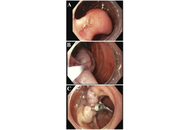





Gangliocytic paraganglioma (GP) is a rare tumor that involves the gastrointestinal system and often occurs in the second portion of the duodenum. This is the case of a 73-year-old female presenting for an unintentional 10-pound weight loss over the previous year and a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showing a mass in the second portion of the duodenum with omental nodules. She had no other symptoms. An upper endoscopy revealed a pedunculated 5 cm polypoid mass that was endoscopically resected and found to be a GP on pathology. GP is the third most frequent histopathologic type of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NET) after gastrinomas and somatostatinomas. Clinical presentations vary from asymptomatic patients to those having gastrointestinal bleeding, melena, anemia, and abdominal pain. GP presents as a single solid well-demarcated mass that is polypoid, pedunculated, or sessile. Histological features of GP show three cell types: spindle cells, ganglion or ganglion-like cells, and epithelioid cells. Biopsy specimens might not contain all 3 characteristic cell types; thus, definitive diagnosis could be challenging. Periampullary GP should be considered as a tumor with malignant potential. The optimal treatment has not been clarified, but endoscopic resection remains the most common treatment of choice. En bloc resection with negative margins for a pedunculated lesion is possible. This is a rare case of GP in a female patient presenting with weight loss only. It highlights the importance of considering GP in the differential diagnosis for duodenal masses, while keeping a broad differential due to the low rates of diagnostic biopsies. More research is needed to establish standardized management protocols for GP and improve patient care.
Gangliocytic paraganglioma (GP) is a rare tumor that involves the gastrointestinal system and often occurs in the second portion of the duodenum. This is the case of a 73-year-old female presenting for an unintentional 10-pound weight loss over the previous year and a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showing a mass in the second portion of the duodenum with omental nodules. She had no other symptoms. An upper endoscopy revealed a pedunculated 5 cm polypoid mass that was endoscopically resected and found to be a GP on pathology. GP is the third most frequent histopathologic type of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (NET) after gastrinomas and somatostatinomas. Clinical presentations vary from asymptomatic patients to those having gastrointestinal bleeding, melena, anemia, and abdominal pain. GP presents as a single solid well-demarcated mass that is polypoid, pedunculated, or sessile. Histological features of GP show three cell types: spindle cells, ganglion or ganglion-like cells, and epithelioid cells. Biopsy specimens might not contain all 3 characteristic cell types; thus, definitive diagnosis could be challenging. Periampullary GP should be considered as a tumor with malignant potential. The optimal treatment has not been clarified, but endoscopic resection remains the most common treatment of choice. En bloc resection with negative margins for a pedunculated lesion is possible. This is a rare case of GP in a female patient presenting with weight loss only. It highlights the importance of considering GP in the differential diagnosis for duodenal masses, while keeping a broad differential due to the low rates of diagnostic biopsies. More research is needed to establish standardized management protocols for GP and improve patient care.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2025.1005113

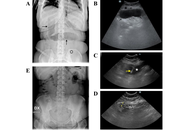
In the context of the various management options available for obesity, intragastric balloons (IGBs) represent a solution for patients at high surgical risk. Swallowable IGBs are devices that can be ingested orally and then inflated within the stomach to aid in weight loss. Although generally well tolerated, these devices may migrate and cause gastrointestinal obstructive symptoms. Here we report on two cases where these obstructive complications of swallowable IGBs were promptly and non-invasively diagnosed with ultrasonography (US), which also permitted conservative management via US-guided percutaneous aspiration of the impacted balloons. These cases demonstrate that the US may provide a rapid and effective tool for managing IGBs migration, potentially reducing the need for surgical intervention.
In the context of the various management options available for obesity, intragastric balloons (IGBs) represent a solution for patients at high surgical risk. Swallowable IGBs are devices that can be ingested orally and then inflated within the stomach to aid in weight loss. Although generally well tolerated, these devices may migrate and cause gastrointestinal obstructive symptoms. Here we report on two cases where these obstructive complications of swallowable IGBs were promptly and non-invasively diagnosed with ultrasonography (US), which also permitted conservative management via US-guided percutaneous aspiration of the impacted balloons. These cases demonstrate that the US may provide a rapid and effective tool for managing IGBs migration, potentially reducing the need for surgical intervention.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2026.1005114
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification

Background:
Urine screening is a critical diagnostic tool in healthcare that supports the detection of a wide range of health conditions, including kidney diseases, metabolic disorders, and infections. Traditionally, urine tests are performed in clinical settings with results that often take time to be delivered. Such delays can hinder timely diagnosis, treatment initiation, and effective disease management. Recent advancements in digital health technologies, particularly the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, create opportunities for real-time data acquisition, integration, and analysis within routine urine screening. This systematic review synthesizes the current landscape of IoT-enabled urine screening technologies and evaluates their clinical, engineering, and computational foundations. The review also examines their integration with digital health architectures, edge computing systems, and tech driven personalized care.
Methods:
A structured literature search was conducted across PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, and Google Scholar for studies published between 2000 and 2025. Predefined search terms related to urinalysis, IoT, digital health, and microfluidics were applied. Sixty-five studies met the inclusion criteria. Data extraction focused on sensor technologies, digital health platforms, and reported case studies that demonstrated successful system deployment across diverse healthcare settings.
Results:
IoT-based urine screening technologies support real-time monitoring of biomarkers such as glucose, protein, and pH, which are essential for diagnosing conditions including diabetes, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Emerging devices utilize optical, and acoustofluidic modalities, while BLE, Wi-Fi, and LPWAN serve as the primary connectivity standards.
Discussion:
IoT-driven digital transformation demonstrates strong potential to enhance the accessibility, efficiency, and diagnostic accuracy of urine screening. The convergence of biosensing, microfluidics and HDTs enables scalable, continuous, and personalized urine monitoring solutions. Despite these advancements, challenges related to data privacy, infrastructure readiness, and regulatory compliance remain significant barriers.
Background:
Urine screening is a critical diagnostic tool in healthcare that supports the detection of a wide range of health conditions, including kidney diseases, metabolic disorders, and infections. Traditionally, urine tests are performed in clinical settings with results that often take time to be delivered. Such delays can hinder timely diagnosis, treatment initiation, and effective disease management. Recent advancements in digital health technologies, particularly the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, create opportunities for real-time data acquisition, integration, and analysis within routine urine screening. This systematic review synthesizes the current landscape of IoT-enabled urine screening technologies and evaluates their clinical, engineering, and computational foundations. The review also examines their integration with digital health architectures, edge computing systems, and tech driven personalized care.
Methods:
A structured literature search was conducted across PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, and Google Scholar for studies published between 2000 and 2025. Predefined search terms related to urinalysis, IoT, digital health, and microfluidics were applied. Sixty-five studies met the inclusion criteria. Data extraction focused on sensor technologies, digital health platforms, and reported case studies that demonstrated successful system deployment across diverse healthcare settings.
Results:
IoT-based urine screening technologies support real-time monitoring of biomarkers such as glucose, protein, and pH, which are essential for diagnosing conditions including diabetes, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Emerging devices utilize optical, and acoustofluidic modalities, while BLE, Wi-Fi, and LPWAN serve as the primary connectivity standards.
Discussion:
IoT-driven digital transformation demonstrates strong potential to enhance the accessibility, efficiency, and diagnostic accuracy of urine screening. The convergence of biosensing, microfluidics and HDTs enables scalable, continuous, and personalized urine monitoring solutions. Despite these advancements, challenges related to data privacy, infrastructure readiness, and regulatory compliance remain significant barriers.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2026.101188

Background:
Climate change-driven wildfires are increasing in frequency and intensity. The 2025 Manitoba wildfire season, which burned over one million hectares, exposed rural and Indigenous lung cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy to unprecedented levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and triggered widespread evacuations, severely threatening treatment continuity and outcomes. This systematic review examines the evidence (2010–2023) on the impact of wildfire smoke exposure on radiation oncology outcomes in rural and Indigenous lung cancer patients, with particular attention to its applicability to the Manitoba context.
Methods:
PRISMA-guided systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (1 January 2010–31 July 2025). Studies were included if they addressed wildfire smoke or PM2.5 exposure, lung cancer, radiation therapy outcomes, and rural or Indigenous populations. Quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for observational studies and CASP checklists for reviews/qualitative studies. Findings were narratively synthesized.
Results:
Fifteen moderate-to-high-quality studies were included (four cohort, two qualitative, five reviews, two meta-analysis, one scoping review, one observational). Wildfire-derived PM2.5 exacerbates radiation-induced lung toxicities (e.g., pneumonitis reported in up to 30% of thoracic radiotherapy patients) via oxidative stress and inflammation. High PM2.5 exposure is linked to increased mortality/complications (adjusted OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.05–1.26) and respiratory hospitalizations (RR 1.12, 95% CI 1.07–1.18). Treatment interruptions exceeding 7 days—common during wildfire evacuations—reduce local control by ∼10% and elevate mortality risk (HR 1.14, 95% CI 1.03–1.26). Rural and Indigenous patients experience disproportionate barriers, including limited healthcare access, long travel distances, socioeconomic constraints, and culturally insensitive services.
Discussion:
Wildfire smoke significantly worsens radiation therapy outcomes in rural lung cancer patients through synergistic pulmonary toxicity and treatment disruptions. No Manitoba-specific studies were identified, highlighting a critical evidence gap. Urgent interventions are needed: mobile radiation units, subsidized high-efficiency air filtration, culturally safe care models, telehealth expansion, and province-specific research to address climate-related health inequities in radiation oncology.
Background:
Climate change-driven wildfires are increasing in frequency and intensity. The 2025 Manitoba wildfire season, which burned over one million hectares, exposed rural and Indigenous lung cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy to unprecedented levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and triggered widespread evacuations, severely threatening treatment continuity and outcomes. This systematic review examines the evidence (2010–2023) on the impact of wildfire smoke exposure on radiation oncology outcomes in rural and Indigenous lung cancer patients, with particular attention to its applicability to the Manitoba context.
Methods:
PRISMA-guided systematic review of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (1 January 2010–31 July 2025). Studies were included if they addressed wildfire smoke or PM2.5 exposure, lung cancer, radiation therapy outcomes, and rural or Indigenous populations. Quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for observational studies and CASP checklists for reviews/qualitative studies. Findings were narratively synthesized.
Results:
Fifteen moderate-to-high-quality studies were included (four cohort, two qualitative, five reviews, two meta-analysis, one scoping review, one observational). Wildfire-derived PM2.5 exacerbates radiation-induced lung toxicities (e.g., pneumonitis reported in up to 30% of thoracic radiotherapy patients) via oxidative stress and inflammation. High PM2.5 exposure is linked to increased mortality/complications (adjusted OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.05–1.26) and respiratory hospitalizations (RR 1.12, 95% CI 1.07–1.18). Treatment interruptions exceeding 7 days—common during wildfire evacuations—reduce local control by ∼10% and elevate mortality risk (HR 1.14, 95% CI 1.03–1.26). Rural and Indigenous patients experience disproportionate barriers, including limited healthcare access, long travel distances, socioeconomic constraints, and culturally insensitive services.
Discussion:
Wildfire smoke significantly worsens radiation therapy outcomes in rural lung cancer patients through synergistic pulmonary toxicity and treatment disruptions. No Manitoba-specific studies were identified, highlighting a critical evidence gap. Urgent interventions are needed: mobile radiation units, subsidized high-efficiency air filtration, culturally safe care models, telehealth expansion, and province-specific research to address climate-related health inequities in radiation oncology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001386

Aim:
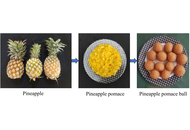
Bangladesh produces a huge number of pineapples in the hilly areas with its medium-high land. The country has several pineapple jam and jelly processing industries. But after processing into jelly, the pomace is dumped here and there, which creates environmental pollution. Thus, the objective of the study was to utilize the pineapple pomace for processing into pomace balls as laddus with its better shelf life and quality studies.
Methods:
The pineapple pomaces were treated with different proportions of potassium metabisulfite (KMS) and potassium sorbate (KS). Then the prepared laddus were packed into polyethylene terephthalate (PET) boxes and kept at room temperature for further studies.
Results:
The laddus treated with preservatives had higher total soluble solids, energy value, crude fiber, crude protein, vitamin C, β-carotene, and total sugars. Both laddus showed a trend of decreasing water activity. After 60 days of storage, tests for microbes and mycotoxins showed that the treated laddus were free of both, while the control sample showed some microbial activity. The developed pomace balls (T2, T3, and T4) also had acceptable levels of preservatives, KMS, and KS, both alone and in combination (KMS + KS). The levels were 71.28 ppm, 78.01 ppm, and 110.31 ppm, respectively. T4 laddus were the best of the formulations when it was evaluated for its color, texture, and low water activity. The cost-benefit ratio was evaluated considering the inputs required and the benefits of the product.
Conclusions:
The preservative-treated laddus could be stored for more than 60 days, whereas the control laddus could only be stored for 30 days. The cost-benefit ratio for the laddus was 1:1.33. The agro-food processing industries and small-scale pineapple processors could apply this technology for producing and marketing the pomace ball with a shelf life of up to 60 days.
Aim:
Bangladesh produces a huge number of pineapples in the hilly areas with its medium-high land. The country has several pineapple jam and jelly processing industries. But after processing into jelly, the pomace is dumped here and there, which creates environmental pollution. Thus, the objective of the study was to utilize the pineapple pomace for processing into pomace balls as laddus with its better shelf life and quality studies.
Methods:
The pineapple pomaces were treated with different proportions of potassium metabisulfite (KMS) and potassium sorbate (KS). Then the prepared laddus were packed into polyethylene terephthalate (PET) boxes and kept at room temperature for further studies.
Results:
The laddus treated with preservatives had higher total soluble solids, energy value, crude fiber, crude protein, vitamin C, β-carotene, and total sugars. Both laddus showed a trend of decreasing water activity. After 60 days of storage, tests for microbes and mycotoxins showed that the treated laddus were free of both, while the control sample showed some microbial activity. The developed pomace balls (T2, T3, and T4) also had acceptable levels of preservatives, KMS, and KS, both alone and in combination (KMS + KS). The levels were 71.28 ppm, 78.01 ppm, and 110.31 ppm, respectively. T4 laddus were the best of the formulations when it was evaluated for its color, texture, and low water activity. The cost-benefit ratio was evaluated considering the inputs required and the benefits of the product.
Conclusions:
The preservative-treated laddus could be stored for more than 60 days, whereas the control laddus could only be stored for 30 days. The cost-benefit ratio for the laddus was 1:1.33. The agro-food processing industries and small-scale pineapple processors could apply this technology for producing and marketing the pomace ball with a shelf life of up to 60 days.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010119

Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are increasingly used in drafting scientific papers. While they can improve clarity and efficiency, a troubling issue has emerged: the inclusion of fabricated references—nonexistent citations that can mislead, especially in biomedical research where evidence integrity is crucial. Studies indicate that 69% of references in ChatGPT’s medical queries are false, and only 7% of AI-generated medical articles contain accurate references. These fake citations often mimic real authors and journals, making detection difficult. Such inaccuracies can compromise research integrity, skew citation metrics, and reduce trust in scientific literature. To address this, journals are adopting policies requiring disclosure of AI use and human verification of references. Nonetheless, detecting AI-related misinformation remains challenging, and many experts believe the problem is bigger than currently known. Going forward, authors should avoid relying solely on LLMs, and reviewers must scrutinize references carefully. The scientific community needs to balance AI’s usefulness with rigorous oversight, ensuring that the pursuit of efficiency doesn't undermine credibility. Ultimately, safeguarding research from AI-generated misinformation will require combined efforts of transparency, vigilance, and adherence to ethical principles, preserving the integrity of biomedical science.
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are increasingly used in drafting scientific papers. While they can improve clarity and efficiency, a troubling issue has emerged: the inclusion of fabricated references—nonexistent citations that can mislead, especially in biomedical research where evidence integrity is crucial. Studies indicate that 69% of references in ChatGPT’s medical queries are false, and only 7% of AI-generated medical articles contain accurate references. These fake citations often mimic real authors and journals, making detection difficult. Such inaccuracies can compromise research integrity, skew citation metrics, and reduce trust in scientific literature. To address this, journals are adopting policies requiring disclosure of AI use and human verification of references. Nonetheless, detecting AI-related misinformation remains challenging, and many experts believe the problem is bigger than currently known. Going forward, authors should avoid relying solely on LLMs, and reviewers must scrutinize references carefully. The scientific community needs to balance AI’s usefulness with rigorous oversight, ensuring that the pursuit of efficiency doesn't undermine credibility. Ultimately, safeguarding research from AI-generated misinformation will require combined efforts of transparency, vigilance, and adherence to ethical principles, preserving the integrity of biomedical science.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001385

Aim:
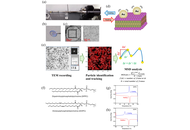
This study aims to develop and validate a transmission electron microscopy (TEM)–based approach for probing nanoscale lipid membrane dynamics by tracking the motion of gold nanoparticles dispersed on membrane surfaces.
Methods:
Lipid thin films composed of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) or dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (DOPC) were prepared over 2 μm holes in Quantifoil grids, and 5 nm gold nanocolloids were introduced as tracer particles. Sequential TEM imaging was performed during controlled heating and cooling cycles, and nanoparticle trajectories were analyzed to obtain mean squared displacement (MSD) curves. These measurements enabled quantification of thermally driven membrane dynamics. The temperature dependent behavior was further compared with differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of dehydrated lipid samples.
Results:
DPPC exhibited a pronounced MSD peak near 52.5 °C during the first heating cycle, corresponding to its main phase transition, whereas DOPC showed gradual and continuous mobility changes consistent with its intrinsically disordered acyl chains. Differences between electron beam molecular dynamics (EBMD) and DSC transition temperatures likely arose from dehydration and thin film geometry. Across repeated thermal cycles, DPPC membranes displayed cycle dependent changes in MSD profiles, suggesting annealing induced homogenization and potential beam induced structural alterations.
Conclusions:
EBMD provides real space, time resolved visualization of nanoscale membrane fluctuations and complements ensemble techniques such as DSC, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The TEM based particle tracking approach reliably distinguishes ordered versus disordered lipid systems and offers a versatile platform for investigating soft biological membranes, including systems containing proteins or heterogeneous lipid compositions.
Aim:
This study aims to develop and validate a transmission electron microscopy (TEM)–based approach for probing nanoscale lipid membrane dynamics by tracking the motion of gold nanoparticles dispersed on membrane surfaces.
Methods:
Lipid thin films composed of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) or dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (DOPC) were prepared over 2 μm holes in Quantifoil grids, and 5 nm gold nanocolloids were introduced as tracer particles. Sequential TEM imaging was performed during controlled heating and cooling cycles, and nanoparticle trajectories were analyzed to obtain mean squared displacement (MSD) curves. These measurements enabled quantification of thermally driven membrane dynamics. The temperature dependent behavior was further compared with differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of dehydrated lipid samples.
Results:
DPPC exhibited a pronounced MSD peak near 52.5 °C during the first heating cycle, corresponding to its main phase transition, whereas DOPC showed gradual and continuous mobility changes consistent with its intrinsically disordered acyl chains. Differences between electron beam molecular dynamics (EBMD) and DSC transition temperatures likely arose from dehydration and thin film geometry. Across repeated thermal cycles, DPPC membranes displayed cycle dependent changes in MSD profiles, suggesting annealing induced homogenization and potential beam induced structural alterations.
Conclusions:
EBMD provides real space, time resolved visualization of nanoscale membrane fluctuations and complements ensemble techniques such as DSC, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The TEM based particle tracking approach reliably distinguishes ordered versus disordered lipid systems and offers a versatile platform for investigating soft biological membranes, including systems containing proteins or heterogeneous lipid compositions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2026.101361

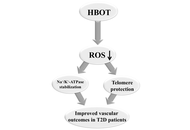
Diabetes mellitus is one of the biggest public health issues of modern society, with a constant increase in prevalence. It is a complex metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and impaired insulin signaling, leading to redox imbalance and, consequently, blood vessel dysfunction. One of the key factors in the regulation of vascular tone and contractility is the sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase (Na+/K+-ATPase), whose reduced expression and altered activity contribute to the development of vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes (T2D). Impaired redox balance and increased production of reactive oxygen species, which directly affect Na+/K+-ATPase activity, also affect the telomere-telomerase system, leading to telomere shortening, DNA damage, and cell apoptosis. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to treat ischemic lesions and vascular complications of diabetes, but the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects on Na+/K+-ATPase and telomere length in T2D patients remain incompletely elucidated.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the biggest public health issues of modern society, with a constant increase in prevalence. It is a complex metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and impaired insulin signaling, leading to redox imbalance and, consequently, blood vessel dysfunction. One of the key factors in the regulation of vascular tone and contractility is the sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase (Na+/K+-ATPase), whose reduced expression and altered activity contribute to the development of vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes (T2D). Impaired redox balance and increased production of reactive oxygen species, which directly affect Na+/K+-ATPase activity, also affect the telomere-telomerase system, leading to telomere shortening, DNA damage, and cell apoptosis. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to treat ischemic lesions and vascular complications of diabetes, but the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects on Na+/K+-ATPase and telomere length in T2D patients remain incompletely elucidated.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001384

