




Background:
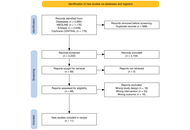
Docetaxel is a cornerstone chemotherapy for metastatic hormone-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Although the standard triweekly regimen is widely used, weekly and biweekly schedules are often employed to improve tolerability, particularly in elderly or frail patients. The comparative efficacy and safety of these dosing strategies remain unclear. This study aimed to systematically compare weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens using a network meta-analysis.
Methods:
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from inception to February 2025. Randomized controlled trials and observational retrospective studies comparing weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens were included. Outcomes assessed were prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate, time to treatment failure or progression, and adverse events. A frequentist random-effects network meta-analysis was conducted using R software.
Results:
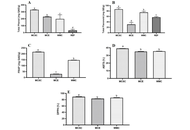
Eleven studies involving 1,238 patients were included. PSA response rates did not differ significantly among regimens; triweekly docetaxel showed a numerically lower response compared with weekly dosing (RR = 0.79, 95% CI 0.52–1.22; I2 = 41.1%). Time to treatment failure was significantly longer with triweekly dosing compared with weekly dosing (mean difference = 10.91 months, 95% CI 6.94–14.87; I2 = 96.8%). Biweekly and triweekly regimens were associated with significantly higher hepatotoxicity compared with weekly dosing (RR = 3.71 and RR = 3.21, respectively; I2 = 0%). Vomiting was more frequent with triweekly docetaxel (RR = 2.47, 95% CI 1.31–4.63). No significant differences were observed for overall adverse events, hematologic toxicity, neuropathy, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, nausea, anorexia, or diarrhea.
Discussion:
Docetaxel dosing schedules show comparable PSA response rates. Triweekly dosing prolongs time to treatment failure but is associated with greater toxicity, whereas weekly dosing offers better tolerability. Treatment decisions should balance efficacy and safety based on individual patient characteristics.
Background:
Docetaxel is a cornerstone chemotherapy for metastatic hormone-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Although the standard triweekly regimen is widely used, weekly and biweekly schedules are often employed to improve tolerability, particularly in elderly or frail patients. The comparative efficacy and safety of these dosing strategies remain unclear. This study aimed to systematically compare weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens using a network meta-analysis.
Methods:
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from inception to February 2025. Randomized controlled trials and observational retrospective studies comparing weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens were included. Outcomes assessed were prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate, time to treatment failure or progression, and adverse events. A frequentist random-effects network meta-analysis was conducted using R software.
Results:
Eleven studies involving 1,238 patients were included. PSA response rates did not differ significantly among regimens; triweekly docetaxel showed a numerically lower response compared with weekly dosing (RR = 0.79, 95% CI 0.52–1.22; I2 = 41.1%). Time to treatment failure was significantly longer with triweekly dosing compared with weekly dosing (mean difference = 10.91 months, 95% CI 6.94–14.87; I2 = 96.8%). Biweekly and triweekly regimens were associated with significantly higher hepatotoxicity compared with weekly dosing (RR = 3.71 and RR = 3.21, respectively; I2 = 0%). Vomiting was more frequent with triweekly docetaxel (RR = 2.47, 95% CI 1.31–4.63). No significant differences were observed for overall adverse events, hematologic toxicity, neuropathy, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, nausea, anorexia, or diarrhea.
Discussion:
Docetaxel dosing schedules show comparable PSA response rates. Triweekly dosing prolongs time to treatment failure but is associated with greater toxicity, whereas weekly dosing offers better tolerability. Treatment decisions should balance efficacy and safety based on individual patient characteristics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002360

This review goes over the impact of caffeine consumption in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), examining epidemiology, clinical outcomes, mechanistic studies, and translational research. Caffeine, a widely consumed methylxanthine, exerts diverse physiological effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Mechanistic and preclinical data offer plausible biological pathways by which caffeine could influence the IBD course. Caffeine’s antagonism of adenosine receptors may modulate immune cell activation and cytokine release; its effects on gut motility and secretion can alter symptom perception, and caffeine-mediated changes in intestinal epithelial barrier function, oxidative stress, and the gut microbiome have been demonstrated. These effects make it a lucrative investigational option, and various studies have demonstrated that caffeine intake may reduce the incidence of IBD and may even have disease-modifying effects in regular consumers. However, differences in caffeine source (coffee, tea, soda), dose, concurrent dietary patterns, and disease subtype (Crohn’s disease versus ulcerative colitis) limit definitive causal inference. Clinical implications remain cautious: while moderate caffeine intake may be tolerable and even helpful for many patients, individualized assessment is advisable, particularly for those with symptom-triggering sensitivity or overlapping functional bowel disorders. Future research should target mechanistic links and clinically meaningful outcomes to inform evidence-based dietary guidance for people with IBD.
This review goes over the impact of caffeine consumption in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), examining epidemiology, clinical outcomes, mechanistic studies, and translational research. Caffeine, a widely consumed methylxanthine, exerts diverse physiological effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Mechanistic and preclinical data offer plausible biological pathways by which caffeine could influence the IBD course. Caffeine’s antagonism of adenosine receptors may modulate immune cell activation and cytokine release; its effects on gut motility and secretion can alter symptom perception, and caffeine-mediated changes in intestinal epithelial barrier function, oxidative stress, and the gut microbiome have been demonstrated. These effects make it a lucrative investigational option, and various studies have demonstrated that caffeine intake may reduce the incidence of IBD and may even have disease-modifying effects in regular consumers. However, differences in caffeine source (coffee, tea, soda), dose, concurrent dietary patterns, and disease subtype (Crohn’s disease versus ulcerative colitis) limit definitive causal inference. Clinical implications remain cautious: while moderate caffeine intake may be tolerable and even helpful for many patients, individualized assessment is advisable, particularly for those with symptom-triggering sensitivity or overlapping functional bowel disorders. Future research should target mechanistic links and clinically meaningful outcomes to inform evidence-based dietary guidance for people with IBD.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2026.1005112
This article belongs to the special issue Inflammatory Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract

Ageing is a gradual, multifactorial process that leads to the deterioration of physical and mental health, increasing the risk of disease and eventually death. Indicators of ageing manifest at the molecular level, including genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of proteostasis, and dysregulation of key signalling pathways such as the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and insulin signalling. These molecular hallmarks of ageing are interconnected, amplifying one another over time. The resulting cellular stress triggers apoptosis or drives cells into a pathological state known as cellular senescence, in which they secrete inflammatory, pro-ageing factors. Consequently, there is a progressive decline in tissue function and regenerative capacity, accompanied by atrophy and stem cell exhaustion under a chronically inflamed microenvironment. Although functional decline with age is irreversible, research indicates it can be delayed. In this review, we discuss the hallmarks of ageing, conventional pharmacological interventions with demonstrated anti-ageing effects in cellular and animal models, and emerging therapeutic strategies being explored as ageing becomes increasingly recognized as a major risk factor for disease development.
Ageing is a gradual, multifactorial process that leads to the deterioration of physical and mental health, increasing the risk of disease and eventually death. Indicators of ageing manifest at the molecular level, including genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of proteostasis, and dysregulation of key signalling pathways such as the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and insulin signalling. These molecular hallmarks of ageing are interconnected, amplifying one another over time. The resulting cellular stress triggers apoptosis or drives cells into a pathological state known as cellular senescence, in which they secrete inflammatory, pro-ageing factors. Consequently, there is a progressive decline in tissue function and regenerative capacity, accompanied by atrophy and stem cell exhaustion under a chronically inflamed microenvironment. Although functional decline with age is irreversible, research indicates it can be delayed. In this review, we discuss the hallmarks of ageing, conventional pharmacological interventions with demonstrated anti-ageing effects in cellular and animal models, and emerging therapeutic strategies being explored as ageing becomes increasingly recognized as a major risk factor for disease development.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2026.1008152

