2 and SEPT9 promoters methylation in plasma cfDNA to detect colorectal and precancerous lesionsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Analysis of circulating free DNA (cfDNA) is now broadly used to diagnose, assess treatment response, and recurrence of various tumor types. Detection of aberrant cfDNA methylation in plasma [...] Read more.Viktoria Borobova ... Sergey KovalenkoPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001322
Analysis of SDC2 and SEPT9 promoters methylation in plasma cfDNA to detect colorectal and precancerous lesionsOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Analysis of circulating free DNA (cfDNA) is now broadly used to diagnose, assess treatment response, and recurrence of various tumor types. Detection of aberrant cfDNA methylation in plasma [...] Read more.Viktoria Borobova ... Sergey KovalenkoPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001322
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001322
This article belongs to the special issue Molecular Diagnostics in Oncology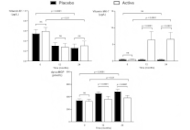 Adherence to dietary supplementation with menaquinone-7, a vitamin K2 analogueOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The VitaK-CAC (vitamin K-coronary artery calcification) trial is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with pre-existent CAC who were treated for two years with ei [...] Read more.Liv M Vossen ... Peter W de LeeuwPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001321
Adherence to dietary supplementation with menaquinone-7, a vitamin K2 analogueOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The VitaK-CAC (vitamin K-coronary artery calcification) trial is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with pre-existent CAC who were treated for two years with ei [...] Read more.Liv M Vossen ... Peter W de LeeuwPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001321
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001321 Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in breast cancer across Asian and European populations: insights into molecular pathways and biomarkersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy among women and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Early detection and prediction are crucial for prognosis and targeted therapy se [...] Read more.Prabhu Meganathan ... Shreshta ReddyPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001320
Comparative analysis of differentially expressed genes in breast cancer across Asian and European populations: insights into molecular pathways and biomarkersOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy among women and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Early detection and prediction are crucial for prognosis and targeted therapy se [...] Read more.Prabhu Meganathan ... Shreshta ReddyPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001320
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001320 The effect of acupressure on anxiety, fatigue, and blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study determined the effect of acupressure on anxiety, fatigue, and blood pressure in hemodialysis patients. Methods: This randomized controlled clinical trial study was co [...] Read more.Manizhe Nasirizade ... Hamidreza Bahrami-TaghanakiPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001319
The effect of acupressure on anxiety, fatigue, and blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study determined the effect of acupressure on anxiety, fatigue, and blood pressure in hemodialysis patients. Methods: This randomized controlled clinical trial study was co [...] Read more.Manizhe Nasirizade ... Hamidreza Bahrami-TaghanakiPublished: May 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001319
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001319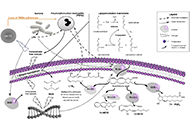 Artificial intelligence and complex natural products for cardiovascular infection prevention and oxidative damage mitigationOpen AccessReviewThe cardiovascular system remains vulnerable to a multitude of threats, including infections, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These factors contribute significantly to the development and progre [...] Read more.Jose M. Prieto-GarciaPublished: May 09, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001318
Artificial intelligence and complex natural products for cardiovascular infection prevention and oxidative damage mitigationOpen AccessReviewThe cardiovascular system remains vulnerable to a multitude of threats, including infections, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These factors contribute significantly to the development and progre [...] Read more.Jose M. Prieto-GarciaPublished: May 09, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001318
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001318
This article belongs to the special issue Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Medicine The prevalence of hypertension and diabetes, and associated factors among people receiving antiretroviral therapy in EthiopiaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to assess the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes and the factors associated with these conditions in adult patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It a [...] Read more.Yadessa Tegene Woldie ... Mark SpigtPublished: May 08, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001317
The prevalence of hypertension and diabetes, and associated factors among people receiving antiretroviral therapy in EthiopiaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to assess the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes and the factors associated with these conditions in adult patients living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It a [...] Read more.Yadessa Tegene Woldie ... Mark SpigtPublished: May 08, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001317
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001317
This article belongs to the special issue Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era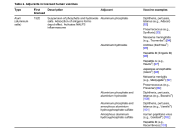 One Health adjuvant selection for vaccines against zoonotic infectionsOpen AccessReviewVaccines are typically designed either for human or veterinary use. Using One Health principles it would be more efficient to develop a single vaccine to cover all animal and human species at threat [...] Read more.Anna Antipov, Nikolai PetrovskyPublished: May 07, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001316
One Health adjuvant selection for vaccines against zoonotic infectionsOpen AccessReviewVaccines are typically designed either for human or veterinary use. Using One Health principles it would be more efficient to develop a single vaccine to cover all animal and human species at threat [...] Read more.Anna Antipov, Nikolai PetrovskyPublished: May 07, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001316
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001316
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Infectious Diseases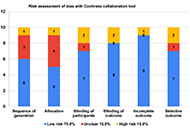 Innovative technologies for identifying oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic reviewOpen AccessSystematic ReviewThe cardiovascular system remains vulnerable to a multitude of threats, including infections, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These factors contribute significantly to the development and progre [...] Read more.Supraja Salwaji ... Giuseppe MinerviniPublished: May 05, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001315
Innovative technologies for identifying oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic reviewOpen AccessSystematic ReviewThe cardiovascular system remains vulnerable to a multitude of threats, including infections, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These factors contribute significantly to the development and progre [...] Read more.Supraja Salwaji ... Giuseppe MinerviniPublished: May 05, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001315
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001315
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Oral Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapeutics The viral oncogenesis of COVID-19 and its impact on cancer progression, long-term risks, treatment complexities, and research strategiesOpen AccessReviewThe interaction between cancer and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) poses significant challenges, particularly for immunocompromised individuals who are at heightened risk for acute infections an [...] Read more.Moawiah M Naffaa, Ola A Al-EwaidatPublished: April 28, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001314
The viral oncogenesis of COVID-19 and its impact on cancer progression, long-term risks, treatment complexities, and research strategiesOpen AccessReviewThe interaction between cancer and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) poses significant challenges, particularly for immunocompromised individuals who are at heightened risk for acute infections an [...] Read more.Moawiah M Naffaa, Ola A Al-EwaidatPublished: April 28, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001314
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001314 An unusual case of coexistence of Familial Mediterranean Fever with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren’s syndromeOpen AccessCase ReportWe report a rare case of a female patient with multiple rheumatological conditions. The patient initially presented with periodic, diffuse abdominal pain. This complaint was not fully investigated b [...] Read more.Fadi Altamimi ... Yasmeen AlabdallatPublished: April 27, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001313
An unusual case of coexistence of Familial Mediterranean Fever with rheumatoid arthritis and Sjögren’s syndromeOpen AccessCase ReportWe report a rare case of a female patient with multiple rheumatological conditions. The patient initially presented with periodic, diffuse abdominal pain. This complaint was not fully investigated b [...] Read more.Fadi Altamimi ... Yasmeen AlabdallatPublished: April 27, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001313
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001313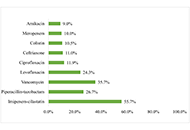 Evaluation of empiric therapy appropriateness, resistance patterns, and mortality in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in JordanOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic thera [...] Read more.Savana Sobh ... Rana K. Abu-FarhaPublished: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001312
Evaluation of empiric therapy appropriateness, resistance patterns, and mortality in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in JordanOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic thera [...] Read more.Savana Sobh ... Rana K. Abu-FarhaPublished: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001312
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001312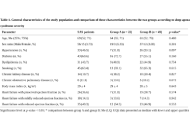 Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters predict severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with heart failureOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome. Meth [...] Read more.Saoussen Antit ... Lilia ZakhamaPublished: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001311
Right ventricular echocardiographic parameters predict severe sleep apnea syndrome in patients with heart failureOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The study aimed to determine which right ventricle echocardiography parameters were associated with severe sleep apnea syndrome in heart failure patients with sleep apnea syndrome. Meth [...] Read more.Saoussen Antit ... Lilia ZakhamaPublished: April 23, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001311
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001311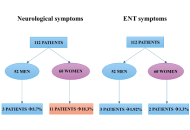 Long-term neurological and otolaryngological sequelae of COVID-19: a retrospective studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological [...] Read more.Wael Abu Ruqa ... Antonio MinniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001310
