
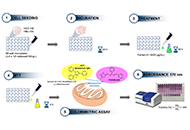



Aim:
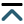
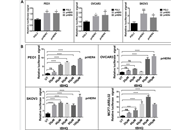
B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)-like protein-10 (Bcl2L10) is the less studied member of Bcl-2 family proteins, with the controversial role in different cancer histotypes. Very recently, Bcl2L10 expression in melanoma tumor specimens and its role in melanoma response to therapy have been demonstrated. Here, the involvement of Bcl2L10 on the in vitro and in vivo properties associated with melanoma aggressive features has been investigated.
Methods:
Endogenous Bcl2L10 protein expression was detected by western blotting analysis in a panel of patient-derived and commercially available human melanoma cells. In vitro assays to evaluate clonogenicity, cell proliferation, cell migration, cell invasion, and in vitro capillary-like structure formation [vasculogenic mimicry (VM)] have been performed by u
Results:
Results demonstrated that Bcl2L10 acts as an inducer of in vitro cell migration, invasion, and VM, while in vitro cell proliferation, in vivo tumor growth, as well as colony formation properties were not affected. Dissecting different signaling pathways, it was found that Bcl2L10 positively affects the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and the expression of markers of cell invasion, such as urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Of note, Bcl2L10-dependent in vitro migration, invasion, and VM are linked to uPAR. Bcl2L10 also negatively regulates the intracellular calcium level. Finally, reduced invasion capability in 3D spheroid invasion assay of melanoma cells transiently overexpres
Conclusions:
Overall, data reported in this paper provide evidence supporting a positive role of Bcl2L10 in melanoma aggressive features.
Aim:
B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)-like protein-10 (Bcl2L10) is the less studied member of Bcl-2 family proteins, with the controversial role in different cancer histotypes. Very recently, Bcl2L10 expression in melanoma tumor specimens and its role in melanoma response to therapy have been demonstrated. Here, the involvement of Bcl2L10 on the in vitro and in vivo properties associated with melanoma aggressive features has been investigated.
Methods:
Endogenous Bcl2L10 protein expression was detected by western blotting analysis in a panel of patient-derived and commercially available human melanoma cells. In vitro assays to evaluate clonogenicity, cell proliferation, cell migration, cell invasion, and in vitro capillary-like structure formation [vasculogenic mimicry (VM)] have been performed by u
Results:
Results demonstrated that Bcl2L10 acts as an inducer of in vitro cell migration, invasion, and VM, while in vitro cell proliferation, in vivo tumor growth, as well as colony formation properties were not affected. Dissecting different signaling pathways, it was found that Bcl2L10 positively affects the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and the expression of markers of cell invasion, such as urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Of note, Bcl2L10-dependent in vitro migration, invasion, and VM are linked to uPAR. Bcl2L10 also negatively regulates the intracellular calcium level. Finally, reduced invasion capability in 3D spheroid invasion assay of melanoma cells transiently overexpres
Conclusions:
Overall, data reported in this paper provide evidence supporting a positive role of Bcl2L10 in melanoma aggressive features.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2022.00068
This article belongs to the special issue The Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Cancer Progression and Their Relevance to Cancer Therapy

Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) is a relatively common, but largely understudied neurological syndrome which has affected the lives of many globally. The common symptoms of SFN include pain, dysesthesia, and autonomic dysfunction, which are caused by damage to small nerve fibers. Due to its heterogeneous nature, SFN causes a multitude of symptoms which makes the disease and its subtypes difficult to diagnose. Furthermore, as the pathophysiology of SFN remains largely enigmatic, no cause is found in around 50% of the cases and these are classified as idiopathic SFN (iSFN). The difficult task of diagno
Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) is a relatively common, but largely understudied neurological syndrome which has affected the lives of many globally. The common symptoms of SFN include pain, dysesthesia, and autonomic dysfunction, which are caused by damage to small nerve fibers. Due to its heterogeneous nature, SFN causes a multitude of symptoms which makes the disease and its subtypes difficult to diagnose. Furthermore, as the pathophysiology of SFN remains largely enigmatic, no cause is found in around 50% of the cases and these are classified as idiopathic SFN (iSFN). The difficult task of diagno
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2022.00033
This article belongs to the special issue The Future of Biomarkers in CNS Diseases