Aim:
To assess healthcare professionals’ awareness, attitudes, and utilization of community-based digital health platforms for preventive care in underserved districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, and to identify key barriers associated with routine use.
Methods:
A cross-sectional survey was conducted between December 2024 and February 2025 among 400 healthcare professionals (doctors, nurses, and allied health practitioners) working in primary, secondary, and tertiary facilities in Swabi and Mardan. Participants were recruited using purposive, stratified (quota-based) sampling. The questionnaire captured knowledge/awareness, attitudes, self-reported utilization, and perceived barriers (infrastructure, training, and privacy). Descriptive statistics were produced, and multivariable regression was used to examine factors associated with utilization.
Results:
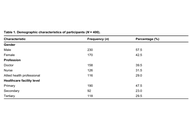
Among the 400 respondents, 332 (83.0%) reported awareness of digital health platforms and 312 (78.0%) reported positive attitudes toward their use. Overall, 297 (74.3%) reported using digital health platforms in practice. The most frequently reported barriers were lack of infrastructure (n = 309, 77.3%), limited training (n = 297, 74.3%), and data privacy concerns (n = 295, 73.8%). In the adjusted logistic regression model, greater knowledge of digital health platforms was associated with higher odds of routine use (aOR = 10.56, 95% CI: 2.36–47.35; p = 0.002), whereas attitude and infrastructure barriers were not significant (p > 0.05).
Conclusions:
Healthcare professionals in Swabi and Mardan reported high awareness and favorable attitudes toward community-based digital health platforms, but infrastructure gaps, limited training, and data privacy concerns were common barriers. Greater platform knowledge predicted routine use. Strengthening facility readiness, workflow-based training, and practical safeguards to address data privacy concerns may enable safer, more equitable scale-up; findings are context-specific due to non-probability sampling.
Aim:
To assess healthcare professionals’ awareness, attitudes, and utilization of community-based digital health platforms for preventive care in underserved districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, and to identify key barriers associated with routine use.
Methods:
A cross-sectional survey was conducted between December 2024 and February 2025 among 400 healthcare professionals (doctors, nurses, and allied health practitioners) working in primary, secondary, and tertiary facilities in Swabi and Mardan. Participants were recruited using purposive, stratified (quota-based) sampling. The questionnaire captured knowledge/awareness, attitudes, self-reported utilization, and perceived barriers (infrastructure, training, and privacy). Descriptive statistics were produced, and multivariable regression was used to examine factors associated with utilization.
Results:
Among the 400 respondents, 332 (83.0%) reported awareness of digital health platforms and 312 (78.0%) reported positive attitudes toward their use. Overall, 297 (74.3%) reported using digital health platforms in practice. The most frequently reported barriers were lack of infrastructure (n = 309, 77.3%), limited training (n = 297, 74.3%), and data privacy concerns (n = 295, 73.8%). In the adjusted logistic regression model, greater knowledge of digital health platforms was associated with higher odds of routine use (aOR = 10.56, 95% CI: 2.36–47.35; p = 0.002), whereas attitude and infrastructure barriers were not significant (p > 0.05).
Conclusions:
Healthcare professionals in Swabi and Mardan reported high awareness and favorable attitudes toward community-based digital health platforms, but infrastructure gaps, limited training, and data privacy concerns were common barriers. Greater platform knowledge predicted routine use. Strengthening facility readiness, workflow-based training, and practical safeguards to address data privacy concerns may enable safer, more equitable scale-up; findings are context-specific due to non-probability sampling.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2026.101187

The significant medicinal constituents and pharmacological potential of several botanicals suggest promising therapeutic applications. Scorzonera undulata displayed a diverse phytochemical profile, with 25 volatile and 21 phenolic compounds identified, including quinic and chlorogenic acids, along with flavonoids such as kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin derivatives, quercitrin, and naringin—mostly concentrated in the aerial parts. These extracts exhibited notable antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities, especially methanolic extracts against MCF-7 breast cancer cells, indicating therapeutic relevance. Andrographis paniculata extracts, rich in andrographolide, showed clinical potential in alleviating mild COVID-19 symptoms. However, the compound’s nonlinear pharmacokinetics highlight the need for optimized delivery strategies. Morinda citrifolia fruit extracts demonstrated considerable in vitro antimicrobial effects and moderate cytotoxicity, supported by UPLC–Orbitrap MS identification of unique bioactives. These findings reinforce the need for further pharmacological and clinical validation. The antiviral efficacy of Houttuynia cordata against dengue virus type 2 was evident, with aqueous extracts showing strong virucidal action and inhibition of viral replication. Hyperoside was identified as the dominant active constituent, supported by a rich phytochemical profile including flavonoids, aristolactams, and triterpenoids. Genotoxicity assessments indicated a favorable safety profile, suggesting potential for phytotherapeutic development. Achillea millefolium (yarrow) contained essential oils enriched in camphor, 1,8-cineole, artemisia ketone, and azulene derivatives, alongside phenolic acids and flavonoids like chlorogenic acid, apigenin, luteolin, and quercetin. These contributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and hemostatic effects, validating traditional medicinal applications and warranting clinical standardization. Flavonoids such as luteolin and apigenin offered anticancer and cardiovascular benefits by inhibiting PD-L1 via STAT3 suppression and promoting autophagy to counter vascular calcification. Bryophyllum pinnatum demonstrated broad pharmacological activity attributed to bufadienolides, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, supporting its ethnomedicinal use while emphasizing the need for clinical safety validation.
The significant medicinal constituents and pharmacological potential of several botanicals suggest promising therapeutic applications. Scorzonera undulata displayed a diverse phytochemical profile, with 25 volatile and 21 phenolic compounds identified, including quinic and chlorogenic acids, along with flavonoids such as kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin derivatives, quercitrin, and naringin—mostly concentrated in the aerial parts. These extracts exhibited notable antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities, especially methanolic extracts against MCF-7 breast cancer cells, indicating therapeutic relevance. Andrographis paniculata extracts, rich in andrographolide, showed clinical potential in alleviating mild COVID-19 symptoms. However, the compound’s nonlinear pharmacokinetics highlight the need for optimized delivery strategies. Morinda citrifolia fruit extracts demonstrated considerable in vitro antimicrobial effects and moderate cytotoxicity, supported by UPLC–Orbitrap MS identification of unique bioactives. These findings reinforce the need for further pharmacological and clinical validation. The antiviral efficacy of Houttuynia cordata against dengue virus type 2 was evident, with aqueous extracts showing strong virucidal action and inhibition of viral replication. Hyperoside was identified as the dominant active constituent, supported by a rich phytochemical profile including flavonoids, aristolactams, and triterpenoids. Genotoxicity assessments indicated a favorable safety profile, suggesting potential for phytotherapeutic development. Achillea millefolium (yarrow) contained essential oils enriched in camphor, 1,8-cineole, artemisia ketone, and azulene derivatives, alongside phenolic acids and flavonoids like chlorogenic acid, apigenin, luteolin, and quercetin. These contributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and hemostatic effects, validating traditional medicinal applications and warranting clinical standardization. Flavonoids such as luteolin and apigenin offered anticancer and cardiovascular benefits by inhibiting PD-L1 via STAT3 suppression and promoting autophagy to counter vascular calcification. Bryophyllum pinnatum demonstrated broad pharmacological activity attributed to bufadienolides, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, supporting its ethnomedicinal use while emphasizing the need for clinical safety validation.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2026.1008151

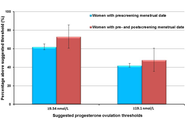
The dominant paradigm for healthy ageing in women+ (all genders) focuses on estrogen and sees the menopause, per se, as a major health problem (with low estrogen and progesterone levels). In reality, the risks for diseases that increase at older ages originate during the menstruating years. Rarely discussed evidence supports the central role of progesterone and normally ovulatory menstrual cycles in preventing early cardiovascular disease, fragility fractures, dementia, and cancers. Menstrual cycles with normal and predictable lengths but disturbed ovulation, including short luteal phases with lower progesterone production as well as anovulation without progesterone, likely occur in over 25% of all such cycles. These Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances are usually an adaptive and protective response to physiological, sociocultural, or emotional stressors. Ovulatory disturbances and risks for health issues during ageing are intrinsically related to the social determinants of health—wholesome food, plentiful physical activity, strong communities, and access to timely and appropriate medical care. This review discusses the empirical evidence that normal ovulation and progesterone production during the premenopausal years lead to the prevention of early heart attacks and fragility fractures. Few studies document the effects of prevalent Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances on brain issues (sleep, night sweats, ischemic strokes, pain, and addictions) and cancer risks. Serious gaps in women+’s fundamental reproductive physiology must be addressed with unbiased (population-based), rigorously collected longitudinal physiological, hormonal, and sociocultural data. Progesterone therapy during perimenopause and menopause also indirectly leads to healthy ageing through effective treatment of night sweats, hot flushes, and disturbed sleep, which are associated with cardiovascular problems and osteoporosis. Not only is progesterone effective for vasomotor symptoms in menopause, but also effective in perimenopause, a time of high and chaotic estrogen levels. In sum, strong summarized evidence suggests that progesterone and ovulation need further exploration for their important roles in promoting healthy ageing for women+.
The dominant paradigm for healthy ageing in women+ (all genders) focuses on estrogen and sees the menopause, per se, as a major health problem (with low estrogen and progesterone levels). In reality, the risks for diseases that increase at older ages originate during the menstruating years. Rarely discussed evidence supports the central role of progesterone and normally ovulatory menstrual cycles in preventing early cardiovascular disease, fragility fractures, dementia, and cancers. Menstrual cycles with normal and predictable lengths but disturbed ovulation, including short luteal phases with lower progesterone production as well as anovulation without progesterone, likely occur in over 25% of all such cycles. These Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances are usually an adaptive and protective response to physiological, sociocultural, or emotional stressors. Ovulatory disturbances and risks for health issues during ageing are intrinsically related to the social determinants of health—wholesome food, plentiful physical activity, strong communities, and access to timely and appropriate medical care. This review discusses the empirical evidence that normal ovulation and progesterone production during the premenopausal years lead to the prevention of early heart attacks and fragility fractures. Few studies document the effects of prevalent Subclinical Ovulatory Disturbances on brain issues (sleep, night sweats, ischemic strokes, pain, and addictions) and cancer risks. Serious gaps in women+’s fundamental reproductive physiology must be addressed with unbiased (population-based), rigorously collected longitudinal physiological, hormonal, and sociocultural data. Progesterone therapy during perimenopause and menopause also indirectly leads to healthy ageing through effective treatment of night sweats, hot flushes, and disturbed sleep, which are associated with cardiovascular problems and osteoporosis. Not only is progesterone effective for vasomotor symptoms in menopause, but also effective in perimenopause, a time of high and chaotic estrogen levels. In sum, strong summarized evidence suggests that progesterone and ovulation need further exploration for their important roles in promoting healthy ageing for women+.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101460
This article belongs to the special issue The Fountain of Youth: Decoding the Hormonal Regulation of Aging

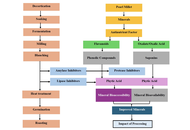
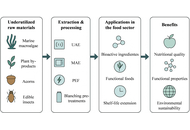
Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) is known for its agronomic, economic, and nutritional functionalities coupled with its important position as a “Smart food” in the food ecosystem. However, among agronomic products, pearl millet is now considered an “orphan crop” due to its neglect. As a result, numerous scientific methods have been investigated to clarify the antinutritional factors that prevent the bioaccessibility of minerals in pearl millet. To meet the biological needs of consumers, this review examines the various sustainable food processing techniques employed to enhance the mineral bioaccessibility of pearl millet. Additionally, the benefits of pearl millet for health are mentioned. The application of the INFOGEST digestion model as a method for comprehending mineral bioaccessibility in vitro is presented. Some well-known millet food products are reportedly being adopted to encourage and prevent the underutilization of pearl millet. In summary, the results offer optimization strategies to reduce the bioaccessibility issues associated with pearl millet minerals for human nutrition, hidden hunger, and public health mineral deficiency interventions.
Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) is known for its agronomic, economic, and nutritional functionalities coupled with its important position as a “Smart food” in the food ecosystem. However, among agronomic products, pearl millet is now considered an “orphan crop” due to its neglect. As a result, numerous scientific methods have been investigated to clarify the antinutritional factors that prevent the bioaccessibility of minerals in pearl millet. To meet the biological needs of consumers, this review examines the various sustainable food processing techniques employed to enhance the mineral bioaccessibility of pearl millet. Additionally, the benefits of pearl millet for health are mentioned. The application of the INFOGEST digestion model as a method for comprehending mineral bioaccessibility in vitro is presented. Some well-known millet food products are reportedly being adopted to encourage and prevent the underutilization of pearl millet. In summary, the results offer optimization strategies to reduce the bioaccessibility issues associated with pearl millet minerals for human nutrition, hidden hunger, and public health mineral deficiency interventions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010116

Aim:
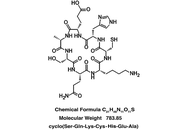
A seven amino acid cyclic peptide has been applied to human blood plasma treated with glucose metabolite methylglyoxal (MG) in “proof of concept” experiments to determine the peptide’s ability to counteract pathologies associated with hyperglycemia. Similar pathologies are evident during aging and in age-related disorders. In fact, elevated MG levels in the blood lead directly to diabetic complications and accelerated aging, including cognitive decline. These changes are attributed to oxidant stress and amyloidogenesis, the latter involving toxic accumulations of blood and tissue proteins.
Methods:
cSKE7 was redesigned from cell survival-promoting and anti-inflammatory fragments near the N-terminus of human/primate “orphan” protein DSEP/Dermcidin and incubated at low micromolar concentrations with the MG-stressed human plasma for 24 hours. The modified design of the new compound offers several practical advantages over predecessors including cyclic stability and a marked increase in aqueous solubility.
Results:
The peptide dispersed thioflavin-T-stained amyloid aggregates and reduced oxidant stress as measured by plasma levels of free thiols and of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) activity. Since these N-terminal fragments of DSEP/Dermcidin have been shown to bind and influence the activity of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), HSP70 inhibitor pifithrin-μ was added to the plasma prior to peptide treatment. The inhibitor disrupted amyloid dispersion and both peptide-induced and, in some cases, normally occurring antioxidant effects, suggesting these reparative activities are HSP70 dependent.
Conclusions:
The results are discussed in terms of their potential use in new therapies for the complications of metabolic disease and disorders of aging that result from a deterioration of the quality control mechanisms of proteostasis.
Aim:
A seven amino acid cyclic peptide has been applied to human blood plasma treated with glucose metabolite methylglyoxal (MG) in “proof of concept” experiments to determine the peptide’s ability to counteract pathologies associated with hyperglycemia. Similar pathologies are evident during aging and in age-related disorders. In fact, elevated MG levels in the blood lead directly to diabetic complications and accelerated aging, including cognitive decline. These changes are attributed to oxidant stress and amyloidogenesis, the latter involving toxic accumulations of blood and tissue proteins.
Methods:
cSKE7 was redesigned from cell survival-promoting and anti-inflammatory fragments near the N-terminus of human/primate “orphan” protein DSEP/Dermcidin and incubated at low micromolar concentrations with the MG-stressed human plasma for 24 hours. The modified design of the new compound offers several practical advantages over predecessors including cyclic stability and a marked increase in aqueous solubility.
Results:
The peptide dispersed thioflavin-T-stained amyloid aggregates and reduced oxidant stress as measured by plasma levels of free thiols and of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) activity. Since these N-terminal fragments of DSEP/Dermcidin have been shown to bind and influence the activity of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), HSP70 inhibitor pifithrin-μ was added to the plasma prior to peptide treatment. The inhibitor disrupted amyloid dispersion and both peptide-induced and, in some cases, normally occurring antioxidant effects, suggesting these reparative activities are HSP70 dependent.
Conclusions:
The results are discussed in terms of their potential use in new therapies for the complications of metabolic disease and disorders of aging that result from a deterioration of the quality control mechanisms of proteostasis.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2026.1008150
This article belongs to the special issue Peptide Science Without Borders: Novel Insights for Drug Discovery

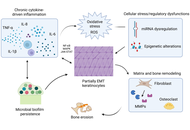
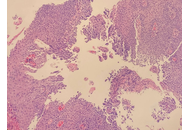
Acquired middle-ear cholesteatoma is a histologically benign keratinizing squamous epithelial lesion that paradoxically exhibits locally destructive, recurrent, and invasive behavior, often resulting in ossicular erosion, hearing loss, labyrinthine fistula, and, rarely, intracranial complications. Surgical excision remains the primary management strategy; however, recurrence is common due to persistent microenvironmental drivers. Recent mechanistic studies—including single-cell transcriptomics, spatial proteomics, and epigenetic profiling—reveal a multifactorial pathogenesis orchestrated by chronic inflammation, proteolytic extracellular-matrix remodeling, osteoclast activation via RANKL and activin A, epithelial plasticity with partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and a dysbiotic, biofilm-forming microbiome. Emerging evidence further implicates oxidative stress, RNA and epigenetic modifications, miRNA dysregulation, and immune cell infiltration as central modulators of lesion chronicity and bone resorption. Collectively, these processes establish a self-sustaining pro-osteolytic microenvironment that drives bone erosion and postoperative recurrence. Cholesteatoma recapitulates several features of malignant lesions—hyperproliferation, local invasion, and stromal/immune cell recruitment—yet remains fundamentally benign, lacking metastatic potential and genomic instability. Its aggression is ecological rather than genetic, highlighting the potential for microenvironment-directed, precision-based strategies. Adjunctive approaches may include local delivery of modulatory agents, targeted interference with inflammatory, proteolytic, osteoclastogenic, and microbial axes, and biomarker-guided patient stratification. Preclinical and early-phase experimental studies assessing target engagement, radiologic stabilization, and molecular surrogates of efficacy could inform safer, mechanism-driven interventions that complement surgery, reduce recurrence, and preserve hearing. Integrating molecular pathobiology with clinical strategy positions cholesteatoma as a model for benign yet locally aggressive, microenvironment-driven disease, providing a roadmap for translational therapies with direct relevance to surgical practice.
Acquired middle-ear cholesteatoma is a histologically benign keratinizing squamous epithelial lesion that paradoxically exhibits locally destructive, recurrent, and invasive behavior, often resulting in ossicular erosion, hearing loss, labyrinthine fistula, and, rarely, intracranial complications. Surgical excision remains the primary management strategy; however, recurrence is common due to persistent microenvironmental drivers. Recent mechanistic studies—including single-cell transcriptomics, spatial proteomics, and epigenetic profiling—reveal a multifactorial pathogenesis orchestrated by chronic inflammation, proteolytic extracellular-matrix remodeling, osteoclast activation via RANKL and activin A, epithelial plasticity with partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and a dysbiotic, biofilm-forming microbiome. Emerging evidence further implicates oxidative stress, RNA and epigenetic modifications, miRNA dysregulation, and immune cell infiltration as central modulators of lesion chronicity and bone resorption. Collectively, these processes establish a self-sustaining pro-osteolytic microenvironment that drives bone erosion and postoperative recurrence. Cholesteatoma recapitulates several features of malignant lesions—hyperproliferation, local invasion, and stromal/immune cell recruitment—yet remains fundamentally benign, lacking metastatic potential and genomic instability. Its aggression is ecological rather than genetic, highlighting the potential for microenvironment-directed, precision-based strategies. Adjunctive approaches may include local delivery of modulatory agents, targeted interference with inflammatory, proteolytic, osteoclastogenic, and microbial axes, and biomarker-guided patient stratification. Preclinical and early-phase experimental studies assessing target engagement, radiologic stabilization, and molecular surrogates of efficacy could inform safer, mechanism-driven interventions that complement surgery, reduce recurrence, and preserve hearing. Integrating molecular pathobiology with clinical strategy positions cholesteatoma as a model for benign yet locally aggressive, microenvironment-driven disease, providing a roadmap for translational therapies with direct relevance to surgical practice.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002359

