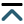






The dominant paradigm for healthy ageing in women+ (all genders) focuses on estrogen and sees the menopause, per se, as a major health problem (with low estrogen and progesterone levels). In reality, the risks for diseases that increase at older ages originate during the menstruating years. Rarely discussed evidence supports the central role of progesterone and normally ovulatory menstrual cycles in preventing early cardiovascular disease, fragility fractures, dementia, and cancers. Menstrual cycles with normal and predictable lengths but disturbed ovulation, including short luteal phases with lower progesterone production as well as anovulation without progesterone, likely occur in over 25% of all such cycles. These Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances are usually an adaptive and protective response to physiological, sociocultural, or emotional stressors. Ovulatory disturbances and risks for health issues during ageing are intrinsically related to the social determinants of health—wholesome food, plentiful physical activity, strong communities, and access to timely and appropriate medical care. This review discusses the empirical evidence that normal ovulation and progesterone production during the premenopausal years lead to the prevention of early heart attacks and fragility fractures. Few studies document the effects of prevalent Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances on brain issues (sleep, night sweats, ischemic strokes, pain, and addictions) and cancer risks. Serious gaps in women+’s fundamental reproductive physiology must be addressed with unbiased (population-based), rigorously collected longitudinal physiological, hormonal, and sociocultural data. Progesterone therapy during perimenopause and menopause also indirectly leads to healthy ageing through effective treatment of night sweats, hot flushes, and disturbed sleep, which are associated with cardiovascular problems and osteoporosis. Not only is progesterone effective for vasomotor symptoms in menopause, but also effective in perimenopause, a time of high and chaotic estrogen levels. In sum, strong summarized evidence suggests that progesterone and ovulation need further exploration for their important roles in promoting healthy ageing for women+.
The dominant paradigm for healthy ageing in women+ (all genders) focuses on estrogen and sees the menopause, per se, as a major health problem (with low estrogen and progesterone levels). In reality, the risks for diseases that increase at older ages originate during the menstruating years. Rarely discussed evidence supports the central role of progesterone and normally ovulatory menstrual cycles in preventing early cardiovascular disease, fragility fractures, dementia, and cancers. Menstrual cycles with normal and predictable lengths but disturbed ovulation, including short luteal phases with lower progesterone production as well as anovulation without progesterone, likely occur in over 25% of all such cycles. These Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances are usually an adaptive and protective response to physiological, sociocultural, or emotional stressors. Ovulatory disturbances and risks for health issues during ageing are intrinsically related to the social determinants of health—wholesome food, plentiful physical activity, strong communities, and access to timely and appropriate medical care. This review discusses the empirical evidence that normal ovulation and progesterone production during the premenopausal years lead to the prevention of early heart attacks and fragility fractures. Few studies document the effects of prevalent Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances on brain issues (sleep, night sweats, ischemic strokes, pain, and addictions) and cancer risks. Serious gaps in women+’s fundamental reproductive physiology must be addressed with unbiased (population-based), rigorously collected longitudinal physiological, hormonal, and sociocultural data. Progesterone therapy during perimenopause and menopause also indirectly leads to healthy ageing through effective treatment of night sweats, hot flushes, and disturbed sleep, which are associated with cardiovascular problems and osteoporosis. Not only is progesterone effective for vasomotor symptoms in menopause, but also effective in perimenopause, a time of high and chaotic estrogen levels. In sum, strong summarized evidence suggests that progesterone and ovulation need further exploration for their important roles in promoting healthy ageing for women+.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101460
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging

Aim:
Hypertriglyceridemia is linked to increased risk of diabetes diagnosis, incidence, and mortality. However, whether individuals with normal triglyceride levels (i.e., < 1.7 mmol/L) uniformly exhibit low diabetes risk remains underexplored. Specifically, it is unclear whether triglyceride levels within the normal range are associated with plasma glucose levels and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). This study aimed to address these gaps by examining the associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose, as well as between triglyceride levels and T2DM, in individuals with triglycerides in the normal range.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included 16,706 Chinese adults with triglyceride levels below 1.7 mmol/L. Among them, 1,067 had T2DM. Associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose were assessed using linear regression, while associations with T2DM were evaluated using binary logistic regression. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was determined via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results:
Triglyceride levels were positively associated with fasting plasma glucose after multivariate adjustment (β = 0.034, P < 0.001). A one-unit increase in the natural log of triglyceride levels was associated with a 61% higher adjusted odds of T2DM [odds ratio (OR), 1.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.19–2.17; P = 0.002]. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was 1.09 mmol/L. Participants with triglyceride levels ≥ 1.09 mmol/L had a 28% higher odds of T2DM (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.07–1.53; P = 0.006) compared to those with levels below the cut-off.
Conclusions:
Among individuals with normal triglyceride levels, higher triglyceride concentrations were associated with higher odds of T2DM diagnosis, with an optimal diagnostic cut-off of 1.09 mmol/L. These findings suggest that adults with triglyceride levels more than 1.09 mmol/L may benefit from closer monitoring for T2DM development.
Aim:
Hypertriglyceridemia is linked to increased risk of diabetes diagnosis, incidence, and mortality. However, whether individuals with normal triglyceride levels (i.e., < 1.7 mmol/L) uniformly exhibit low diabetes risk remains underexplored. Specifically, it is unclear whether triglyceride levels within the normal range are associated with plasma glucose levels and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). This study aimed to address these gaps by examining the associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose, as well as between triglyceride levels and T2DM, in individuals with triglycerides in the normal range.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included 16,706 Chinese adults with triglyceride levels below 1.7 mmol/L. Among them, 1,067 had T2DM. Associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose were assessed using linear regression, while associations with T2DM were evaluated using binary logistic regression. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was determined via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results:
Triglyceride levels were positively associated with fasting plasma glucose after multivariate adjustment (β = 0.034, P < 0.001). A one-unit increase in the natural log of triglyceride levels was associated with a 61% higher adjusted odds of T2DM [odds ratio (OR), 1.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.19–2.17; P = 0.002]. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was 1.09 mmol/L. Participants with triglyceride levels ≥ 1.09 mmol/L had a 28% higher odds of T2DM (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.07–1.53; P = 0.006) compared to those with levels below the cut-off.
Conclusions:
Among individuals with normal triglyceride levels, higher triglyceride concentrations were associated with higher odds of T2DM diagnosis, with an optimal diagnostic cut-off of 1.09 mmol/L. These findings suggest that adults with triglyceride levels more than 1.09 mmol/L may benefit from closer monitoring for T2DM development.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101459
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

