


Aim:
The social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, has emerged as a significant hub for healthcare-related conversations and sharing information. This study aims to investigate the impact and reach of the #physiotherapy hashtag on the X platform.
Methods:
We collected and analyzed tweets containing the hashtag #physiotherapy posted between September 1, 2022, and September 1, 2023. Data was retrieved from X using the Fedica analytics platform on October 26, 2023. The data were analyzed and expressed in number and percentage and categorical data were tested by chi-square test.
Results:
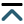
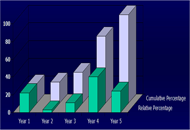
Over the course of one year, a total of 57,788 tweets were shared using #physiotherapy by 21,244 users, generating a remarkable 108,743,911 impressions. On average, there were 6 tweets posted per day (with a range from 3 to 9). Among the users, the majority (42%) had between 100 and 1000
Conclusions:
The examination of tweets related to #physiotherapy unveiled a vibrant global dialogue, with active engagement from diverse backgrounds. Notably, contributions from the UK, India, and the USA were prominent.
Aim:
The social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, has emerged as a significant hub for healthcare-related conversations and sharing information. This study aims to investigate the impact and reach of the #physiotherapy hashtag on the X platform.
Methods:
We collected and analyzed tweets containing the hashtag #physiotherapy posted between September 1, 2022, and September 1, 2023. Data was retrieved from X using the Fedica analytics platform on October 26, 2023. The data were analyzed and expressed in number and percentage and categorical data were tested by chi-square test.
Results:
Over the course of one year, a total of 57,788 tweets were shared using #physiotherapy by 21,244 users, generating a remarkable 108,743,911 impressions. On average, there were 6 tweets posted per day (with a range from 3 to 9). Among the users, the majority (42%) had between 100 and 1000
Conclusions:
The examination of tweets related to #physiotherapy unveiled a vibrant global dialogue, with active engagement from diverse backgrounds. Notably, contributions from the UK, India, and the USA were prominent.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2024.00016
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Aim:
Longitudinal cohort study designs are considered the gold standard for investigating associations between environmental exposures and human health yet they are characterized by limitations including participant attrition, and the resource implications associated with cohort recruitment and follow-up. Attrition compromises the integrity of research by threatening both the internal and external validity of empirical results, weakening the accuracy of statistical inferences and the generalizability of findings. This pilot study aimed to trace participants from a historical cohort study, the Hamilton Child Cohort Study (HCC) (n = 3,202), (1976–1986, 2003–2008) which was originally designed to examine the relative contribution of indoor and outdoor exposure to air pollution on respiratory health.
Methods:
Original participants were traced through social networking sites (SNS) by leveraging personal identifying data (name, age, sex, educational affiliation, and geographical locations) from the HCC entered into SNS search engines.
Results:
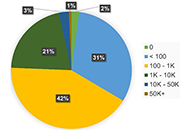
Of the original cohort (n = 3,166), 21% (n = 665) were identified as having social media presence (SMP) on a single social media platform, with 15% (n = 479) found on Facebook, 6% (n = 185) on LinkedIn, < 1% (n = 9) on
Conclusions:
This study underscores social media’s potential for tracing participants in longitudinal studies while advising a multi-faceted approach to overcome inherent limitations and biases. A full-scale study is necessary to determine whether utilizing SNS to trace participants for longitudinal research is an effective tool for re-engaging research participants lost to attrition.
Aim:
Longitudinal cohort study designs are considered the gold standard for investigating associations between environmental exposures and human health yet they are characterized by limitations including participant attrition, and the resource implications associated with cohort recruitment and follow-up. Attrition compromises the integrity of research by threatening both the internal and external validity of empirical results, weakening the accuracy of statistical inferences and the generalizability of findings. This pilot study aimed to trace participants from a historical cohort study, the Hamilton Child Cohort Study (HCC) (n = 3,202), (1976–1986, 2003–2008) which was originally designed to examine the relative contribution of indoor and outdoor exposure to air pollution on respiratory health.
Methods:
Original participants were traced through social networking sites (SNS) by leveraging personal identifying data (name, age, sex, educational affiliation, and geographical locations) from the HCC entered into SNS search engines.
Results:
Of the original cohort (n = 3,166), 21% (n = 665) were identified as having social media presence (SMP) on a single social media platform, with 15% (n = 479) found on Facebook, 6% (n = 185) on LinkedIn, < 1% (n = 9) on
Conclusions:
This study underscores social media’s potential for tracing participants in longitudinal studies while advising a multi-faceted approach to overcome inherent limitations and biases. A full-scale study is necessary to determine whether utilizing SNS to trace participants for longitudinal research is an effective tool for re-engaging research participants lost to attrition.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2024.00017
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Aim:
The spread of suicide and non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) content on social media has raised ongoing concerns about user safety and mental health. In response, social media platforms like Twitter (now X) and Meta (i.e., Facebook and
Methods:
A corpus of 3,846 tweets was analyzed. Within this corpus, tweets spanning 32 weeks from October 18, 2018, to May 29, 2019, were selected. These dates were chosen to encompass approximately 16 weeks before and after the enactment of the policy on February 7, 2019. Tweets were categorized according to slant, tweet category, and theme.
Results:
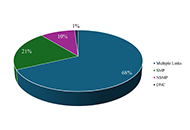
The findings revealed notable shifts in online discourse. There was a significant decrease in the proportion of tweets identified as anti-self-harm tweets and a corresponding increase in the proportion of tweets aimed at understanding self-harm, many of which were coded as personal opinions or informative content. These trends suggest that while content promoting self-harm did not increase, the tone of discourse shifted toward greater nuance and reflection. This may reflect users’ growing efforts to process, contextualize, and share perspectives on self-harm in a policy-regulated environment.
Conclusions:
Meta’s graphic self-harm imagery ban appeared to influence how users communicated about suicide and NSSI on Twitter, prompting more content centered on understanding and discussion. However, the findings also highlight challenges in balancing harm reduction with space for personal narratives. These insights emphasize the role of policy in shaping public discourse and the need for clear moderation strategies that distinguish harmful promotion from lived experience and peer support.
Aim:
The spread of suicide and non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) content on social media has raised ongoing concerns about user safety and mental health. In response, social media platforms like Twitter (now X) and Meta (i.e., Facebook and
Methods:
A corpus of 3,846 tweets was analyzed. Within this corpus, tweets spanning 32 weeks from October 18, 2018, to May 29, 2019, were selected. These dates were chosen to encompass approximately 16 weeks before and after the enactment of the policy on February 7, 2019. Tweets were categorized according to slant, tweet category, and theme.
Results:
The findings revealed notable shifts in online discourse. There was a significant decrease in the proportion of tweets identified as anti-self-harm tweets and a corresponding increase in the proportion of tweets aimed at understanding self-harm, many of which were coded as personal opinions or informative content. These trends suggest that while content promoting self-harm did not increase, the tone of discourse shifted toward greater nuance and reflection. This may reflect users’ growing efforts to process, contextualize, and share perspectives on self-harm in a policy-regulated environment.
Conclusions:
Meta’s graphic self-harm imagery ban appeared to influence how users communicated about suicide and NSSI on Twitter, prompting more content centered on understanding and discussion. However, the findings also highlight challenges in balancing harm reduction with space for personal narratives. These insights emphasize the role of policy in shaping public discourse and the need for clear moderation strategies that distinguish harmful promotion from lived experience and peer support.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2025.101154
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Health Innovations in the Battle Against Psychological Problems: Progress, Hurdles, and Prospects

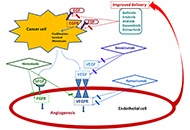
Several preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit from combined treatment with inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and angiogenesis, both effective in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In pretreated patients with advanced EGFR wild type NSCLC, bevacizumab plus erlotinib improved progression-free survival as second-line therapy in the BeTa study and as maintenance therapy in the ATLAS trial, although the benefit was modest and did not translate into an advantage in overall survival. Disappointing results were reported with oral VEGF inhibitors plus erlotinib in pretreated patients with EGFR wild type NSCLC. On the contrary, erlotinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab showed a clinically relevant improvement of progression-free survival in naïve patients with EGFR mutations, leading to the approval of these two regimens as first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutant tumors. Several clinical studies are evaluating the feasibility and activity of osimertinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab. However, limits that could affect its use in clinical practice are the need of an intravenous infusion for angiogenesis inhibitors, the increased incidence of treatment associated adverse events, the exclusion of patients with tumors located in central position or at risk of hemorrhage. The identification of predictive biomarkers is an important goal of research to optimize the combined use of these agents.
Several preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit from combined treatment with inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and angiogenesis, both effective in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In pretreated patients with advanced EGFR wild type NSCLC, bevacizumab plus erlotinib improved progression-free survival as second-line therapy in the BeTa study and as maintenance therapy in the ATLAS trial, although the benefit was modest and did not translate into an advantage in overall survival. Disappointing results were reported with oral VEGF inhibitors plus erlotinib in pretreated patients with EGFR wild type NSCLC. On the contrary, erlotinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab showed a clinically relevant improvement of progression-free survival in naïve patients with EGFR mutations, leading to the approval of these two regimens as first-line treatment of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutant tumors. Several clinical studies are evaluating the feasibility and activity of osimertinib plus bevacizumab or ramucirumab. However, limits that could affect its use in clinical practice are the need of an intravenous infusion for angiogenesis inhibitors, the increased incidence of treatment associated adverse events, the exclusion of patients with tumors located in central position or at risk of hemorrhage. The identification of predictive biomarkers is an important goal of research to optimize the combined use of these agents.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00008

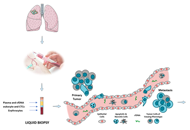
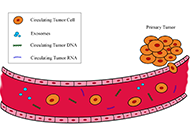
Lung cancer represents the world’s most common cause of cancer death. In recent years, we moved from a generic therapeutic strategy to a personalized approach, based on the molecular characterization of the tumor. In this view, liquid biopsy is becoming an important tool for assessing the progress or onset of lung disease. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive procedure able to isolate circulating tumor cells, tumor educated platelets, exosomes and free circulating tumor DNA from body fluids. The characterization of these liquid biomarkers can help to choose the therapeutic strategy for each different case. In this review, the authors will analyze the main aspects of lung cancer and the applications currently in use focusing on the benefits associated with this approach for predicting the prognosis and monitoring the clinical conditions of lung cancer disease.
Lung cancer represents the world’s most common cause of cancer death. In recent years, we moved from a generic therapeutic strategy to a personalized approach, based on the molecular characterization of the tumor. In this view, liquid biopsy is becoming an important tool for assessing the progress or onset of lung disease. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive procedure able to isolate circulating tumor cells, tumor educated platelets, exosomes and free circulating tumor DNA from body fluids. The characterization of these liquid biomarkers can help to choose the therapeutic strategy for each different case. In this review, the authors will analyze the main aspects of lung cancer and the applications currently in use focusing on the benefits associated with this approach for predicting the prognosis and monitoring the clinical conditions of lung cancer disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00015
This article belongs to the special issue Liquid Biopsy in Thoracic Cancer

The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the close relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are multiple, complex and only partially known. The purpose of this paper was to review the current knowledge of these mechanisms in a unified manner. Subjects with NAFLD and T2DM have established insulin resistance (IR), which exacerbates the two comorbidities. IR worsens NAFLD by increasing the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) in the liver. This occurs due to an increase in the influx of FFAs from peripheral adipose tissue by the activation of hormone-sensitive lipase. In addition, there is de novo increased lipogenesis, a transcription factor, the sterols regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c), which activates the expression of several genes strongly promotes lipogenesis by the liver and facilitate storage of triglycerides. Lipids accumulation in the liver induces a chronic stress in the endoplasmic reticulum of the hepatocytes. Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic variants associated with NAFLD severity, but unrelated to IR. In particular, the alteration of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 contributes to the susceptibility to NAFLD. Furthermore, the lipotoxicity of ceramides and diacylglycerol, well known in T2DM, triggers a chronic inflammatory process favoring the progression from hepatic steatosis to steatohepatitis. Reactive oxygen species produced by mitochondrial dysfunction trigger both liver inflammation and beta-cells damage, promoting the progression of both NAFLD and T2DM. The close association between NAFLD and T2DM is bidirectional, as T2DM may trigger both NAFLD onset and its progression, but NAFLD itself may contribute to the development of IR and T2DM. Future studies on the mechanisms will have to deepen the knowledge of the interaction between the two pathologies and should allow the identification of new therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, currently substantially absent.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00019
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring NAFLD/NASH