Herpes simplex esophagitis (HSE) is a viral infection of the esophagus caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), most commonly HSV-1. It predominantly presents among immunosuppressed individuals. Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, inflammatory, immune-mediated disease characterized by significant eosinophilic infiltration in the esophageal mucosa. It is often associated with atopic diseases, including asthma, food allergies, and eczema. Coexistence of HSE and EoE is rare and may be underdiagnosed due to challenges in diagnosing both conditions simultaneously. A major diagnostic dilemma can be traced to their histopathological similarities and differences. HSE is typically characterized by multinuclear giant cells containing intranuclear inclusions, while EoE involves eosinophilic infiltration in the esophageal epithelium. This report highlights the rare but remarkable coexistence between HSE and EoE secondary to a unique patient case. Although each condition may cause esophagitis individually, together—particularly in immunocompetent individuals—they do present a different diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
Herpes simplex esophagitis (HSE) is a viral infection of the esophagus caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), most commonly HSV-1. It predominantly presents among immunosuppressed individuals. Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, inflammatory, immune-mediated disease characterized by significant eosinophilic infiltration in the esophageal mucosa. It is often associated with atopic diseases, including asthma, food allergies, and eczema. Coexistence of HSE and EoE is rare and may be underdiagnosed due to challenges in diagnosing both conditions simultaneously. A major diagnostic dilemma can be traced to their histopathological similarities and differences. HSE is typically characterized by multinuclear giant cells containing intranuclear inclusions, while EoE involves eosinophilic infiltration in the esophageal epithelium. This report highlights the rare but remarkable coexistence between HSE and EoE secondary to a unique patient case. Although each condition may cause esophagitis individually, together—particularly in immunocompetent individuals—they do present a different diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2026.1005111

Background:
Sepsis is a major cause of disease worldwide. Mobile applications (apps) have been developed to assist clinical practice. Current evidence evaluating such apps is diverse. This scoping review aimed to map currently available literature investigating the usage of mobile apps for sepsis-related healthcare. This will highlight evidence gaps, and areas for future innovation and app development.
Methods:
Databases MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched in June 2023 (updated in July 2024). Studies containing original research investigating mobile apps for sepsis-related healthcare were included and analysed in three categories identified from the primary purpose of the app: (1) education and awareness, (2) clinical assistance, and (3) biomarker or pathogen detection.
Results:
A total of 1,755 studies were identified and 27 included following screening, of which 19 (70%) were published in 2020 or later. Most of the 27 studies investigated apps for clinical assistance (70%, n = 19). These apps were diverse, acting as digital solutions for data collection (n = 2), triage (n = 6), clinical guideline access (n = 5), alert delivery (n = 1), and outcome prediction (n = 5). There were five apps (19%) used to assist biomarker or pathogen detection. Of these, most (80%, n = 4) mobile apps were used to detect and quantify colorimetric signals in combination with assays, and all five apps had attachments necessary for laboratory processes. Lastly, three apps (11%) were designed to enhance education and awareness, two targeting medical education and one targeting public awareness.
Discussion:
Mobile applications offer innovative and exciting digital solutions for biomarker detection, education, and clinical support in sepsis-related healthcare. Current literature is highly heterogenous and rapidly developing.
Background:
Sepsis is a major cause of disease worldwide. Mobile applications (apps) have been developed to assist clinical practice. Current evidence evaluating such apps is diverse. This scoping review aimed to map currently available literature investigating the usage of mobile apps for sepsis-related healthcare. This will highlight evidence gaps, and areas for future innovation and app development.
Methods:
Databases MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, Scopus, and Web of Science were searched in June 2023 (updated in July 2024). Studies containing original research investigating mobile apps for sepsis-related healthcare were included and analysed in three categories identified from the primary purpose of the app: (1) education and awareness, (2) clinical assistance, and (3) biomarker or pathogen detection.
Results:
A total of 1,755 studies were identified and 27 included following screening, of which 19 (70%) were published in 2020 or later. Most of the 27 studies investigated apps for clinical assistance (70%, n = 19). These apps were diverse, acting as digital solutions for data collection (n = 2), triage (n = 6), clinical guideline access (n = 5), alert delivery (n = 1), and outcome prediction (n = 5). There were five apps (19%) used to assist biomarker or pathogen detection. Of these, most (80%, n = 4) mobile apps were used to detect and quantify colorimetric signals in combination with assays, and all five apps had attachments necessary for laboratory processes. Lastly, three apps (11%) were designed to enhance education and awareness, two targeting medical education and one targeting public awareness.
Discussion:
Mobile applications offer innovative and exciting digital solutions for biomarker detection, education, and clinical support in sepsis-related healthcare. Current literature is highly heterogenous and rapidly developing.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2026.101186

Aim:
Malabar chestnut seed from Nigeria is an underutilized seed in Africa that possesses different nutritional, functional, and medicinal characteristics. Nevertheless, there is no quality information on the antioxidant properties of the embryo, the whole seed, and the seed coat of the Pachira glabra. This research investigated the nutritional composition and antioxidant properties of the Malabar chestnut embryo (MCE), whole Malabar chestnut (WMC), and Malabar chestnut seed coat (MCSC).
Methods:
The nuts were sorted, and the seed coat was separated from the embryo. This was processed to get the WMC, MCE, and MCSC flours, and they were analyzed for proximate composition, minerals, amino acid profiles, antinutrients, and antioxidant properties.
Results:
The proximate composition (g/100 g) showed high protein and fat content, total ash (2.50–3.50), crude fiber (2.04–11.43), moisture (3.62–7.93), and carbohydrate (13.29–37.92). The results also showed higher deposition of minerals in the seed coat, with phosphorus (2.82–5.26) and potassium (2.77–4.90) being the most abundant. This indicates that the seed can be used as a supplement for these nutrients. Low lead content was recorded in all samples. The antinutritional compositions were relatively lower in the embryo compared to the seed coat and whole seed. Furthermore, the high ratio of essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (0.63–0.87), particularly in MCE, positions the seed as a potential high-quality protein source. The antioxidant properties demonstrated a high scavenging power, with a viable level of total phenol (198.65–330.41) mg GAE/g, total flavonoid (30.74–86.49) mg QE/g, as well as ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) and DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl).
Conclusions:
The seed coat and the embryo of the Malabar chestnut showed superior nutritional composition and antioxidant properties; therefore, they can be used for medicinal purposes and as an antioxidant in the management of chronic diet-based diseases.
Aim:
Malabar chestnut seed from Nigeria is an underutilized seed in Africa that possesses different nutritional, functional, and medicinal characteristics. Nevertheless, there is no quality information on the antioxidant properties of the embryo, the whole seed, and the seed coat of the Pachira glabra. This research investigated the nutritional composition and antioxidant properties of the Malabar chestnut embryo (MCE), whole Malabar chestnut (WMC), and Malabar chestnut seed coat (MCSC).
Methods:
The nuts were sorted, and the seed coat was separated from the embryo. This was processed to get the WMC, MCE, and MCSC flours, and they were analyzed for proximate composition, minerals, amino acid profiles, antinutrients, and antioxidant properties.
Results:
The proximate composition (g/100 g) showed high protein and fat content, total ash (2.50–3.50), crude fiber (2.04–11.43), moisture (3.62–7.93), and carbohydrate (13.29–37.92). The results also showed higher deposition of minerals in the seed coat, with phosphorus (2.82–5.26) and potassium (2.77–4.90) being the most abundant. This indicates that the seed can be used as a supplement for these nutrients. Low lead content was recorded in all samples. The antinutritional compositions were relatively lower in the embryo compared to the seed coat and whole seed. Furthermore, the high ratio of essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (0.63–0.87), particularly in MCE, positions the seed as a potential high-quality protein source. The antioxidant properties demonstrated a high scavenging power, with a viable level of total phenol (198.65–330.41) mg GAE/g, total flavonoid (30.74–86.49) mg QE/g, as well as ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) and DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl).
Conclusions:
The seed coat and the embryo of the Malabar chestnut showed superior nutritional composition and antioxidant properties; therefore, they can be used for medicinal purposes and as an antioxidant in the management of chronic diet-based diseases.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010115

