Affiliation:
1Center for Invasive Cardiology, Electrotherapy, and Angiology, 33-300 Nowy Sącz, Poland
2Clinical Research Center Intercard, 31-514 Kraków, Poland
Email: marektomala@gmail.com
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7882-9255
Explor Cardiol. 2025;3:101275 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2025.101275
Received: July 25, 2025 Accepted: September 15, 2025 Published: October 15, 2025
Academic Editor: Teresa Tsang, University of British Columbia, Canada
The article belongs to the special issue Multimodality Imaging in Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, highlighting the necessity for better diagnostic modalities. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being used with multimodal cardiovascular diagnostic testing to provide standardized and reproducible assessment methodologies that have been shown to detect subtle signals beyond human recognition. This state-of-the-art review will summarize the various applications of AI across key modalities: describing its use in electrocardiography to risk-stratify patients; in coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) for quantitative plaque and stenosis measurements as well as measuring fractional flow reserve (FFR) derived from imaging; in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to automatically segment cardiac chambers and characterize tissue; and in intracoronary imaging [specifically intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT)], where automation is evolving. We will also discuss combining these sources of data through clinical decision support systems (CDSS) that can enhance the comprehensive evaluation of IHD. We anticipate several issues for implementation, including validation, regulation, transparency, and clinical integration. Overall, AI can help reduce the number of time-consuming manual measurements used to augment quantitative features of an assessment and improve physiology-based decision-making. However, there were marked differences in performance based on the task and dataset, and AI was not always better than the human experts. Ultimately, AI must be validated prospectively, must be generalizable, and reported transparently for safe adoption in IHD care globally.
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is still the leading cause of death and morbidity around the world, affecting millions of patients and contributing to significant healthcare costs [1]. IHD is presented in different ways: stable angina and acute coronary syndromes fall on a spectrum of coronary artery disease (CAD), making the selection of appropriate diagnostic pathways challenging and patient-specific. The latest European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2024 guidelines on chronic coronary syndromes emphasize a tailored approach—including identification of patients with very low likelihood of obstructive CAD who may not require testing, and the use of noninvasive imaging [computed tomography (CT) or functional tests] as first-line diagnostics based on pre-test probability [2]. Historically, the diagnosis of IHD has relied on clinical assessment (including history and examination) and various procedures and tests, such as electrocardiography, biochemical markers, and imaging. The limitations of traditional paradigms of diagnostic assessment include inter-observer variability between researchers, subjective inference, and the inability to adequately describe the complexity of IHD. These limitations have led to a renewed interest in enhancing the diagnostic evaluation methods for IHD [3].
This review surveys the current state-of-the-art algorithmic methods for diagnosing IHD [4], exploring the combination of artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML) and multimodal imaging, advanced intracoronary assessment, and new-age diagnostic platforms that could revolutionize modern cardiovascular practice in the future.
While contemporary diagnostic pathways for chronic coronary syndromes have advanced since the last guideline update, emphasizing pre-test clinical likelihood, appropriate use of anatomic and functional testing, and the incorporation of risk modifiers, we accordingly position AI/ML advances within the context of the current pathways’ logic to better delineate where algorithmic tools can supplement, rather than supplant standard approaches. Thus, in this context, we examine task-specific applications: an AI-electrocardiogram (ECG) for risk stratification [e.g., reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) screening] [5, 6]; coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) for quantitative plaque/stenosis analysis and machine-learning-enabled fractional flow reserve (FFR)-CT [7–9]; cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) for automation of chamber/function/tissue characterization [10, 11]; and certain intracoronary uses [intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)/optical coherence tomography (OCT)] where automation is emerging [12–14]. Finally, we clarify considerations related to validation, implementation, and regulation to highlight demonstrated clinical utility from aspirational prototypes.
ML applications in cardiovascular medicine employ various algorithmic approaches, each with its advantages for specific diagnostic questions. Supervised learning algorithms, such as support vector machines, random forests, and neural networks, have demonstrated excellent performance in classification tasks related to pattern identification, particularly in detecting CAD [15].
Deep learning (DL) architectures such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have changed medical image analysis by automatically extracting differentiating features from complex imaging data without significant manual feature engineering. CNNs can simultaneously process large amounts of imaging data and identify subtle patterns and relationships that are beyond human perception [16].