Long-term neurological and otolaryngological sequelae of COVID-19: a retrospective studyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological [...] Read more.Wael Abu Ruqa ... Antonio MinniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001310
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001310
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Infectious Diseases Cytocompatibility and bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric acid nanogel with insights into zebrafish toxicologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied usi [...] Read more.Ameena Mustafa ... Giuseppe MinerviniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001309
Cytocompatibility and bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric acid nanogel with insights into zebrafish toxicologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The present study explored the bone regeneration potential of chitosan-thiocolchicoside-lauric (CTL) nanogel using MG-63 cell lines. The cytocompatibility of CTL nanogel was also studied usi [...] Read more.Ameena Mustafa ... Giuseppe MinerviniPublished: April 21, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001309
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001309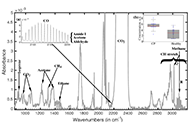 Breath analysis using FTIR spectroscopyOpen AccessReviewBreath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created int [...] Read more.Andrei A. Bunaciu, Hassan Y. Aboul-EneinPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001308
Breath analysis using FTIR spectroscopyOpen AccessReviewBreath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created int [...] Read more.Andrei A. Bunaciu, Hassan Y. Aboul-EneinPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001308
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001308 Joint mobilization strategies for chronic ankle instability: comparing active and passive approaches in a randomized controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We [...] Read more.Hyunjoong Kim ... Mingyun KoPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001307
Joint mobilization strategies for chronic ankle instability: comparing active and passive approaches in a randomized controlled trialOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: This study aimed to evaluate the differential effects of active joint mobilization (AJM) versus traditional passive joint mobilization (PJM) in individuals with chronic ankle instability. We [...] Read more.Hyunjoong Kim ... Mingyun KoPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001307
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001307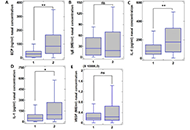 Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretion in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis with or without polyposis and hypertrophic sinonasal mucosaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been cl [...] Read more.Svetlana Viktorovna Krasilnikova ... Nailya Iskhakovna KubyshevaPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001306
Inflammatory mediators in nasal secretion in patients with bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis with or without polyposis and hypertrophic sinonasal mucosaOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: The pathogenetic mechanisms and predictors of the development of polyposis and hypertrophy of the sinonasal mucosa (SM) in patients with chronic allergic airway inflammation have not been cl [...] Read more.Svetlana Viktorovna Krasilnikova ... Nailya Iskhakovna KubyshevaPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001306
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001306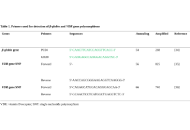 Vitamin D receptor genetic variations in association to the susceptibility to prostate cancer: a case-control study in a Moroccan populationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: It has been shown that the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene and its biological functions can be affected by genetic alterations in the VDR gene. These genetic alterations particularly (rs154441 [...] Read more.Kawtar Nabil ... Moulay Mustapha EnnajiPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001305
Vitamin D receptor genetic variations in association to the susceptibility to prostate cancer: a case-control study in a Moroccan populationOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: It has been shown that the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene and its biological functions can be affected by genetic alterations in the VDR gene. These genetic alterations particularly (rs154441 [...] Read more.Kawtar Nabil ... Moulay Mustapha EnnajiPublished: April 17, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001305
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001305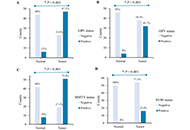 Prevalence of HPV, EBV, MMTV and SV40 co-infection in women with invasive breast cancer: as a potential new viral etiologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Breast cancer (BC) is the leading cause of female cancer-related death worldwide. The high incidence of BC has sparked interest in the viral agents role in its development. Identifying co-in [...] Read more.Kaoutar Anouar Tadlaoui ... Moulay Mustapha EnnajiPublished: April 16, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001304
Prevalence of HPV, EBV, MMTV and SV40 co-infection in women with invasive breast cancer: as a potential new viral etiologyOpen AccessOriginal ArticleAim: Breast cancer (BC) is the leading cause of female cancer-related death worldwide. The high incidence of BC has sparked interest in the viral agents role in its development. Identifying co-in [...] Read more.Kaoutar Anouar Tadlaoui ... Moulay Mustapha EnnajiPublished: April 16, 2025 Explor Med. 2025;6:1001304
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001304
This article belongs to the special issue Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Advances -