Medicinal Plants and Bioactive Phytochemicals in Neuroprotection
Guest Editor
Prof. Marcello Iriti E-Mail
Professor of Plant Biology and Pathology at the Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, Milan State University, Milan, Italy
Research Keywords: Phytotherapeutics, neuroprotection, natural products, neurodegenerative diseases, disease prevention, nutraceuticals
About the Special lssue
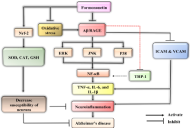
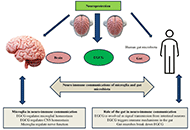
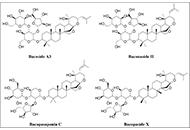
Medicinal and food plants represent an unlimited source of bioactive phytochemicals available for improving human health and preventing chronic, degenerative diseases. Indeed, a single plant contains hundreds or thousands of active metabolites able to target different mechanisms involved in brain aging and neurodegeneration including oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and immunosenescence associated with the often-irreversible deterioration of intellectual and cognitive faculties, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease. From this perspective, phytotherapy and nutritional therapy can represent an effective preventive strategy to counteract the global burden of neurodegenerative disorders in association with physical activity and other lifestyles responsible for healthy ageing. However, for a suitable neuroprotective agent, a very important property is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), to reach target sites of the central nervous system (CNS). A limited number of studies, both in vitro and in animal models, have focused on the ability of phytochemicals to cross the endothelial cell layer of the BBB, depending on the compound lipophilicity and the activity of specific plasma membrane transporters or receptors. Therefore, a better understanding of the bioavailability of dietary phytochemicals is crucial to correctly evaluate their bioactivity, interpret experimental results and design new approaches, particularly in the CNS. In fact, the biokinetic data supporting their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the human body are still fragmentary, despite the huge number of indications on their bioactivity. Finally, although the presence of phytochemical receptors or transporters in brain tissues remains to be ascertained, compounds with multiple targets appear as a potential and promising class of therapeutics for the treatment of diseases of multifactorial etiology.
Keywords: Neurodegenerative diseases, amyloidosis, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, neuroaging, immunosenescence, phytotherapeutics, herbal remedies, nutritional therapy, bioactive phytochemicals, nutraceuticals, functional foods, ethnopharmacology
Published Articles