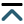
An overview of supervised, reinforcement, and unsupervised learning across ECG, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and echocardiography (ECHO) is shown in Figure 1, which illustrates how multimodal inputs feed algorithmic pipelines to generate diagnostic outputs.
Algorithmic approaches in cardiovascular diagnosis. Schematic overview showing how multimodal inputs—ECG, cardiac magnetic resonance (MRI), and transthoracic echocardiography (ECHO)—feed algorithmic pipelines to produce diagnostic outputs. The figure contrasts three learning paradigms: (1) supervised learning (labeled data → model training → predictions and model update with new data); (2) reinforcement learning (agent-environment loop using state, action, and reward to improve policy); and (3) unsupervised learning (clustering/structure discovery from unlabeled data). The end-point is a workstation rendering of a cardiac diagnosis. ECG: electrocardiogram; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging. Created in BioRender. Tomala, M. (2025) https://www.biorender.com/7ykr1qa.
AI-facilitated electrocardiographic interpretation exemplifies a modern achievement of effective identification in the cardiovascular sphere. Early studies are also exploring AI-enabled ECG models to identify patients with silent ischemia or obstructive CAD despite normal ECG findings; however, this approach is not yet validated for routine practice [17–19]. DL networks have learned patterns from millions of ECG recordings and can detect subtle changes potentially associated with CAD, in some cases achieving performance comparable to experienced clinicians [16].
CCTA has evolved from an anatomical imaging modality to a diagnostic tool through algorithmic advancements. Modern AI-based CCTA analysis platforms can determine the presence, quantity, and type of coronary plaque with high accuracy and reproducibility [20, 21].
ML algorithms applied to CCTA data can identify high-risk plaque features, such as positive remodeling, low-attenuation plaques, spotty calcifications, and the napkin-ring sign—all of which are linked with increased risk of acute coronary syndromes. These systems exhibit high consistency compared to human interpretation, saving time on analysis [8].
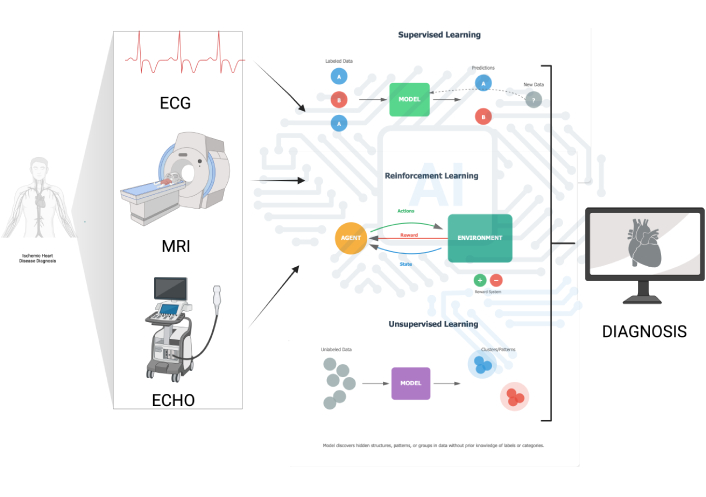
The clinical workflow and system architecture for AI-enabled CCTA analysis are summarized in Figure 2.
AI-enhanced CCTA analysis protocol. Panel A—Clinical workflow & AI processing pipeline. Image acquisition (premedication as required; heart-rate control; ECG-gated CCTA with contrast; standard technical parameters and quality control) is followed by AI processing (automated coronary segmentation; plaque and stenosis detection/quantification using convolutional neural networks). Clinical output includes CAD-RADS 2.0 grading (categories 0–5), stenosis/severity assessment, risk stratification (e.g., MACE prediction with calibrated probabilities and confidence intervals), and structured reporting; integration options include HL7/FHIR and accelerated reporting. Panel B—System integration architecture. CT scanner (DICOM) → AI processing service → validation/quality check → structured report (DICOM SR TID 1500) → PACS archive → EMR for the finalized clinical report. AI: artificial intelligence; CAD-RADS: Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; EMR: electronic medical record; FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources; HL7: Health Level Seven; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; PACS: picture archiving and communication system; CT: computed tomography; DICOM: Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine; ECG: electrocardiogram.