Aim:
Although the prevalence of coronary heart disease (CHD) and hypertension which are the most common causes of the development and progression of chronic heart failure (CHF) is high, 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring (ABPM) in patients with CHF is not mandatory to be performed. The growing number of evidence suggests that excessive decrease in BP which clearly reflects increased BP variability (BPV) affects the survival of patients with heart failure (HF). The objective of the study was to investigate the relationship between the parameters specific to CHF severity and features of daily BP profiles in patients with ischemic CHF and hypertension.
Methods:
Ninety patients with functional class II–IV of CHF and CHD (the main group) and 50 non-CHF patients with hypertension (the comparative group) were examined. The transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) [atrial end-systolic dimension (ESD), ventricular end-diastolic dimension (EDD), left ventricular mass index (LVMI), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)] and 24-hour ABPM (BPV parameters and proportions of hypotensive episodes) were performed. The relationships between the abovementioned parameters were evaluated u
Results:
Higher functional class of CHF is found to be associated with a higher incidence of daytime systolic BP (SBP) decline and nighttime SBP and diastolic BP (DBP) variability while higher LVEF is related to the hypotensive episodes regardless of CHF.
Conclusions:
It appears that the larger trials involving CHF patients with reduced LVEF should be conducted to clarify the obtained results.
Aim:
Although the prevalence of coronary heart disease (CHD) and hypertension which are the most common causes of the development and progression of chronic heart failure (CHF) is high, 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring (ABPM) in patients with CHF is not mandatory to be performed. The growing number of evidence suggests that excessive decrease in BP which clearly reflects increased BP variability (BPV) affects the survival of patients with heart failure (HF). The objective of the study was to investigate the relationship between the parameters specific to CHF severity and features of daily BP profiles in patients with ischemic CHF and hypertension.
Methods:
Ninety patients with functional class II–IV of CHF and CHD (the main group) and 50 non-CHF patients with hypertension (the comparative group) were examined. The transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) [atrial end-systolic dimension (ESD), ventricular end-diastolic dimension (EDD), left ventricular mass index (LVMI), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)] and 24-hour ABPM (BPV parameters and proportions of hypotensive episodes) were performed. The relationships between the abovementioned parameters were evaluated u
Results:
Higher functional class of CHF is found to be associated with a higher incidence of daytime systolic BP (SBP) decline and nighttime SBP and diastolic BP (DBP) variability while higher LVEF is related to the hypotensive episodes regardless of CHF.
Conclusions:
It appears that the larger trials involving CHF patients with reduced LVEF should be conducted to clarify the obtained results.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00209

Aim:
In the present study, bunch stem and cane extracts (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Malbec) rich in phenolic compounds (PCs) like flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes are studied as potential anticancer candidates.
Methods:
Twenty-three PCs were quantified by liquid chromatography-diode array fluorescence detection (LC-DAD-FLD). In vitro cytotoxic activity of both extracts on healthy (HBL-100) and colorectal cancer (HCT-116) human cell lines was assessed by 3-(4,5-di-methylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction assay.
Results:
Cane extract did not show cytotoxic effect for the tested lines, which can be considered as an advantage for its application in the pharmaceutical industry. Conversely, the bunch stem extract showed a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on HCT-116 and an IC50 of 680 µg/mL after 48 h of incubation; but not reported cytotoxic activity on the healthy cell line, evidencing a beneficial selective activity. The reported results encourage further investigation of these extracts as potential preventive and/or therapeutic drugs, or their combined use with chemotherapeutic treatments that lead to a potential dose reduction.
Conclusions:
The results preliminarily demonstrated that the extracts have potential anticancer properties or do not cause damage at the cellular level, encouraging their application as functional/nutraceutical or phytotherapeutic agents.
Aim:
In the present study, bunch stem and cane extracts (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Malbec) rich in phenolic compounds (PCs) like flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes are studied as potential anticancer candidates.
Methods:
Twenty-three PCs were quantified by liquid chromatography-diode array fluorescence detection (LC-DAD-FLD). In vitro cytotoxic activity of both extracts on healthy (HBL-100) and colorectal cancer (HCT-116) human cell lines was assessed by 3-(4,5-di-methylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction assay.
Results:
Cane extract did not show cytotoxic effect for the tested lines, which can be considered as an advantage for its application in the pharmaceutical industry. Conversely, the bunch stem extract showed a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect on HCT-116 and an IC50 of 680 µg/mL after 48 h of incubation; but not reported cytotoxic activity on the healthy cell line, evidencing a beneficial selective activity. The reported results encourage further investigation of these extracts as potential preventive and/or therapeutic drugs, or their combined use with chemotherapeutic treatments that lead to a potential dose reduction.
Conclusions:
The results preliminarily demonstrated that the extracts have potential anticancer properties or do not cause damage at the cellular level, encouraging their application as functional/nutraceutical or phytotherapeutic agents.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00049
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease

Aim:
The germination of maize leads to many physiological changes in the plant. These changes are responsible for the appearance, disappearance, and variation in concentration of numerous compounds, including secondary metabolites. The aim of this study was to compare the secondary metabolite profile of two maize varieties germinated under controlled optimal conditions.
Methods:
To achieve this, the Atp-Y variety was soaked for 25.12 h at 25.54˚C in the presence of 0.5238% plant ash, germinated for 144.37 h, and matured for 37.65 h. For the Coca-sr variety, the grains were soaked for 1.608 h at 36.63˚C in the presence of 1.1093% plant ash. Germination and ripening took 144.37 h and 27.07 h, respectively. The compounds were extracted in methanol (HPLC grade) before being injected into a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) equipped with an Rtx-5MS column for metabolite profiling.
Results:
These analyses showed that variety and optimum germination conditions influenced the secondary metabolite profile. This profiling identified 15 and 12 compounds in the Atp-Y and Coca-sr varieties, respectively. Of these compounds, 8 were identified in both varieties. The groups of compounds identified were fatty acids, esters, ketones, phenols, polyols, alcohols, sterols, and unclassified substances. Fatty acids were the most abundant, with proportions of 90.93% and 91.08% Atp-Y and Coca-sr, respectively. Within this group of compounds, (Z,Z)-9,12-octadecadienoic acid was the most abundant (46.58% for Atp-Y and 53.84% for Coca-sr), followed by (E)-9-octadecenoic acid (30.39% for Atp-Y and 25.09% for Coca-sr). 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol, a phenolic compound, was identified and quantified at 0.28% only in the Coca-sr variety, while the only polyol, 1,4-anhydro-D-mannitol, was identified in the Atp-Y variety.
Conclusions:
In view of these results, we would suggest u
Aim:
The germination of maize leads to many physiological changes in the plant. These changes are responsible for the appearance, disappearance, and variation in concentration of numerous compounds, including secondary metabolites. The aim of this study was to compare the secondary metabolite profile of two maize varieties germinated under controlled optimal conditions.
Methods:
To achieve this, the Atp-Y variety was soaked for 25.12 h at 25.54˚C in the presence of 0.5238% plant ash, germinated for 144.37 h, and matured for 37.65 h. For the Coca-sr variety, the grains were soaked for 1.608 h at 36.63˚C in the presence of 1.1093% plant ash. Germination and ripening took 144.37 h and 27.07 h, respectively. The compounds were extracted in methanol (HPLC grade) before being injected into a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) equipped with an Rtx-5MS column for metabolite profiling.
Results:
These analyses showed that variety and optimum germination conditions influenced the secondary metabolite profile. This profiling identified 15 and 12 compounds in the Atp-Y and Coca-sr varieties, respectively. Of these compounds, 8 were identified in both varieties. The groups of compounds identified were fatty acids, esters, ketones, phenols, polyols, alcohols, sterols, and unclassified substances. Fatty acids were the most abundant, with proportions of 90.93% and 91.08% Atp-Y and Coca-sr, respectively. Within this group of compounds, (Z,Z)-9,12-octadecadienoic acid was the most abundant (46.58% for Atp-Y and 53.84% for Coca-sr), followed by (E)-9-octadecenoic acid (30.39% for Atp-Y and 25.09% for Coca-sr). 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol, a phenolic compound, was identified and quantified at 0.28% only in the Coca-sr variety, while the only polyol, 1,4-anhydro-D-mannitol, was identified in the Atp-Y variety.
Conclusions:
In view of these results, we would suggest u
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101087