Lung cancer is still one of the main causes of cancer-related death, together with prostate and colorectal cancers in males and breast and colorectal cancers in females. The prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is strictly dependent on feasibility of a complete surgical resection of the tumor at diagnosis. Since surgery is indicated only in early stages tumors, it is necessary to anticipate the timing of diagnosis in clinical practice. In the diagnostic and therapeutic pathway for NSCLC, sampling of neoplastic tissue is usually obtained using invasive methods that are not free from disadvantages and complications. A valid alternative to the standard biopsy is the liquid biopsy (LB), that is, the analysis of samples from peripheral blood, urine, and other biological fluids, with a simple and non-invasive collection. In particular, it is possible to detect in the blood different tumor derivatives, such as cell-free DNA (cfDNA) with its subtype circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), cell-free RNA (cfRNA), and circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Plasma-based testing seems to have several advantages over tumor tissue biopsy; firstly, it reduces medical costs, risk of complications related to invasive procedures, and turnaround times; moreover, the analysis of genes alteration, such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and BRAF is faster and safer with this method, compared to tissue biopsy. Despite all these advantages, the evidences in literatures indicate that assays performed on liquid biopsies have a low sensitivity, making them unsuitable for screening in lung cancer at the current state. This is caused by lack of standardization in sampling and preparation of specimen and by the low concentration of biomarkers in the bloodstream. Instead, routinely use of LB should be preferred in revaluation of patients with advanced NSCLC resistant to chemotherapy, due to onset of new mutations.
Lung cancer is still one of the main causes of cancer-related death, together with prostate and colorectal cancers in males and breast and colorectal cancers in females. The prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is strictly dependent on feasibility of a complete surgical resection of the tumor at diagnosis. Since surgery is indicated only in early stages tumors, it is necessary to anticipate the timing of diagnosis in clinical practice. In the diagnostic and therapeutic pathway for NSCLC, sampling of neoplastic tissue is usually obtained using invasive methods that are not free from disadvantages and complications. A valid alternative to the standard biopsy is the liquid biopsy (LB), that is, the analysis of samples from peripheral blood, urine, and other biological fluids, with a simple and non-invasive collection. In particular, it is possible to detect in the blood different tumor derivatives, such as cell-free DNA (cfDNA) with its subtype circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), cell-free RNA (cfRNA), and circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Plasma-based testing seems to have several advantages over tumor tissue biopsy; firstly, it reduces medical costs, risk of complications related to invasive procedures, and turnaround times; moreover, the analysis of genes alteration, such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and BRAF is faster and safer with this method, compared to tissue biopsy. Despite all these advantages, the evidences in literatures indicate that assays performed on liquid biopsies have a low sensitivity, making them unsuitable for screening in lung cancer at the current state. This is caused by lack of standardization in sampling and preparation of specimen and by the low concentration of biomarkers in the bloodstream. Instead, routinely use of LB should be preferred in revaluation of patients with advanced NSCLC resistant to chemotherapy, due to onset of new mutations.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00020
This article belongs to the special issue Liquid Biopsy in Thoracic Cancer

Aim:
Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are predictive of future dementia.
Methods:
Participants were recruited from the Framingham Heart Study. The vocal responses to neuropsychological tests were recorded, which were then diarized to identify participant voice segments. Acoustic features were extracted with the OpenSMILE toolkit (v2.1). The association of each acoustic feature with incident dementia was assessed by Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
Our study included 6, 528 voice recordings from 4, 849 participants (mean age 63 ± 15 years old, 54.6% women). The majority of participants (71.2%) had one voice recording, 23.9% had two voice recordings, and the remaining participants (4.9%) had three or more voice recordings. Although all asymptomatic at the time of examination, participants who developed dementia tended to have shorter segments than those who were dementia free (P < 0.001). Additionally, 14 acoustic features were significantly associated with dementia after adjusting for multiple testing (P < 0.05 / 48 = 1 × 10–3). The most significant acoustic feature was jitterDDP_sma_de (P = 7.9 × 10–7), which represents the differential frame-to-frame Jitter. A voice based linear classifier was also built that was capable of predicting incident dementia with area under curve of 0.812.
Conclusions:
Multiple acoustic and linguistic features are identified that are associated with incident dementia among asymptomatic participants, which could be used to build better prediction models for passive cognitive health monitoring.
Aim:
Human voice contains rich information. Few longitudinal studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of voice to monitor cognitive health. The objective of this study is to identify voice biomarkers that are predictive of future dementia.
Methods:
Participants were recruited from the Framingham Heart Study. The vocal responses to neuropsychological tests were recorded, which were then diarized to identify participant voice segments. Acoustic features were extracted with the OpenSMILE toolkit (v2.1). The association of each acoustic feature with incident dementia was assessed by Cox proportional hazards models.
Results:
Our study included 6, 528 voice recordings from 4, 849 participants (mean age 63 ± 15 years old, 54.6% women). The majority of participants (71.2%) had one voice recording, 23.9% had two voice recordings, and the remaining participants (4.9%) had three or more voice recordings. Although all asymptomatic at the time of examination, participants who developed dementia tended to have shorter segments than those who were dementia free (P < 0.001). Additionally, 14 acoustic features were significantly associated with dementia after adjusting for multiple testing (P < 0.05 / 48 = 1 × 10–3). The most significant acoustic feature was jitterDDP_sma_de (P = 7.9 × 10–7), which represents the differential frame-to-frame Jitter. A voice based linear classifier was also built that was capable of predicting incident dementia with area under curve of 0.812.
Conclusions:
Multiple acoustic and linguistic features are identified that are associated with incident dementia among asymptomatic participants, which could be used to build better prediction models for passive cognitive health monitoring.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2020.00028
This article belongs to the special issue Digital Biomarkers: The New Frontier for Medicine and Research

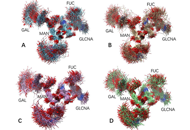
Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate Fc conformations and functions, and glycan may also regulate antigen recognition. In the antibody drug development, glycosylation patterns affect antibody drug characteristics and quality control. In order to provide a global feature of N-glycan interactions in response to antigen and Fc receptor bindings, the interactions among Fc N-glycans and N-glycans’ interaction with Fc CH2 and CH3 domains have been studied.
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate Fc conformations and functions, and glycan may also regulate antigen recognition. In the antibody drug development, glycosylation patterns affect antibody drug characteristics and quality control. In order to provide a global feature of N-glycan interactions in response to antigen and Fc receptor bindings, the interactions among Fc N-glycans and N-glycans’ interaction with Fc CH2 and CH3 domains have been studied.
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2021.00004

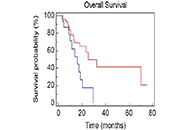
Aim:
The role of tumor burden (TB) for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving immunotherapy is still unknown. The aim of this analysis was to analyze the prognostic value of TB in a real-world sample of advanced NSCLC patients.
Methods:
Sixty-five consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC treated with immunotherapy as first or second line therapy were retrospectively analyzed between August 2015 and February 2018. TB was recorded at baseline considering sites and number of metastases, thoracic vs. extrathoracic disease, measurable disease (MD) vs. not-MD (NMD) and evaluating dimensional aspects as maximum lesion diameter (cut-off = 6.3 cm), sum of the 5 major lesions diameters (cut-off = 14.3 cm), and number of sites of metastases (cut-off > 4). All cut-offs were calculated by receiver operating characteristic curves. Median overall survival (OS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. A Cox regression model was carried out for univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results:
Median age was 70 years and most patients (86.2%) had a good performance status (PS-Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group < 2). No significant difference in OS was noted between subgroups of patients according to TB. Bone metastases (BM) had a negative prognostic impact [median OS (mOS), 13.8 vs. 70.0 months, P = 0.0009; median progression free survival in the second line (mPFS2) 2.97 vs. 8.63 months; P = 0.0037]. Patients with NMD had a poorer prognosis (mOS, 15.9 months vs. not reached, P < 0.0001; mPFS2 3.8 vs. 12.2 months; P = 0.0199). Patients with disease limited to the thorax had a better prognosis compared to patients with involvement of extrathoracic sites (mOS, 70 vs. 17.3 months; P = 0.0136). Having more than 4 metastatic sites resulted as a negative prognostic factor (mOS, 15.9 vs. 25.2 months; P = 0.0106). At multivariate analysis, BM, NMD, extrathoracic disease and number of sites of metastases > 4 were negative prognostic factors (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
This study underlines the negative prognostic impact of specific metastatic sites, presence of NMD and extrathoracic disease in advanced NSCLC patients treated with immunotherapy. However, TB does not appear to affect the outcome of these patients.
Aim:
The role of tumor burden (TB) for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving immunotherapy is still unknown. The aim of this analysis was to analyze the prognostic value of TB in a real-world sample of advanced NSCLC patients.
Methods:
Sixty-five consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC treated with immunotherapy as first or second line therapy were retrospectively analyzed between August 2015 and February 2018. TB was recorded at baseline considering sites and number of metastases, thoracic vs. extrathoracic disease, measurable disease (MD) vs. not-MD (NMD) and evaluating dimensional aspects as maximum lesion diameter (cut-off = 6.3 cm), sum of the 5 major lesions diameters (cut-off = 14.3 cm), and number of sites of metastases (cut-off > 4). All cut-offs were calculated by receiver operating characteristic curves. Median overall survival (OS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. A Cox regression model was carried out for univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results:
Median age was 70 years and most patients (86.2%) had a good performance status (PS-Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group < 2). No significant difference in OS was noted between subgroups of patients according to TB. Bone metastases (BM) had a negative prognostic impact [median OS (mOS), 13.8 vs. 70.0 months, P = 0.0009; median progression free survival in the second line (mPFS2) 2.97 vs. 8.63 months; P = 0.0037]. Patients with NMD had a poorer prognosis (mOS, 15.9 months vs. not reached, P < 0.0001; mPFS2 3.8 vs. 12.2 months; P = 0.0199). Patients with disease limited to the thorax had a better prognosis compared to patients with involvement of extrathoracic sites (mOS, 70 vs. 17.3 months; P = 0.0136). Having more than 4 metastatic sites resulted as a negative prognostic factor (mOS, 15.9 vs. 25.2 months; P = 0.0106). At multivariate analysis, BM, NMD, extrathoracic disease and number of sites of metastases > 4 were negative prognostic factors (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
This study underlines the negative prognostic impact of specific metastatic sites, presence of NMD and extrathoracic disease in advanced NSCLC patients treated with immunotherapy. However, TB does not appear to affect the outcome of these patients.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00043
This article belongs to the special issue Immunotherapy in Cancer Patients

Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant proliferative disease of monoclonal plasma cells (PCs) and is characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of PCs and excessive production of specific types of immunoglobulins. Since PCs are terminally differentiated B cells, the World Health Organization (WHO) classifies MM as lymphoproliferative B-cell disease. The incidence of MM is 6–7 cases per 100,000 people in the world every year and the second most common cancer in the blood system. Due to the effects of drug resistance and malignant regeneration of MM cells in the microenvironment, all current treatment methods can prolong both overall and symptom-free survival rates of patients with MM but cannot cure MM. Both basic and clinical studies have proven that targeted therapy leads to a clear and significant prolongation of the survival of patients with MM, but when the disease recurs again, resistance to the previous treatment will occur. Therefore, the discovery of new targets and treatment methods plays a vital role in the treatment of MM. This article introduces and summarizes targeted MM therapy, potential new targets, and future precision medicine in MM.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant proliferative disease of monoclonal plasma cells (PCs) and is characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of PCs and excessive production of specific types of immunoglobulins. Since PCs are terminally differentiated B cells, the World Health Organization (WHO) classifies MM as lymphoproliferative B-cell disease. The incidence of MM is 6–7 cases per 100,000 people in the world every year and the second most common cancer in the blood system. Due to the effects of drug resistance and malignant regeneration of MM cells in the microenvironment, all current treatment methods can prolong both overall and symptom-free survival rates of patients with MM but cannot cure MM. Both basic and clinical studies have proven that targeted therapy leads to a clear and significant prolongation of the survival of patients with MM, but when the disease recurs again, resistance to the previous treatment will occur. Therefore, the discovery of new targets and treatment methods plays a vital role in the treatment of MM. This article introduces and summarizes targeted MM therapy, potential new targets, and future precision medicine in MM.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00057

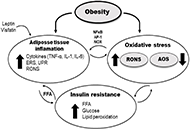
Since obesity is one of the main factors in the development of insulin resistance (IR) and is also associated with increased oxidative stress (OxS) rate, this study aims to review the published literature to collate and provide a comprehensive summary of the studies related to the status of the OxS in the pathogenesis of obesity and related IR. OxS represents an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and the capacity of the antioxidant defense system (AOS) to neutralize RONS. A steady-state of RONS level is maintained through endogenous enzymatic and non-enzymatic AOS components. Three crucial enzymes, which suppress the formation of free radicals, are superoxide dismutases, catalases, and glutathione peroxidases. The second line of AOS includes non-enzymatic components such as vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q, and glutathione which neutralizes free radicals by donating electrons to RONS. Emerging evidence suggests that high RONS levels contribute to the progression of OxS in obesity by activating inflammatory pathways and thus leading to the development of pathological states, including IR. In addition, decreased level of AOS components in obesity increases the susceptibility to oxidative tissue damage and further progression of its comorbidities. Increased OxS in accumulated adipose tissue should be an imperative target for developing new therapies in obesity-related IR.
Since obesity is one of the main factors in the development of insulin resistance (IR) and is also associated with increased oxidative stress (OxS) rate, this study aims to review the published literature to collate and provide a comprehensive summary of the studies related to the status of the OxS in the pathogenesis of obesity and related IR. OxS represents an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and the capacity of the antioxidant defense system (AOS) to neutralize RONS. A steady-state of RONS level is maintained through endogenous enzymatic and non-enzymatic AOS components. Three crucial enzymes, which suppress the formation of free radicals, are superoxide dismutases, catalases, and glutathione peroxidases. The second line of AOS includes non-enzymatic components such as vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q, and glutathione which neutralizes free radicals by donating electrons to RONS. Emerging evidence suggests that high RONS levels contribute to the progression of OxS in obesity by activating inflammatory pathways and thus leading to the development of pathological states, including IR. In addition, decreased level of AOS components in obesity increases the susceptibility to oxidative tissue damage and further progression of its comorbidities. Increased OxS in accumulated adipose tissue should be an imperative target for developing new therapies in obesity-related IR.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00074
This article belongs to the special issue Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Pathophysiological Conditions

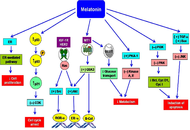
Melatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, immunomodulation, neuro-protection, and cancer progression. The precise functions of melatonin are mediated by guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein (G-protein) coupled melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and MT2 receptors. However, nuclear receptors are also associated with melatonin activity. Circadian rhythm disruption, shift work, and light exposure at night hamper melatonin production. Impaired melatonin level promotes various pathophysiological changes, including cancer. In our modern society, breast cancer is a serious problem throughout the world. Several studies have been indicated the link between low levels of melatonin and breast cancer development. Melatonin has oncostatic properties in breast cancer cells. This indolamine advances apoptosis, which arrests the cell cycle and regulates metabolic activity. Moreover, melatonin increases the treatment efficacy of cancer and can be used as an adjuvant with chemotherapeutic agents.
Melatonin is the primary hormone of the pineal gland that is secreted at night. It regulates many physiological functions, including the sleep-wake cycle, gonadal activity, free radical scavenging, immunomodulation, neuro-protection, and cancer progression. The precise functions of melatonin are mediated by guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein (G-protein) coupled melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and MT2 receptors. However, nuclear receptors are also associated with melatonin activity. Circadian rhythm disruption, shift work, and light exposure at night hamper melatonin production. Impaired melatonin level promotes various pathophysiological changes, including cancer. In our modern society, breast cancer is a serious problem throughout the world. Several studies have been indicated the link between low levels of melatonin and breast cancer development. Melatonin has oncostatic properties in breast cancer cells. This indolamine advances apoptosis, which arrests the cell cycle and regulates metabolic activity. Moreover, melatonin increases the treatment efficacy of cancer and can be used as an adjuvant with chemotherapeutic agents.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00078

Although a large number of preventative human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trials have been carried out during the last 30 years, it is remarkable that an effective HIV vaccine has not yet been developed. Research paradigms correspond to theoretical assumptions and particular strategies that scientists use when they try to solve a particular problem. Many paradigms used successfully in vaccinology were ineffective with HIV. For instance: 1) The structure-based reverse vaccinology approach failed because investigators tried to generate a vaccine starting with the antigenic structure of HIV-envelope (Env) epitopes bound to neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) derived from HIV-infected individuals. They assumed that this antigenic structure would also possess the immunogenic capacity of inducing in vaccinees a polyclonal antibody (Ab) response with the same neutralizing capacity as the mAb. 2) The structures observed in epitope-paratope crystallographic complexes result from mutually induced fit between the two partners and do not correspond to the structures present in the free molecules before they had interacted. 3) The affinity-matured neutralizing mAbs obtained from chronically infected individuals did not recognize the germline predecessors of these Abs present in vaccinees. 4) The HIV p17 matrix protein that lines the inner surface of the viral membrane is one of the most disordered proteins identified on our planet and this prevents the induced Abs from binding to the glycosylated HIV gp120 protein. 5) Vaccinologists need to solve so-called inverse problems, for instance, guessing what are the multiple causes that produced an earlier wanted beneficial effect such as the absence of deleterious HIV infection in elite controllers. Since the immune system consists of numerous subsystems that have not yet been elucidated, it is impossible to solve the inverse problems posed by each subsystem. 6) Vaccinology is an empirical science that only sometimes succeeds because we do not understand the complex mechanisms that lead to protective immune responses.
Although a large number of preventative human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vaccine trials have been carried out during the last 30 years, it is remarkable that an effective HIV vaccine has not yet been developed. Research paradigms correspond to theoretical assumptions and particular strategies that scientists use when they try to solve a particular problem. Many paradigms used successfully in vaccinology were ineffective with HIV. For instance: 1) The structure-based reverse vaccinology approach failed because investigators tried to generate a vaccine starting with the antigenic structure of HIV-envelope (Env) epitopes bound to neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) derived from HIV-infected individuals. They assumed that this antigenic structure would also possess the immunogenic capacity of inducing in vaccinees a polyclonal antibody (Ab) response with the same neutralizing capacity as the mAb. 2) The structures observed in epitope-paratope crystallographic complexes result from mutually induced fit between the two partners and do not correspond to the structures present in the free molecules before they had interacted. 3) The affinity-matured neutralizing mAbs obtained from chronically infected individuals did not recognize the germline predecessors of these Abs present in vaccinees. 4) The HIV p17 matrix protein that lines the inner surface of the viral membrane is one of the most disordered proteins identified on our planet and this prevents the induced Abs from binding to the glycosylated HIV gp120 protein. 5) Vaccinologists need to solve so-called inverse problems, for instance, guessing what are the multiple causes that produced an earlier wanted beneficial effect such as the absence of deleterious HIV infection in elite controllers. Since the immune system consists of numerous subsystems that have not yet been elucidated, it is impossible to solve the inverse problems posed by each subsystem. 6) Vaccinology is an empirical science that only sometimes succeeds because we do not understand the complex mechanisms that lead to protective immune responses.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2022.00043
This article belongs to the special issue Old and New Paradigms in Viral Vaccinology

Aim:
While it is commonly thought that left ventricular (LV) systolic function may insidiously deteriorate in hypertensive patients, few prospective data are available to support this notion.
Methods:
We evaluated 680 hypertensive patients (66 ± 7 years; 45% women) with electrocardiographic (ECG)-LV hypertrophy (ECG-LVH) enrolled in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension (LIFE) echo-sub-study free of prevalent cardiovascular disease and with baseline ejection fraction (EF) ≥ 55%. Echocardiographic examinations were performed annually for 5 years during anti-hypertensive treatment. Development of reduced systolic function was defined as incident EF < 50%.
Results:
During a mean follow-up of 4.8 ± 1 years, 37 patients developed reduced EF without an inter-current myocardial infarction (5.4%). In analysis of covariance, patients who developed reduced EF were more often men, had greater baseline LV diameter and LV mass, lower mean EF (all P < 0.05), and similar diastolic function indices. At the last available examination before EF reduction, independently of covariates, patients with reduced EF showed a significant increase in left atrium (LA) size, LV diameter, end-systolic stress and mitral E/A ratio, as compared to those who did not develop reduced EF (all P < 0.05). In time-varying Cox regression analysis, also controlling for baseline EF, predictors of developing reduced EF were higher in-treatment LV diameter [hazard ratio (HR) = 5.19 per cm; 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.58–10.41] and higher in-treatment mitral E/A ratio (HR = 2.37 per unit; 95% CI: 1.58–3.56; both P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
In treated hypertensive patients with ECG-LVH at baseline, incident reduced EF is associated with the development of dilated LV chamber and signs of increased LV filling pressure (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00338260).
Aim:
While it is commonly thought that left ventricular (LV) systolic function may insidiously deteriorate in hypertensive patients, few prospective data are available to support this notion.
Methods:
We evaluated 680 hypertensive patients (66 ± 7 years; 45% women) with electrocardiographic (ECG)-LV hypertrophy (ECG-LVH) enrolled in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension (LIFE) echo-sub-study free of prevalent cardiovascular disease and with baseline ejection fraction (EF) ≥ 55%. Echocardiographic examinations were performed annually for 5 years during anti-hypertensive treatment. Development of reduced systolic function was defined as incident EF < 50%.
Results:
During a mean follow-up of 4.8 ± 1 years, 37 patients developed reduced EF without an inter-current myocardial infarction (5.4%). In analysis of covariance, patients who developed reduced EF were more often men, had greater baseline LV diameter and LV mass, lower mean EF (all P < 0.05), and similar diastolic function indices. At the last available examination before EF reduction, independently of covariates, patients with reduced EF showed a significant increase in left atrium (LA) size, LV diameter, end-systolic stress and mitral E/A ratio, as compared to those who did not develop reduced EF (all P < 0.05). In time-varying Cox regression analysis, also controlling for baseline EF, predictors of developing reduced EF were higher in-treatment LV diameter [hazard ratio (HR) = 5.19 per cm; 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.58–10.41] and higher in-treatment mitral E/A ratio (HR = 2.37 per unit; 95% CI: 1.58–3.56; both P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
In treated hypertensive patients with ECG-LVH at baseline, incident reduced EF is associated with the development of dilated LV chamber and signs of increased LV filling pressure (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00338260).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2022.00082
This article belongs to the special issue Angiotensins—A Century of Progress

Improving the survival of patients with cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) has long proved challenging, although the treatment of this disease nowadays is on advancement. The historical invariability of survival outcomes and the limited number of agents known to be effective in the treatment of this disease has increased the number of studies designed to identify genetic targetable hits that can be efficacious for novel therapies. In this respect, the increasing feasibility of molecular profiling starting either from tumor tissue or circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has led to an increased understanding of CCA biology. Intrahepatic CCA (iCCA) and extrahepatic CCA (eCCA) display different and typical patterns of actionable genomic alterations, which offer opportunity for therapeutic intervention. This review article will summarize the current knowledge on the genomic alterations of iCCA and eCCA, provide information on the main technologies for genomic profiling using either tumor tissue or cfDNA, and briefly discuss the main clinical trials with targeted agents in this disease.
Improving the survival of patients with cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) has long proved challenging, although the treatment of this disease nowadays is on advancement. The historical invariability of survival outcomes and the limited number of agents known to be effective in the treatment of this disease has increased the number of studies designed to identify genetic targetable hits that can be efficacious for novel therapies. In this respect, the increasing feasibility of molecular profiling starting either from tumor tissue or circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has led to an increased understanding of CCA biology. Intrahepatic CCA (iCCA) and extrahepatic CCA (eCCA) display different and typical patterns of actionable genomic alterations, which offer opportunity for therapeutic intervention. This review article will summarize the current knowledge on the genomic alterations of iCCA and eCCA, provide information on the main technologies for genomic profiling using either tumor tissue or cfDNA, and briefly discuss the main clinical trials with targeted agents in this disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00079
This article belongs to the special issue Precision Medicine for Cholangiocarcinoma

Aim:
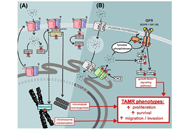
Zinc is a key secondary messenger that can regulate multiple signalling pathways within cancer cells, thus its levels need to be strictly controlled. The Zrt, Irt-like protein (ZIP, SLC39A) family of zinc transporters increase cytosolic zinc from either extracellular or intracellular stores. This study examines the relevance of zinc transporters ZIP7 and ZIP6 as therapeutic targets in tamoxifen resistant (TAMR) breast cancer.
Methods:
A series of in vitro assays, including immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and western blotting were used to evaluate levels and activity of ZIP7 and ZIP6 in models of TAMR and sensitive (MCF-7) breast cancer. Analyses of these transporters in the clinical setting were performed using publicly available online resources: Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA)2 and Kaplan-Meier Plotter (KmPlot).
Results:
Both
Conclusions:
TAMR cells displayed increased activity of both ZIP7 and ZIP6 transporters compared to anti-hormone responsive cells, suggesting their potential as novel therapeutic targets following development of resistant disease.
Aim:
Zinc is a key secondary messenger that can regulate multiple signalling pathways within cancer cells, thus its levels need to be strictly controlled. The Zrt, Irt-like protein (ZIP, SLC39A) family of zinc transporters increase cytosolic zinc from either extracellular or intracellular stores. This study examines the relevance of zinc transporters ZIP7 and ZIP6 as therapeutic targets in tamoxifen resistant (TAMR) breast cancer.
Methods:
A series of in vitro assays, including immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and western blotting were used to evaluate levels and activity of ZIP7 and ZIP6 in models of TAMR and sensitive (MCF-7) breast cancer. Analyses of these transporters in the clinical setting were performed using publicly available online resources: Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA)2 and Kaplan-Meier Plotter (KmPlot).
Results:
Both
Conclusions:
TAMR cells displayed increased activity of both ZIP7 and ZIP6 transporters compared to anti-hormone responsive cells, suggesting their potential as novel therapeutic targets following development of resistant disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00080
This article belongs to the special issue Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer

Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is an aggressive tumor characterized by a poor prognosis. In the latest years, targetable genetic alterations have been discovered in BTC patients, leading to the approval of new targeted therapies. Liquid biopsy, which is a non-invasive method for detecting tumor biomarkers from fluid samples, is a useful tool for diagnosis and molecular characterization, but also for prognosis assessment and monitoring of treatment response. In this review, recent works on liquid biopsy in BTC patients were analyzed, focusing on some relevant aspects for clinical use and trying to depict the future role of this technique. Moreover, differences between plasma and bile samples were pointed out, in light of the peculiar biology of BTC and the possibility of using bile as an alternative source of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for genomic analysis. In the era of precision oncology, the increasing adoption of liquid biopsy in BTC patients will certainly improve the management of this disease.
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is an aggressive tumor characterized by a poor prognosis. In the latest years, targetable genetic alterations have been discovered in BTC patients, leading to the approval of new targeted therapies. Liquid biopsy, which is a non-invasive method for detecting tumor biomarkers from fluid samples, is a useful tool for diagnosis and molecular characterization, but also for prognosis assessment and monitoring of treatment response. In this review, recent works on liquid biopsy in BTC patients were analyzed, focusing on some relevant aspects for clinical use and trying to depict the future role of this technique. Moreover, differences between plasma and bile samples were pointed out, in light of the peculiar biology of BTC and the possibility of using bile as an alternative source of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for genomic analysis. In the era of precision oncology, the increasing adoption of liquid biopsy in BTC patients will certainly improve the management of this disease.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00087
This article belongs to the special issue The Implementation of Liquid Biopsy in Clinical Practice for Different Solid Tumor

