19 results in Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy
Latest
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Commentary
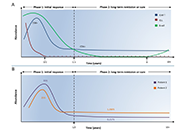
A decade of CD4+ chimeric antigen receptor T-cell evolution in two chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients: were chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells present?
Dimitrios Bouzianas, Stella Bouziana
Published: October 31, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1128–1135
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Strategies and Targets for Immunotherapy of Cancer
Open Access
Perspective
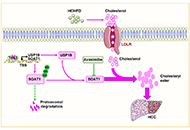
Cholesterol esterification and p53-mediated tumor suppression
Youjun Li ... Edward V. Prochownik
Published: October 31, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1122–1127
This article belongs to the special issue Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Original Article
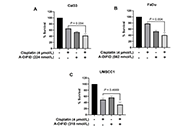
Acryl-3,5-bis(2,4-difluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone targeting cellular JUN proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression
Levi Arnold ... Sufi Mary Thomas
Published: October 31, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1104–1121
This article belongs to the special issue Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Systematic Review
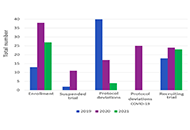
Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on good clinical practice trials in oncology
Veronica Agostinelli ... Rossana Berardi
Published: October 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1095–1103
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer
Open Access
Review
Coronavirus disease 2019 and lung cancer: where are we?
Abrahams Ocanto ... Felipe Couñago
Published: October 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1082–1094
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer
Open Access
Review
Overcoming phenotypic switching: targeting protein-protein interactions in cancer
Christos Ladias ... Nikolaos A. Papanikolaou
Published: October 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1071–1081
This article belongs to the special issue Off-label drugs and -omics data in cancer treatment
Open Access
Original Article
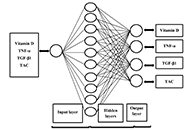
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory markers and total antioxidant capacity in breast cancer women using a machine learning technique
Marzieh Tahmasebi ... Amir Jamshidnezhad
Published: October 30, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1059–1070
Open Access
Systematic Review
Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 on diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review
Afrooz Mazidimoradi ... Hamid Salehiniya
Published: October 26, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1039–1058
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer
Open Access
Review
Integration of signaling pathway and bromodomain and extra-terminal domain inhibition for the treatment of mutant Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog cancer
Gerhard Hamilton ... Barbara Rath
Published: October 26, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:1027–1038
This article belongs to the special issue Integrated Approaches for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Open Access
Review
A review on in silico virtual screening methods in COVID-19 using anticancer drugs and other natural/chemical inhibitors
Babak Sokouti
Published: October 26, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:994–1026
Open Access
Review
Melatonin, BAG-1 and cortisol circadian interactions in tumor pathogenesis and patterned immune responses
George Anderson
Published: October 25, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:962–993
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Insights into Immunotherapy Targeting Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer
Open Access
Review
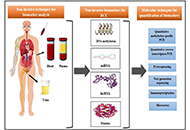
Biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma and their targeted therapies: a review
Shruti Gupta, Shamsher Singh Kanwar
Published: October 25, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:941–961
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Open Access
Systematic Review
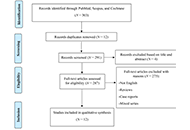
Current role of artificial intelligence in head and neck cancer surgery: a systematic review of literature
Antonella Loperfido ... Gianluca Bellocchi
Published: October 24, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:933–940
This article belongs to the special issue Artificial Intelligence for Precision Oncology
Open Access
Review
Molecular interaction of metastasis suppressor genes and tumor microenvironment in breast cancer
Sathammai Sathappa Supuramanian ... Sitaram Harihar
Published: October 11, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:912–932
This article belongs to the special issue Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment
Open Access
Original Article
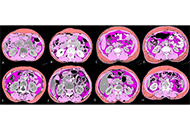
Exploring the implications of modified advanced lung cancer inflammation index on outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Abhishek Mahajan ... Kumar Prabhash
Published: October 11, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:896–911
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Open Access
Review
Understanding the feasibility of chemotherapeutic and immunotherapeutic targets against non-small cell lung cancers: an update of resistant responses and recent combinatorial therapies
Parth Malik ... Tapan Kumar Mukherjee
Published: October 10, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:850–895
This article belongs to the special issue Integrated Approaches for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
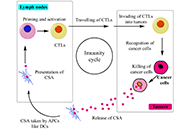
Open Access
Review
AGEs and RAGE: metabolic and molecular signatures of the glycation-inflammation axis in malignant or metastatic cancers
Gowri Palanissami, Solomon F.D. Paul
Published: September 28, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:812–849
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
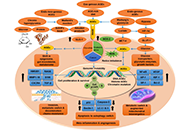
Open Access
Review
Malignant tumors of the external auditory canal: diagnosis, treatment, genetic landscape, biomarkers, and clinical outcome
Pinelopi Samara ... Ioannis Athanasopoulos
Published: September 21, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:801–811
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
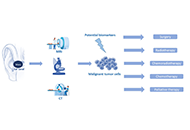
Open Access
Original Article
A single experience in the conduction of clinical trial during COronaVIrusDisease-2019 pandemic
Zelmira Ballatore ... Rossana Berardi
Published: September 07, 2023 Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4:793–800
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer