Remedial benefits of natural products in inflammation and cancer
Guest Editors
Noah Isakov E-Mail
Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Beer Sheva, Israel
Research Keywords: cancer immunobiology; T cell activation; signal transduction; protooncogenes; adaptor proteins; kinase; phosphatase; isomerase
Ruby John Anto E-Mail
Molecular Bioassay Laboratory, Institute of Advanced Virology, Thiruvananthapuram, India
Research Keywords: bioprospecting for anticancer molecules; chemosensitization; chemoprevention; carcinogenesis; chemotherapeutics
About the Special lssue
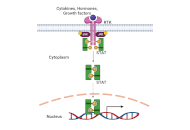
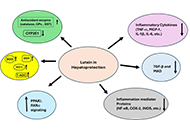
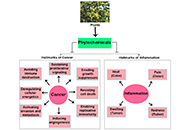
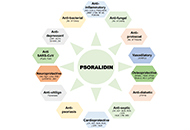
The utilization of natural products as remedies for the treatment of a wide range of diseases has been practiced since ancient times. The earliest indication of human use of natural products was found in the cuneiform writing on clay tablets, dating to circa 2600 B.C, illustrating that people from the Near East region of Mesopotamia had been making use of the health benefits of oil extracts from plants such as Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens) and Myrrh (Commiphora), to relieve conditions like coughs and inflammation. Interestingly, these extracts are still being used today as remedies for these illnesses. Over the past few decades, tremendous effort has gone into isolating and characterizing novel natural compounds from plants, animals, and other living organisms. Ethno-pharmacological studies and more recent usage of cutting-edge molecular technologies, have led to the discovery of numerous active natural compounds and structurally related analogues. Some of these compounds are currently being used as effective medications for the treatment of distinct types of cancer as well as inflammatory and infectious diseases.
This Special Issue on remedial benefits of natural products in inflammation and cancer is devoted to in-depth research on natural products, descriptions of their biological effects, evaluation of their therapeutic properties, and investigation of their mechanisms of action.
Areas of interest include, but are not limited to:
Discovery, identification, and characterization of natural products
Technological advances in the discovery of drugs derived from natural products
Pharmacological models in the study of natural products
The therapeutic benefits of natural products and their derivatives
Effect of natural products on immune functions and anti-cancer responses
Both original research papers and review manuscripts are welcome.
Keywords: natural products; plant extract; bioactive compound; remedies; drug discovery; cancer; inflammation
Published Articles