By integrating FFR derived from CT (FFR-CT) with ML algorithms, the diagnostic capabilities of CCTA have advanced further. AI-enhanced FFR-CT analysis can determine the hemodynamic significance of coronary stenosis with similar diagnostic accuracy to invasive pressure wire measures, but non-invasively [9]. For example, the commercially available HeartFlow FFR-CT platform has been shown in multicenter studies to improve CCTA’s diagnostic performance by correctly reclassifying non-significant lesions and matching invasive FFR measurements [9].
By incorporating AI enhancements, CMR imaging enables the comprehensive assessment of myocardial anatomy, function, and tissue characteristics on a broader scale than previously possible. More recent automated analysis programs can segment cardiac chambers with minimal user input, measure ejection fraction, and detect myocardial scarring (e.g., myocarditis) with accuracy and timeliness [11].
Moving outside the typical CMR anatomical analysis, new DL models applied to CMR perfusion imaging identify subtle perfusion abnormalities associated with CAD, with improved sensitivity compared to visual analysis. These algorithms examine dynamic sequences of perfusion, including quantitative perfusion mapping, and quantify regional perfusion defects with high diagnostic accuracy [10].
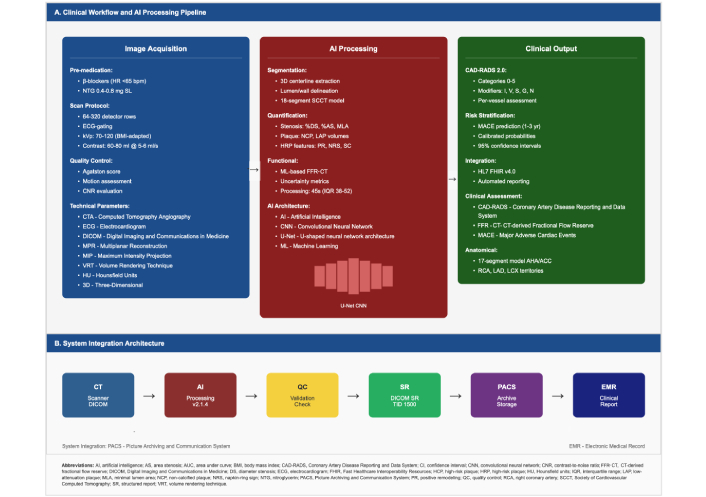
The AI-integrated pipeline for chamber segmentation, tissue characterization, and perfusion mapping is depicted in Figure 3, which summarizes the CMR preprocessing, DL analysis, and standardized reporting steps.
Automated cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) analysis workflow with AI integration. Stage 1—DICOM download of multi-sequence CMR (cine, LGE, T1/T2 mapping, perfusion, etc.). Stage 2—AI preprocessing (denoising, motion correction, intensity normalization, quality assurance). Stage 3—DL analysis for automated LV/RV chamber and myocardial segmentation, feature extraction, perfusion, and strain metrics. Stage 4—Clinical parameters: ejection fraction, ventricular volumes, mass, strain, and flow/valve quantification. Stage 5—Clinical report: automated, standardized, and structured. System performance/implementation notes: processing designed to complete within minutes per study, supports batch processing, exhibits high segmentation accuracy and reproducibility, is DICOM-compatible, and integrates with HL7/FHIR and electronic medical record (EMR) systems. DICOM: Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine; DL: deep learning; LV/RV: left/right ventricle; LGE: late gadolinium enhancement; AI: artificial intelligence; HL7: Health Level Seven; FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources.
Key AI applications, typical performance ranges, and primary use cases are summarized in Table 1. Table 1 provides a modality-by-modality overview relevant to screening, anatomic, and physiologic assessment.
