



Background:
Irreversible pulpitis is commonly associated with reduced success of inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) during root canal treatment, often leading to inadequate intraoperative pain control. Inflammatory mediators can decrease local anesthetic effectiveness and alter nerve response. Preoperative administration of anti-inflammatory drugs has been proposed as a strategy to improve anesthetic success. This review evaluates whether preoperative anti-inflammatory medication enhances the efficacy of IANB in patients with irreversible pulpitis.
Methods:
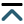
Thirteen articles published between 2014 and 2024 were included in the qualitative analysis following a screening of titles, abstracts, and full texts. The quality of the studies was assessed using the ROBINS tool.
Results:
Premedication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids significantly improves the success of IANB in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Success rates in treated groups generally range between 55% and 73%, compared to less than 40% in control groups. Ibuprofen, ketorolac, and dexamethasone were among the most effective agents.
Discussion:
Premedication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids, especially ibuprofen and dexamethasone, improves the efficacy of IANB in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis, enhancing anesthetic success and reducing intraoperative pain.
Background:
Irreversible pulpitis is commonly associated with reduced success of inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) during root canal treatment, often leading to inadequate intraoperative pain control. Inflammatory mediators can decrease local anesthetic effectiveness and alter nerve response. Preoperative administration of anti-inflammatory drugs has been proposed as a strategy to improve anesthetic success. This review evaluates whether preoperative anti-inflammatory medication enhances the efficacy of IANB in patients with irreversible pulpitis.
Methods:
Thirteen articles published between 2014 and 2024 were included in the qualitative analysis following a screening of titles, abstracts, and full texts. The quality of the studies was assessed using the ROBINS tool.
Results:
Premedication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids significantly improves the success of IANB in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Success rates in treated groups generally range between 55% and 73%, compared to less than 40% in control groups. Ibuprofen, ketorolac, and dexamethasone were among the most effective agents.
Discussion:
Premedication with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids, especially ibuprofen and dexamethasone, improves the efficacy of IANB in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis, enhancing anesthetic success and reducing intraoperative pain.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001381

Aim:
Polypharmacy is a major health concern among older adults and is associated with increased vulnerability and adverse health outcomes. However, limited evidence exists regarding its association with sensory, oral, and dietary functions. This study examined the effects of polypharmacy on these functions using nationally representative data from the 2023 Korean Elderly Survey.
Methods:
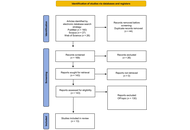
A total of 10,078 community-dwelling adults aged ≥ 65 years were analyzed. Polypharmacy was defined as the use of five or more medications. Sensory function (vision and hearing), oral function (chewing difficulty, swallowing difficulty, denture use, unmet dental needs), and dietary intake (meal frequency, fruit and vegetable consumption) were assessed using structured questionnaires. Chi-square tests and logistic regression analyses were performed. Model 1 adjusted for demographic factors, and Model 2 additionally adjusted for the number of chronic diseases.
Results:
Older adults with polypharmacy showed substantially poorer sensory and oral function than those without polypharmacy. Higher prevalence was observed for vision difficulty (60.5% vs. 40.6%), hearing difficulty (48.7% vs. 20.6%), chewing difficulty (58.9% vs. 30.1%), swallowing difficulty (20.9% vs. 6.7%), and unmet dental care needs (9.6% vs. 3.0%) (all p < 0.001). In the fully adjusted model, polypharmacy remained significantly associated with hearing difficulty, chewing difficulty, swallowing difficulty, denture use, and unmet dental care needs. However, associations between polypharmacy and dietary intake indicators were not statistically significant after adjustment.
Conclusions:
Polypharmacy is significantly associated with hearing and oral functional impairments among older adults, and these associations were attenuated but not fully explained after adjusting for chronic disease burden. These findings highlight the importance of comprehensive geriatric assessment and multidisciplinary care that integrates medication management and oral health. Strategies promoting rational prescribing and monitoring of functional outcomes are essential to mitigate the adverse effects of polypharmacy and support healthy aging.
Aim:
Polypharmacy is a major health concern among older adults and is associated with increased vulnerability and adverse health outcomes. However, limited evidence exists regarding its association with sensory, oral, and dietary functions. This study examined the effects of polypharmacy on these functions using nationally representative data from the 2023 Korean Elderly Survey.
Methods:
A total of 10,078 community-dwelling adults aged ≥ 65 years were analyzed. Polypharmacy was defined as the use of five or more medications. Sensory function (vision and hearing), oral function (chewing difficulty, swallowing difficulty, denture use, unmet dental needs), and dietary intake (meal frequency, fruit and vegetable consumption) were assessed using structured questionnaires. Chi-square tests and logistic regression analyses were performed. Model 1 adjusted for demographic factors, and Model 2 additionally adjusted for the number of chronic diseases.
Results:
Older adults with polypharmacy showed substantially poorer sensory and oral function than those without polypharmacy. Higher prevalence was observed for vision difficulty (60.5% vs. 40.6%), hearing difficulty (48.7% vs. 20.6%), chewing difficulty (58.9% vs. 30.1%), swallowing difficulty (20.9% vs. 6.7%), and unmet dental care needs (9.6% vs. 3.0%) (all p < 0.001). In the fully adjusted model, polypharmacy remained significantly associated with hearing difficulty, chewing difficulty, swallowing difficulty, denture use, and unmet dental care needs. However, associations between polypharmacy and dietary intake indicators were not statistically significant after adjustment.
Conclusions:
Polypharmacy is significantly associated with hearing and oral functional impairments among older adults, and these associations were attenuated but not fully explained after adjusting for chronic disease burden. These findings highlight the importance of comprehensive geriatric assessment and multidisciplinary care that integrates medication management and oral health. Strategies promoting rational prescribing and monitoring of functional outcomes are essential to mitigate the adverse effects of polypharmacy and support healthy aging.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2026.1001380

Aim:
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, and it is often treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Misuse of fluoroquinolones is a known driver of antimicrobial resistance, and de-escalation of antibiotics is not only effective for patient outcomes but also reduces resistance. The aim of this study was to assess the association of fluoroquinolone de-escalation with length of stay (LOS), mortality, and other microbiological culture results in hospitalized adults with CAP.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort investigation took place with adult patients suspected of CAP in a tertiary care center in Jordan. The study examined outcomes for fluoroquinolone de-escalation that included hospital LOS, mortality, and examined the relationship between the results of microbial cultures and the outcome of de-escalation.
Results:
The study sample consisted of 125 patients with a median age of 73 years [interquartile range (IQR) = 24]. Around 65% (n = 81) of the patients were male, and 35% (n = 44) were female. The fluoroquinolone therapy was mostly levofloxacin (99.2%, n = 124). Fluoroquinolone de-escalation was medically justified in 32.8% (n = 41) of patients. When comparing the rate of successful de-escalation between those with positive and negative cultures (after the exclusion of 3 patients), positive cultures were statistically more likely to de-escalate than negative cultures, 61.5% (16/26) to 26.0% (25/96) (p = 0.002). Patients in the successful de-escalation had a statistically shorter length of hospital stay; 12 days (IQR = 8) against the failed/inappropriate group, 18 days (IQR = 11) (p = 0.004). There was no significant difference in mortality; 70.1% (n = 29) survived in the de-escalated group and 76.5% (n = 62) in the failed/inappropriate group (p = 0.514).
Conclusions:
In CAP, fluoroquinolone de-escalation may result in shorter hospital stays but does not alter mortality rates. However, limitations in establishing appropriateness for de-escalation imply the need for further studies to validate the findings.
Aim:
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, and it is often treated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Misuse of fluoroquinolones is a known driver of antimicrobial resistance, and de-escalation of antibiotics is not only effective for patient outcomes but also reduces resistance. The aim of this study was to assess the association of fluoroquinolone de-escalation with length of stay (LOS), mortality, and other microbiological culture results in hospitalized adults with CAP.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort investigation took place with adult patients suspected of CAP in a tertiary care center in Jordan. The study examined outcomes for fluoroquinolone de-escalation that included hospital LOS, mortality, and examined the relationship between the results of microbial cultures and the outcome of de-escalation.
Results:
The study sample consisted of 125 patients with a median age of 73 years [interquartile range (IQR) = 24]. Around 65% (n = 81) of the patients were male, and 35% (n = 44) were female. The fluoroquinolone therapy was mostly levofloxacin (99.2%, n = 124). Fluoroquinolone de-escalation was medically justified in 32.8% (n = 41) of patients. When comparing the rate of successful de-escalation between those with positive and negative cultures (after the exclusion of 3 patients), positive cultures were statistically more likely to de-escalate than negative cultures, 61.5% (16/26) to 26.0% (25/96) (p = 0.002). Patients in the successful de-escalation had a statistically shorter length of hospital stay; 12 days (IQR = 8) against the failed/inappropriate group, 18 days (IQR = 11) (p = 0.004). There was no significant difference in mortality; 70.1% (n = 29) survived in the de-escalated group and 76.5% (n = 62) in the failed/inappropriate group (p = 0.514).
Conclusions:
In CAP, fluoroquinolone de-escalation may result in shorter hospital stays but does not alter mortality rates. However, limitations in establishing appropriateness for de-escalation imply the need for further studies to validate the findings.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001379

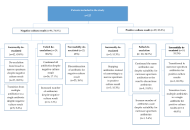
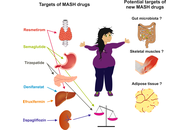
The management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) has evolved significantly, transitioning from a lack of therapeutic options to resmetiroma and semaglutide being licensed for use in MASH. With this evolving backdrop, this perspective article aims to explore the biological and clinical activities of tirzepatide, denifanstat, semaglutide, dapagliflozin, and efruxifermin, for which robust evidence of activity has been published. Tirzepatide and semaglutide, both GLP-1 receptor agonists, have shown significant efficacy in weight loss and metabolic improvements, while dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, offers renal protection alongside metabolic benefits. Denifanstat represents a novel approach targeting inflammation in MASH, potentially addressing the underlying pathophysiology. Efruxifermin is emerging as an innovative agent with dual mechanisms aimed at liver health and metabolic regulation. As we navigate this landscape of therapeutic options, we will discuss the implications for clinical practice and the necessity for personalized treatment strategies in managing MASH effectively. The rapid development of these therapies prompts critical evaluation—are we moving towards optimal treatment paradigms or encountering the challenge of over-treatment? This article seeks to provide insights into these evolving dynamics in MASH management.
The management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) has evolved significantly, transitioning from a lack of therapeutic options to resmetiroma and semaglutide being licensed for use in MASH. With this evolving backdrop, this perspective article aims to explore the biological and clinical activities of tirzepatide, denifanstat, semaglutide, dapagliflozin, and efruxifermin, for which robust evidence of activity has been published. Tirzepatide and semaglutide, both GLP-1 receptor agonists, have shown significant efficacy in weight loss and metabolic improvements, while dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, offers renal protection alongside metabolic benefits. Denifanstat represents a novel approach targeting inflammation in MASH, potentially addressing the underlying pathophysiology. Efruxifermin is emerging as an innovative agent with dual mechanisms aimed at liver health and metabolic regulation. As we navigate this landscape of therapeutic options, we will discuss the implications for clinical practice and the necessity for personalized treatment strategies in managing MASH effectively. The rapid development of these therapies prompts critical evaluation—are we moving towards optimal treatment paradigms or encountering the challenge of over-treatment? This article seeks to provide insights into these evolving dynamics in MASH management.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001378

Aim:
Early and accurate diagnosis of brain tumors is critical for treatment success, but manual magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interpretation has limitations. This study evaluates state-of-the-art Transformer-based architectures to enhance diagnostic efficiency and robustness for this task, aiming to identify models that balance high accuracy with computational feasibility.
Methods:
We systematically compared the performance and computational cost of eleven models from the Vision Transformer (ViT), Data-efficient Image Transformer (DeiT), and Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows (Swin) Transformer families. A publicly available four-class MRI dataset (Glioma, Meningioma, Pituitary, No Tumor) was used for multi-class classification. The dataset was partitioned using stratified sampling and extensively augmented to improve model generalization.
Results:
All evaluated models demonstrated high accuracy (> 98.8%). The Swin-Small and Swin-Large models achieved the highest accuracy of 99.37%. Remarkably, Swin-Small delivered this top-tier performance at a fraction of the computational cost of the Swin-Large model, which is nearly four times its size and with more than double the inference speed (0.54 ms vs. 1.29 ms), showcasing superior operational efficiency.
Conclusions:
The largest model does not inherently guarantee the best performance. Architecturally efficient, mid-sized models like Swin-Small provide an optimal trade-off between diagnostic accuracy and practical clinical applicability. This finding highlights a key direction for developing feasible and effective AI-based diagnostic systems in neuroradiology.
Aim:
Early and accurate diagnosis of brain tumors is critical for treatment success, but manual magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interpretation has limitations. This study evaluates state-of-the-art Transformer-based architectures to enhance diagnostic efficiency and robustness for this task, aiming to identify models that balance high accuracy with computational feasibility.
Methods:
We systematically compared the performance and computational cost of eleven models from the Vision Transformer (ViT), Data-efficient Image Transformer (DeiT), and Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows (Swin) Transformer families. A publicly available four-class MRI dataset (Glioma, Meningioma, Pituitary, No Tumor) was used for multi-class classification. The dataset was partitioned using stratified sampling and extensively augmented to improve model generalization.
Results:
All evaluated models demonstrated high accuracy (> 98.8%). The Swin-Small and Swin-Large models achieved the highest accuracy of 99.37%. Remarkably, Swin-Small delivered this top-tier performance at a fraction of the computational cost of the Swin-Large model, which is nearly four times its size and with more than double the inference speed (0.54 ms vs. 1.29 ms), showcasing superior operational efficiency.
Conclusions:
The largest model does not inherently guarantee the best performance. Architecturally efficient, mid-sized models like Swin-Small provide an optimal trade-off between diagnostic accuracy and practical clinical applicability. This finding highlights a key direction for developing feasible and effective AI-based diagnostic systems in neuroradiology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001377
This article belongs to the special issue Artificial Intelligence in Precision Imaging: Innovations Shaping the Future of Clinical Diagnostics

Aim:
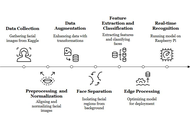
Early screening for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using facial images is promising but often limited by small datasets and the lack of deployable models for resource-constrained settings. To develop and evaluate a lightweight framework that combines a multi-scale vision transformer (MS-ViT) with edge optimization for ASD classification from children’s facial images.
Methods:
We analyzed 2,940 RGB facial images of children obtained from a publicly available Kaggle dataset. Faces were detected, aligned, and cropped (ROI extraction), then normalized; training used standard augmentations. The backbone was an MS-ViT with multi-scale feature aggregation. We performed an 80/20 stratified split (training/testing) and used five-fold cross-validation within the training set for validation (i.e., ~64% training, ~16% validation, and 20% testing per fold). Edge deployment was enabled through post-training optimization. Performance was assessed using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, AUC-ROC, and per-image inference time.
Results:
The best configuration (MS-ViT + Edge + Augmented) achieved an accuracy of 96.85%, sensitivity of 96.09%, specificity of 97.92%, and AUC-ROC of 0.9874. On a Raspberry Pi-class device, the model reached ~181 milliseconds per image, supporting real-time screening.
Conclusions:
The proposed “MS-ViT + Edge + Augmented” framework offers near-state-of-the-art accuracy with low latency on low-power hardware, making it a practical candidate for early ASD screening in clinics and schools. Limitations include dataset size and demographic diversity; prospective clinical validation on larger, multi-site cohorts is warranted.
Aim:
Early screening for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using facial images is promising but often limited by small datasets and the lack of deployable models for resource-constrained settings. To develop and evaluate a lightweight framework that combines a multi-scale vision transformer (MS-ViT) with edge optimization for ASD classification from children’s facial images.
Methods:
We analyzed 2,940 RGB facial images of children obtained from a publicly available Kaggle dataset. Faces were detected, aligned, and cropped (ROI extraction), then normalized; training used standard augmentations. The backbone was an MS-ViT with multi-scale feature aggregation. We performed an 80/20 stratified split (training/testing) and used five-fold cross-validation within the training set for validation (i.e., ~64% training, ~16% validation, and 20% testing per fold). Edge deployment was enabled through post-training optimization. Performance was assessed using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, AUC-ROC, and per-image inference time.
Results:
The best configuration (MS-ViT + Edge + Augmented) achieved an accuracy of 96.85%, sensitivity of 96.09%, specificity of 97.92%, and AUC-ROC of 0.9874. On a Raspberry Pi-class device, the model reached ~181 milliseconds per image, supporting real-time screening.
Conclusions:
The proposed “MS-ViT + Edge + Augmented” framework offers near-state-of-the-art accuracy with low latency on low-power hardware, making it a practical candidate for early ASD screening in clinics and schools. Limitations include dataset size and demographic diversity; prospective clinical validation on larger, multi-site cohorts is warranted.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001376

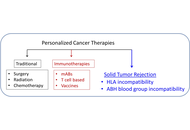
Cancer immunotherapies have become mainstream, targeting tumor elimination via various mechanisms, albeit with varied effectiveness. Here, we review briefly the current landscape of cancer immunotherapies and the central role of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) in them. We then propose a new kind of immunotherapy for solid tumors, where the key is the involvement of antigens and antibodies unrelated to the tumor itself. In this approach, we consider the tumor as akin to a transplanted organ, which can be rejected by two different mechanisms of incompatibility. The first involves the intra-tumor administration of mRNA blueprints of incompatible (to the patient) HLA proteins, leading to their synthesis and, hopefully, elicitation of an anti-tumor immune reaction, assuming immunocompetency. The second therapy involves the direct, intra-tumor administration of anti-A/B/H blood group antibodies lining the blood and lymph vessels of the tumor. In organ transplantation, AB incompatibility leads to organ rejection, and the same effect would be expected when anti-A/B/H antibodies (depending on the patient’s ABO group) are injected into the tumor. Notably, the anti-tumor effect by the preformed anti-blood group antibodies is complement-mediated and should not be affected by tumor immunoevasion. This proposed cancer immunotherapy aimed at promoting tumor rejection via antigen incompatibility offers a novel cancer treatment approach that warrants further investigation.
Cancer immunotherapies have become mainstream, targeting tumor elimination via various mechanisms, albeit with varied effectiveness. Here, we review briefly the current landscape of cancer immunotherapies and the central role of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) in them. We then propose a new kind of immunotherapy for solid tumors, where the key is the involvement of antigens and antibodies unrelated to the tumor itself. In this approach, we consider the tumor as akin to a transplanted organ, which can be rejected by two different mechanisms of incompatibility. The first involves the intra-tumor administration of mRNA blueprints of incompatible (to the patient) HLA proteins, leading to their synthesis and, hopefully, elicitation of an anti-tumor immune reaction, assuming immunocompetency. The second therapy involves the direct, intra-tumor administration of anti-A/B/H blood group antibodies lining the blood and lymph vessels of the tumor. In organ transplantation, AB incompatibility leads to organ rejection, and the same effect would be expected when anti-A/B/H antibodies (depending on the patient’s ABO group) are injected into the tumor. Notably, the anti-tumor effect by the preformed anti-blood group antibodies is complement-mediated and should not be affected by tumor immunoevasion. This proposed cancer immunotherapy aimed at promoting tumor rejection via antigen incompatibility offers a novel cancer treatment approach that warrants further investigation.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001375
This article belongs to the special issue Personalized Medicine in Cancer Therapy

Despite antiretroviral therapy (ART) effectively suppressing viral replication and reducing transmission risk, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection still sustains cycles of chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and dysbiosis of microbiota, driving barrier disruption, microbial translocation, and systemic inflammation. These pathological states accelerate cluster of differentiation 4+ (CD4+) T cell depletion, contribute to viral persistence, and exacerbate the risk of death caused by complications. Current microbiome interventions, such as prebiotics and fecal microbiota transplantations (FMTs), exhibit limited efficacy in regulating HIV infection-associated chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and dysbiosis of microbiota due to transient colonization and poor pathogen specificity. Bacteriophages (phages), which are viruses that precisely target bacteria, represent a promising alternative to ameliorate these intervention deficiencies and to optimize microbiome modulation, especially in HIV patients. Their precise host range and genetic tractability enable targeted modulation of pathogenic, commensal, and pathobiontic microbiota, which in turn enhances immunity against imbalanced microbiome-associated diseases. In this review, we explored phage therapy’s potential to disrupt HIV-associated pathologies affecting the host microbiome. We elucidated the mechanisms by which phage therapy targeted dysbiotic bacteria in HIV and reviewed the supporting preclinical and early clinical evidence for its role in preventing acquisition, enhancing viral clearance, restoring immunity, and managing comorbidities. Finally, we analyzed the challenges in translating phage therapy into clinical practice, which mainly include phage selection, regulatory frameworks, and delivery systems, and evaluated potential solutions to address these challenges. Collectively, our review emphasized how phage therapy can bring a paradigm shift in HIV management, where integrating microbiome-immune crosstalk with virology and synthetic biology may enable a functional cure within the next decade.
Despite antiretroviral therapy (ART) effectively suppressing viral replication and reducing transmission risk, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection still sustains cycles of chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and dysbiosis of microbiota, driving barrier disruption, microbial translocation, and systemic inflammation. These pathological states accelerate cluster of differentiation 4+ (CD4+) T cell depletion, contribute to viral persistence, and exacerbate the risk of death caused by complications. Current microbiome interventions, such as prebiotics and fecal microbiota transplantations (FMTs), exhibit limited efficacy in regulating HIV infection-associated chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction, and dysbiosis of microbiota due to transient colonization and poor pathogen specificity. Bacteriophages (phages), which are viruses that precisely target bacteria, represent a promising alternative to ameliorate these intervention deficiencies and to optimize microbiome modulation, especially in HIV patients. Their precise host range and genetic tractability enable targeted modulation of pathogenic, commensal, and pathobiontic microbiota, which in turn enhances immunity against imbalanced microbiome-associated diseases. In this review, we explored phage therapy’s potential to disrupt HIV-associated pathologies affecting the host microbiome. We elucidated the mechanisms by which phage therapy targeted dysbiotic bacteria in HIV and reviewed the supporting preclinical and early clinical evidence for its role in preventing acquisition, enhancing viral clearance, restoring immunity, and managing comorbidities. Finally, we analyzed the challenges in translating phage therapy into clinical practice, which mainly include phage selection, regulatory frameworks, and delivery systems, and evaluated potential solutions to address these challenges. Collectively, our review emphasized how phage therapy can bring a paradigm shift in HIV management, where integrating microbiome-immune crosstalk with virology and synthetic biology may enable a functional cure within the next decade.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001373
This article belongs to the special issue Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era