Glioblastoma (GBM) is a complex condition with a poorly understood pathophysiology and no effective treatment to date. The present article highlights the role of canonical and non-canonical signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interactions with nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in the modulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in GBM microenvironment pathophysiology. The capacity of STAT3 and NF-κB to interact to upregulate the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway is suppressed systemically over the course of aging, thereby attenuating the capacity to achieve inflammation resolution. The suppressed capacity to induce the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway systemically is partly driven by the dramatic 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin over aging. The attenuation of pineal melatonin in the first half of sleep over aging and aging-accelerating conditions disinhibits the effects of cortisol in the second half of sleep. This decrease in the melatonin/cortisol ratio alters the nature of night-time dampening and resetting in preparation for the coming day by altering cellular and intercellular homeostatic interactions. Aging and aging-accelerating conditions, by impacting the night-time melatonin/cortisol ratio, also suppress the capacity of the vagal nerve to resolve inflammation. This further contributes to systemic changes that influence GBM pathoetiology and ongoing pathophysiology. Aging-associated changes in night-time dampening and resetting provide a novel framework on which many previously disparate bodies of data on GBM pathophysiology can be collated. This has numerous future research, prevention, and treatment implications.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a complex condition with a poorly understood pathophysiology and no effective treatment to date. The present article highlights the role of canonical and non-canonical signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interactions with nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in the modulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in GBM microenvironment pathophysiology. The capacity of STAT3 and NF-κB to interact to upregulate the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway is suppressed systemically over the course of aging, thereby attenuating the capacity to achieve inflammation resolution. The suppressed capacity to induce the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway systemically is partly driven by the dramatic 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin over aging. The attenuation of pineal melatonin in the first half of sleep over aging and aging-accelerating conditions disinhibits the effects of cortisol in the second half of sleep. This decrease in the melatonin/cortisol ratio alters the nature of night-time dampening and resetting in preparation for the coming day by altering cellular and intercellular homeostatic interactions. Aging and aging-accelerating conditions, by impacting the night-time melatonin/cortisol ratio, also suppress the capacity of the vagal nerve to resolve inflammation. This further contributes to systemic changes that influence GBM pathoetiology and ongoing pathophysiology. Aging-associated changes in night-time dampening and resetting provide a novel framework on which many previously disparate bodies of data on GBM pathophysiology can be collated. This has numerous future research, prevention, and treatment implications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002358

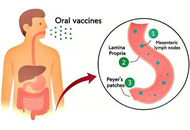
For decades, vaccines have been a key tool against microbial infections. However, the high cost of production and purification renders vaccines largely inaccessible to many developing countries. The limitations of conventional vaccines can be overcome by edible vaccines. To produce an oral vaccine, favourable vectors, such as plants and probiotics, are used. Recent studies have revealed the immunomodulatory effects of probiotics. To improve the efficacy of these vaccines, several adjuvant approaches have been employed. Postbiotics can be used as promising therapy for preventing infections and enhancing the host immune system due to their unique biochemical and microbial-derived properties. In this review, we discuss the feasibility of postbiotics as adjuvants for oral vaccines, highlighting their mechanisms of action, safety profile, and potential to enhance both mucosal and systemic immune responses.
For decades, vaccines have been a key tool against microbial infections. However, the high cost of production and purification renders vaccines largely inaccessible to many developing countries. The limitations of conventional vaccines can be overcome by edible vaccines. To produce an oral vaccine, favourable vectors, such as plants and probiotics, are used. Recent studies have revealed the immunomodulatory effects of probiotics. To improve the efficacy of these vaccines, several adjuvant approaches have been employed. Postbiotics can be used as promising therapy for preventing infections and enhancing the host immune system due to their unique biochemical and microbial-derived properties. In this review, we discuss the feasibility of postbiotics as adjuvants for oral vaccines, highlighting their mechanisms of action, safety profile, and potential to enhance both mucosal and systemic immune responses.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2026.1003237

