118 results in Exploration of Drug Science
Most Downloaded
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Review
Critical review on nutritional, bioactive and medicinal potential of Bunium persicum
Prachi Bhatt ... Mamta Baunthiyal
Published: February 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100893

Open Access
Original Article
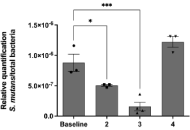
Efficacy of propolis varnish in reducing Streptococcus mutans counts
Mariana Passos De Luca ... Vagner Rodrigues Santos
Published: March 20, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100899
Open Access
Original Article
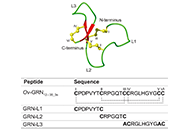
Identification of an inter-cysteine loop potentially involved in the activity of Opisthorchis viverrini-granulin-1
Rozita Takjoo ... Norelle L. Daly
Published: June 30, 2023 Explor Drug Sci. 2023;1:172–179
This article belongs to the special issue Exploring Potential Drugs from Natural Products
Open Access
Review
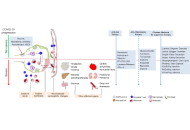
Novel progression on clinical therapy of COVID-19: Western and Traditional Chinese Medicines
Yongjia Xiong ... Feiyue Xing
Published: March 26, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008102
Open Access
Review
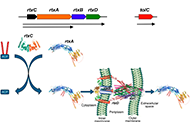
Potential use of peptides mimicking CRAC/CARC domains as antivirulence therapies to inhibit RTX toxins activities
Vanesa Herlax
Published: November 20, 2024 Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2:836–850
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides: Pioneering Innovations in Latin American Research
Open Access
Review
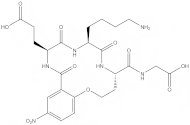
Dimeric dipeptide mimetics of neurotrophins as molecular tools and potential neuroprotective drugs
Tatiana Gudasheva ... Vladimir Dorofeev
Published: March 21, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008100
Open Access
Original Article
Interaction of brequinar and analogs with PD-L1: a molecular docking analysis
Gérard Vergoten, Christian Bailly
Published: June 09, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008113
Open Access
Original Article
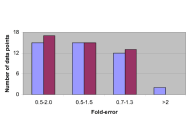
A simple quantitative model for the prediction of exposure of renally excreted drugs in pregnant women: a comparison with whole body PBPK model
Iftekhar Mahmood
Published: July 01, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008115
Open Access
Retraction
Retraction: Controlled release of dexamethasone phosphate from modified mesoporous biocompatible silica nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and kinetic studies
Juan Manuel Galdopórpora ... María Victoria Tuttolomondo
Published: March 17, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100896

Open Access
Mini Review
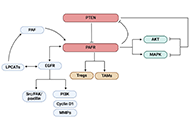
Impact of the crosstalk between the PTEN and PAFR as well as PAFR and EGFR pathways in cancer
Anita Thyagarajan ... Ravi P. Sahu
Published: January 14, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100883
Open Access
Original Article
Control of diabetic nephropathy in male Wistar rats using ethanolic extract of Monodora myristica seeds and its biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles
Babalola Ola Yusuf ... Rasheed Bolaji Ibrahim
Published: February 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100889
Open Access
Original Article
Revolutionizing diabetes treatment: computational insights into 4-hydroxy isoleucine derivatives and advanced molecular screening for antidiabetic compounds
Lakshmi Mounika Kelam ... M. Elizabeth Sobhia
Published: April 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008104
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Molecules from Natural Sources
Open Access
Original Article
High-risk neuroblastoma stage 4 (NBS4): multi-target inhibitors for c-Src kinases (Csk) and retinoic acid (RA) signalling pathways
Amgad Gerges, Una Canning
Published: May 09, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008109
Open Access
Review
Inflammatory bowel disease in Africa: the current landscape of pharmacological treatments and the promise of emerging innovations
Murtada A. Oshi
Published: July 10, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008117
Open Access
Review
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic prospects of 4-aminobenzoic acid in neuropsychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review of neurotransmitter modulation, anti-inflammatory pathways, and antioxidant defense
Siyu Chen ... Yangyang Liu
Published: March 19, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:100898
Open Access
Original Article
Combinatorial and fragment-based in silico design of PI3K-alpha natural hybrid antagonists for breast cancer therapeutics
Navya Aggarwal ... Banashree Bondhopadhyay
Published: April 29, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008108
Open Access
Original Article
Cytochrome P450 2C9-mediated interactions: molecular docking studies of natural anti-arthritic compounds
Boon Hooi Tan ... Chin Eng Ong
Published: May 27, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008111
Open Access
Review
Prominent events in the development of a simultaneous multidiagnostic system with synthetic peptides
Oscar Noya ... Sandra Losada
Published: July 17, 2025 Explor Drug Sci. 2025;3:1008118
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development
Journal Information