Aim:
To describe the first major epidemic thunderstorm asthma (ETSA) event detected in France in June 2023.
Methods:
Data on local meteorology, visits to the emergency room (ER) for asthma and hospitalization after a visit, aerobiological composition of the atmosphere (pollens and spores), phenological information on the flowering of grasses, and regional air pollution were collected, aggregated, and analyzed.
Results:
The ETSA was centered on the Paris region. An excess of 1,900 emergency visits for asthma was recorded over the period 10, 11, and 12 June. The people most affected were men aged 14 to 44. The hospitalization rate following a visit to the ER for asthma increased to 13%. ER visits for asthma began at around 6 pm on 10 June, just after an intense gust (15 m/s) triggering a PM10 resuspension episode, and peaked at around 10 pm on 11 June. Concentrations of mold spores (Cladosporium and Ascosporium) rose sharply during the night of 10–11 June, at the same time as the intake peak. The ETSA occurred during the grass and Urticaceae pollen season, with pollen concentrations lower (< 100 pollen grains/m3) compared to the days preceding the event (> 200 pollen grains/m3). A fraction of the pollen was observed without cytoplasm, but there was no apparent link with the ETSA. Phenological observations in the Paris pollinarium showed that the ETSA coincided with the start of the Lolium perenne (ryegrass) pollen season.
Conclusions:
Although the data collected did not allow the identification of a single cause for the occurrence of the ETSA, they pointed to multifactorial causes such as the occurrence of an ozone pollution episode, strong winds before the storm, an episode of resuspension of PM10 particles, the presence of broken pollen, and the significant increase in mold spores just after the stormy episode.
Aim:
To describe the first major epidemic thunderstorm asthma (ETSA) event detected in France in June 2023.
Methods:
Data on local meteorology, visits to the emergency room (ER) for asthma and hospitalization after a visit, aerobiological composition of the atmosphere (pollens and spores), phenological information on the flowering of grasses, and regional air pollution were collected, aggregated, and analyzed.
Results:
The ETSA was centered on the Paris region. An excess of 1,900 emergency visits for asthma was recorded over the period 10, 11, and 12 June. The people most affected were men aged 14 to 44. The hospitalization rate following a visit to the ER for asthma increased to 13%. ER visits for asthma began at around 6 pm on 10 June, just after an intense gust (15 m/s) triggering a PM10 resuspension episode, and peaked at around 10 pm on 11 June. Concentrations of mold spores (Cladosporium and Ascosporium) rose sharply during the night of 10–11 June, at the same time as the intake peak. The ETSA occurred during the grass and Urticaceae pollen season, with pollen concentrations lower (< 100 pollen grains/m3) compared to the days preceding the event (> 200 pollen grains/m3). A fraction of the pollen was observed without cytoplasm, but there was no apparent link with the ETSA. Phenological observations in the Paris pollinarium showed that the ETSA coincided with the start of the Lolium perenne (ryegrass) pollen season.
Conclusions:
Although the data collected did not allow the identification of a single cause for the occurrence of the ETSA, they pointed to multifactorial causes such as the occurrence of an ozone pollution episode, strong winds before the storm, an episode of resuspension of PM10 particles, the presence of broken pollen, and the significant increase in mold spores just after the stormy episode.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2026.1009114
This article belongs to the special issue Climate Change, Allergy, and Immunotherapy

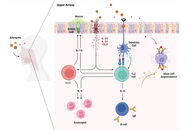
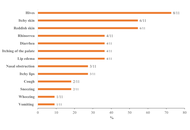
This review describes the eosinophil journey through the various physiological and pathophysiological phases, from production, maturation, and activation by chemokines and cytokines [especially eotaxin, interleukin (IL)-5, IL-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)], to interaction with the innate and adaptive immune system and tissue homing. Excessive production and activation of eosinophils lead to the release of granule proteins, such as major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, eosinophil peroxidase, and others, resulting in inflammation, cell cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. The pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnostic processes, and the latest therapeutic approaches to the resulting diseases—which affect the upper and lower airways, gastrointestinal tract, skin, myocardium, and may occur systemically—are discussed.
This review describes the eosinophil journey through the various physiological and pathophysiological phases, from production, maturation, and activation by chemokines and cytokines [especially eotaxin, interleukin (IL)-5, IL-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)], to interaction with the innate and adaptive immune system and tissue homing. Excessive production and activation of eosinophils lead to the release of granule proteins, such as major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, eosinophil peroxidase, and others, resulting in inflammation, cell cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. The pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnostic processes, and the latest therapeutic approaches to the resulting diseases—which affect the upper and lower airways, gastrointestinal tract, skin, myocardium, and may occur systemically—are discussed.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2026.1009111

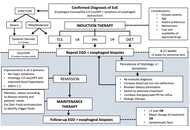
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the esophagus that has emerged as a major cause of esophageal dysfunction in all ages. Over the past two decades, its frequency has increased worldwide, reflecting both heightened recognition and a rise in occurrence. EoE predominantly affects males and frequently coexists with atopic conditions, underscoring its relationship with allergy. The pathogenesis involves genetic susceptibility, epithelial barrier dysfunction, and dysregulated type 2 immune responses. Variants in genes related to epithelial integrity and immune signaling, such as TSLP and CAPN14, predispose susceptible individuals to aberrant immune responses to food antigens, leading to eosinophil recruitment, mast cell activation, and chronic inflammation, which in turn promotes tissue remodeling and progression toward fibrostenotic disease. Clinical presentation varies with age. Infants and younger children often exhibit feeding difficulties, vomiting, and abdominal pain, whereas older children and adolescents usually present with dysphagia and food impaction. Diagnosis requires integration of clinical symptoms with histologic confirmation of esophageal eosinophilia (≥ 15 eosinophils per high-power field) and exclusion of alternative causes. Management of pediatric EoE aims to achieve and maintain clinical and histologic remission while preventing long-term complications and preserving quality of life. First-line therapeutic options include proton pump inhibitors, swallowed topical corticosteroids, and dietary elimination strategies. Biologic therapy has expanded treatment options for severe or refractory disease. Because symptom improvement alone does not reliably reflect disease control, objective reassessment with endoscopy and biopsies is recommended after treatment and during follow-up. Long-term outcomes of EoE are strongly influenced by diagnostic timing and adequacy of treatment. Early diagnosis, sustained anti-inflammatory therapy, and transition from pediatric to adult care are critical components of an appropriate management. Future directions include the development of precision medicine, identification of biomarkers to guide therapy selection, non-invasive tools for disease monitoring, and strategies aimed at disease modification.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the esophagus that has emerged as a major cause of esophageal dysfunction in all ages. Over the past two decades, its frequency has increased worldwide, reflecting both heightened recognition and a rise in occurrence. EoE predominantly affects males and frequently coexists with atopic conditions, underscoring its relationship with allergy. The pathogenesis involves genetic susceptibility, epithelial barrier dysfunction, and dysregulated type 2 immune responses. Variants in genes related to epithelial integrity and immune signaling, such as TSLP and CAPN14, predispose susceptible individuals to aberrant immune responses to food antigens, leading to eosinophil recruitment, mast cell activation, and chronic inflammation, which in turn promotes tissue remodeling and progression toward fibrostenotic disease. Clinical presentation varies with age. Infants and younger children often exhibit feeding difficulties, vomiting, and abdominal pain, whereas older children and adolescents usually present with dysphagia and food impaction. Diagnosis requires integration of clinical symptoms with histologic confirmation of esophageal eosinophilia (≥ 15 eosinophils per high-power field) and exclusion of alternative causes. Management of pediatric EoE aims to achieve and maintain clinical and histologic remission while preventing long-term complications and preserving quality of life. First-line therapeutic options include proton pump inhibitors, swallowed topical corticosteroids, and dietary elimination strategies. Biologic therapy has expanded treatment options for severe or refractory disease. Because symptom improvement alone does not reliably reflect disease control, objective reassessment with endoscopy and biopsies is recommended after treatment and during follow-up. Long-term outcomes of EoE are strongly influenced by diagnostic timing and adequacy of treatment. Early diagnosis, sustained anti-inflammatory therapy, and transition from pediatric to adult care are critical components of an appropriate management. Future directions include the development of precision medicine, identification of biomarkers to guide therapy selection, non-invasive tools for disease monitoring, and strategies aimed at disease modification.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2026.1009112
This article belongs to the special issue Beyond Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies

Scombroid syndrome is a frequent cause of fish poisoning and typically presents with mild, self-limiting symptoms. Severe anaphylaxis-like reactions are uncommon, and a biphasic clinical course has not previously been reported. We describe the case of a 19-year-old woman who developed flushing, headache, generalized urticaria, facial edema, dyspnea, and hypotension approximately 30 minutes after ingesting raw amberjack tartare. Emergency treatment with adrenaline, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and intravenous fluids led to initial clinical improvement; however, three hours later, she experienced a recurrence of cutaneous, respiratory, and gastrointestinal symptoms, consistent with a biphasic reaction. The patient subsequently developed chest pain associated with transient electrocardiographic changes and mild troponin elevation, prompting further evaluation for suspected Kounis syndrome. Allergy assessment, including specific IgE testing and skin-prick testing with fresh fish, was negative, supporting a toxic rather than IgE-mediated mechanism. This case expands the clinical spectrum of scombroid syndrome by documenting a biphasic anaphylaxis-like presentation and underscores the importance of considering histamine fish poisoning in the differential diagnosis of severe food-related reactions. Careful evaluation is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and unnecessary long-term dietary restrictions.
Scombroid syndrome is a frequent cause of fish poisoning and typically presents with mild, self-limiting symptoms. Severe anaphylaxis-like reactions are uncommon, and a biphasic clinical course has not previously been reported. We describe the case of a 19-year-old woman who developed flushing, headache, generalized urticaria, facial edema, dyspnea, and hypotension approximately 30 minutes after ingesting raw amberjack tartare. Emergency treatment with adrenaline, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and intravenous fluids led to initial clinical improvement; however, three hours later, she experienced a recurrence of cutaneous, respiratory, and gastrointestinal symptoms, consistent with a biphasic reaction. The patient subsequently developed chest pain associated with transient electrocardiographic changes and mild troponin elevation, prompting further evaluation for suspected Kounis syndrome. Allergy assessment, including specific IgE testing and skin-prick testing with fresh fish, was negative, supporting a toxic rather than IgE-mediated mechanism. This case expands the clinical spectrum of scombroid syndrome by documenting a biphasic anaphylaxis-like presentation and underscores the importance of considering histamine fish poisoning in the differential diagnosis of severe food-related reactions. Careful evaluation is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and unnecessary long-term dietary restrictions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2026.1009113

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2026.101298

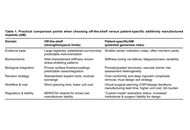
Three-dimensional metal printing has made anatomical perfection readily achievable in orthopaedic reconstruction. Yet, as patient-specific implants transition from salvage solutions to routine applications, a critical question emerges: Does geometric precision improve long-term outcomes, or merely perfect existing problems? The article argues that customization defined by shape alone fails to address fundamental biological constraints, including stiffness mismatch, stress shielding, vascular compromise, and the inevitability of revision surgery. While additive manufacturing enables porous architectures and tailored mechanics, unchecked integration and over-conformity may jeopardize bone preservation and future surgical options. The article further highlights the professional and economic costs of patient-specific workflows and the limitations of static digital planning. True innovation, it is argued, lies not in achieving the “perfect fit,” but in designing implants that participate in bone biology and remain surgically defensible decades after implantation.
Three-dimensional metal printing has made anatomical perfection readily achievable in orthopaedic reconstruction. Yet, as patient-specific implants transition from salvage solutions to routine applications, a critical question emerges: Does geometric precision improve long-term outcomes, or merely perfect existing problems? The article argues that customization defined by shape alone fails to address fundamental biological constraints, including stiffness mismatch, stress shielding, vascular compromise, and the inevitability of revision surgery. While additive manufacturing enables porous architectures and tailored mechanics, unchecked integration and over-conformity may jeopardize bone preservation and future surgical options. The article further highlights the professional and economic costs of patient-specific workflows and the limitations of static digital planning. True innovation, it is argued, lies not in achieving the “perfect fit,” but in designing implants that participate in bone biology and remain surgically defensible decades after implantation.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2026.101360
This article belongs to the special issue Metal 3D Printing of Biometals for Prostheses and Implants