Background:
Nurses perform many daily care tasks that expose them to work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). Many studies have reported a high prevalence worldwide. Analyses by continent have provided a better understanding of the WMSD occurrence, but none have yet been conducted among African nurses. The aim was to conduct a systematic review analysis with meta-analysis of the overall WMSD prevalence and the prevalence by body area among nurses in Africa.
Methods:
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) method was used to present the results in the form of a systematic review analysis with meta-analysis. PubMed/Medline, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, Mendeley, and Science.gov were explored between August 20 and 29, 2025 to identify studies that investigated the overall and body area WMSD prevalence among African nurses of any specialty without a date limit. Studies were included if they were cross sectional survey assessing the WMSD prevalence among nurses of any specialty or department working in Africa. Any study that was not a peer-reviewed cross-sectional survey published in English, that did not involve African nurses, or that did not report, or sufficiently detail data on the prevalence was excluded. The quality of each article included was assessed using the cross-sectional study assessment tool (AXIS). A meta-analysis with quantification of heterogeneity (Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistic) was conducted. Based on these parameters, a fixed or random effects model was selected to estimate the prevalence. Forest plots were used to summarize the overall, neck, upper back, lower back, shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle WMSD prevalence.
Results:
Nineteen cross-sectional studies were selected from the 4,305 identified studies, involving 4,670 African nurses from 10 countries. A significant heterogeneity was highlighted between studies (Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistic). Lower back [59.5%, 95% confidence interval (CI): 52.8–66.2%, 4,670 participants], neck (35.4%, 95% CI: 28.0–42.8%, 4,670 participants), and knee (34.4%, 95% CI: 27.2–41.6%, 4,601 participants) were the most exposed areas. The overall WMSD prevalence was pooled at 74.6% (95% CI: 67.0−82.3%, 4,266 nurses).
Discussion:
Comparison of these results with the literature showed that African nurses were less affected than those on other continents. However, the data were highly heterogeneous. Due to the numerous risk factors associated with nursing work, it is necessary to continue research projects and educational activities, as well as the development of health policies aimed at improving quality of life at work, specifically by expanding the investigation using subgroup analysis.
Background:
Nurses perform many daily care tasks that expose them to work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). Many studies have reported a high prevalence worldwide. Analyses by continent have provided a better understanding of the WMSD occurrence, but none have yet been conducted among African nurses. The aim was to conduct a systematic review analysis with meta-analysis of the overall WMSD prevalence and the prevalence by body area among nurses in Africa.
Methods:
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) method was used to present the results in the form of a systematic review analysis with meta-analysis. PubMed/Medline, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, Mendeley, and Science.gov were explored between August 20 and 29, 2025 to identify studies that investigated the overall and body area WMSD prevalence among African nurses of any specialty without a date limit. Studies were included if they were cross sectional survey assessing the WMSD prevalence among nurses of any specialty or department working in Africa. Any study that was not a peer-reviewed cross-sectional survey published in English, that did not involve African nurses, or that did not report, or sufficiently detail data on the prevalence was excluded. The quality of each article included was assessed using the cross-sectional study assessment tool (AXIS). A meta-analysis with quantification of heterogeneity (Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistic) was conducted. Based on these parameters, a fixed or random effects model was selected to estimate the prevalence. Forest plots were used to summarize the overall, neck, upper back, lower back, shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle WMSD prevalence.
Results:
Nineteen cross-sectional studies were selected from the 4,305 identified studies, involving 4,670 African nurses from 10 countries. A significant heterogeneity was highlighted between studies (Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistic). Lower back [59.5%, 95% confidence interval (CI): 52.8–66.2%, 4,670 participants], neck (35.4%, 95% CI: 28.0–42.8%, 4,670 participants), and knee (34.4%, 95% CI: 27.2–41.6%, 4,601 participants) were the most exposed areas. The overall WMSD prevalence was pooled at 74.6% (95% CI: 67.0−82.3%, 4,266 nurses).
Discussion:
Comparison of these results with the literature showed that African nurses were less affected than those on other continents. However, the data were highly heterogeneous. Due to the numerous risk factors associated with nursing work, it is necessary to continue research projects and educational activities, as well as the development of health policies aimed at improving quality of life at work, specifically by expanding the investigation using subgroup analysis.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2026.1007116
This article belongs to the special issue Prevalence and Risk Factors of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2026.1010114
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine–metabolic condition that carries a higher cardiovascular risk than currently reflected by traditional screening tools. Emerging evidence suggests that resting tachycardia and autonomic dysfunction may serve as early, non-invasive indicators of cardiovascular dysregulation in this population. This review synthesizes current data on resting heart rate (RHR), heart rate variability (HRV), and direct autonomic markers in women with PCOS, drawing from human studies published between 2000 and 2025. Across 32 eligible studies, most reported increased sympathetic activity, reduced parasympathetic tone, elevated RHR, and impaired HRV patterns observed even in normal-weight or metabolically mild PCOS phenotypes. These alterations correlate with endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis, underscoring their cardiovascular relevance. Mechanistic insights highlight the contributions of insulin resistance, hyperandrogenism, inflammation, adipokine imbalance, chemoreflex sensitization, and altered cortisol metabolism to autonomic disruption. Despite consistent findings, methodological variability in HRV protocols and inadequate adjustment for major confounders limit definitive interpretation. RHR, due to its simplicity and accessibility, including through wearable devices, holds promise as a supportive early risk signal; however, it should not be used in isolation. Future studies must adopt standardized autonomic measurements, including diverse cohorts, and evaluate whether modifying autonomic markers translates into improved cardiometabolic outcomes. Integrating RHR and HRV with metabolic and endocrine markers may enhance early cardiovascular risk stratification in women with PCOS.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine–metabolic condition that carries a higher cardiovascular risk than currently reflected by traditional screening tools. Emerging evidence suggests that resting tachycardia and autonomic dysfunction may serve as early, non-invasive indicators of cardiovascular dysregulation in this population. This review synthesizes current data on resting heart rate (RHR), heart rate variability (HRV), and direct autonomic markers in women with PCOS, drawing from human studies published between 2000 and 2025. Across 32 eligible studies, most reported increased sympathetic activity, reduced parasympathetic tone, elevated RHR, and impaired HRV patterns observed even in normal-weight or metabolically mild PCOS phenotypes. These alterations correlate with endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis, underscoring their cardiovascular relevance. Mechanistic insights highlight the contributions of insulin resistance, hyperandrogenism, inflammation, adipokine imbalance, chemoreflex sensitization, and altered cortisol metabolism to autonomic disruption. Despite consistent findings, methodological variability in HRV protocols and inadequate adjustment for major confounders limit definitive interpretation. RHR, due to its simplicity and accessibility, including through wearable devices, holds promise as a supportive early risk signal; however, it should not be used in isolation. Future studies must adopt standardized autonomic measurements, including diverse cohorts, and evaluate whether modifying autonomic markers translates into improved cardiometabolic outcomes. Integrating RHR and HRV with metabolic and endocrine markers may enhance early cardiovascular risk stratification in women with PCOS.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2026.101295

The Gerbode defect is characterized by a high ventricular septal defect associated with a defect in the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve, allowing blood to enter the right atrium from the left ventricle. It accounts for approximately 0.08% of intracardiac shunts and may be congenital or acquired. We describe a rare case of Gerbode defect secondary to tricuspid valve endocarditis. A 58-year-old male patient presented with acute infective endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus, related to central venous access. Echocardiography showed a tricuspid valve with thickened leaflets and a small mobile image on the atrial side of the septal leaflet, as well as moderate to severe regurgitation. After completion of the antibiotic regimen with resolution of the infectious condition, the patient was discharged asymptomatic, and a new echocardiogram showed no vegetation on the tricuspid valve. During outpatient follow-up, he presented dyspnea on mild exertion, and consecutive echocardiograms showed moderate tricuspid insufficiency and significant pulmonary hypertension with a pulmonary artery systolic pressure of 83 mmHg (reference: 30 mmHg). He underwent right and left cardiac catheterization, which showed a Gerbode defect, and a transesophageal echocardiogram showed a shunt in the subaortic region measuring 6 to 8 mm, with a maximum gradient of 56 mmHg. He underwent elective surgery to correct the Gerbode defect and tricuspid valve repair, with a good clinical result. The Gerbode defect is rare, and the diagnosis can be challenging because it simulates other conditions. Treatment consists of closing the defect when it generates refractory symptoms or complications. The reported case was surgically corrected, with a good result and favorable evolution.
The Gerbode defect is characterized by a high ventricular septal defect associated with a defect in the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve, allowing blood to enter the right atrium from the left ventricle. It accounts for approximately 0.08% of intracardiac shunts and may be congenital or acquired. We describe a rare case of Gerbode defect secondary to tricuspid valve endocarditis. A 58-year-old male patient presented with acute infective endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus, related to central venous access. Echocardiography showed a tricuspid valve with thickened leaflets and a small mobile image on the atrial side of the septal leaflet, as well as moderate to severe regurgitation. After completion of the antibiotic regimen with resolution of the infectious condition, the patient was discharged asymptomatic, and a new echocardiogram showed no vegetation on the tricuspid valve. During outpatient follow-up, he presented dyspnea on mild exertion, and consecutive echocardiograms showed moderate tricuspid insufficiency and significant pulmonary hypertension with a pulmonary artery systolic pressure of 83 mmHg (reference: 30 mmHg). He underwent right and left cardiac catheterization, which showed a Gerbode defect, and a transesophageal echocardiogram showed a shunt in the subaortic region measuring 6 to 8 mm, with a maximum gradient of 56 mmHg. He underwent elective surgery to correct the Gerbode defect and tricuspid valve repair, with a good clinical result. The Gerbode defect is rare, and the diagnosis can be challenging because it simulates other conditions. Treatment consists of closing the defect when it generates refractory symptoms or complications. The reported case was surgically corrected, with a good result and favorable evolution.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2026.101296

Aim:
Hypertriglyceridemia is linked to increased risk of diabetes diagnosis, incidence, and mortality. However, whether individuals with normal triglyceride levels (i.e., < 1.7 mmol/L) uniformly exhibit low diabetes risk remains underexplored. Specifically, it is unclear whether triglyceride levels within the normal range are associated with plasma glucose levels and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). This study aimed to address these gaps by examining the associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose, as well as between triglyceride levels and T2DM, in individuals with triglycerides in the normal range.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included 16,706 Chinese adults with triglyceride levels below 1.7 mmol/L. Among them, 1,067 had T2DM. Associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose were assessed using linear regression, while associations with T2DM were evaluated using binary logistic regression. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was determined via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results:
Triglyceride levels were positively associated with fasting plasma glucose after multivariate adjustment (β = 0.034, P < 0.001). A one-unit increase in the natural log of triglyceride levels was associated with a 61% higher adjusted odds of T2DM [odds ratio (OR), 1.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.19–2.17; P = 0.002]. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was 1.09 mmol/L. Participants with triglyceride levels ≥ 1.09 mmol/L had a 28% higher odds of T2DM (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.07–1.53; P = 0.006) compared to those with levels below the cut-off.
Conclusions:
Among individuals with normal triglyceride levels, higher triglyceride concentrations were associated with higher odds of T2DM diagnosis, with an optimal diagnostic cut-off of 1.09 mmol/L. These findings suggest that adults with triglyceride levels more than 1.09 mmol/L may benefit from closer monitoring for T2DM development.
Aim:
Hypertriglyceridemia is linked to increased risk of diabetes diagnosis, incidence, and mortality. However, whether individuals with normal triglyceride levels (i.e., < 1.7 mmol/L) uniformly exhibit low diabetes risk remains underexplored. Specifically, it is unclear whether triglyceride levels within the normal range are associated with plasma glucose levels and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). This study aimed to address these gaps by examining the associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose, as well as between triglyceride levels and T2DM, in individuals with triglycerides in the normal range.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study included 16,706 Chinese adults with triglyceride levels below 1.7 mmol/L. Among them, 1,067 had T2DM. Associations between triglyceride levels and fasting plasma glucose were assessed using linear regression, while associations with T2DM were evaluated using binary logistic regression. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was determined via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results:
Triglyceride levels were positively associated with fasting plasma glucose after multivariate adjustment (β = 0.034, P < 0.001). A one-unit increase in the natural log of triglyceride levels was associated with a 61% higher adjusted odds of T2DM [odds ratio (OR), 1.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.19–2.17; P = 0.002]. The optimal triglyceride cut-off for T2DM diagnosis was 1.09 mmol/L. Participants with triglyceride levels ≥ 1.09 mmol/L had a 28% higher odds of T2DM (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.07–1.53; P = 0.006) compared to those with levels below the cut-off.
Conclusions:
Among individuals with normal triglyceride levels, higher triglyceride concentrations were associated with higher odds of T2DM diagnosis, with an optimal diagnostic cut-off of 1.09 mmol/L. These findings suggest that adults with triglyceride levels more than 1.09 mmol/L may benefit from closer monitoring for T2DM development.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2026.101459
This article belongs to the special issue Current Views on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications and Related Conditions

The emergence of stem-cell-derived enamel organoids and dentin-producing dental pulp stem cell constructs presents new possibilities for restoring carious lesions using autologous enamel–dentin inlays. This overview outlines the biological and technological advances supporting this approach and proposes a workflow oriented toward clinical application. The benefits of tissue-based inlays, including inherent biomechanical compatibility, aesthetic accuracy, and potential for biological integration, are contrasted with those of purely artificial materials. Significant regenerative developments include the formation of human enamel organoids and odontoblast-lineage cells in vitro, 3D bioprinting of tooth-shaped constructs with demineralised dentin matrix and poly(ε‑caprolactone) scaffolds, and fibre-guiding periodontal ligament scaffolds that restore Sharpey’s fibres in vivo. The mechanical performance of adhesive resin cements, with bond strengths of approximately 4–7 MPa to enamel and dentin, and their durability in reattaching natural tooth fragments, supports the feasibility of bonding biological inlays. Practical considerations include controlling the slow degradation and hydrophobicity of poly(ε-caprolactone) through the use of ceramic or natural polymer additives, employing multi-material 3D printing to co-print mineralized enamel and cell-laden dentin layers, and achieving the desired shade, microstructure, and mechanical properties, exemplified by a compressive strength of approximately 677 MPa for 3D-printed zirconia crowns. Despite regulatory and translational challenges, the integration of digital dentistry, bioprinting, and stem cell science points toward future “grow and glue” restorations that may replace traditional drill-and-fill methods.
The emergence of stem-cell-derived enamel organoids and dentin-producing dental pulp stem cell constructs presents new possibilities for restoring carious lesions using autologous enamel–dentin inlays. This overview outlines the biological and technological advances supporting this approach and proposes a workflow oriented toward clinical application. The benefits of tissue-based inlays, including inherent biomechanical compatibility, aesthetic accuracy, and potential for biological integration, are contrasted with those of purely artificial materials. Significant regenerative developments include the formation of human enamel organoids and odontoblast-lineage cells in vitro, 3D bioprinting of tooth-shaped constructs with demineralised dentin matrix and poly(ε‑caprolactone) scaffolds, and fibre-guiding periodontal ligament scaffolds that restore Sharpey’s fibres in vivo. The mechanical performance of adhesive resin cements, with bond strengths of approximately 4–7 MPa to enamel and dentin, and their durability in reattaching natural tooth fragments, supports the feasibility of bonding biological inlays. Practical considerations include controlling the slow degradation and hydrophobicity of poly(ε-caprolactone) through the use of ceramic or natural polymer additives, employing multi-material 3D printing to co-print mineralized enamel and cell-laden dentin layers, and achieving the desired shade, microstructure, and mechanical properties, exemplified by a compressive strength of approximately 677 MPa for 3D-printed zirconia crowns. Despite regulatory and translational challenges, the integration of digital dentistry, bioprinting, and stem cell science points toward future “grow and glue” restorations that may replace traditional drill-and-fill methods.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2026.101359
This article belongs to the special issue Innovations in Biomaterials for Dentistry and Oral Surgery
 Previous
Previous