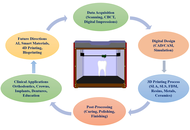
The advent of three-dimensional (3D) printing has transformed modern dentistry by introducing innovative approaches that enhance customization, precision, and efficiency in clinical and educational settings. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent developments and emerging trends in 3D printing applications within dentistry. It explores key domains, including Applications in Orthodontics, Applications in Crown Production, Applications in Implants and Surgical Guides, 3D Printing Applications in Dentures, and Applications in Dental Models and Educational Tools. In orthodontics, 3D printing facilitates the production of patient-specific aligners, brackets, and retainers, improving treatment accuracy and reducing turnaround times. In crown production, the integration of computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) with additive manufacturing allows for the fabrication of highly precise and esthetic prosthetic crowns with rapid chairside delivery. One of the most impactful uses is seen in implants and surgical guides, where 3D printing supports the creation of customized surgical templates and implant components, thus enhancing procedural outcomes and reducing surgical risks. 3D printing has revolutionized denture fabrication by enabling the production of complete and partial dentures with improved fit, material efficiency, and reduced laboratory time. In dental education, the technology is increasingly employed to produce anatomical models, simulated teeth, and other educational tools that improve student training and diagnostic planning. The novelty of this review lies in its integrative perspective linking technical advancements with practical dental applications and highlighting material innovations such as nanocomposites and biocompatible polymers. It also discussed future prospects such as AI-driven design optimization and the role of smart materials in expanding clinical applicability. By presenting a structured overview across multiple specialties, this paper offers valuable insights into how 3D printing is reshaping the future of dental care and education.
The advent of three-dimensional (3D) printing has transformed modern dentistry by introducing innovative approaches that enhance customization, precision, and efficiency in clinical and educational settings. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent developments and emerging trends in 3D printing applications within dentistry. It explores key domains, including Applications in Orthodontics, Applications in Crown Production, Applications in Implants and Surgical Guides, 3D Printing Applications in Dentures, and Applications in Dental Models and Educational Tools. In orthodontics, 3D printing facilitates the production of patient-specific aligners, brackets, and retainers, improving treatment accuracy and reducing turnaround times. In crown production, the integration of computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) with additive manufacturing allows for the fabrication of highly precise and esthetic prosthetic crowns with rapid chairside delivery. One of the most impactful uses is seen in implants and surgical guides, where 3D printing supports the creation of customized surgical templates and implant components, thus enhancing procedural outcomes and reducing surgical risks. 3D printing has revolutionized denture fabrication by enabling the production of complete and partial dentures with improved fit, material efficiency, and reduced laboratory time. In dental education, the technology is increasingly employed to produce anatomical models, simulated teeth, and other educational tools that improve student training and diagnostic planning. The novelty of this review lies in its integrative perspective linking technical advancements with practical dental applications and highlighting material innovations such as nanocomposites and biocompatible polymers. It also discussed future prospects such as AI-driven design optimization and the role of smart materials in expanding clinical applicability. By presenting a structured overview across multiple specialties, this paper offers valuable insights into how 3D printing is reshaping the future of dental care and education.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001374

The brain lipid profile is a complex and dynamic system playing a critical role in regulating various functions, including mood swings, perception, and emotional behavior. Explicitly, the enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the brain and membranes exposes them to reactive free radical species [reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS)], leading to lipid peroxidation (LP), which may result in disruption of cell fluidity and membrane permeability, hindering cellular functions. An increase in LP end products specifically triggers apoptosis and necrosis, potentially resulting in the onset of serious ailments such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, atherosclerosis, and diabetes. Cells are equipped with antioxidant defense systems to combat and scavenge harmful reactive free radical species, thereby maintaining redox homeostasis. Indisputably, the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key player in regulating the cellular antioxidant response by controlling gene expression related to oxidative and electrophilic stress. Nrf2 also influences various cellular processes such as metabolism, inflammation, drug detoxification, and DNA repair. In recent years, several compounds have emerged as Nrf2 modulators, including curcumin, quercetin, anthocyanins, tea polyphenols, kaempferol, hesperetin, and icariin. These compounds play a vital role in regulating various essential Nrf2 upstream activators, thereby modulating Nrf2 pathways, predominantly upregulated by several phytochemical compounds, such as terpenoids like monoterpenes (aucubin, catapol), diterpenes (ginkgolides), triterpenes (ginsenosides), and carotenoids (astaxanthin, lycopene). This review is a modest attempt to provide a comprehensive literature appraisal, facilitating a deeper understanding of the significant role of Nrf2 modulators in obstructing LP and treating serious diseases such as cancer.
The brain lipid profile is a complex and dynamic system playing a critical role in regulating various functions, including mood swings, perception, and emotional behavior. Explicitly, the enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the brain and membranes exposes them to reactive free radical species [reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS)], leading to lipid peroxidation (LP), which may result in disruption of cell fluidity and membrane permeability, hindering cellular functions. An increase in LP end products specifically triggers apoptosis and necrosis, potentially resulting in the onset of serious ailments such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, atherosclerosis, and diabetes. Cells are equipped with antioxidant defense systems to combat and scavenge harmful reactive free radical species, thereby maintaining redox homeostasis. Indisputably, the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key player in regulating the cellular antioxidant response by controlling gene expression related to oxidative and electrophilic stress. Nrf2 also influences various cellular processes such as metabolism, inflammation, drug detoxification, and DNA repair. In recent years, several compounds have emerged as Nrf2 modulators, including curcumin, quercetin, anthocyanins, tea polyphenols, kaempferol, hesperetin, and icariin. These compounds play a vital role in regulating various essential Nrf2 upstream activators, thereby modulating Nrf2 pathways, predominantly upregulated by several phytochemical compounds, such as terpenoids like monoterpenes (aucubin, catapol), diterpenes (ginkgolides), triterpenes (ginsenosides), and carotenoids (astaxanthin, lycopene). This review is a modest attempt to provide a comprehensive literature appraisal, facilitating a deeper understanding of the significant role of Nrf2 modulators in obstructing LP and treating serious diseases such as cancer.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001372
This article belongs to the special issue Lipid Peroxidation and Cancer

Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a significant global health challenge due to its high incidence and mortality, underscoring the need for early detection and precise diagnosis to improve survival outcomes. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning and machine learning (ML), have revolutionized medical imaging and reshaped CRC screening, diagnosis, and prognosis. AI algorithms demonstrate strong performance in analyzing computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and endoscopic images, achieving superior sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency in detecting and characterizing colorectal lesions. These developments enhance lesion identification, risk stratification, and treatment planning, advancing the broader goal of precision medicine. Importantly, AI has the potential to reduce health disparities by extending access to high-quality diagnostic capabilities in low-resource regions where shortages of expert radiologists delay detection. Despite these advantages, implementation in clinical practice remains limited by several challenges, including data bias, lack of population diversity in training datasets, limited generalizability, operator dependency, and integration difficulties within existing workflows. Moreover, ethical and economic considerations—such as algorithm transparency, data privacy, and cost-effectiveness—continue to shape adoption. This review synthesizes current evidence on AI applications in CRC imaging, emphasizing methodological progress, clinical performance, and translational challenges. It also evaluates the readiness of AI systems for real-world use, highlighting ongoing needs for validation, regulatory oversight, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Ultimately, AI holds transformative potential to enhance CRC detection and management, improve diagnostic accuracy, and promote equitable access to advanced screening worldwide, provided that technological, ethical, and implementation barriers are effectively addressed.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a significant global health challenge due to its high incidence and mortality, underscoring the need for early detection and precise diagnosis to improve survival outcomes. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning and machine learning (ML), have revolutionized medical imaging and reshaped CRC screening, diagnosis, and prognosis. AI algorithms demonstrate strong performance in analyzing computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and endoscopic images, achieving superior sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency in detecting and characterizing colorectal lesions. These developments enhance lesion identification, risk stratification, and treatment planning, advancing the broader goal of precision medicine. Importantly, AI has the potential to reduce health disparities by extending access to high-quality diagnostic capabilities in low-resource regions where shortages of expert radiologists delay detection. Despite these advantages, implementation in clinical practice remains limited by several challenges, including data bias, lack of population diversity in training datasets, limited generalizability, operator dependency, and integration difficulties within existing workflows. Moreover, ethical and economic considerations—such as algorithm transparency, data privacy, and cost-effectiveness—continue to shape adoption. This review synthesizes current evidence on AI applications in CRC imaging, emphasizing methodological progress, clinical performance, and translational challenges. It also evaluates the readiness of AI systems for real-world use, highlighting ongoing needs for validation, regulatory oversight, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Ultimately, AI holds transformative potential to enhance CRC detection and management, improve diagnostic accuracy, and promote equitable access to advanced screening worldwide, provided that technological, ethical, and implementation barriers are effectively addressed.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001371

Background:
Although accurate pain assessment is crucial in clinical care, pain evaluation is traditionally based on self-report or observer-based scales. Artificial intelligence (AI) applied to facial expression recognition is promising for objective, automated, and real-time pain assessment.
Methods:
The study followed PRISMA guidelines. We searched PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and the IEEE Xplore databases for the literature published between 2015 and 2025 on the applications of AI for pain assessment via facial expression analysis. Eligible studies included original articles in English applying different AI techniques. Exclusion criteria were neonatal/pediatric populations, non-facial approaches, reviews, case reports, letters, and editorials. Methodological quality was assessed using the RoB 2 tool (for RCTs) and adapted appraisal criteria for AI development studies. This systematic review was registered in PROSPERO (https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/N9PZA).
Results:
A total of 25 studies met the inclusion criteria. Sample sizes ranged from small experimental datasets (n < 30) to larger clinical datasets (n > 500). AI strategies included machine learning models, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks such as long short-term memory (LSTM), transformers, and multimodal fusion models. The accuracy in pain detection varied between ~70% and > 90%, with higher performance observed in deep learning and multimodal frameworks. The risk of bias was overall moderate, with frequent concerns related to small datasets and lack of external validation. No meta-analysis was performed due to heterogeneity in datasets, methodologies, and outcome measures.
Discussion:
AI-based facial expression recognition shows promising accuracy for automated pain assessment, particularly in controlled settings and binary classification tasks. However, evidence remains limited by small sample sizes, methodological heterogeneity, and scarce external validation. Large-scale multicenter studies are required to confirm clinical applicability and to strengthen the certainty of evidence for use in diverse patient populations.
Background:
Although accurate pain assessment is crucial in clinical care, pain evaluation is traditionally based on self-report or observer-based scales. Artificial intelligence (AI) applied to facial expression recognition is promising for objective, automated, and real-time pain assessment.
Methods:
The study followed PRISMA guidelines. We searched PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and the IEEE Xplore databases for the literature published between 2015 and 2025 on the applications of AI for pain assessment via facial expression analysis. Eligible studies included original articles in English applying different AI techniques. Exclusion criteria were neonatal/pediatric populations, non-facial approaches, reviews, case reports, letters, and editorials. Methodological quality was assessed using the RoB 2 tool (for RCTs) and adapted appraisal criteria for AI development studies. This systematic review was registered in PROSPERO (https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/N9PZA).
Results:
A total of 25 studies met the inclusion criteria. Sample sizes ranged from small experimental datasets (n < 30) to larger clinical datasets (n > 500). AI strategies included machine learning models, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks such as long short-term memory (LSTM), transformers, and multimodal fusion models. The accuracy in pain detection varied between ~70% and > 90%, with higher performance observed in deep learning and multimodal frameworks. The risk of bias was overall moderate, with frequent concerns related to small datasets and lack of external validation. No meta-analysis was performed due to heterogeneity in datasets, methodologies, and outcome measures.
Discussion:
AI-based facial expression recognition shows promising accuracy for automated pain assessment, particularly in controlled settings and binary classification tasks. However, evidence remains limited by small sample sizes, methodological heterogeneity, and scarce external validation. Large-scale multicenter studies are required to confirm clinical applicability and to strengthen the certainty of evidence for use in diverse patient populations.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001370
This article belongs to the special issue Innovative Approaches to Chronic Pain Management: from Multidisciplinary Strategies to Artificial Intelligence Perspectives

Aim:
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), especially when multidrug-resistant bacteria cause them, pose serious challenges resulting in higher healthcare expenses, increased morbidity, and higher mortality, and thus, there is a need for new antimicrobial agents. Repurposing an old drug for new applications is an important trend, and in the present study, an anti-breast cancer drug, Tamoxifen, has been screened alone and in combination with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized using Abutilon indicum Linn. against Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus, which are involved in HAIs.
Methods:
The drug and the combination were subjected to antimicrobial potential analysis and the determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) by agar diffusion and microdilution methods. Biofilm formation assays were performed using the crystal violet method to understand biofilm prevention and eradication efficiencies. The synergism in the activities of the drug and the combination with selected antibiotics was studied using checkerboard assay, and the cytotoxic effects of the drug and the combination on L929 cells were analyzed using MTT assay.
Results:
Tamoxifen and the AgNPs showed promising antibacterial activities, and the MICs of the drug were found to be 62.5 µg/mL (E. coli), 31 µg/mL (S. aureus), and 125 µg/mL (E. faecalis). When combined with AgNPs, Tamoxifen showed a 4-fold reduction in the MIC. The drug also displayed promising antibiofilm activities as it reduced mature S. aureus biofilms by 91%, E. faecalis biofilms by 88%, and E. coli biofilms by 73%. AgNPs alone reduced 91%, 91%, and 81% of biofilms by S. aureus, E. faecalis, and E. coli, respectively, and the combination treatment revealed 92% of S. aureus, 94% of E. faecalis, and 82% of E. coli biofilm eradication at their MICs. Tamoxifen also showed synergism when combined with antibiotics—ampicillin and rifampicin and the AgNPs in combination with Tamoxifen revealed no cytotoxic effect on L929 cells at their MICs.
Conclusions:
All the mentioned studies suggest that Tamoxifen alone and in combination with AgNPs has promising antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities, and it can be developed for better treatment options against HAIs as they are safe for eukaryotic cells.
Aim:
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), especially when multidrug-resistant bacteria cause them, pose serious challenges resulting in higher healthcare expenses, increased morbidity, and higher mortality, and thus, there is a need for new antimicrobial agents. Repurposing an old drug for new applications is an important trend, and in the present study, an anti-breast cancer drug, Tamoxifen, has been screened alone and in combination with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized using Abutilon indicum Linn. against Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus, which are involved in HAIs.
Methods:
The drug and the combination were subjected to antimicrobial potential analysis and the determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) by agar diffusion and microdilution methods. Biofilm formation assays were performed using the crystal violet method to understand biofilm prevention and eradication efficiencies. The synergism in the activities of the drug and the combination with selected antibiotics was studied using checkerboard assay, and the cytotoxic effects of the drug and the combination on L929 cells were analyzed using MTT assay.
Results:
Tamoxifen and the AgNPs showed promising antibacterial activities, and the MICs of the drug were found to be 62.5 µg/mL (E. coli), 31 µg/mL (S. aureus), and 125 µg/mL (E. faecalis). When combined with AgNPs, Tamoxifen showed a 4-fold reduction in the MIC. The drug also displayed promising antibiofilm activities as it reduced mature S. aureus biofilms by 91%, E. faecalis biofilms by 88%, and E. coli biofilms by 73%. AgNPs alone reduced 91%, 91%, and 81% of biofilms by S. aureus, E. faecalis, and E. coli, respectively, and the combination treatment revealed 92% of S. aureus, 94% of E. faecalis, and 82% of E. coli biofilm eradication at their MICs. Tamoxifen also showed synergism when combined with antibiotics—ampicillin and rifampicin and the AgNPs in combination with Tamoxifen revealed no cytotoxic effect on L929 cells at their MICs.
Conclusions:
All the mentioned studies suggest that Tamoxifen alone and in combination with AgNPs has promising antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities, and it can be developed for better treatment options against HAIs as they are safe for eukaryotic cells.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001369

Aim:
Aging is associated with reduced inhibitory control, leading to challenges in attention, decision-making, and everyday cognitive tasks. To better understand these difficulties, it is important to adopt well-designed experimental approaches that specifically assess inhibitory control mechanisms. A commonly used tool to assess how inhibitory control changes with age is the Stroop Color and Word Test, which evaluates the capacity to suppress automatic responses in favor of appropriate behavior.
Methods:
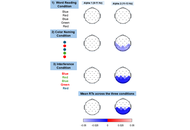
In the present study, a sample of 91 healthy individuals was examined to investigate how cognitive functions underlying Stroop task performance vary across the adult lifespan. Pearson correlations were computed between participants’ age and response times (RTs) recorded in each of the three Stroop conditions, as well as the mean RTs across all conditions. Furthermore, to assess whether these behavioral patterns were mirrored at the neurophysiological level, power spectral density (PSD) analyses were performed on resting-state electroencephalographic recordings.
Results:
In all cases, Pearson correlations were strongly significant, with stronger effects observed as task difficulty increased. At the neurophysiological level, a correlation emerged between RTs and PSD in the occipital region within the alpha 2 frequency band, which, like the behavioral effects, became progressively stronger with increasing task difficulty. In contrast, no significant correlations were observed for the alpha 1 band, suggesting that these neurophysiological changes are specific to higher alpha frequencies linked to increased cognitive demands and inhibitory control processes.
Conclusions:
These findings contribute to a better understanding of the neural mechanisms underlying age-related declines in inhibitory control and may inform the development of interventions aimed at mitigating cognitive deficits in older adults.
Aim:
Aging is associated with reduced inhibitory control, leading to challenges in attention, decision-making, and everyday cognitive tasks. To better understand these difficulties, it is important to adopt well-designed experimental approaches that specifically assess inhibitory control mechanisms. A commonly used tool to assess how inhibitory control changes with age is the Stroop Color and Word Test, which evaluates the capacity to suppress automatic responses in favor of appropriate behavior.
Methods:
In the present study, a sample of 91 healthy individuals was examined to investigate how cognitive functions underlying Stroop task performance vary across the adult lifespan. Pearson correlations were computed between participants’ age and response times (RTs) recorded in each of the three Stroop conditions, as well as the mean RTs across all conditions. Furthermore, to assess whether these behavioral patterns were mirrored at the neurophysiological level, power spectral density (PSD) analyses were performed on resting-state electroencephalographic recordings.
Results:
In all cases, Pearson correlations were strongly significant, with stronger effects observed as task difficulty increased. At the neurophysiological level, a correlation emerged between RTs and PSD in the occipital region within the alpha 2 frequency band, which, like the behavioral effects, became progressively stronger with increasing task difficulty. In contrast, no significant correlations were observed for the alpha 1 band, suggesting that these neurophysiological changes are specific to higher alpha frequencies linked to increased cognitive demands and inhibitory control processes.
Conclusions:
These findings contribute to a better understanding of the neural mechanisms underlying age-related declines in inhibitory control and may inform the development of interventions aimed at mitigating cognitive deficits in older adults.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001368
This article belongs to the special issue Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia

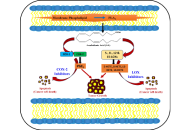
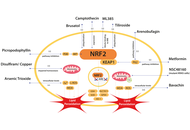
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide and is characterized by a high recurrence rate, limited treatment options, and frequent resistance to systemic therapy. A key factor in this resistance is the persistent activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), a transcription factor that normally protects against oxidative stress but, in malignant hepatocytes, suppresses ferroptosis by restricting lipid peroxidation. This dual function positions NRF2 as a key target for therapeutic modulation in HCC. Recent preclinical studies demonstrate that NRF2 maintains tumor survival by regulating antioxidant and iron management pathways, such as GPX4, SLC7A11, and ferritin, which together mitigate lipid peroxidation and prevent ferroptotic cell death. Multiple pharmacological strategies have been evaluated to counteract this effect, including direct NRF2 inhibitors such as camptothecin (CPT) and brusatol, preoperative modulators such as metformin and picropodophyllin (PPP), and natural compounds such as tiliroside, bavaquine, and arenobufagin. These interventions often show synergistic activity with sorafenib and other standard treatments, while postoperative effectors such as CYP4F11 and the NRF2-SLC7A11-GPX4 axis have emerged as promising additional intervention points. Despite compelling results in vitro and animal model results, several challenges limit its application to clinical practice. These include the lack of dedicated clinical trials, the limited specificity of available inhibitors, tumor heterogeneity, and potential safety concerns in cirrhotic livers. Future research focuses on the development of selective NRF2 modulators, hepatocyte-targeted approaches such as proteolysis-targeted chimeras (PROTACs) and GalNAc-conjugated oligonucleotides, and biomarker-based patient stratification using genomic, immunohistochemical, and transcriptomic indicators of NRF2 activation. Taken together, contextual NRF2 modulation represents a promising strategy to restore sensitivity to ferroptosis, overcome drug resistance, and improve outcomes in HCC patients.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide and is characterized by a high recurrence rate, limited treatment options, and frequent resistance to systemic therapy. A key factor in this resistance is the persistent activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), a transcription factor that normally protects against oxidative stress but, in malignant hepatocytes, suppresses ferroptosis by restricting lipid peroxidation. This dual function positions NRF2 as a key target for therapeutic modulation in HCC. Recent preclinical studies demonstrate that NRF2 maintains tumor survival by regulating antioxidant and iron management pathways, such as GPX4, SLC7A11, and ferritin, which together mitigate lipid peroxidation and prevent ferroptotic cell death. Multiple pharmacological strategies have been evaluated to counteract this effect, including direct NRF2 inhibitors such as camptothecin (CPT) and brusatol, preoperative modulators such as metformin and picropodophyllin (PPP), and natural compounds such as tiliroside, bavaquine, and arenobufagin. These interventions often show synergistic activity with sorafenib and other standard treatments, while postoperative effectors such as CYP4F11 and the NRF2-SLC7A11-GPX4 axis have emerged as promising additional intervention points. Despite compelling results in vitro and animal model results, several challenges limit its application to clinical practice. These include the lack of dedicated clinical trials, the limited specificity of available inhibitors, tumor heterogeneity, and potential safety concerns in cirrhotic livers. Future research focuses on the development of selective NRF2 modulators, hepatocyte-targeted approaches such as proteolysis-targeted chimeras (PROTACs) and GalNAc-conjugated oligonucleotides, and biomarker-based patient stratification using genomic, immunohistochemical, and transcriptomic indicators of NRF2 activation. Taken together, contextual NRF2 modulation represents a promising strategy to restore sensitivity to ferroptosis, overcome drug resistance, and improve outcomes in HCC patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001367
This article belongs to the special issue Lipid Peroxidation and Cancer

Background:
Current treatment for medulloblastoma involves craniospinal irradiation (CSI) with a radiation boost to the posterior fossa and adjuvant chemotherapy following surgical resection. Due to neurotoxic effects of CSI—particularly its impact on cognitive function and intelligence quotient (IQ)—recent efforts have focused on reducing CSI dosage. This systematic review compares standard-dose CSI (SDCSI) versus low-dose CSI (LDCSI) in terms of relapse rate, event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Methods:
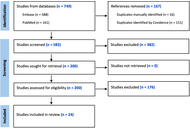
A systematic search was conducted in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Two reviewers independently screened studies for eligibility and extracted data on study design, patient demographics, CSI dosage, chemotherapy regimens, EFS, OS, relapse rates, and reported side effects.
Results:
Out of 749 identified studies, 24 met the inclusion criteria for this review. Reported 5-year EFS ranged from 27.3% to 83%, and 5-year OS ranged from 41 ± 8% to 94.7 ± 3.4%. Commonly reported adverse effects included hematologic toxicity, secondary malignancies, disease progression, nausea/vomiting, and cognitive impairment. IQ outcomes ranged from 71 to 98.6, with studies consistently showing that LDCSI was associated with a smaller decline in IQ compared to SDCSI. Factors such as age, molecular subgroup, and histological features were identified as important variables for risk stratification.
Discussion:
LDCSI combined with chemotherapy may provide sufficient treatment efficacy for medulloblastoma while mitigating neurocognitive decline. Future research should focus on optimizing chemotherapy regimens and refining treatment stratification based on molecular and histological subtypes, particularly in standard- versus high-risk patients.
Background:
Current treatment for medulloblastoma involves craniospinal irradiation (CSI) with a radiation boost to the posterior fossa and adjuvant chemotherapy following surgical resection. Due to neurotoxic effects of CSI—particularly its impact on cognitive function and intelligence quotient (IQ)—recent efforts have focused on reducing CSI dosage. This systematic review compares standard-dose CSI (SDCSI) versus low-dose CSI (LDCSI) in terms of relapse rate, event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Methods:
A systematic search was conducted in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Two reviewers independently screened studies for eligibility and extracted data on study design, patient demographics, CSI dosage, chemotherapy regimens, EFS, OS, relapse rates, and reported side effects.
Results:
Out of 749 identified studies, 24 met the inclusion criteria for this review. Reported 5-year EFS ranged from 27.3% to 83%, and 5-year OS ranged from 41 ± 8% to 94.7 ± 3.4%. Commonly reported adverse effects included hematologic toxicity, secondary malignancies, disease progression, nausea/vomiting, and cognitive impairment. IQ outcomes ranged from 71 to 98.6, with studies consistently showing that LDCSI was associated with a smaller decline in IQ compared to SDCSI. Factors such as age, molecular subgroup, and histological features were identified as important variables for risk stratification.
Discussion:
LDCSI combined with chemotherapy may provide sufficient treatment efficacy for medulloblastoma while mitigating neurocognitive decline. Future research should focus on optimizing chemotherapy regimens and refining treatment stratification based on molecular and histological subtypes, particularly in standard- versus high-risk patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001366

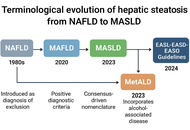
The transition from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) reflects a paradigm shift in hepatology and highlights the need for a more pathophysiologically based classification. The aim of this review is to critically examine the conceptual evolution from NAFLD to MASLD, highlighting the implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, risk stratification, and therapeutic strategies within the broader context of systemic metabolic dysfunction. Unlike the exclusion-based NAFLD definition, MASLD is grounded in positive diagnostic criteria and recognizes hepatic steatosis as a manifestation of metabolic disease. This reclassification improves clinical risk assessment and aligns hepatic care with cardiometabolic management. MASLD is closely linked to insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, chronic inflammation, and gut dysbiosis, which contribute to cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Non-invasive tools (e.g., FIB-4, elastography, ELF score) and emerging biomarkers (e.g., miR-122, CK-18, FGF21) support early diagnosis and personalized approaches. Therapeutically, MASLD management includes lifestyle modification, antidiabetic agents (GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors), PPAR agonists, and novel drugs such as resmetirom. This evolving framework demands integrated, multidisciplinary strategies to address the systemic burden and clinical heterogeneity of MASLD.
The transition from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) reflects a paradigm shift in hepatology and highlights the need for a more pathophysiologically based classification. The aim of this review is to critically examine the conceptual evolution from NAFLD to MASLD, highlighting the implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, risk stratification, and therapeutic strategies within the broader context of systemic metabolic dysfunction. Unlike the exclusion-based NAFLD definition, MASLD is grounded in positive diagnostic criteria and recognizes hepatic steatosis as a manifestation of metabolic disease. This reclassification improves clinical risk assessment and aligns hepatic care with cardiometabolic management. MASLD is closely linked to insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, chronic inflammation, and gut dysbiosis, which contribute to cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Non-invasive tools (e.g., FIB-4, elastography, ELF score) and emerging biomarkers (e.g., miR-122, CK-18, FGF21) support early diagnosis and personalized approaches. Therapeutically, MASLD management includes lifestyle modification, antidiabetic agents (GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors), PPAR agonists, and novel drugs such as resmetirom. This evolving framework demands integrated, multidisciplinary strategies to address the systemic burden and clinical heterogeneity of MASLD.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001365