This commentary discusses a recent article (J Diabetes 2025;17(3):e70063), focusing on interpreting the study’s sex-stratified results in a broader clinical and mechanistic context. The authors of this systematic review and meta-analysis of 14 randomized trials demonstrate that women achieve greater weight loss induced by glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists compared to men (mean difference of 1.04 kg or 1.69%). Analyses specific to different drugs consistently show that women benefit more from dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and retatrutide, with trials focused on obesity further emphasizing this gap. Sensitivity analyses confirm the reliability of these findings and indicate the absence of publication bias. We discuss the clinical implications of these results, suggesting that healthcare providers should consider sex differences when counseling, monitoring, and dosing patients. We also advocate for future trials that are adequately powered and stratified by sex to evaluate factors such as adherence, adverse events, and body composition. Mechanistic hypotheses, such as sex-related pharmacokinetics, estrogen-GLP-1 synergy, and varying inflammatory responses, should be investigated further to inform precision dosing. Lastly, we recommend that regulatory agencies revisit current labeling, which claims no sex differences, as more sex-stratified evidence becomes available. It is important to acknowledge the existing heterogeneity and remaining uncertainties in this area of research.
This commentary discusses a recent article (J Diabetes 2025;17(3):e70063), focusing on interpreting the study’s sex-stratified results in a broader clinical and mechanistic context. The authors of this systematic review and meta-analysis of 14 randomized trials demonstrate that women achieve greater weight loss induced by glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists compared to men (mean difference of 1.04 kg or 1.69%). Analyses specific to different drugs consistently show that women benefit more from dulaglutide, liraglutide, semaglutide, and retatrutide, with trials focused on obesity further emphasizing this gap. Sensitivity analyses confirm the reliability of these findings and indicate the absence of publication bias. We discuss the clinical implications of these results, suggesting that healthcare providers should consider sex differences when counseling, monitoring, and dosing patients. We also advocate for future trials that are adequately powered and stratified by sex to evaluate factors such as adherence, adverse events, and body composition. Mechanistic hypotheses, such as sex-related pharmacokinetics, estrogen-GLP-1 synergy, and varying inflammatory responses, should be investigated further to inform precision dosing. Lastly, we recommend that regulatory agencies revisit current labeling, which claims no sex differences, as more sex-stratified evidence becomes available. It is important to acknowledge the existing heterogeneity and remaining uncertainties in this area of research.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101458

A pro-inflammatory state with elevated cytokines influenced by both environmental and genetic factors is a key characteristic of both type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Cytokines promote immune cell infiltration and degradation of the pancreatic islets, which play a direct role in the development of insulin resistance in T1DM. Cytokines also interfere with insulin signaling pathways and lead to metabolic dysfunction, contributing to the development of insulin resistance in patients with T2DM. In this narrative review, we have discussed the mechanisms of action and specific effects on insulin resistance of different cytokines, the influence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and genetic factors that alter cytokine levels, and the development of insulin resistance. Further, we have discussed the complication of diabetes with a focus on diabetic foot ulcers, wounds, impaired wound healing, and reduced angiogenesis in association with the role of cytokines. Finally, the discussion addresses interventions for managing cytokines, such as Treg-based therapies, along with the various challenges presented by therapies targeting cytokine dysregulation and their effects on insulin resistance.
A pro-inflammatory state with elevated cytokines influenced by both environmental and genetic factors is a key characteristic of both type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Cytokines promote immune cell infiltration and degradation of the pancreatic islets, which play a direct role in the development of insulin resistance in T1DM. Cytokines also interfere with insulin signaling pathways and lead to metabolic dysfunction, contributing to the development of insulin resistance in patients with T2DM. In this narrative review, we have discussed the mechanisms of action and specific effects on insulin resistance of different cytokines, the influence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and genetic factors that alter cytokine levels, and the development of insulin resistance. Further, we have discussed the complication of diabetes with a focus on diabetic foot ulcers, wounds, impaired wound healing, and reduced angiogenesis in association with the role of cytokines. Finally, the discussion addresses interventions for managing cytokines, such as Treg-based therapies, along with the various challenges presented by therapies targeting cytokine dysregulation and their effects on insulin resistance.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101457
This article belongs to the special issue Role of Dysregulated Cytokine Signaling Pathways in Metabolic Disease

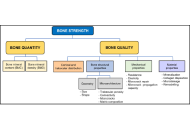
Osteoporosis is a disabling disease with a significant impact on the global population, particularly among older men and postmenopausal women. Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of osteoporosis, including greater life expectancy and the absence of symptoms in its early stages. The morbidity, mortality, and substantial economic burden associated with osteoporosis, especially due to hip fractures and related complications, constitute a major public health concern. Diagnosis should involve a comprehensive biochemical profile, along with additional tests to rule out secondary causes, which are often underdiagnosed and can influence the progression of the disease. Preventive measures and early diagnosis are essential to maintaining bone health and preventing fractures and disability. This review will focus on the definition, diagnostic approach, and key considerations prior to initiating treatment in patients with osteoporosis. Fracture risk prediction tools, including Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), and treatment strategies are not addressed, as this review focuses on the appropriate diagnostic evaluation of osteoporosis and the systematic exclusion of secondary causes.
Osteoporosis is a disabling disease with a significant impact on the global population, particularly among older men and postmenopausal women. Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of osteoporosis, including greater life expectancy and the absence of symptoms in its early stages. The morbidity, mortality, and substantial economic burden associated with osteoporosis, especially due to hip fractures and related complications, constitute a major public health concern. Diagnosis should involve a comprehensive biochemical profile, along with additional tests to rule out secondary causes, which are often underdiagnosed and can influence the progression of the disease. Preventive measures and early diagnosis are essential to maintaining bone health and preventing fractures and disability. This review will focus on the definition, diagnostic approach, and key considerations prior to initiating treatment in patients with osteoporosis. Fracture risk prediction tools, including Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), and treatment strategies are not addressed, as this review focuses on the appropriate diagnostic evaluation of osteoporosis and the systematic exclusion of secondary causes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101456