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2026.1008153

Peanut allergy (PA) is a significant public health problem in Western countries; however, while some previous work has been conducted in Mexico among specific subgroups, the national prevalence of PA in the Mexican population remains unknown. This ENRADAL-MEX study aimed to estimate the prevalence of PA among Mexican schoolchildren. A total of 4,269 children aged 6–12 years were included (mean age: 8.7 years; 51.7% male). The national prevalence of adverse food reactions was 9.5%; among these, 16 cases (0.37%) were associated with peanut consumption, but only 11 presented symptoms within the first hour after ingestion, yielding a PA prevalence of 0.26% (95% CI: 0.14–0.47%). Five cases corresponded to convincing non-severe reactions, and the other five to convincing severe reactions (prevalence of 0.12%; 95% CI: 0.06–0.28%, each). Oral symptoms occurred in 54.5% of cases, and 63.6% also had tree nut allergy, with no reactions to other legumes. Since this national study is the first of its kind and indicates that PA is not currently a public health problem among Mexican schoolchildren, further research is encouraged for more comprehensive results.
Peanut allergy (PA) is a significant public health problem in Western countries; however, while some previous work has been conducted in Mexico among specific subgroups, the national prevalence of PA in the Mexican population remains unknown. This ENRADAL-MEX study aimed to estimate the prevalence of PA among Mexican schoolchildren. A total of 4,269 children aged 6–12 years were included (mean age: 8.7 years; 51.7% male). The national prevalence of adverse food reactions was 9.5%; among these, 16 cases (0.37%) were associated with peanut consumption, but only 11 presented symptoms within the first hour after ingestion, yielding a PA prevalence of 0.26% (95% CI: 0.14–0.47%). Five cases corresponded to convincing non-severe reactions, and the other five to convincing severe reactions (prevalence of 0.12%; 95% CI: 0.06–0.28%, each). Oral symptoms occurred in 54.5% of cases, and 63.6% also had tree nut allergy, with no reactions to other legumes. Since this national study is the first of its kind and indicates that PA is not currently a public health problem among Mexican schoolchildren, further research is encouraged for more comprehensive results.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2026.1009110
This article belongs to the special issue Practical Issues in Pediatric Allergy

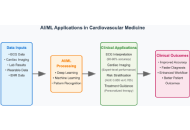
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of global mortality with nearly 19 million deaths annually, while exponential growth in multimodal imaging, continuous monitoring, and electronic health record data has created analytical challenges exceeding traditional methods. This narrative review examines artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications in cardiovascular medicine through a comprehensive literature analysis from 2019 to 2025, focusing on clinical validation and regulatory approvals. Current applications demonstrate significant clinical utility: automated ECG interpretation achieves > 90% accuracy in arrhythmia detection and predicts life-threatening arrhythmias up to two weeks before clinical onset; deep learning cardiac imaging analysis matches expert performance while reducing analysis time from 45 minutes to under 5 minutes; and ML risk prediction outperforms traditional scores with area under the curve values of 0.865 vs. 0.765. The FDA has approved 122 cardiology AI algorithms representing 14% of all clinical AI in the U.S. market, including ECG interpretation, echocardiographic measurement, and imaging analysis systems. Real-world implementations demonstrate 15–25% reductions in diagnostic errors and 20–30% faster emergency intervention times. However, substantial challenges persist: data quality limitations, algorithmic bias with 10–15% performance variation across populations, workflow integration barriers, and validation requirements. Future directions include multimodal systems, continuously learning algorithms, precision medicine applications, and equitable global implementation. Successful integration requires addressing limitations through diverse training datasets, transparent development, standardized validation, provider education, and maintaining physician autonomy. AI and ML represent powerful augmentation tools that, through evidence-based implementation, can transform cardiovascular care while preserving clinical expertise in decision-making.
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of global mortality with nearly 19 million deaths annually, while exponential growth in multimodal imaging, continuous monitoring, and electronic health record data has created analytical challenges exceeding traditional methods. This narrative review examines artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications in cardiovascular medicine through a comprehensive literature analysis from 2019 to 2025, focusing on clinical validation and regulatory approvals. Current applications demonstrate significant clinical utility: automated ECG interpretation achieves > 90% accuracy in arrhythmia detection and predicts life-threatening arrhythmias up to two weeks before clinical onset; deep learning cardiac imaging analysis matches expert performance while reducing analysis time from 45 minutes to under 5 minutes; and ML risk prediction outperforms traditional scores with area under the curve values of 0.865 vs. 0.765. The FDA has approved 122 cardiology AI algorithms representing 14% of all clinical AI in the U.S. market, including ECG interpretation, echocardiographic measurement, and imaging analysis systems. Real-world implementations demonstrate 15–25% reductions in diagnostic errors and 20–30% faster emergency intervention times. However, substantial challenges persist: data quality limitations, algorithmic bias with 10–15% performance variation across populations, workflow integration barriers, and validation requirements. Future directions include multimodal systems, continuously learning algorithms, precision medicine applications, and equitable global implementation. Successful integration requires addressing limitations through diverse training datasets, transparent development, standardized validation, provider education, and maintaining physician autonomy. AI and ML represent powerful augmentation tools that, through evidence-based implementation, can transform cardiovascular care while preserving clinical expertise in decision-making.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001383
This article belongs to the special issue Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Medicine