Imaging modalities and AI applications.
| Modality | Algorithm type | Diagnostic accuracy | Main applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECG | DL neural network (AI-ECG) | AI-ECG models demonstrate AUROC 0.85–0.94 for CAD phenotypes | CAD detection and risk stratification from resting ECG | [17] |
| CCTA | CNN, ML algorithms (automated plaque analysis) | DL plaque/stenosis: Sens ~ 84–89%, Spec ~ 85–96% (Han et al. [20] 2020; Jin et al. [21] 2022); FFR-CT: accuracy ~ 85–87% vs. invasive FFR (MACHINE) | Automated plaque quantification; identification of high-risk plaque features; non-invasive FFR-CT | [7, 9, 20, 21] |
| CMR | DL (fully convolutional networks) | High accuracy of automated segmentation; AI-perfusion with improved sensitivity vs. visual assessment | LV/RV segmentation; quantitative tissue characterization of ischemic scar | [10, 11] |
| HD-IVUS | ML, neural networks | High concordance with experts; lumen ~ 85%, stent area ~ 97% | Automated lumen/media segmentation; plaque composition; PCI optimization in IHD | [22, 23] |
| OCT | ML algorithms (high-resolution wall analysis) | Comparable to expert analysis (task-specific) | TCFA identification; macrophage assessment; stent implantation optimization (lumen segmentation, landing zone selection) | [12–14] |
| FFR (image-derived) | ML, 3D reconstruction | Accuracy ~ 85% vs. invasive FFR (CT/FFR/angiography-derived) | Non-invasive hemodynamic assessment of stenosis significance; potential reduction in pressure wire use | [9, 14] |
AI: artificial intelligence; CAD: coronary artery disease; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CMR: cardiovascular magnetic resonance; CT: computed tomography; ECG: electrocardiogram; FFR: fractional flow reserve; FFR-CT: FFR derived from CT; HD-IVUS: high-definition intravascular ultrasound; ML: machine learning; OCT: optical coherence tomography; AUROC: area under the ROC curve; CNN: convolutional neural network; DL: deep learning; LV/RV: left/right ventricle; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma; 3D: three-dimensional; IHD: ischemic heart disease.
HD-IVUS represents a significant advancement in intracoronary visualization strategies, providing an unprecedented understanding of coronary vessel wall morphology and plaque features. The integration of AI algorithms with HD-IVUS has transformed our understanding of plaque analysis and procedural guidance [24].
State-of-the-art HD-IVUS systems with ML capabilities can automatically identify vessel boundaries, quantify plaque burden, and characterize plaques in terms of their components. These algorithms can differentiate fibrous, fibro-fatty, necrotic core, and dense calcium features, providing a more thorough plaque analysis to guide therapy decisions [25].
The end-to-end AI pipeline for HD-IVUS acquisition, analysis, and reporting is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 illustrates automated lumen/media segmentation, plaque characterization, and decision-support outputs.
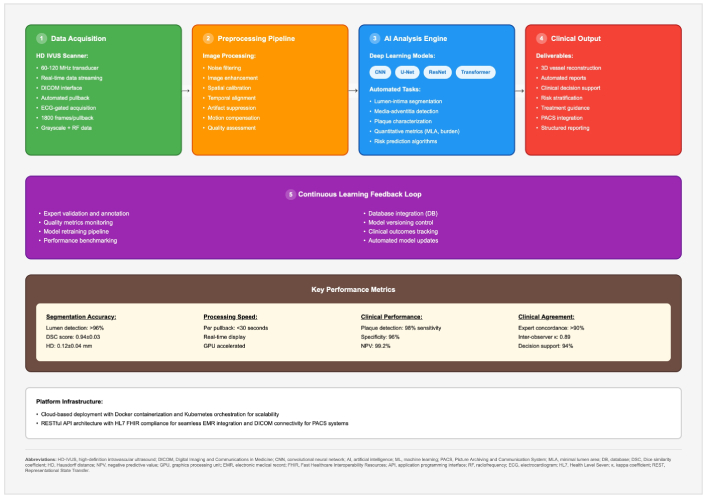
HD-IVUS algorithm analysis platform. HD-IVUS: high-definition intravascular ultrasound.
End-to-end workflow for automated analysis of HD-IVUS, showing:
Data acquisition—HD-IVUS scanner with automatic pullback, ECG-gated acquisition, Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) interface, and storage of raw/RF frames.
Pre-processing pipeline—noise filtering, speckle reduction, image enhancement, temporal alignment, artefact suppression, motion compensation, and quality assessment.
AI analysis engine DL models (e.g., CNN, U-Net, ResNet, Transformer) performing lumen/media segmentation, plaque characterization, disease/stenosis detection, quantitative metrics (e.g., minimum lumen area, plaque burden), and risk-prediction algorithms.
Clinical output—three-dimensional (3D) vessel reconstruction, automated stenosis report, decision-support summaries for risk stratification and treatment guidance, picture archiving and communication system (PACS)/electronic medical record (EMR) integration, and structured reporting.
Continuous learning feedback loop—expert validation/annotation, quality-metrics monitoring, dataset curation, model versioning, clinical-outcomes tracking, and automated model updates.
Key performance domains. Segmentation accuracy, processing speed (per pullback/real-time capability), diagnostic performance [sensitivity/specificity/negative predictive value (NPV)/positive predictive value (PPV) by task], and clinical agreement with experts.
Platform infrastructure (implementation example): cloud-native deployment with containerization/orchestration for scalability, RESTful APIs with Health Level Seven (HL7)/Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) interoperability, and DICOM connectivity to PACS systems.
The AVVIGO+ Automated Lesional Assessment platform is an example of the integration of AI with HD-IVUS imaging. This platform provides automated measurement of luminal area, vessel area, and plaque burden in real-time, with 85% agreement for lumen assessments and 97% agreement for stent area measurements [22].
Advanced neural networks applied to HD-IVUS data can predict procedural outcomes related to optimal stent size, expansion characteristics, and potential complications. These predictive models can analyze the overall geometry of the vessel, the distribution of plaque, and the characteristics of the underlying tissue to recommend personalized procedural strategies for each patient [26].
OCT is currently the highest-resolution imaging modality for coronary vessels, providing detailed information on plaque microstructure and the characteristics of the vessel wall. The advent of AI to enhance the analysis of images derived from OCT has enabled OCT to become a powerful diagnostic and therapeutic guidance tool [12].
ML applications to OCT data have automated the identification and quantification of thin-cap fibroatheromas (TCFAs), lipid pools, macrophage infiltration, and other components of high-risk plaque with greater accuracy than expert human analysis. Furthermore, these ML algorithms are capable of analyzing terabytes of data across thousands of OCT cross-section images in seconds, leading to a robust assessment of the entire vessel [13].
As shown in Figure 5, the OCT AI engine automates lumen and wall segmentation, feature extraction, and high-risk plaque characterization. Figure 5 displays the processing steps and clinical outputs used for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) planning and follow-up.
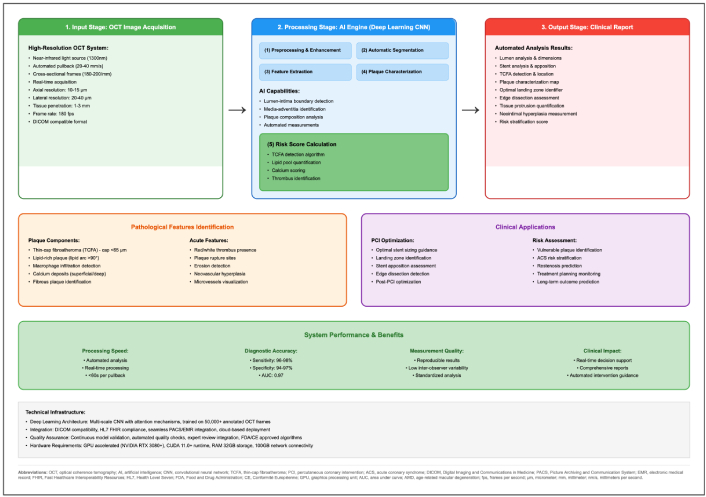
AI-enhanced optical coherence tomography (OCT) analysis platform: automated intracoronary image processing workflow. Input—OCT acquisition. High-resolution intracoronary pullbacks in a DICOM-compatible format. Processing—AI engine (deep learning CNN). (1) Preprocessing & enhancement; (2) automatic lumen/wall segmentation; (3) feature extraction; (4) plaque characterization; optional (5) risk-score calculators and automated measurements. Screenshot—user interface view showing automated lumen and wall segmentation overlays, plaque characterization outputs, and stent-planning suggestions (sizing and landing zones). Output—clinical report. Automated identification of lesions and high-risk features (e.g., TCFA, macrophage signal, calcium burden), quantification, stent-planning suggestions, and longitudinal follow-up visualization. Clinical applications. PCI optimization (device sizing, landing-zone selection, post-stent assessment) and risk assessment (event prediction, restenosis monitoring). System performance & benefits. Fast processing, high reproducibility/standardization, improved measurement quality, and comprehensive structured reports. CNN: convolutional neural network; DICOM: Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma; AI: artificial intelligence.