Background:
Metabolic syndrome and dyslipidaemia increase the risk of death by two or three times. In this context, the role of apolipoprotein A-I (Apo A-I), the main structural protein of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), stands out, since its anti-inflammatory potential reduces cardiovascular risk. Further, genetic modifications, such as the rs670 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), in the promoter region of the APOA1 gene are associated with the development of cardiovascular events, dyslipidemia, and diabetes, as well as metabolic syndrome. Thus, this study aims to investigate the relation between the occurrence of dyslipidemia and the rs670 SNP genotypes.
Methods:
An integrative and systematic review was performed with the LitVar2 database according to the PRISMA protocol standards. Studies were researched up to August 2025. Then, a meta-analysis was performed using the fixed-effects model, since the study was considered homogeneous based on the I2 value (< 50%).
Results:
Of the 99 found articles in the database, 5 referred to metabolic disorders (n = 7,705—4 Chinese studies and 1 Iranian study) and were published between 2015 and 2018. Three (n = 2,784 patients or 36.13%) of the articles indicated an association between the polymorphic allele and a higher risk of developing dyslipidemia with a relative risk of 1.16 (IC 95% 1.09–1.23, p < 0.01, I2 = 0%). Relative risk (IC 95%) was presented, and p < 0.05 was defined as the significance criterion.
Discussion:
This study reinforces a possible association between the influence of SNP rs670 and dyslipidemia. This emphasizes the importance of conducting further research incorporating a larger and more diverse study group, as well as investigating the genetic and environmental influence on the phenotypic expression of the rs670 SNP.
Background:
Metabolic syndrome and dyslipidaemia increase the risk of death by two or three times. In this context, the role of apolipoprotein A-I (Apo A-I), the main structural protein of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), stands out, since its anti-inflammatory potential reduces cardiovascular risk. Further, genetic modifications, such as the rs670 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), in the promoter region of the APOA1 gene are associated with the development of cardiovascular events, dyslipidemia, and diabetes, as well as metabolic syndrome. Thus, this study aims to investigate the relation between the occurrence of dyslipidemia and the rs670 SNP genotypes.
Methods:
An integrative and systematic review was performed with the LitVar2 database according to the PRISMA protocol standards. Studies were researched up to August 2025. Then, a meta-analysis was performed using the fixed-effects model, since the study was considered homogeneous based on the I2 value (< 50%).
Results:
Of the 99 found articles in the database, 5 referred to metabolic disorders (n = 7,705—4 Chinese studies and 1 Iranian study) and were published between 2015 and 2018. Three (n = 2,784 patients or 36.13%) of the articles indicated an association between the polymorphic allele and a higher risk of developing dyslipidemia with a relative risk of 1.16 (IC 95% 1.09–1.23, p < 0.01, I2 = 0%). Relative risk (IC 95%) was presented, and p < 0.05 was defined as the significance criterion.
Discussion:
This study reinforces a possible association between the influence of SNP rs670 and dyslipidemia. This emphasizes the importance of conducting further research incorporating a larger and more diverse study group, as well as investigating the genetic and environmental influence on the phenotypic expression of the rs670 SNP.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101455

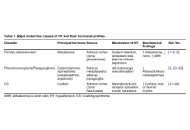
Endocrine hypertension (HT) includes a group of secondary hypertensive disorders caused by hormonal excess, primarily primary aldosteronism (PA), pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL), and Cushing syndrome (CS). Although relatively uncommon, these conditions confer a disproportionately high cardiovascular risk that extends beyond blood pressure elevation. Aldosterone, catecholamines, and cortisol each induce myocardial fibrosis, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction, leading to left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), arrhythmias, and heart failure. In PA, chronic aldosterone excess activates mineralocorticoid receptors in cardiac and vascular tissues, promoting collagen deposition, diastolic dysfunction, and atrial fibrillation (AF) that may regress after adrenalectomy or pharmacologic blockade. PPGL causes episodic catecholamine surges resulting in β-adrenergic overstimulation, calcium overload, and microvascular ischemia, producing reversible or sometimes persistent catecholamine-induced cardiotoxicity. CS induces concentric hypertrophy, metabolic derangements, and vascular injury through prolonged glucocorticoid exposure, with cardiovascular recovery often incomplete after biochemical remission. Despite distinct hormonal origins, these disorders share convergent mechanisms, including fibroblast activation, mitochondrial injury, and maladaptive remodeling, that define endocrine cardiomyopathy. Early detection and targeted hormonal treatment can reverse much of the cardiac and vascular damage, whereas delayed recognition leads to irreversible fibrosis and persistent diastolic dysfunction. Recognition of these hormone-specific mechanisms is crucial for clinicians to anticipate, manage, and prevent these deleterious cardiovascular effects. Advances in molecular genetics, cardiac imaging, and biomarker research are improving our understanding of genotype-phenotype relationships and long-term reversibility of injury. Endocrine HT should therefore be recognized as a systemic cardiovascular disorder in which hormonal excess functions as a primary pathogenic driver; timely diagnosis and multidisciplinary care remain key to reducing morbidity and mortality.
Endocrine hypertension (HT) includes a group of secondary hypertensive disorders caused by hormonal excess, primarily primary aldosteronism (PA), pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL), and Cushing syndrome (CS). Although relatively uncommon, these conditions confer a disproportionately high cardiovascular risk that extends beyond blood pressure elevation. Aldosterone, catecholamines, and cortisol each induce myocardial fibrosis, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction, leading to left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), arrhythmias, and heart failure. In PA, chronic aldosterone excess activates mineralocorticoid receptors in cardiac and vascular tissues, promoting collagen deposition, diastolic dysfunction, and atrial fibrillation (AF) that may regress after adrenalectomy or pharmacologic blockade. PPGL causes episodic catecholamine surges resulting in β-adrenergic overstimulation, calcium overload, and microvascular ischemia, producing reversible or sometimes persistent catecholamine-induced cardiotoxicity. CS induces concentric hypertrophy, metabolic derangements, and vascular injury through prolonged glucocorticoid exposure, with cardiovascular recovery often incomplete after biochemical remission. Despite distinct hormonal origins, these disorders share convergent mechanisms, including fibroblast activation, mitochondrial injury, and maladaptive remodeling, that define endocrine cardiomyopathy. Early detection and targeted hormonal treatment can reverse much of the cardiac and vascular damage, whereas delayed recognition leads to irreversible fibrosis and persistent diastolic dysfunction. Recognition of these hormone-specific mechanisms is crucial for clinicians to anticipate, manage, and prevent these deleterious cardiovascular effects. Advances in molecular genetics, cardiac imaging, and biomarker research are improving our understanding of genotype-phenotype relationships and long-term reversibility of injury. Endocrine HT should therefore be recognized as a systemic cardiovascular disorder in which hormonal excess functions as a primary pathogenic driver; timely diagnosis and multidisciplinary care remain key to reducing morbidity and mortality.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101454

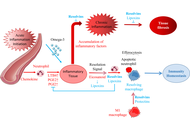
The global prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)—the most common metabolic disorders—has reached epidemic proportions over the past half-century, with obesity being a key driver of insulin resistance and T2DM development. These disorders are characterized by metaflammation (chronic low-grade inflammation across multiple metabolic organs like adipose tissue, liver, muscle, and the gut), which disrupts metabolic homeostasis, exacerbates insulin resistance, impairs insulin secretion, and links to other comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases. A major advance in understanding inflammation resolution is the identification of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), a family of lipid mediators including resolvins, lipoxins, protectins, and maresins. Derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g., EPA, DHA), SPMs actively regulate inflammation resolution by constraining pro-inflammatory cell infiltration (e.g., neutrophils), promoting anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization (M2), enhancing efferocytosis (clearance of apoptotic cells), and preserving tissue barrier integrity—without inducing immunosuppression. This review summarizes evidence from human and animal studies on obesity-related metaflammation in metabolic tissues and the role of SPMs in resolving this inflammation. It details SPM mechanisms (e.g., maintaining adipose tissue homeostasis, improving insulin sensitivity, alleviating hepatic steatosis) and highlights their dysregulation in obesity (e.g., impaired biosynthesis, reduced receptor expression) as a critical driver of metabolic dysfunction. Finally, the review discusses the therapeutic potential of SPM-targeted strategies (e.g., ω-3 PUFA supplementation, SPM receptor activation) for alleviating obesity, T2DM, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MAFLD), and other metabolic disorders, along with future research directions in this field.
The global prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)—the most common metabolic disorders—has reached epidemic proportions over the past half-century, with obesity being a key driver of insulin resistance and T2DM development. These disorders are characterized by metaflammation (chronic low-grade inflammation across multiple metabolic organs like adipose tissue, liver, muscle, and the gut), which disrupts metabolic homeostasis, exacerbates insulin resistance, impairs insulin secretion, and links to other comorbidities such as cardiovascular diseases. A major advance in understanding inflammation resolution is the identification of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), a family of lipid mediators including resolvins, lipoxins, protectins, and maresins. Derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (e.g., EPA, DHA), SPMs actively regulate inflammation resolution by constraining pro-inflammatory cell infiltration (e.g., neutrophils), promoting anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization (M2), enhancing efferocytosis (clearance of apoptotic cells), and preserving tissue barrier integrity—without inducing immunosuppression. This review summarizes evidence from human and animal studies on obesity-related metaflammation in metabolic tissues and the role of SPMs in resolving this inflammation. It details SPM mechanisms (e.g., maintaining adipose tissue homeostasis, improving insulin sensitivity, alleviating hepatic steatosis) and highlights their dysregulation in obesity (e.g., impaired biosynthesis, reduced receptor expression) as a critical driver of metabolic dysfunction. Finally, the review discusses the therapeutic potential of SPM-targeted strategies (e.g., ω-3 PUFA supplementation, SPM receptor activation) for alleviating obesity, T2DM, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MAFLD), and other metabolic disorders, along with future research directions in this field.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101453

Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and dual incretin agonists have demonstrated significant potential in improving adipose tissue function beyond their established effects on appetite suppression and weight loss. These agents not only reduce overall fat mass but also induce favorable changes in fat distribution and adipose tissue quality. Notably, they enhance brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity and promote the browning of white adipose tissue (WAT), thereby increasing energy expenditure. They are associated with reductions in adipocyte size, particularly within visceral fat depots, alongside improvements in metabolic health markers. The aim of this publication is to provide a literature review on the effects of GLP-1RAs and dual incretin agonists on adipocyte type and size, adipose tissue functional remodeling, and their implications for obesity management. These findings highlight the capacity of incretin-based therapies to modulate adipose tissue biology, offering metabolic benefits that extend beyond weight reduction.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and dual incretin agonists have demonstrated significant potential in improving adipose tissue function beyond their established effects on appetite suppression and weight loss. These agents not only reduce overall fat mass but also induce favorable changes in fat distribution and adipose tissue quality. Notably, they enhance brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity and promote the browning of white adipose tissue (WAT), thereby increasing energy expenditure. They are associated with reductions in adipocyte size, particularly within visceral fat depots, alongside improvements in metabolic health markers. The aim of this publication is to provide a literature review on the effects of GLP-1RAs and dual incretin agonists on adipocyte type and size, adipose tissue functional remodeling, and their implications for obesity management. These findings highlight the capacity of incretin-based therapies to modulate adipose tissue biology, offering metabolic benefits that extend beyond weight reduction.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101452

The glucocorticoid receptor alpha (GRα) is traditionally viewed as a stress-response element with anti-inflammatory properties. Mechanistically, convergent evidence from global and tissue-specific knockout models, translational clinical studies, and evolutionary analyses indicates that GRα’s vital role in maintaining systemic homeostasis challenges its peripheral classification in clinical medicine. To reconceptualize GRα as a master regulator of organismal survival by analyzing its non-redundant, multisystemic functions and evaluating its relevance in health, development, and critical illness. This narrative synthesis combines structured searches performed using the Consensus AI research platform with evidence from genetic knockout models, tissue-specific deletion studies, and translational clinical research. Key findings are framed within comparative receptor analyses and integrated into broader physiological models of homeostasis and allostasis. Evolutionarily, global loss of GRα is perinatally lethal, characterized by failure of lung maturation and respiratory adaptation, accompanied by metabolic and neuroendocrine dysregulation. Tissue-specific deletions reveal essential roles in immune regulation, mitochondrial bioenergetics, cardiovascular function, and neuroendocrine stability. While several other receptors (including MR) are also essential for survival, GRα is distinctive for the breadth of cross-system coordination it provides. GRα exhibits both genomic and non-genomic actions that support rapid stress adaptation and promote restoration of systemic stability. Clinically, despite this broad integrative role, GRα’s survival-critical functions remain underrecognized in therapeutic strategies. Overall, the evidence supports GRα as a central integrator of postnatal survival, metabolic resilience, and immunological competence. GRα is a vital receptor whose systemic regulatory functions exceed its historical classification as a stress hormone mediator. Its role is not ancillary but foundational, anchoring survival across immune, metabolic, cardiovascular, and neuroendocrine systems. The collapse of this receptor’s function is not simply a component of disease—it is the tipping point that drives the organism from adaptation toward systemic breakdown. Recognizing GRα as a master survival receptor redefines therapeutic priorities, guiding biomarker-driven restoration of homeostasis in critical illness.
The glucocorticoid receptor alpha (GRα) is traditionally viewed as a stress-response element with anti-inflammatory properties. Mechanistically, convergent evidence from global and tissue-specific knockout models, translational clinical studies, and evolutionary analyses indicates that GRα’s vital role in maintaining systemic homeostasis challenges its peripheral classification in clinical medicine. To reconceptualize GRα as a master regulator of organismal survival by analyzing its non-redundant, multisystemic functions and evaluating its relevance in health, development, and critical illness. This narrative synthesis combines structured searches performed using the Consensus AI research platform with evidence from genetic knockout models, tissue-specific deletion studies, and translational clinical research. Key findings are framed within comparative receptor analyses and integrated into broader physiological models of homeostasis and allostasis. Evolutionarily, global loss of GRα is perinatally lethal, characterized by failure of lung maturation and respiratory adaptation, accompanied by metabolic and neuroendocrine dysregulation. Tissue-specific deletions reveal essential roles in immune regulation, mitochondrial bioenergetics, cardiovascular function, and neuroendocrine stability. While several other receptors (including MR) are also essential for survival, GRα is distinctive for the breadth of cross-system coordination it provides. GRα exhibits both genomic and non-genomic actions that support rapid stress adaptation and promote restoration of systemic stability. Clinically, despite this broad integrative role, GRα’s survival-critical functions remain underrecognized in therapeutic strategies. Overall, the evidence supports GRα as a central integrator of postnatal survival, metabolic resilience, and immunological competence. GRα is a vital receptor whose systemic regulatory functions exceed its historical classification as a stress hormone mediator. Its role is not ancillary but foundational, anchoring survival across immune, metabolic, cardiovascular, and neuroendocrine systems. The collapse of this receptor’s function is not simply a component of disease—it is the tipping point that drives the organism from adaptation toward systemic breakdown. Recognizing GRα as a master survival receptor redefines therapeutic priorities, guiding biomarker-driven restoration of homeostasis in critical illness.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101451

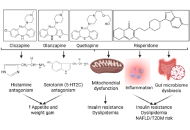
Psychiatric medication is vital in the treatment of a wide range of mental and behavioral health conditions, but has moderate metabolic consequences. The common side effects are weight gain, dyslipidemia, increased adiposity, elevated body mass index, increased insulin resistance, and metabolic alterations. Metabolic risk is lower with antidepressants than with antipsychotics. The side effects are linked to the metabolic syndrome, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular diseases, dysglycemia and diabetes, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome are common complications associated with the use of antipsychotics. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend the metabolic alterations and develop strategies for early detection and intervention to mitigate these effects. This review discusses the metabolic alterations associated with common antipsychotic medications, followed by strategies to attenuate the effects.
Psychiatric medication is vital in the treatment of a wide range of mental and behavioral health conditions, but has moderate metabolic consequences. The common side effects are weight gain, dyslipidemia, increased adiposity, elevated body mass index, increased insulin resistance, and metabolic alterations. Metabolic risk is lower with antidepressants than with antipsychotics. The side effects are linked to the metabolic syndrome, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular diseases, dysglycemia and diabetes, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome are common complications associated with the use of antipsychotics. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend the metabolic alterations and develop strategies for early detection and intervention to mitigate these effects. This review discusses the metabolic alterations associated with common antipsychotic medications, followed by strategies to attenuate the effects.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101450
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance

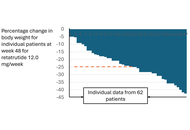
In this Commentary, we highlight the following issues concerning the development of increasingly more powerful incretin-based therapeutics (IBT) that to date have not been addressed with the attention they may deserve: 1. The appropriateness of BMI-based inclusion criteria for a drug capable of producing weight loss approaching that seen after bariatric surgery; 2. significant limitations inherent in communicating the results of an obesity trial involving a potent IBT; 3. the one-size-fits-all dosing strategies in trials may introduce new challenges for sponsors in the race to develop increasingly powerful IBT; 4. the currently imposed limitations on what can be communicated in the approved IBT product label create an advantageously unlevel playing field for opportunists such as compounding pharmacies. Proposals on how to address these issues are made in the text. While it is realized that the presented topics and solutions are not without controversy, they are intended to provoke further discussion.
In this Commentary, we highlight the following issues concerning the development of increasingly more powerful incretin-based therapeutics (IBT) that to date have not been addressed with the attention they may deserve: 1. The appropriateness of BMI-based inclusion criteria for a drug capable of producing weight loss approaching that seen after bariatric surgery; 2. significant limitations inherent in communicating the results of an obesity trial involving a potent IBT; 3. the one-size-fits-all dosing strategies in trials may introduce new challenges for sponsors in the race to develop increasingly powerful IBT; 4. the currently imposed limitations on what can be communicated in the approved IBT product label create an advantageously unlevel playing field for opportunists such as compounding pharmacies. Proposals on how to address these issues are made in the text. While it is realized that the presented topics and solutions are not without controversy, they are intended to provoke further discussion.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101449
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance

Aim:
To investigate the natural history and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in Chinese adults using a community-based longitudinal cohort.
Methods:
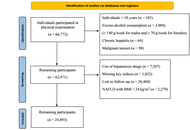
We analyzed data from 24,893 adults in the Beijing Health Management Cohort (2016–2021) with annual follow-up, including questionnaires, physical examinations, and laboratory tests. Participants were categorized into three states: healthy (S1, n = 17,906), NAFLD with body mass index (BMI) < 24 kg/m2 (S2, n = 1,139), and NAFLD with BMI ≥ 24 kg/m2 (S3, n = 5,848). Transition probabilities, mean sojourn times, and determinants of progression were estimated using a multi-state Markov model, with analyses stratified by sex.
Results:
Most individuals remained in their baseline state. Females in S1 were more likely to stay healthy than males (93.76% vs. 83.52%), while males had a higher risk of progression to S3 (12.59% vs. 4.23%). Females in S3 had a greater chance of reverting to S1 (21.33% vs. 18.18%). Mean sojourn time in S1 was longer for females (18.58 vs. 6.97 years), whereas males spent more time in S3 (5.37 vs. 4.18 years). Age, hyperuricemia, abdominal obesity, high triglycerides, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) significantly increased the risk of progression.
Conclusions:
Sex differences strongly affect NAFLD progression in Chinese adults. Males are more likely to deteriorate, while females show higher recovery. Metabolic factors and obesity are key targets for early prevention and intervention.
Aim:
To investigate the natural history and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in Chinese adults using a community-based longitudinal cohort.
Methods:
We analyzed data from 24,893 adults in the Beijing Health Management Cohort (2016–2021) with annual follow-up, including questionnaires, physical examinations, and laboratory tests. Participants were categorized into three states: healthy (S1, n = 17,906), NAFLD with body mass index (BMI) < 24 kg/m2 (S2, n = 1,139), and NAFLD with BMI ≥ 24 kg/m2 (S3, n = 5,848). Transition probabilities, mean sojourn times, and determinants of progression were estimated using a multi-state Markov model, with analyses stratified by sex.
Results:
Most individuals remained in their baseline state. Females in S1 were more likely to stay healthy than males (93.76% vs. 83.52%), while males had a higher risk of progression to S3 (12.59% vs. 4.23%). Females in S3 had a greater chance of reverting to S1 (21.33% vs. 18.18%). Mean sojourn time in S1 was longer for females (18.58 vs. 6.97 years), whereas males spent more time in S3 (5.37 vs. 4.18 years). Age, hyperuricemia, abdominal obesity, high triglycerides, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) significantly increased the risk of progression.
Conclusions:
Sex differences strongly affect NAFLD progression in Chinese adults. Males are more likely to deteriorate, while females show higher recovery. Metabolic factors and obesity are key targets for early prevention and intervention.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101448