Aim:
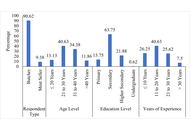
This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of butchers and beef handlers in Bangladesh, and to examine factors associated with their food safety knowledge.
Methods:
A two-stage stratified random sample of 160 respondents was drawn from 16 districts between January 2023 and December 2024. Data were collected using a structured KAP questionnaire. Scores were categorized into low, medium, and high knowledge groups. Descriptive statistics, chi-square (χ²) tests, and a partial proportional odds model (PPOM) were applied.
Results:
Findings showed high awareness of the importance of hygiene and willingness to adopt training (> 90%), yet actual practices were poor. Only 8.8% of butchers performed post-mortem examinations, 2.5% had chilling facilities, and < 1% reported using modern processing technology. Knowledge of GAP, GMP, HACCP, relevant regulations, and withdrawal periods was limited. In the PPOM analysis, higher profit per kilogram of beef (OR = 1.14; 95% CI: 1.04–1.25; p = 0.004) and average practice level (OR = 3.26; 95% CI: 1.02–10.45; p = 0.047) were significantly associated with higher food safety knowledge. Demographic variables were not significant predictors.
Conclusions:
The results highlight substantial gaps between attitudes and actual practices in beef handling. Targeted training, infrastructure support, and regulatory enforcement are recommended to strengthen meat safety in Bangladesh.
Aim:
This study aimed to assess the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of butchers and beef handlers in Bangladesh, and to examine factors associated with their food safety knowledge.
Methods:
A two-stage stratified random sample of 160 respondents was drawn from 16 districts between January 2023 and December 2024. Data were collected using a structured KAP questionnaire. Scores were categorized into low, medium, and high knowledge groups. Descriptive statistics, chi-square (χ²) tests, and a partial proportional odds model (PPOM) were applied.
Results:
Findings showed high awareness of the importance of hygiene and willingness to adopt training (> 90%), yet actual practices were poor. Only 8.8% of butchers performed post-mortem examinations, 2.5% had chilling facilities, and < 1% reported using modern processing technology. Knowledge of GAP, GMP, HACCP, relevant regulations, and withdrawal periods was limited. In the PPOM analysis, higher profit per kilogram of beef (OR = 1.14; 95% CI: 1.04–1.25; p = 0.004) and average practice level (OR = 3.26; 95% CI: 1.02–10.45; p = 0.047) were significantly associated with higher food safety knowledge. Demographic variables were not significant predictors.
Conclusions:
The results highlight substantial gaps between attitudes and actual practices in beef handling. Targeted training, infrastructure support, and regulatory enforcement are recommended to strengthen meat safety in Bangladesh.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010117

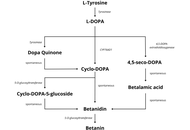
Betacyanins are bioactive compounds found in Caryophyllales, including red beetroots (Beta vulgaris), amaranths (Amaranthus sp.), and red dragon fruits (Hylocereus polyrhizus). Their biosynthesis requires several enzymes, including tyrosinase, 4,5-DOPA-extradiol-dioxygenase (DOD), and 5-O-glucosyl transferase (5GT). Environmentally friendly extraction techniques, such as ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted, supercritical fluid, and pulsed electric field extraction, improve the recovery of betacyanins from natural resources. Betacyanins have commercial value as food coloring agents, for smart food packaging, and in the nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Industrial application is expanding as more innovative methods are discovered. Several factors affect the absorption of betacyanins, including gastrointestinal degradation, the nature of the ingested betacyanins, and the food matrix. Betanin, the main betacyanin, is excreted through urine when given intravenously. However, orally administered betanin showed limited urinary excretion, suggesting extensive modification or digestion in the gastrointestinal tract. Biologically, betacyanins are shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, gut-microbiome-modulatory, antiproliferative, and antimicrobial properties. Recent molecular docking developments showed this compound group’s potential in modulating key target enzymes and proteins.
Betacyanins are bioactive compounds found in Caryophyllales, including red beetroots (Beta vulgaris), amaranths (Amaranthus sp.), and red dragon fruits (Hylocereus polyrhizus). Their biosynthesis requires several enzymes, including tyrosinase, 4,5-DOPA-extradiol-dioxygenase (DOD), and 5-O-glucosyl transferase (5GT). Environmentally friendly extraction techniques, such as ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted, supercritical fluid, and pulsed electric field extraction, improve the recovery of betacyanins from natural resources. Betacyanins have commercial value as food coloring agents, for smart food packaging, and in the nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Industrial application is expanding as more innovative methods are discovered. Several factors affect the absorption of betacyanins, including gastrointestinal degradation, the nature of the ingested betacyanins, and the food matrix. Betanin, the main betacyanin, is excreted through urine when given intravenously. However, orally administered betanin showed limited urinary excretion, suggesting extensive modification or digestion in the gastrointestinal tract. Biologically, betacyanins are shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, gut-microbiome-modulatory, antiproliferative, and antimicrobial properties. Recent molecular docking developments showed this compound group’s potential in modulating key target enzymes and proteins.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010118

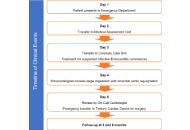
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations, often leading to diagnostic delay. The COVID-19 pandemic has added further complexity by overlapping clinical features and imposing constraints on diagnostic pathways. We report the case of a 48-year-old male who presented with prolonged non-specific symptoms following a recent COVID-19 infection. Multiple emergency department visits resulted in an initial diagnosis of viral illness. Subsequent clinical deterioration prompted further evaluation, which revealed severe aortic regurgitation due to a large aortic valve vegetation on transthoracic echocardiography. Blood cultures grew α-haemolytic Streptococcus mitis fulfilling the modified Duke criteria for IE. The patient developed complications, including heart failure and peripheral arterial embolisation, necessitating urgent surgical aortic valve replacement. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges of IE in the context of recent COVID-19 infection, where overlapping symptoms and altered healthcare pathways may contribute to delayed recognition. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for IE in patients presenting with persistent or atypical symptoms following COVID-19 infection. Early recognition and prompt intervention are essential to prevent serious complications.
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations, often leading to diagnostic delay. The COVID-19 pandemic has added further complexity by overlapping clinical features and imposing constraints on diagnostic pathways. We report the case of a 48-year-old male who presented with prolonged non-specific symptoms following a recent COVID-19 infection. Multiple emergency department visits resulted in an initial diagnosis of viral illness. Subsequent clinical deterioration prompted further evaluation, which revealed severe aortic regurgitation due to a large aortic valve vegetation on transthoracic echocardiography. Blood cultures grew α-haemolytic Streptococcus mitis fulfilling the modified Duke criteria for IE. The patient developed complications, including heart failure and peripheral arterial embolisation, necessitating urgent surgical aortic valve replacement. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges of IE in the context of recent COVID-19 infection, where overlapping symptoms and altered healthcare pathways may contribute to delayed recognition. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for IE in patients presenting with persistent or atypical symptoms following COVID-19 infection. Early recognition and prompt intervention are essential to prevent serious complications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2026.101297
 Previous
Previous