Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases
Guest Editors
Dr. Ta-Yuan Chang E-Mail
Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, New Hampshire, USA
Research Keywords: cholesterol metabolism; membrane proteins; Alzheimer's disease; NPC disease; Vascular dementia
Dr. Catherine Chang E-Mail
Principal Research Scientist, Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, New Hampshire, USA
Research Keywords: cholesterol metabolism; structure and function analysis of ACAT/SOAT; membrane proteins; Alzheimer's disease; NPC disease
About the Special lssue
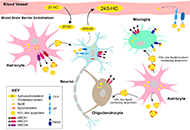
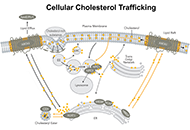
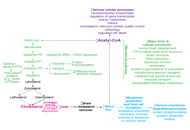
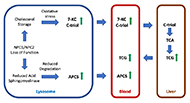
Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that is essential to the structure and function of biological membranes, as well as the growth and maintenance of all mammalian cells. The metabolites of cholesterol, including oxysterols, neurosteroids, and bile acids, play important regulatory roles in mammalian physiology. Increasing evidence implicates the involvement of cholesterol dyshomeostasis in diverse neurological diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, autism, Huntington disease, multiple sclerosis, Niemann-Pick type C disease, Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome, and vascular dementia. The mechanistic connections between cholesterol and the pathophysiology of these diseases are as yet inadequately understood.
To stimulate research in this burgeoning area, we are organizing a special issue of the Journal, entitled “Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases,” that will contain several invited reviews written by leading scientists in the relevant research fields. We are also soliciting additional relevant manuscripts that describe original research, meta-analysis, commentary, or editorial. Manuscripts that address the following areas will be particularly welcome: roles of cholesterol or its metabolites in the brain; brain-penetrating agents to facilitate CNS cholesterol homeostasis; and neurological alterations caused by cholesterol imbalance in the CNS or by hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.
Each qualified manuscript will undergo prompt and thorough peer-review. The published issue will receive wide promotion by the Journal to the international scientific community. The goal of this special issue is ultimately to stimulate the discovery and development of novel, cholesterol-related neuroprotective therapies by scientists working in the basic, translational, and clinical neuroscience arenas. This issue can also be used as a timely resource for graduate students and postdoctoral fellows entering the field of neurodegeneration research.
Keywords: cholesterol; membranes; neuroscience; neuroprotective therapies; neurological disease
Published Articles