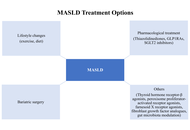
Fatty liver, defined as lipid accumulation in more than 5% of hepatocytes, has become an increasingly important contributor to liver cirrhosis, particularly as viral hepatitis is being brought under control through vaccination and antiviral therapies. Abdominal obesity and insulin resistance play a central role in its pathogenesis. The global burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), continues to rise in parallel with the increasing prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). While meta-analyses indicate that the overall worldwide prevalence of MASLD is approximately 30%, higher rates have been reported in regions such as Latin America and North America. Among individuals with T2DM, the prevalence may reach up to 65%, and MASLD in these patients frequently progresses to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and advanced fibrosis. Shared pathogenic mechanisms—most notably insulin resistance and chronic low-grade inflammation—drive disease progression, contributing to increased morbidity and mortality. The bidirectional relationship is further underscored by the observation that MASLD itself predisposes to the development of T2DM. In addition, the coexistence of MASLD and T2DM may exert a synergistic effect on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, and emerging evidence suggests that MASLD may represent an independent risk factor for CVD. Consequently, individuals with both MASLD and T2DM should be recognized as a particularly high-risk population requiring comprehensive monitoring of both hepatic and cardiovascular health. In this review, we aim to provide a concise overview of the etiopathogenesis, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies related to the MASLD-T2DM interface, a global health challenge that can be regarded as a pandemic of modern times.
Fatty liver, defined as lipid accumulation in more than 5% of hepatocytes, has become an increasingly important contributor to liver cirrhosis, particularly as viral hepatitis is being brought under control through vaccination and antiviral therapies. Abdominal obesity and insulin resistance play a central role in its pathogenesis. The global burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), continues to rise in parallel with the increasing prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). While meta-analyses indicate that the overall worldwide prevalence of MASLD is approximately 30%, higher rates have been reported in regions such as Latin America and North America. Among individuals with T2DM, the prevalence may reach up to 65%, and MASLD in these patients frequently progresses to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and advanced fibrosis. Shared pathogenic mechanisms—most notably insulin resistance and chronic low-grade inflammation—drive disease progression, contributing to increased morbidity and mortality. The bidirectional relationship is further underscored by the observation that MASLD itself predisposes to the development of T2DM. In addition, the coexistence of MASLD and T2DM may exert a synergistic effect on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, and emerging evidence suggests that MASLD may represent an independent risk factor for CVD. Consequently, individuals with both MASLD and T2DM should be recognized as a particularly high-risk population requiring comprehensive monitoring of both hepatic and cardiovascular health. In this review, we aim to provide a concise overview of the etiopathogenesis, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies related to the MASLD-T2DM interface, a global health challenge that can be regarded as a pandemic of modern times.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101446
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

Hormonal dysregulation plays a central role in aging, exerting a profound, multidimensional impact on quality of life. This narrative review examines the impact of hormonal changes in understanding how age-dependent alterations in key hormonal axes, specifically those related to insulin, IGF-1, cortisol, thyroid hormones, parathyroid hormone, and sex hormones, affect metabolic, musculoskeletal, cognitive, and reproductive health. Altered hormone secretion and receptor sensitivity contribute to conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, sarcopenia, cognitive decline, and disrupted sleep patterns. Age-related shifts in thyroid and parathyroid function, including decreased T3 conversion and elevated PTH, further compound these physiological changes. These hormonal imbalances manifest as a multidimensional burden on quality of life, encompassing physical, cognitive, and psychosocial domains, which are particularly pronounced in postmenopausal women. Emerging therapies targeting GH secretion, myostatin inhibition, heat shock proteins, and IGF-1 offer promising avenues for mitigating age-associated symptoms and improving quality of life.
Hormonal dysregulation plays a central role in aging, exerting a profound, multidimensional impact on quality of life. This narrative review examines the impact of hormonal changes in understanding how age-dependent alterations in key hormonal axes, specifically those related to insulin, IGF-1, cortisol, thyroid hormones, parathyroid hormone, and sex hormones, affect metabolic, musculoskeletal, cognitive, and reproductive health. Altered hormone secretion and receptor sensitivity contribute to conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, sarcopenia, cognitive decline, and disrupted sleep patterns. Age-related shifts in thyroid and parathyroid function, including decreased T3 conversion and elevated PTH, further compound these physiological changes. These hormonal imbalances manifest as a multidimensional burden on quality of life, encompassing physical, cognitive, and psychosocial domains, which are particularly pronounced in postmenopausal women. Emerging therapies targeting GH secretion, myostatin inhibition, heat shock proteins, and IGF-1 offer promising avenues for mitigating age-associated symptoms and improving quality of life.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101447
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging

Adenylyl cyclase 5 knockout (AC5 KO) is a healthful longevity model; not only do the AC5 KO mice live a third longer than wild-type (WT) mice, but they are also protected against obesity, diabetes, heart failure, and exercise intolerance, mediated by anti-apoptosis, cell survival, myocardial biogenesis, and anti-oxidative stress mechanisms. To translate these salutary effects to the clinics, we developed a drug, C90, which recapitulates the AC5 KO model of healthful longevity. We then examined its effects on glucose tolerance and exercise capacity. C90 (30 mg/kg/day) or vehicle was chronically administered to age-matched C57BL/6 mice via an osmotic pump. The WT mice receiving C90 exhibited improved glucose tolerance, following glucose i.v. injection, when compared to the vehicle. Furthermore, the C90-treated mice had a lower fasting glucose level when compared to the vehicle-treated mice (113 ± 6.5 mg/dL vs. 129 ± 4.2 mg/dL, p < 0.05). Additionally, the WT group that received C90 exhibited greater exercise capacity, reflected by longer running distance (384 ± 27 m vs. 253 ± 16 m, p < 0.05) and greater work to exhaustion (18.1 ± 1.5 J vs. 12.4 ± 0.7 J, p < 0.05) than mice receiving vehicle. In view of these findings, C90 is an excellent candidate for clinical development as an effective pharmacological treatment for glucose intolerance and enhancing exercise performance.
Adenylyl cyclase 5 knockout (AC5 KO) is a healthful longevity model; not only do the AC5 KO mice live a third longer than wild-type (WT) mice, but they are also protected against obesity, diabetes, heart failure, and exercise intolerance, mediated by anti-apoptosis, cell survival, myocardial biogenesis, and anti-oxidative stress mechanisms. To translate these salutary effects to the clinics, we developed a drug, C90, which recapitulates the AC5 KO model of healthful longevity. We then examined its effects on glucose tolerance and exercise capacity. C90 (30 mg/kg/day) or vehicle was chronically administered to age-matched C57BL/6 mice via an osmotic pump. The WT mice receiving C90 exhibited improved glucose tolerance, following glucose i.v. injection, when compared to the vehicle. Furthermore, the C90-treated mice had a lower fasting glucose level when compared to the vehicle-treated mice (113 ± 6.5 mg/dL vs. 129 ± 4.2 mg/dL, p < 0.05). Additionally, the WT group that received C90 exhibited greater exercise capacity, reflected by longer running distance (384 ± 27 m vs. 253 ± 16 m, p < 0.05) and greater work to exhaustion (18.1 ± 1.5 J vs. 12.4 ± 0.7 J, p < 0.05) than mice receiving vehicle. In view of these findings, C90 is an excellent candidate for clinical development as an effective pharmacological treatment for glucose intolerance and enhancing exercise performance.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101445
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Strategies for Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders: Current and Future Directions

Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), expected to exceed 700 million cases by 2045, is usually attributed to obesity and peripheral resistance but neglects insulin’s structural integrity. This review introduces the Sulfur-Insulin Deformation Hypothesis, positing T2DM as a sulfur metabolism disorder where mitochondrial suffocation disrupts the transsulfuration pathway [methionine to cysteine via cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and γ-lyase (CGL)], depleting cysteine and glutathione (GSH), impairing protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) activity, and deforming insulin’s disulfide bonds (A6–A11, A7–B7, A20–B19) as a primary trigger of insulin resistance. A literature synthesis was conducted (1995–2025) across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms like “sulfur metabolism”, “insulin misfolding”, and “mitochondrial dysfunction”. From 1,202 articles, 113 studies were selected, including in vitro insulin folding models, animal metabolic stress data, human sulfur biomarker analyses, and trials of sulfur donors (e.g., N-acetylcysteine). Mitochondrial dysfunction reduces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), depleting cysteine and GSH by 30–73.8% (red blood cell GSH: 1.78 ± 0.28 µmol/g vs. 6.75 ± 0.47 µmol/g Hb, P < 0.001), elevating reactive oxygen species (ROS). This impairs PDI isoforms (PDIA1, PDIA3, PDIA4), disrupting insulin bonds; the A6–A11 bond loses 50–70% affinity [r = –0.65, P < 0.05 for homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)], hindering phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K-Akt) signaling and glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation. In 225 T2DM patients, PDIA4 elevation correlated with glucose (r = 0.62, P < 0.01) and reduced sensitivity (r = –0.67, P < 0.01). PDIA4 inhibition [presenilin 1 (PS1), IC50 = 4 μM] cuts ROS by 50% (P < 0.01), lowers hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) by 1.2% (P < 0.05), and boosts β-cell survival by 30% (P < 0.05). Redox-mediated chain splitting degrades 20% of insulin (0.40 nmol/kg/min) at –137 mV, modulated by GSH. The hypothesis redefines T2DM as a sulfur-driven structural disorder, unveiling the gut-mitochondria-sulfur-insulin axis and advocating sulfur-centric therapies (e.g., N-acetylcysteine, methylsulfonylmethane).
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), expected to exceed 700 million cases by 2045, is usually attributed to obesity and peripheral resistance but neglects insulin’s structural integrity. This review introduces the Sulfur-Insulin Deformation Hypothesis, positing T2DM as a sulfur metabolism disorder where mitochondrial suffocation disrupts the transsulfuration pathway [methionine to cysteine via cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and γ-lyase (CGL)], depleting cysteine and glutathione (GSH), impairing protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) activity, and deforming insulin’s disulfide bonds (A6–A11, A7–B7, A20–B19) as a primary trigger of insulin resistance. A literature synthesis was conducted (1995–2025) across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms like “sulfur metabolism”, “insulin misfolding”, and “mitochondrial dysfunction”. From 1,202 articles, 113 studies were selected, including in vitro insulin folding models, animal metabolic stress data, human sulfur biomarker analyses, and trials of sulfur donors (e.g., N-acetylcysteine). Mitochondrial dysfunction reduces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), depleting cysteine and GSH by 30–73.8% (red blood cell GSH: 1.78 ± 0.28 µmol/g vs. 6.75 ± 0.47 µmol/g Hb, P < 0.001), elevating reactive oxygen species (ROS). This impairs PDI isoforms (PDIA1, PDIA3, PDIA4), disrupting insulin bonds; the A6–A11 bond loses 50–70% affinity [r = –0.65, P < 0.05 for homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)], hindering phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K-Akt) signaling and glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation. In 225 T2DM patients, PDIA4 elevation correlated with glucose (r = 0.62, P < 0.01) and reduced sensitivity (r = –0.67, P < 0.01). PDIA4 inhibition [presenilin 1 (PS1), IC50 = 4 μM] cuts ROS by 50% (P < 0.01), lowers hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) by 1.2% (P < 0.05), and boosts β-cell survival by 30% (P < 0.05). Redox-mediated chain splitting degrades 20% of insulin (0.40 nmol/kg/min) at –137 mV, modulated by GSH. The hypothesis redefines T2DM as a sulfur-driven structural disorder, unveiling the gut-mitochondria-sulfur-insulin axis and advocating sulfur-centric therapies (e.g., N-acetylcysteine, methylsulfonylmethane).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101444
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

Background:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) frequently coexist, showing a bidirectional relationship. MAFLD increases the risk of T2DM, while T2DM independently raises the likelihood of MAFLD.
Methods:
A comprehensive review was carried out on recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses by searching databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane database of systematic reviews, covering studies from inception to February 2025. Additionally, manual searches of reference lists were conducted. Inclusion criteria involved systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating treatment effects on health outcomes in individuals with T2DM and MAFLD.
Results:
The search yielded 19 meta-analyses and 112 health outcomes from 622 unique articles. Most analyses focused on treatment effects on endocrine metabolic outcomes (n = 28), lipid metabolic indicators (n = 26), liver health indicators (n = 34), and body composition indicators (n = 24). High-quality evidence indicates that high-intensity interval training improves insulin resistance and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. High-quality evidence also indicates sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors improved liver proton density fat fraction and fatty liver index, while glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), particularly liraglutide, enhanced subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT). Moderate-quality evidence shows that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors enhanced insulin resistance and GLP-1RAs benefited triglycerides, aspartate transaminase, liver fat, and visceral adipose tissue. SGLT-2 inhibitors improved controlled attenuation parameter, body mass index (BMI), SAT, visceral fat mass, and moderate-intensity continuous training improved triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Fifty-six outcomes were rated as low-quality evidence, and five as very low-quality.
Discussion:
GLP-1RAs, SGLT-2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, exercise, and Chinese Herbal Medicines benefited liver health, glycemic control in T2DM with MAFLD, and impacted body composition and lipid metabolism.
Background:
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) frequently coexist, showing a bidirectional relationship. MAFLD increases the risk of T2DM, while T2DM independently raises the likelihood of MAFLD.
Methods:
A comprehensive review was carried out on recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses by searching databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane database of systematic reviews, covering studies from inception to February 2025. Additionally, manual searches of reference lists were conducted. Inclusion criteria involved systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating treatment effects on health outcomes in individuals with T2DM and MAFLD.
Results:
The search yielded 19 meta-analyses and 112 health outcomes from 622 unique articles. Most analyses focused on treatment effects on endocrine metabolic outcomes (n = 28), lipid metabolic indicators (n = 26), liver health indicators (n = 34), and body composition indicators (n = 24). High-quality evidence indicates that high-intensity interval training improves insulin resistance and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. High-quality evidence also indicates sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors improved liver proton density fat fraction and fatty liver index, while glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), particularly liraglutide, enhanced subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT). Moderate-quality evidence shows that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors enhanced insulin resistance and GLP-1RAs benefited triglycerides, aspartate transaminase, liver fat, and visceral adipose tissue. SGLT-2 inhibitors improved controlled attenuation parameter, body mass index (BMI), SAT, visceral fat mass, and moderate-intensity continuous training improved triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Fifty-six outcomes were rated as low-quality evidence, and five as very low-quality.
Discussion:
GLP-1RAs, SGLT-2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, exercise, and Chinese Herbal Medicines benefited liver health, glycemic control in T2DM with MAFLD, and impacted body composition and lipid metabolism.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101443
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Strategies for Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders: Current and Future Directions