HIV/AIDS has changed from a deadly disease in the early 1990s to a chronic treatment following huge research efforts. HIV had a great impact due to the long period until its fatal consequences in the form of AIDS appeared. As a consequence, the spread of the disease was global. However, even now, after many years of extensive research, there is still no functional cure or eradication possible. This review provides an overview on HIV/AIDS covering a description of the disease, the mechanism of infection, HIV/AIDS symptoms, the current treatment options, the formation of latent reservoirs, and the efforts to provide a cure of HIV including CCR5Δ32/Δ32 donor stem cell transplantation, gene therapy, broadly neutralizing antibodies, HIV vaccination, chimeric antigen receptor cells, latency-addressing agents, and combination approaches.
HIV/AIDS has changed from a deadly disease in the early 1990s to a chronic treatment following huge research efforts. HIV had a great impact due to the long period until its fatal consequences in the form of AIDS appeared. As a consequence, the spread of the disease was global. However, even now, after many years of extensive research, there is still no functional cure or eradication possible. This review provides an overview on HIV/AIDS covering a description of the disease, the mechanism of infection, HIV/AIDS symptoms, the current treatment options, the formation of latent reservoirs, and the efforts to provide a cure of HIV including CCR5Δ32/Δ32 donor stem cell transplantation, gene therapy, broadly neutralizing antibodies, HIV vaccination, chimeric antigen receptor cells, latency-addressing agents, and combination approaches.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001364
This article belongs to the special issue Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era

Aim:
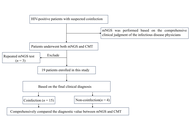
Because of severe immunosuppression, coinfections continue to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality in HIV-infected patients. As the primary method currently used for diagnosing coinfections in HIV-infected patients, conventional microbiological tests (CMTs) often suffer from limitations such as prolonged processing times and low sensitivity, which may delay the initiation of appropriate treatment. This retrospective study aims to explore the applicability of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) as a diagnostic tool compared with CMT.
Methods:
A retrospective study was conducted on HIV-infected patients with coinfections admitted to Peking Union Medical College Hospital between November 2022 and November 2024. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated to evaluate the predictors and determine their sensitivities and specificities. The comprehensive final clinical diagnosis (FCD) was used as the reference standard for evaluating the diagnostic performance of CMT and mNGS. Then, treatment adjustments and outcomes after mNGS and CMT of the HIV-infected patients were also assessed.
Results:
The areas under the ROC curve (AUCs) for CMT and mNGS were 0.600 and 0.775, respectively. When mNGS was combined with CMT, the AUC was 0.833. The sensitivity and specificity of mNGS were 80% and 75%, whereas those of CMT were 20% and 100%. When mNGS was combined with CMT, the sensitivity increased to 86.67%. Among the 15 coinfected HIV patients, 8 patients underwent treatment adjustments on the basis of mNGS results and achieved effective treatment, whereas only 1 patient underwent treatment adjustments solely on the basis of CMT and achieved effective treatment.
Conclusions:
Compared with CMT, mNGS has a better detection rate. mNGS provides an alternative and promising method for identifying coinfections in HIV-positive patients. Thus, the combination of mNGS and CMT is a better diagnostic strategy for coinfections in HIV patients.
Aim:
Because of severe immunosuppression, coinfections continue to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality in HIV-infected patients. As the primary method currently used for diagnosing coinfections in HIV-infected patients, conventional microbiological tests (CMTs) often suffer from limitations such as prolonged processing times and low sensitivity, which may delay the initiation of appropriate treatment. This retrospective study aims to explore the applicability of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) as a diagnostic tool compared with CMT.
Methods:
A retrospective study was conducted on HIV-infected patients with coinfections admitted to Peking Union Medical College Hospital between November 2022 and November 2024. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated to evaluate the predictors and determine their sensitivities and specificities. The comprehensive final clinical diagnosis (FCD) was used as the reference standard for evaluating the diagnostic performance of CMT and mNGS. Then, treatment adjustments and outcomes after mNGS and CMT of the HIV-infected patients were also assessed.
Results:
The areas under the ROC curve (AUCs) for CMT and mNGS were 0.600 and 0.775, respectively. When mNGS was combined with CMT, the AUC was 0.833. The sensitivity and specificity of mNGS were 80% and 75%, whereas those of CMT were 20% and 100%. When mNGS was combined with CMT, the sensitivity increased to 86.67%. Among the 15 coinfected HIV patients, 8 patients underwent treatment adjustments on the basis of mNGS results and achieved effective treatment, whereas only 1 patient underwent treatment adjustments solely on the basis of CMT and achieved effective treatment.
Conclusions:
Compared with CMT, mNGS has a better detection rate. mNGS provides an alternative and promising method for identifying coinfections in HIV-positive patients. Thus, the combination of mNGS and CMT is a better diagnostic strategy for coinfections in HIV patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001363
This article belongs to the special issue Global Perspectives on the Clinical Diagnosis, Treatment, and Functional Cure of HIV Infection in the Post-ART Era

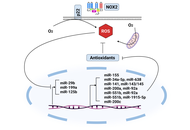
An increasingly popular therapeutic approach for the treatment of cancer is the modification of signaling pathways mediated by oxidative stress. Epigenetic dysregulation serves as a key characteristic of human cancer, as almost half of all cancer cases involve mutations in epigenetic regulators like microRNAs (miRNAs). These small non-coding RNAs play a crucial role by generating functional RNA molecules that range from 18 to 25 nucleotides. miRNAs are essential for regulating gene expression at the mRNA level, but they have also been demonstrated in recent studies to influence the growth and development of cancer. miRNAs play a significant role in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and in various processes influenced by ROS. Therefore, exploring the relationship between ROS and miRNAs is becoming increasingly crucial, as it holds the potential to advance the development of effective cancer therapies and prevention strategies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key characteristics and functional roles of miRNAs that are linked to oxidative stress in different cancers, paving the way for future research and therapeutic innovations. However, a lot of concerns and uncertainties regarding ROS-miRNAs and antioxidant defense systems still need to be resolved despite a great deal of research in this field.
An increasingly popular therapeutic approach for the treatment of cancer is the modification of signaling pathways mediated by oxidative stress. Epigenetic dysregulation serves as a key characteristic of human cancer, as almost half of all cancer cases involve mutations in epigenetic regulators like microRNAs (miRNAs). These small non-coding RNAs play a crucial role by generating functional RNA molecules that range from 18 to 25 nucleotides. miRNAs are essential for regulating gene expression at the mRNA level, but they have also been demonstrated in recent studies to influence the growth and development of cancer. miRNAs play a significant role in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and in various processes influenced by ROS. Therefore, exploring the relationship between ROS and miRNAs is becoming increasingly crucial, as it holds the potential to advance the development of effective cancer therapies and prevention strategies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key characteristics and functional roles of miRNAs that are linked to oxidative stress in different cancers, paving the way for future research and therapeutic innovations. However, a lot of concerns and uncertainties regarding ROS-miRNAs and antioxidant defense systems still need to be resolved despite a great deal of research in this field.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001362
This article belongs to the special issue Lipid Peroxidation and Cancer
 Previous
Previous