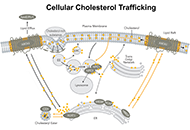
Cholesterol serves as an essential lipid molecule in various membrane organelles of mammalian cells. The metabolites of cholesterol also play important functions. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (ACAT1), also named as sterol O-acyltransferase 1, is a membrane-bound enzyme residing at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It converts cholesterol to cholesteryl esters (CEs) for storage, and is expressed in all cells. CEs cannot partition in membranes; they can only coalesce as cytosolic lipid droplets. Excess CEs are found in the vulnerable region of the brains of patients with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and in cell and mouse models for AD. Reducing CE contents by genetic inactivation of ACAT1, or by pharmacological inhibition of ACAT is shown to reduce amyloidopathy and other hallmarks for AD. To account for the various beneficial actions of the ACAT1 blockade (A1B), a working hypothesis is proposed here: the increase in CE contents observed in the AD brain is caused by damages of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts that are known to occur in neurons affected by AD. These damages cause cholesterol to release from lipid rafts and move to the ER where it will be converted to CEs by ACAT1. In addition, the increase in CE contents may also be caused by overloading with cholesterol-rich substances, or through activation of ACAT1 gene expression by various pro-inflammatory agents. Both scenarios may occur in microglia of the chronically inflamed brain. A1B ameliorates AD by diverting the cholesterol pool destined for CE biosynthesis such that it can be utilized more efficiently to repair membrane damage in various organelles, and to exert regulatory actions more effectively to defend against AD. To test the validity of the A1B hypothesis in cell culture and in vivo, the current status of various anti-ACAT1 agents that could be further developed is briefly discussed.
Cholesterol serves as an essential lipid molecule in various membrane organelles of mammalian cells. The metabolites of cholesterol also play important functions. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (ACAT1), also named as sterol O-acyltransferase 1, is a membrane-bound enzyme residing at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It converts cholesterol to cholesteryl esters (CEs) for storage, and is expressed in all cells. CEs cannot partition in membranes; they can only coalesce as cytosolic lipid droplets. Excess CEs are found in the vulnerable region of the brains of patients with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and in cell and mouse models for AD. Reducing CE contents by genetic inactivation of ACAT1, or by pharmacological inhibition of ACAT is shown to reduce amyloidopathy and other hallmarks for AD. To account for the various beneficial actions of the ACAT1 blockade (A1B), a working hypothesis is proposed here: the increase in CE contents observed in the AD brain is caused by damages of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts that are known to occur in neurons affected by AD. These damages cause cholesterol to release from lipid rafts and move to the ER where it will be converted to CEs by ACAT1. In addition, the increase in CE contents may also be caused by overloading with cholesterol-rich substances, or through activation of ACAT1 gene expression by various pro-inflammatory agents. Both scenarios may occur in microglia of the chronically inflamed brain. A1B ameliorates AD by diverting the cholesterol pool destined for CE biosynthesis such that it can be utilized more efficiently to repair membrane damage in various organelles, and to exert regulatory actions more effectively to defend against AD. To test the validity of the A1B hypothesis in cell culture and in vivo, the current status of various anti-ACAT1 agents that could be further developed is briefly discussed.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2021.00014
This article belongs to the special issue Cholesterol Dyshomeostasis in Neurological Diseases

Aim:
Tamoxifen (TAM) resistance remains a clinical issue in breast cancer. The authors previously reported that 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (HPGD) was significantly downregulated in tamoxifen-resistant (TAMr) breast cancer cell lines. Here, the authors investigated the relationship between HPGD expression, TAM resistance and prediction of outcome in breast cancer.
Methods:
HPGD overexpression and silencing studies were performed in isogenic TAMr and parental human breast cancer cell lines to establish the impact of HPGD expression on TAM resistance. HPGD expression and clinical outcome relationships were explored u
Results:
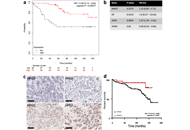
Restoration of HPGD expression and activity sensitised TAMr MCF-7 cells to TAM and 17β-oestradiol, whilst HPGD silencing in parental MCF-7 cells reduced TAM sensitivity. TAMr cells released more prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) than controls, which was reduced in TAMr cells stably transfected with HPGD. Exogenous PGE2 signalled through the EP4 receptor to reduce breast cancer cell sensitivity to TAM. Decreased HPGD expression was associated with decreased overall survival in ERα-positive breast cancer patients.
Conclusions:
HPGD downregulation in breast cancer is associated with reduced response to TAM therapy via PGE2-EP4 signalling and decreases patient survival. The data offer a potential target to develop combination therapies that may overcome acquired tamoxifen resistance.
Aim:
Tamoxifen (TAM) resistance remains a clinical issue in breast cancer. The authors previously reported that 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (HPGD) was significantly downregulated in tamoxifen-resistant (TAMr) breast cancer cell lines. Here, the authors investigated the relationship between HPGD expression, TAM resistance and prediction of outcome in breast cancer.
Methods:
HPGD overexpression and silencing studies were performed in isogenic TAMr and parental human breast cancer cell lines to establish the impact of HPGD expression on TAM resistance. HPGD expression and clinical outcome relationships were explored u
Results:
Restoration of HPGD expression and activity sensitised TAMr MCF-7 cells to TAM and 17β-oestradiol, whilst HPGD silencing in parental MCF-7 cells reduced TAM sensitivity. TAMr cells released more prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) than controls, which was reduced in TAMr cells stably transfected with HPGD. Exogenous PGE2 signalled through the EP4 receptor to reduce breast cancer cell sensitivity to TAM. Decreased HPGD expression was associated with decreased overall survival in ERα-positive breast cancer patients.
Conclusions:
HPGD downregulation in breast cancer is associated with reduced response to TAM therapy via PGE2-EP4 signalling and decreases patient survival. The data offer a potential target to develop combination therapies that may overcome acquired tamoxifen resistance.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2020.00021

Aim:
The present study investigates the influence of various homogenization techniques, namely high-pressure valve homogenization and microfluidization, and different forms of modified sunflower lecithin, including deoiled (DL) and hydrolyzed (HL) variants, on the development of monolayer and bilayer nanoemulsions of chia oil.
Methods:
Oil-in-water (O/W) nanoemulsions with 5% chia seed oil were prepared u
Results:
Overall, the studied modified sunflower lecithin (DL and HL) demonstrated effective capability in stabilizing chia nanoemulsions and facilitating the formation of the double-layered structure following Ch deposition. Concerning the homogenization method, it has been demonstrated that under the same homogenization conditions, microfluidization resulted in significantly smaller droplet sizes and higher apparent viscosities compared to high-pressure valve homogenization. This discrepancy can be attributed to the design of the homogenization chambers, as microfluidization generates a narrow distribution of shear forces, while high-pressure valve homogenization yields a much broader distribution. In contrast to chia monolayer nanoemulsions, the nanoemulsions stabilized by modified sunflower lecithin-Ch demonstrated a noteworthy improvement in their overall stability. This enhancement can be ascribed to their increased apparent viscosity and the highly charged interfaces of the droplets. Furthermore, throughout the entire refrigerated storage period, the omega-3 content in all nanoemulsions remained unchanged.
Conclusions:
In this study, mono and bilayer chia oil nanoemulsions were successfully obtained u
Aim:
The present study investigates the influence of various homogenization techniques, namely high-pressure valve homogenization and microfluidization, and different forms of modified sunflower lecithin, including deoiled (DL) and hydrolyzed (HL) variants, on the development of monolayer and bilayer nanoemulsions of chia oil.
Methods:
Oil-in-water (O/W) nanoemulsions with 5% chia seed oil were prepared u
Results:
Overall, the studied modified sunflower lecithin (DL and HL) demonstrated effective capability in stabilizing chia nanoemulsions and facilitating the formation of the double-layered structure following Ch deposition. Concerning the homogenization method, it has been demonstrated that under the same homogenization conditions, microfluidization resulted in significantly smaller droplet sizes and higher apparent viscosities compared to high-pressure valve homogenization. This discrepancy can be attributed to the design of the homogenization chambers, as microfluidization generates a narrow distribution of shear forces, while high-pressure valve homogenization yields a much broader distribution. In contrast to chia monolayer nanoemulsions, the nanoemulsions stabilized by modified sunflower lecithin-Ch demonstrated a noteworthy improvement in their overall stability. This enhancement can be ascribed to their increased apparent viscosity and the highly charged interfaces of the droplets. Furthermore, throughout the entire refrigerated storage period, the omega-3 content in all nanoemulsions remained unchanged.
Conclusions:
In this study, mono and bilayer chia oil nanoemulsions were successfully obtained u
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00029
This article belongs to the special issue Delivery of Hydrophobic Compounds in Food Systems

Aim:
To evaluate the reach and potential effectiveness of teleteaching of health providers in paediatric rheumatology by observing the pattern of sessions, attendance, and attendees’ feedback in paediatric rheumatology teleteaching sessions across the Asia Pacific region. These were conducted by the Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology (APLAR) Paediatric Rheumatology Special Interest Group (Paeds Rheum SIG) as an APLAR academy activity.
Methods:
A retrospective, descriptive analysis of electronic records of synchronous telehealth sessions held between July 2021 to July 2023. These followed three formats: case-based webinars,
Results:
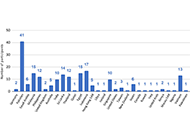
Case-based webinars had an average attendance of 200 per webinar: majority adult rheumatologists, paediatric rheumatologists (PRs), or paediatricians. The modular course consisted of nine sessions with an average of 63 participants per session. Specialties comprised PRs, adult rheumatologists with immunologists, and general paediatricians. The one-day hybrid course had over 600 attendees. Attendees were adult rheumatologists, general physicians, paediatricians, and PRs. Although the majority (79.3%) of attendees from these sessions were from APLAR member nation organisations (MNOs), a significant percentage (20.7%) were from non-APLAR MNOs and even non-Asia Pacific regions. The attendees’ feedback for all three formats showed a high level of satisfaction with case-based webinars being most favoured.
Conclusions:
Teleteaching in paediatric rheumatology has the potential to fulfill the dire need for improved expertise of health professionals managing children with rheumatic diseases. Case-based, interactive sessions of shorter duration and a blended hybrid format may garner the most attendance and best learning outcomes.
Aim:
To evaluate the reach and potential effectiveness of teleteaching of health providers in paediatric rheumatology by observing the pattern of sessions, attendance, and attendees’ feedback in paediatric rheumatology teleteaching sessions across the Asia Pacific region. These were conducted by the Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology (APLAR) Paediatric Rheumatology Special Interest Group (Paeds Rheum SIG) as an APLAR academy activity.
Methods:
A retrospective, descriptive analysis of electronic records of synchronous telehealth sessions held between July 2021 to July 2023. These followed three formats: case-based webinars,
Results:
Case-based webinars had an average attendance of 200 per webinar: majority adult rheumatologists, paediatric rheumatologists (PRs), or paediatricians. The modular course consisted of nine sessions with an average of 63 participants per session. Specialties comprised PRs, adult rheumatologists with immunologists, and general paediatricians. The one-day hybrid course had over 600 attendees. Attendees were adult rheumatologists, general physicians, paediatricians, and PRs. Although the majority (79.3%) of attendees from these sessions were from APLAR member nation organisations (MNOs), a significant percentage (20.7%) were from non-APLAR MNOs and even non-Asia Pacific regions. The attendees’ feedback for all three formats showed a high level of satisfaction with case-based webinars being most favoured.
Conclusions:
Teleteaching in paediatric rheumatology has the potential to fulfill the dire need for improved expertise of health professionals managing children with rheumatic diseases. Case-based, interactive sessions of shorter duration and a blended hybrid format may garner the most attendance and best learning outcomes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2024.00042
This article belongs to the special issue Digital health technologies in rheumatology: emerging evidence and innovation

Aim:
The aim of the present study is to conduct interobserver and intra-observer validation of computer analysis of static ultrasound images of entheseal territories of the Achilles and distal patellar tendons.
Methods:
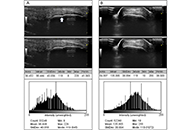
Three rheumatologists with varying levels of experience underwent training in the use of ImageJ software for the analysis of 384 pairs of ultrasound images (long and short axis) from recorded studies of the Achilles and patellar tendons of both spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients and controls. Intra-observer and interobserver tests were conducted by calculating the differences in measurements of the same image at two different times by the same observer and by two different observers asses
Results:
In the intra-observer test, no measurement showed a difference greater than 15%, ranging from 4.10% to 14.14%. In the interobserver test, no measurement exhibited a difference greater than 16%, ranging from 7.96% to 15.87%. The differences detected were evenly distributed among observers in both the intra-observer and inter-observer tests. Higher differences were detected in the analysis of images obtained from patient studies compared to control studies in almost all measurements.
Conclusions:
Whether analyzing control or patient ultrasound images of Achilles and patellar tendons, the intra-observer and interobserver agreement of computer-based analysis of static ultrasound images is more than acceptable and predominantly excellent.
Aim:
The aim of the present study is to conduct interobserver and intra-observer validation of computer analysis of static ultrasound images of entheseal territories of the Achilles and distal patellar tendons.
Methods:
Three rheumatologists with varying levels of experience underwent training in the use of ImageJ software for the analysis of 384 pairs of ultrasound images (long and short axis) from recorded studies of the Achilles and patellar tendons of both spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients and controls. Intra-observer and interobserver tests were conducted by calculating the differences in measurements of the same image at two different times by the same observer and by two different observers asses
Results:
In the intra-observer test, no measurement showed a difference greater than 15%, ranging from 4.10% to 14.14%. In the interobserver test, no measurement exhibited a difference greater than 16%, ranging from 7.96% to 15.87%. The differences detected were evenly distributed among observers in both the intra-observer and inter-observer tests. Higher differences were detected in the analysis of images obtained from patient studies compared to control studies in almost all measurements.
Conclusions:
Whether analyzing control or patient ultrasound images of Achilles and patellar tendons, the intra-observer and interobserver agreement of computer-based analysis of static ultrasound images is more than acceptable and predominantly excellent.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2024.00044
This article belongs to the special issue Digital health technologies in rheumatology: emerging evidence and innovation

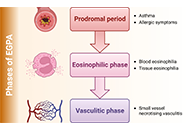
Eo
Eo
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2023.00006
This article belongs to the special issue The Era of Biologics in Allergy

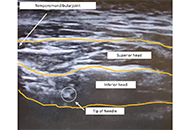
Upon self-reflection, some clinicians privately confess a lack of confidence in being able to safely perform trigger point dry needling (TrPDN) or trigger point injection (TrPI) on craniofacial muscles. Procedural performance anxiety seems to be more pronounced relative to those muscles that cannot be palpated and/or have an increased risk of iatrogenic injury to neurovascular structures. Participatory action ultrasound imaging (PAUI) can be a useful tool in enhancing clinician confidence. A clinician-subject with a left lateral pterygoid trigger point was dry-needled under ultrasound guidance by a clinician-needler with extensive training and experience relative to evaluation and treatment of patients with craniofacial pain. Prior to PAUI, both the clinician-needler and clinician-observer describe low-to-moderate anxiety in the performance of TrPDN of the lateral pterygoid, u
Upon self-reflection, some clinicians privately confess a lack of confidence in being able to safely perform trigger point dry needling (TrPDN) or trigger point injection (TrPI) on craniofacial muscles. Procedural performance anxiety seems to be more pronounced relative to those muscles that cannot be palpated and/or have an increased risk of iatrogenic injury to neurovascular structures. Participatory action ultrasound imaging (PAUI) can be a useful tool in enhancing clinician confidence. A clinician-subject with a left lateral pterygoid trigger point was dry-needled under ultrasound guidance by a clinician-needler with extensive training and experience relative to evaluation and treatment of patients with craniofacial pain. Prior to PAUI, both the clinician-needler and clinician-observer describe low-to-moderate anxiety in the performance of TrPDN of the lateral pterygoid, u
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2024.00033

Aim:
Triticale is a well adaptable crop, tolerant of disease and abiotic stresses, and able to grow with good yields even in poor soil, thus representing a good choice to develop a new industrial agri-chain in Italy in a sustainability contest, to cope with its soil problems due to incoming desertification.
Methods:
Two triticale elite lines were grown in marginal lands in controlled field experiments. The lines were harvested at two different development stages, namely green mass and seeds, and suitable standard protocols were applied to test their potential to produce bioethanol in line with the emerging bioenergy processes.
Results:
The protocols applied were able to obtain bioethanol with a good yield from both feedstocks. In particular, very efficient fermentation kinetics was observed u
Conclusions:
Therefore, the results of this research point to new sustainable potential for industrial applications of triticale crops in Italy. Furthermore, the high activity of the endogenous amylolytic enzymes, mainly α-amylase, and the high starch content suggest the potential use of triticale in other industrial applications, like the brewing industry.
Aim:
Triticale is a well adaptable crop, tolerant of disease and abiotic stresses, and able to grow with good yields even in poor soil, thus representing a good choice to develop a new industrial agri-chain in Italy in a sustainability contest, to cope with its soil problems due to incoming desertification.
Methods:
Two triticale elite lines were grown in marginal lands in controlled field experiments. The lines were harvested at two different development stages, namely green mass and seeds, and suitable standard protocols were applied to test their potential to produce bioethanol in line with the emerging bioenergy processes.
Results:
The protocols applied were able to obtain bioethanol with a good yield from both feedstocks. In particular, very efficient fermentation kinetics was observed u
Conclusions:
Therefore, the results of this research point to new sustainable potential for industrial applications of triticale crops in Italy. Furthermore, the high activity of the endogenous amylolytic enzymes, mainly α-amylase, and the high starch content suggest the potential use of triticale in other industrial applications, like the brewing industry.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00054
This article belongs to the special issue Metrological Aspects in the Analysis of Nutrients, Functional Compounds, Additives and Contaminants in Food and Feed

Aim:
Despite advances in lymphoma treatment, resistance to conventional therapies and insufficient immune-mediated tumor clearance remain major challenges. This study investigates the dual antitumor mechanisms of the mushroom-derived triterpenoid, ganoderic acid DM (GA-DM), exploring its ability to induce programmed cell death while enhancing immune recognition in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Methods:
DLBCL cells (DB and Toledo) were treated with GA-DM (0–40 μM), and cell viability was assessed via MTS assay. Apoptosis was evaluated through caspase-3 activation and inhibition by ZVAD-FMK, while autophagy was measured via LC3 protein expression. Flow cytometry analyzed HLA class II surface expression and antigen presentation to CD4+ T cells (via IL-2 production), with autophagy’s role further confirmed u
Results:
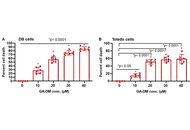
GA-DM exhibited potent and dose-dependent cytotoxicity against DLBCL cells, with concentrations of 30–40 μM inducing over 60% cell death within 24 h. Mechanistic studies revealed that GA-DM activated the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as evidenced by caspase-3 cleavage and the significant reduction in cell death upon ZVAD-FMK treatment. Concurrently, GA-DM treatment upregulated the autophagy marker LC3-II, indicating the induction of autophagy. Strikingly, GA-DM also enhanced the immunogenicity of lymphoma cells by increa
Conclusions:
GA-DM synergistically induces apoptosis and autophagy while promoting immune-mediated tumor clearance through enhanced HLA class II antigen presentation. These findings highlight GA-DM as a promi
Aim:
Despite advances in lymphoma treatment, resistance to conventional therapies and insufficient immune-mediated tumor clearance remain major challenges. This study investigates the dual antitumor mechanisms of the mushroom-derived triterpenoid, ganoderic acid DM (GA-DM), exploring its ability to induce programmed cell death while enhancing immune recognition in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Methods:
DLBCL cells (DB and Toledo) were treated with GA-DM (0–40 μM), and cell viability was assessed via MTS assay. Apoptosis was evaluated through caspase-3 activation and inhibition by ZVAD-FMK, while autophagy was measured via LC3 protein expression. Flow cytometry analyzed HLA class II surface expression and antigen presentation to CD4+ T cells (via IL-2 production), with autophagy’s role further confirmed u
Results:
GA-DM exhibited potent and dose-dependent cytotoxicity against DLBCL cells, with concentrations of 30–40 μM inducing over 60% cell death within 24 h. Mechanistic studies revealed that GA-DM activated the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as evidenced by caspase-3 cleavage and the significant reduction in cell death upon ZVAD-FMK treatment. Concurrently, GA-DM treatment upregulated the autophagy marker LC3-II, indicating the induction of autophagy. Strikingly, GA-DM also enhanced the immunogenicity of lymphoma cells by increa
Conclusions:
GA-DM synergistically induces apoptosis and autophagy while promoting immune-mediated tumor clearance through enhanced HLA class II antigen presentation. These findings highlight GA-DM as a promi
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2025.1003216

Aim:
The aim of this study is to apply untargeted proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and chemometric analysis to obtain the cacao pod husk (CPH) fingerprint and evaluate the effect of dehydration in the CPH metabolome.
Methods:
Phosphate buffer extracts (pH 6.5) were obtained and measured u
Results:
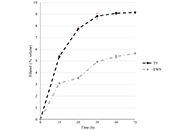
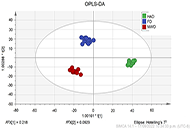
A total of 25 compounds were detected by 1H NMR, methylxanthines, sugars, some amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids were found among the identified compounds. The fingerprint spectra of the three dehydration methods were clustered separately discriminating the metabolome profile of each of the dehydration treatments, finding that metabolome remarkably differed in theanine, myristic acid, fumaric acid, and aspartic acid composition.
Conclusions:
An untargeted metabolomics to obtain the fingerprint of CPH was successfully established. A 1H NMR spectra with a detailed signal assignment aided to identify 25 metabolites present in CPH fresh and dried by different methods. The results complement the information about CPH composition and how it is affected by the temperature used during the dehydration process. The multivariate analysis points out that freeze drying (FD) preserves the metabolites better than microwave drying (MWD) or hot air drying (HAD). FD and MWD are similar in composition maintaining most of the compounds after drying.
Aim:
The aim of this study is to apply untargeted proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) and chemometric analysis to obtain the cacao pod husk (CPH) fingerprint and evaluate the effect of dehydration in the CPH metabolome.
Methods:
Phosphate buffer extracts (pH 6.5) were obtained and measured u
Results:
A total of 25 compounds were detected by 1H NMR, methylxanthines, sugars, some amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids were found among the identified compounds. The fingerprint spectra of the three dehydration methods were clustered separately discriminating the metabolome profile of each of the dehydration treatments, finding that metabolome remarkably differed in theanine, myristic acid, fumaric acid, and aspartic acid composition.
Conclusions:
An untargeted metabolomics to obtain the fingerprint of CPH was successfully established. A 1H NMR spectra with a detailed signal assignment aided to identify 25 metabolites present in CPH fresh and dried by different methods. The results complement the information about CPH composition and how it is affected by the temperature used during the dehydration process. The multivariate analysis points out that freeze drying (FD) preserves the metabolites better than microwave drying (MWD) or hot air drying (HAD). FD and MWD are similar in composition maintaining most of the compounds after drying.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00009

Aim:
To describe the clinical characteristics and frequency of anti-factor H (FH) autoantibody-associated atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) in the first cohort of Argentine patients.
Methods:
The presence of anti-FH autoantibodies in 70 pediatric patients with suspected aHUS was investigated between 2013 and 2022. Clinical and laboratory parameters were collected and compared between patients who were positive and negative for anti-FH antibodies.
Results:
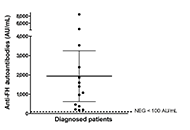
The 70 patients screened for anti-FH autoantibodies presented clinical features of non-immune microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and renal injury. Positive titers were found in 14 children [mean: 1,938 arbitrary units per mL (AU/mL), range 179–8,500]. Due to mis
Conclusions:
The cohort of 70 pediatric patients in this study demonstrated that the frequency of anti-FH autoantibody-associated aHUS in Argentina is 20%. The implementation of anti-FH testing in the country can potentially contribute to improved treatment and follow-up for patients with autoimmune aHUS.
Aim:
To describe the clinical characteristics and frequency of anti-factor H (FH) autoantibody-associated atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) in the first cohort of Argentine patients.
Methods:
The presence of anti-FH autoantibodies in 70 pediatric patients with suspected aHUS was investigated between 2013 and 2022. Clinical and laboratory parameters were collected and compared between patients who were positive and negative for anti-FH antibodies.
Results:
The 70 patients screened for anti-FH autoantibodies presented clinical features of non-immune microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and renal injury. Positive titers were found in 14 children [mean: 1,938 arbitrary units per mL (AU/mL), range 179–8,500]. Due to mis
Conclusions:
The cohort of 70 pediatric patients in this study demonstrated that the frequency of anti-FH autoantibody-associated aHUS in Argentina is 20%. The implementation of anti-FH testing in the country can potentially contribute to improved treatment and follow-up for patients with autoimmune aHUS.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2023.00118
This article belongs to the special issue The Complement System in Health and Disease

Aim:
The extraction of polyphenols is commonly accomplished u
Methods:
The effect of four factors on the extraction of polyphenols (percentage in relation to the initial weight of PDCF) and on the antioxidant activity [quantified by 2,2’-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) methods] was investigated and the UAE and MAE processes were optimized u
Results:
It was found that MAE improved the extraction yield (polyphenol content and antioxidant activity) in shorter extraction times when compared to UAE.
Conclusions:
The application of these alternative green technologies improved the performance of the polyphenol extraction process from PDCF. Overall, both techniques could be used as efficient green alternatives.
Aim:
The extraction of polyphenols is commonly accomplished u
Methods:
The effect of four factors on the extraction of polyphenols (percentage in relation to the initial weight of PDCF) and on the antioxidant activity [quantified by 2,2’-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) methods] was investigated and the UAE and MAE processes were optimized u
Results:
It was found that MAE improved the extraction yield (polyphenol content and antioxidant activity) in shorter extraction times when compared to UAE.
Conclusions:
The application of these alternative green technologies improved the performance of the polyphenol extraction process from PDCF. Overall, both techniques could be used as efficient green alternatives.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00017
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Aim:
To evaluate angioten
Methods:
From the 218 patients recruited (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04411446), 16 participated in this sub-study and were randomized to a
Results:
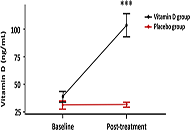
A trend towards an increase in Ang-(1-7) and a decrease in Ang II levels were observed in placebo- and vitD-treated COVID-19 patients compared to baseline values. There was no difference in Ang II and Ang-(1-7) levels between placebo- and vitD-treated COVID-19 patients. Similar results were obtained with ILs profile. COVID-19 patients showed an increase in the protective component of the RAS which was not improved by vitD treatment.
Conclusions:
VitD did not improve RAS disbalance in COVID-19. Notwithstanding, the authors visualize that acute treatment with high doses of vitD may show a trend to a decline in inflammatory ILs and an increase in protective markers. Finally, the authors would like to highlight the limitations of this preliminary study, namely the small number of patients and the use of a large
Aim:
To evaluate angioten
Methods:
From the 218 patients recruited (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04411446), 16 participated in this sub-study and were randomized to a
Results:
A trend towards an increase in Ang-(1-7) and a decrease in Ang II levels were observed in placebo- and vitD-treated COVID-19 patients compared to baseline values. There was no difference in Ang II and Ang-(1-7) levels between placebo- and vitD-treated COVID-19 patients. Similar results were obtained with ILs profile. COVID-19 patients showed an increase in the protective component of the RAS which was not improved by vitD treatment.
Conclusions:
VitD did not improve RAS disbalance in COVID-19. Notwithstanding, the authors visualize that acute treatment with high doses of vitD may show a trend to a decline in inflammatory ILs and an increase in protective markers. Finally, the authors would like to highlight the limitations of this preliminary study, namely the small number of patients and the use of a large
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2023.00137
This article belongs to the special issue Lung Fibrosis—Models and Mechanisms

Aim:
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is a key component in the cell’s response to oxidative and electrophilic stress and is a transcription factor regulating the expression of a collection of anti-oxidative and cytoprotective genes. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4/erbB4) regulates growth and differentiation in many cancer types. Here, NRF2 and HER4 receptor interactions were investigated in a panel of ovarian cancer cell lines.
Methods:
Pharmacological [tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) and retinoid/rexinoid, bexarotene] and genetic [small interfering RNA (siRNA)] manipulations were used to activate or inhibit NRF2 function in the cell line panel (PE01, OVCAR3, SKOV3). Activity of the HER-targeted tyro
Results:
While tBHQ increased the levels of both phosphorylated-NRF2 (pNRF2) and HER4 in PE01, OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells, bexatorene and NRF2-target siRNA treatment decreased pNRF2 and total HER4 levels. The tBHQ-dependent pharmacological activation of NRF2 attenuated the therapeutic effectiveness of ERL and LAP. Analyses of gene expression data from a HER4 driven reporter system and in vitro or in vivo cancer models, support NRF2 regulation of HER4 expression.
Conclusions:
These results support the presence of signaling interaction between the NRF2 and HER4 receptor pathways and suggest that intervention modulating this cross-talk could have anticancer therapeutic value.
Aim:
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is a key component in the cell’s response to oxidative and electrophilic stress and is a transcription factor regulating the expression of a collection of anti-oxidative and cytoprotective genes. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4/erbB4) regulates growth and differentiation in many cancer types. Here, NRF2 and HER4 receptor interactions were investigated in a panel of ovarian cancer cell lines.
Methods:
Pharmacological [tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ) and retinoid/rexinoid, bexarotene] and genetic [small interfering RNA (siRNA)] manipulations were used to activate or inhibit NRF2 function in the cell line panel (PE01, OVCAR3, SKOV3). Activity of the HER-targeted tyro
Results:
While tBHQ increased the levels of both phosphorylated-NRF2 (pNRF2) and HER4 in PE01, OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells, bexatorene and NRF2-target siRNA treatment decreased pNRF2 and total HER4 levels. The tBHQ-dependent pharmacological activation of NRF2 attenuated the therapeutic effectiveness of ERL and LAP. Analyses of gene expression data from a HER4 driven reporter system and in vitro or in vivo cancer models, support NRF2 regulation of HER4 expression.
Conclusions:
These results support the presence of signaling interaction between the NRF2 and HER4 receptor pathways and suggest that intervention modulating this cross-talk could have anticancer therapeutic value.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00040

Hydrogel-based drug delivery systems (DDS) offer promi
Hydrogel-based drug delivery systems (DDS) offer promi
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ebmx.2024.00023
This article belongs to the special issue Bioprinted Hydrogels for Engineering Tissues and Organs
 Previous
Previous