Background:
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), defined as glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy, poses a significant and growing public health challenge in India. With India housing the world’s largest diabetes population, the rising prevalence of GDM has profound implications for maternal and neonatal health, contributing to complications including preeclampsia, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycaemia, and increased lifelong risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for both mother and child.
Methods:
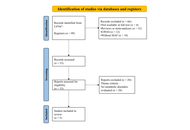
We conducted a systematic literature search of PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library for studies published between January 2019 and December 2024, with seminal works from 2015–2018. Search terms included “gestational diabetes mellitus”, “India”, “screening”, “prevalence”, “management”, and “health systems”. Eligible studies included peer-reviewed articles, government reports, and systematic reviews focusing on Indian populations. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data. The PRISMA 2020 framework guided reporting.
Results:
From 2,847 initial records, 156 studies met the inclusion criteria. GDM prevalence in India ranges from 7.2% to 21.4%, with substantial regional variations. Southern states consistently report higher prevalence (15–22%) compared to northern (10–17%) and eastern regions (8–15%). Key challenges identified include low awareness among pregnant women (32% rural, 58% urban) and healthcare providers, inconsistent adoption of evidence-based guidelines (41% of facilities following standardized protocols), severe resource and infrastructural constraints, and significant socioeconomic barriers. Laboratory facilities for oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) are available in only 34% of community health centers and 12% of primary health centers. Digital health interventions show promise but face implementation barriers, including limited smartphone penetration (45% in rural areas) and inadequate Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) workforce training (34% completion rate).
Discussion:
Despite the escalating burden of GDM in India, numerous unmet needs persist across the care continuum. This review proposes actionable recommendations, including simplified, cost-effective screening strategies, capacity building, integration into existing maternal health programs, and robust postpartum follow-up systems. Success requires sustained commitment to collaborative research, policy initiatives, and integrated, equitable, and sustainable GDM care approaches.
Background:
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), defined as glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy, poses a significant and growing public health challenge in India. With India housing the world’s largest diabetes population, the rising prevalence of GDM has profound implications for maternal and neonatal health, contributing to complications including preeclampsia, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycaemia, and increased lifelong risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for both mother and child.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic literature search of PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library for studies published between January 2019 and December 2024, with seminal works from 2015–2018. Search terms included “gestational diabetes mellitus”, “India”, “screening”, “prevalence”, “management”, and “health systems”. Eligible studies included peer-reviewed articles, government reports, and systematic reviews focusing on Indian populations. Two reviewers independently screened and extracted data. The PRISMA 2020 framework guided reporting.
Results:
From 2,847 initial records, 156 studies met the inclusion criteria. GDM prevalence in India ranges from 7.2% to 21.4%, with substantial regional variations. Southern states consistently report higher prevalence (15–22%) compared to northern (10–17%) and eastern regions (8–15%). Key challenges identified include low awareness among pregnant women (32% rural, 58% urban) and healthcare providers, inconsistent adoption of evidence-based guidelines (41% of facilities following standardized protocols), severe resource and infrastructural constraints, and significant socioeconomic barriers. Laboratory facilities for oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) are available in only 34% of community health centers and 12% of primary health centers. Digital health interventions show promise but face implementation barriers, including limited smartphone penetration (45% in rural areas) and inadequate Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) workforce training (34% completion rate).
Discussion:
Despite the escalating burden of GDM in India, numerous unmet needs persist across the care continuum. This review proposes actionable recommendations, including simplified, cost-effective screening strategies, capacity building, integration into existing maternal health programs, and robust postpartum follow-up systems. Success requires sustained commitment to collaborative research, policy initiatives, and integrated, equitable, and sustainable GDM care approaches.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101442

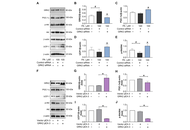
Aim:
Baicalin and ginsenoside Rb1 show the ability to promote adipocyte browning, but their effects, especially combined treatment, and the related mechanisms under pathological conditions are less known. The study investigated the regulation of browning markers by baicalin and Rb1 under lipid overload and explored the potential implication of a serine/threonine protein kinase G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2).
Methods:
The 3T3-L1 cells under palmitic acid (PA) stimulation and male ICR mice on a high-fat diet (HFD) challenge were used to evaluate the effects of drugs.
Results:
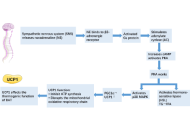
GRK2 silencing and overexpression inversely regulated the protein abundance of PGC-1α and UCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Baicalin, Rb1, and their combination decreased the PA-induced elevation of GRK2 while increasing the thermogenetic markers at the protein and mRNA levels. In vivo, the tested drugs restored the expression of thermogenetic and mitochondrial biogenetic markers in the inguinal white adipose tissue (WAT) of HFD-fed mice. Consistently, the drug-treated mice displayed an improved metabolic profile. The baicalin-Rb1 combination showed a more potent effect in some examinations, and its effect was comparable to that of GRK2 inhibitor paroxetine or AMP-activated protein kinase activator metformin.
Conclusions:
Baicalin and Rb1, alone or in combination, improved the browning of adipocytes during differentiation and prevented the whitening shift of WAT on an HFD, which was associated with the downregulation of GRK2. The study expands the understanding of the anti-obesity effects of baicalin and Rb1 and the potential of Scutellariae Radix-Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma compatibility for treating obesity-associated metabolic diseases.
Aim:
Baicalin and ginsenoside Rb1 show the ability to promote adipocyte browning, but their effects, especially combined treatment, and the related mechanisms under pathological conditions are less known. The study investigated the regulation of browning markers by baicalin and Rb1 under lipid overload and explored the potential implication of a serine/threonine protein kinase G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2).
Methods:
The 3T3-L1 cells under palmitic acid (PA) stimulation and male ICR mice on a high-fat diet (HFD) challenge were used to evaluate the effects of drugs.
Results:
GRK2 silencing and overexpression inversely regulated the protein abundance of PGC-1α and UCP-1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Baicalin, Rb1, and their combination decreased the PA-induced elevation of GRK2 while increasing the thermogenetic markers at the protein and mRNA levels. In vivo, the tested drugs restored the expression of thermogenetic and mitochondrial biogenetic markers in the inguinal white adipose tissue (WAT) of HFD-fed mice. Consistently, the drug-treated mice displayed an improved metabolic profile. The baicalin-Rb1 combination showed a more potent effect in some examinations, and its effect was comparable to that of GRK2 inhibitor paroxetine or AMP-activated protein kinase activator metformin.
Conclusions:
Baicalin and Rb1, alone or in combination, improved the browning of adipocytes during differentiation and prevented the whitening shift of WAT on an HFD, which was associated with the downregulation of GRK2. The study expands the understanding of the anti-obesity effects of baicalin and Rb1 and the potential of Scutellariae Radix-Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma compatibility for treating obesity-associated metabolic diseases.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101441
This article belongs to the special issue Regulators of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism and Energy Balance
 Previous
Previous