Aim:
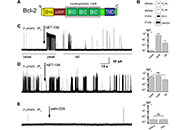
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) is a ubiquitous calcium (Ca2+) channel involved in the regulation of cellular fate and motility. Its modulation by anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) plays an important role in cancer progression. Disrupting this interaction could overcome apoptosis avoidance, one of the hallmarks of cancer, and is, thus, of great interest. Earlier reports have shown the involvement of both the Bcl-2 homology 4 (BH4) and the transmembrane domains (TMDs) of Bcl-2 in regulating IP3R activity, while the Bcl-2 hydrophobic cleft was associated primarily with its anti-apoptotic and IP3R-independent action at the mitochondria (Oncotarget. 2016;7:55704–20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11005). The aim of this study was to investigate how targeting the BH3 hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2 affects IP3R:Bcl-2 interaction.
Methods:
Organelle membrane-derived (OMD) patch-clamp and circular dichroism (CD) thermal melting experiments were used to elucidate the effects of the ABT-199 (venetoclax) on the IP3R:Bcl-2 interaction. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of free and ABT-199 bound Bcl-2 were used to propose a molecular model of such interaction.
Results:
It was shown that occlusion of Bcl-2’s hydrophobic cleft by the drug ABT-199 finely modulates IP3R gating in the low open probability (Po) regime, characteristic of the basal IP3R activity in non-excited cells. Complementary MD simulations allowed to propose a model of this modulation, involving an allosteric interaction with the BH4 domain on the opposite side of Bcl-2.
Conclusions:
Bcl-2 is an important regulator of IP3R activity and, thus of Ca2+ release from internal stores and associated processes, including cellular proliferation and death. The presence of multiple regulatory domains in both proteins suggests a complex interaction. Thus, it was found that the occlusion of the hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2 by ABT-199 disrupts IP3R activity, leading to Bcl-2 rebinding with smaller affinity and lesser inhibitory effect. MDs simulations of free and ABT-199 bound Bcl-2 propose a molecular model of such disruption, involving an allosteric interaction with the BH4 domain on the opposite side of Bcl-2.
Aim:
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) is a ubiquitous calcium (Ca2+) channel involved in the regulation of cellular fate and motility. Its modulation by anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) plays an important role in cancer progression. Disrupting this interaction could overcome apoptosis avoidance, one of the hallmarks of cancer, and is, thus, of great interest. Earlier reports have shown the involvement of both the Bcl-2 homology 4 (BH4) and the transmembrane domains (TMDs) of Bcl-2 in regulating IP3R activity, while the Bcl-2 hydrophobic cleft was associated primarily with its anti-apoptotic and IP3R-independent action at the mitochondria (Oncotarget. 2016;7:55704–20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11005). The aim of this study was to investigate how targeting the BH3 hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2 affects IP3R:Bcl-2 interaction.
Methods:
Organelle membrane-derived (OMD) patch-clamp and circular dichroism (CD) thermal melting experiments were used to elucidate the effects of the ABT-199 (venetoclax) on the IP3R:Bcl-2 interaction. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of free and ABT-199 bound Bcl-2 were used to propose a molecular model of such interaction.
Results:
It was shown that occlusion of Bcl-2’s hydrophobic cleft by the drug ABT-199 finely modulates IP3R gating in the low open probability (Po) regime, characteristic of the basal IP3R activity in non-excited cells. Complementary MD simulations allowed to propose a model of this modulation, involving an allosteric interaction with the BH4 domain on the opposite side of Bcl-2.
Conclusions:
Bcl-2 is an important regulator of IP3R activity and, thus of Ca2+ release from internal stores and associated processes, including cellular proliferation and death. The presence of multiple regulatory domains in both proteins suggests a complex interaction. Thus, it was found that the occlusion of the hydrophobic cleft of Bcl-2 by ABT-199 disrupts IP3R activity, leading to Bcl-2 rebinding with smaller affinity and lesser inhibitory effect. MDs simulations of free and ABT-199 bound Bcl-2 propose a molecular model of such disruption, involving an allosteric interaction with the BH4 domain on the opposite side of Bcl-2.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00088
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Cancer Progression and Their Relevance to Cancer Therapy

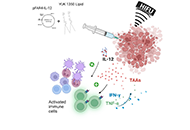
Aim:
Gene-based immunotherapy against cancer is limited by low gene transfer efficiency. In the literature, interleukin-12 (IL-12) encoding plasmid associated with sonoporation has been shown to enhance antitumoral activity. Moreover, non-viral carriers and high-frequency ultrasound have both been shown to promote immune response activation. Here, IL-12 encoding plasmid, non-viral carrier stimulating the immune response and focused ultrasound were combined in order to improve the antitumoral efficiency.
Methods:
In order to enhance a gene-based antitumoral immune response, home-made lipids Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) agonists and plasmid free of antibiotic resistance version 4 (pFAR4), a mini-plasmid, encoding the IL-12 cytokine were combined with high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). The lipid composition and the combination conditions were selected following in vitro and in vivo preliminary studies. The expression of IL-12 from our plasmid construct was measured in vitro and in vivo. The combination strategy was evaluated in mice bearing colon carcinoma cells (CT26) tumors following their weight, tumor volume, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels in the serum and produced by splenocytes exposed to CT26 tumor cells.
Results:
Lipid-mediated cell transfection and intratumoral injection into CT26 tumor mice using pFAR4-IL-12 led to the secretion of the IL-12 cytokine into cell supernatant and mice sera, respectively. Conditions of thermal deposition using HIFU were optimized. The plasmid encoding pFAR4-IL-12 or TLR2 agonist alone had no impact on tumor growth compared with control mice, whereas the complete treatment consisting of pFAR4-IL-12, TLR2 lipid agonist, and HIFU limited tumor growth. Moreover, only the complete treatment increased significantly mice survival and provided an abscopal effect on a metastatic CT26 model.
Conclusions:
The HIFU condition was highly efficient to stop tumor growth. The combined therapy was the most efficient in terms of IL-12 and IFN-γ production and mice survival. The study showed the feasibility and the limits of this combined therapy which has the potential to be improved.
Aim:
Gene-based immunotherapy against cancer is limited by low gene transfer efficiency. In the literature, interleukin-12 (IL-12) encoding plasmid associated with sonoporation has been shown to enhance antitumoral activity. Moreover, non-viral carriers and high-frequency ultrasound have both been shown to promote immune response activation. Here, IL-12 encoding plasmid, non-viral carrier stimulating the immune response and focused ultrasound were combined in order to improve the antitumoral efficiency.
Methods:
In order to enhance a gene-based antitumoral immune response, home-made lipids Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) agonists and plasmid free of antibiotic resistance version 4 (pFAR4), a mini-plasmid, encoding the IL-12 cytokine were combined with high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). The lipid composition and the combination conditions were selected following in vitro and in vivo preliminary studies. The expression of IL-12 from our plasmid construct was measured in vitro and in vivo. The combination strategy was evaluated in mice bearing colon carcinoma cells (CT26) tumors following their weight, tumor volume, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels in the serum and produced by splenocytes exposed to CT26 tumor cells.
Results:
Lipid-mediated cell transfection and intratumoral injection into CT26 tumor mice using pFAR4-IL-12 led to the secretion of the IL-12 cytokine into cell supernatant and mice sera, respectively. Conditions of thermal deposition using HIFU were optimized. The plasmid encoding pFAR4-IL-12 or TLR2 agonist alone had no impact on tumor growth compared with control mice, whereas the complete treatment consisting of pFAR4-IL-12, TLR2 lipid agonist, and HIFU limited tumor growth. Moreover, only the complete treatment increased significantly mice survival and provided an abscopal effect on a metastatic CT26 model.
Conclusions:
The HIFU condition was highly efficient to stop tumor growth. The combined therapy was the most efficient in terms of IL-12 and IFN-γ production and mice survival. The study showed the feasibility and the limits of this combined therapy which has the potential to be improved.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00090
This article belongs to the special issue Gene Delivery Approach to Fight Cancer
 Previous
Previous