


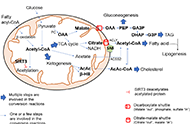
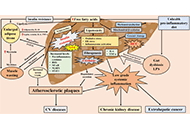

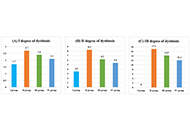
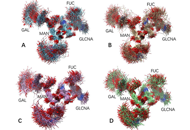
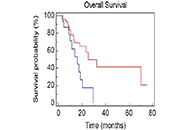
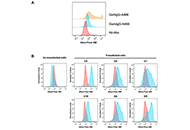


Lynch syndrome
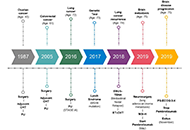
Lynch syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00044

Systemic inflammatory rheumatic disorders are associated with an increased risk of malignancy. The mechanism linking malignancy and rheumatic diseases
Systemic inflammatory rheumatic disorders are associated with an increased risk of malignancy. The mechanism linking malignancy and rheumatic diseases
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2025.100797

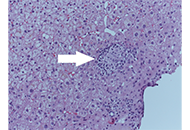
Primary biliary cholangit
Primary biliary cholangit
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00033
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Therapeutics in Hepato-Gastroenterology

Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of th
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been known for a long time, but our understanding of th
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2024.00061

Background:
Multiple myeloma (MM)
Methods:
We conducted a comprehensive literature search using Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases from inception through July 22nd, 2024. Phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing isatuximab in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) reporting pneumonia, URTIs, and VTE as adverse events were included. Mantel-Haenszel (MH) method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-statistic. Random effects model was applied.
Results:
A total of 1,044 patients from three phase III RCTs (ICARIA-MM, IKEMA, IMROZ) were included for pneumonia and URTI analysis, while 1,403 patients from three trials (IKEMA, IMROZ, GMMG-HD7) were included for VTE evaluation. The incidence of any-grade pneumonia was higher in the isatuximab group (30.1% vs. 23.2%; RR, 1.31; 95% CI 1.06–1.61; P = 0.01), as was high-grade pneumonia (20.8% vs. 15.3%; RR, 1.38; 95% CI 1.06–1.81; P = 0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed between the isatuximab and control groups for any-grade URTIs, high-grade URTIs, or VTE.
Discussion:
Th
Background:
Multiple myeloma (MM)
Methods:
We conducted a comprehensive literature search using Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases from inception through July 22nd, 2024. Phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing isatuximab in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) reporting pneumonia, URTIs, and VTE as adverse events were included. Mantel-Haenszel (MH) method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-statistic. Random effects model was applied.
Results:
A total of 1,044 patients from three phase III RCTs (ICARIA-MM, IKEMA, IMROZ) were included for pneumonia and URTI analysis, while 1,403 patients from three trials (IKEMA, IMROZ, GMMG-HD7) were included for VTE evaluation. The incidence of any-grade pneumonia was higher in the isatuximab group (30.1% vs. 23.2%; RR, 1.31; 95% CI 1.06–1.61; P = 0.01), as was high-grade pneumonia (20.8% vs. 15.3%; RR, 1.38; 95% CI 1.06–1.81; P = 0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed between the isatuximab and control groups for any-grade URTIs, high-grade URTIs, or VTE.
Discussion:
Th
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002300

Amyotrophic lateral scleros
Amyotrophic lateral scleros
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2023.00045

Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are a class of zinc (Zn)-dependent metalloenzymes that are responsible for epigenetic modifications. HDACs are largely associated with histone proteins that regulate gene expression at the DNA level. Th
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are a class of zinc (Zn)-dependent metalloenzymes that are responsible for epigenetic modifications. HDACs are largely associated with histone proteins that regulate gene expression at the DNA level. Th
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00166
This article belongs to the special issue Posttranslational Modifications in Health and Disease

Catatonia
Catatonia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00032

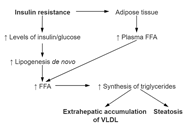
Mitochondria are present in all mammalian cells except matured red blood cells. Mitochondria consist of several metabolic pathways for glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and bioenergetic pathways for ATP synthesis, membrane potential, and reactive oxygen production. In the liver, hepatic mitochondria play a key role in hepatic steatos
Mitochondria are present in all mammalian cells except matured red blood cells. Mitochondria consist of several metabolic pathways for glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and bioenergetic pathways for ATP synthesis, membrane potential, and reactive oxygen production. In the liver, hepatic mitochondria play a key role in hepatic steatos
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2024.00039
This article belongs to the special issue Mitochondria and Lipid Signalling in Liver Diseases

Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001281

Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2022.00083

Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00014
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Aim:
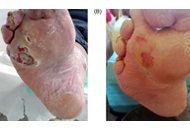
Diabetic foot syndrome (DFS)
Methods:
In all patients admitted, the approach was performed through a multidisciplinary team (Diabetic Foot Care Team) and described in a specific diagnostic-therapeutic-assistance program. Criteria of inclusion were presence of seps
Results:
Among 75 consecutive patients (mean age 70.9 years) enrolled, prevalence of acute DFS was higher among men (M/F 3:1). Poor glycemic control [mean hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 67.9 ± 22.3 mmol/mol], long duration of diabetes (mean 19 ± 16.3 years), high low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (mean 89.5 ± 45.1 mg/ dL) and obesity (mean Body Mass Index 30.2 ± 7.6 kg/m2) were common. Diabetes-related complications as peripheral arterial disease (PAD) (76%), ischemic heart disease (48%), retinopathy (40.5%), hepatic steatos
Conclusions:
Male sex, co-morbidity, PAD, systemic inflammation and poor glycemic control are major features of acute hospitalized DFS. An approach through a multidisciplinary team
Aim:
Diabetic foot syndrome (DFS)
Methods:
In all patients admitted, the approach was performed through a multidisciplinary team (Diabetic Foot Care Team) and described in a specific diagnostic-therapeutic-assistance program. Criteria of inclusion were presence of seps
Results:
Among 75 consecutive patients (mean age 70.9 years) enrolled, prevalence of acute DFS was higher among men (M/F 3:1). Poor glycemic control [mean hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 67.9 ± 22.3 mmol/mol], long duration of diabetes (mean 19 ± 16.3 years), high low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (mean 89.5 ± 45.1 mg/ dL) and obesity (mean Body Mass Index 30.2 ± 7.6 kg/m2) were common. Diabetes-related complications as peripheral arterial disease (PAD) (76%), ischemic heart disease (48%), retinopathy (40.5%), hepatic steatos
Conclusions:
Male sex, co-morbidity, PAD, systemic inflammation and poor glycemic control are major features of acute hospitalized DFS. An approach through a multidisciplinary team
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2021.00035
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

Aim:
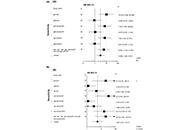
The study aims to evaluate the incidence of recurrent thromboses in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) and its association with the presence of different antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs) and known thrombogenic risk factors.
Methods:
Th
Results:
Recurrent thrombos
Conclusions:
Recurrent thrombos
Aim:
The study aims to evaluate the incidence of recurrent thromboses in patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) and its association with the presence of different antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs) and known thrombogenic risk factors.
Methods:
Th
Results:
Recurrent thrombos
Conclusions:
Recurrent thrombos
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2023.00114
This article belongs to the special issue Autoantibodies Associated to Thrombosis and Hemostasis

Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostos
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostos
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2023.00022
This article belongs to the special issue Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis- A common but neglected disease

Aim:
Th
Methods:
An enzymatic method was used to diagnose and monitor the degree of oral dysbios
Results:
The research established that oral dysbios
Conclusions:
The association of periodontit
Aim:
Th
Methods:
An enzymatic method was used to diagnose and monitor the degree of oral dysbios
Results:
The research established that oral dysbios
Conclusions:
The association of periodontit
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00241
This article belongs to the special issue Oral Health Interconnections and Multidisciplinary Approaches

Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2021.00004

Aim:
The role of tumor burden (TB) for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving immunotherapy
Methods:
Sixty-five consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC treated with immunotherapy as first or second line therapy were retrospectively analyzed between August 2015 and February 2018. TB was recorded at baseline considering sites and number of metastases, thoracic vs. extrathoracic disease, measurable disease (MD) vs. not-MD (NMD) and evaluating dimensional aspects as maximum lesion diameter (cut-off = 6.3 cm), sum of the 5 major lesions diameters (cut-off = 14.3 cm), and number of sites of metastases (cut-off > 4). All cut-offs were calculated by receiver operating characteristic curves. Median overall survival (OS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. A Cox regression model was carried out for univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results:
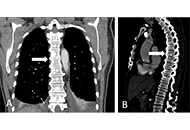
Median age was 70 years and most patients (86.2%) had a good performance status (PS-Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group < 2). No significant difference in OS was noted between subgroups of patients according to TB. Bone metastases (BM) had a negative prognostic impact [median OS (mOS), 13.8 vs. 70.0 months, P = 0.0009; median progression free survival in the second line (mPFS2) 2.97 vs. 8.63 months; P = 0.0037]. Patients with NMD had a poorer prognos
Conclusions:
Th
Aim:
The role of tumor burden (TB) for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving immunotherapy
Methods:
Sixty-five consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC treated with immunotherapy as first or second line therapy were retrospectively analyzed between August 2015 and February 2018. TB was recorded at baseline considering sites and number of metastases, thoracic vs. extrathoracic disease, measurable disease (MD) vs. not-MD (NMD) and evaluating dimensional aspects as maximum lesion diameter (cut-off = 6.3 cm), sum of the 5 major lesions diameters (cut-off = 14.3 cm), and number of sites of metastases (cut-off > 4). All cut-offs were calculated by receiver operating characteristic curves. Median overall survival (OS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. A Cox regression model was carried out for univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results:
Median age was 70 years and most patients (86.2%) had a good performance status (PS-Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group < 2). No significant difference in OS was noted between subgroups of patients according to TB. Bone metastases (BM) had a negative prognostic impact [median OS (mOS), 13.8 vs. 70.0 months, P = 0.0009; median progression free survival in the second line (mPFS2) 2.97 vs. 8.63 months; P = 0.0037]. Patients with NMD had a poorer prognos
Conclusions:
Th
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00043
This article belongs to the special issue Immunotherapy in Cancer Patients

Aim:
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
Aim:
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00188
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Strategies and Targets for Immunotherapy of Cancer

Psorias
Psorias
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2024.00029
 Previous
Previous