The Ultreon OCT software is a clinical example of AI-enabled software for OCT-guided interventions. The Ultreon system uses ML algorithms that automate lumen segmentation, make stent sizing recommendations, and identify optimal landing zones, with the aim of improving clinical outcomes.
Sophisticated OCT AI algorithms have emerged that can predict stent under-expansion for calcified lesions based on pre-procedural imaging analysis, which enables the identification of the best methods to address calcifications and plan for procedural optimization strategies. The predictive models of stent expansion in calcified lesions analyze calcification geometry and patterns, plaque morphology, and vessel geometry to inform deployment decisions, demonstrating significant potential [27].
The combination of AI with FFR assessment has significantly enhanced the accuracy and capability for performing physiological assessments of coronary arteries. ML algorithms can take angiographic image inputs to create 3D reconstructions of the vessels’ geometry to calculate pressure gradients across stenotic regions [28].
Recent AI-enabled FFR systems [including quantitative flow ratio (QFR) derived from angiography] demonstrate diagnostic accuracy in the mid-80% range for identifying hemodynamically significant stenoses when compared to invasive pressure-wire FFR, albeit with some variability depending on lesion complexity. Non-invasive techniques diminish the need for pressure wire introduction in many cases, thereby decreasing the complexity and risk of invasive procedures [29].
Potential clinical applications:
Cathlab decision-making: immediate clinical assessment of the significance of stenosis and the option for transcatheter pressure wire measurement.
Pre-procedure planning: possibility for simulated ex vivo effect of planned stenting on FFR.
Population-based ML: accumulating anonymized results for collective benefit in a shotgun effect to improve, train, and validate subsequent predictive models continually.
The incorporation of FFR calculations with intravascular imaging data enables a multifaceted assessment that includes not only anatomic but also physiological characteristics. Advanced algorithms can connect the hemodynamic effect of plaques with their anatomical features and may ultimately result in tailored therapeutic approaches based upon variables specific to the lesion [30].
Currently, clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are state-of-the-art solutions that integrate various diagnostic modalities and utilize advanced AI technology to provide a comprehensive evaluation of cardiovascular health. These CDSS include an analysis of electrocardiographic data, pathways, and scores based on biochemical markers, imaging characteristics, and clinical details, providing personalized risk evaluations and treatment recommendations for patients [31].
In such decision-support applications, AI recommendations were found to be feasible and concordant with expert interventional cardiologists’ plans, highlighting that AI can assist without compromising decision quality. However, the ultimate judgment remains with the physician. A side-by-side comparison of AI vs. standard practice is shown in Table 2. Table 2 details endpoints, throughput, and cost implications by modality.
Comparison of AI and human performance across imaging modalities.
| Modality | Metric/Endpoint | AI performance | Human/Standard comparator | Throughput/Time (min) | Cost implications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECG | Detection of CAD phenotypes from resting ECG (obstructive CAD, high CAC, regional akinesia) | AUROC: CAC ≥ 300 0.88; obstructive CAD 0.85; regional akinesis 0.94 | N/A (no direct human ECG comparator in cited study) | Not reported | Lowest | [17] |
| CCTA | Automated plaque and stenosis quantification | High agreement with experts (ICC 0.964 plaque; 0.879 %stenosis); agreement with IVUS; predicts MI | Manual quantitative analysis typically requires tens of minutes | ≤ 1 min (AI) vs. 25–30 min (manual) | Medium-high | [7] |
| SPECT MPI | Classification of ischemia/obstructive CAD (SPECT) | DL outperforms TPD (total perfusion deficit) (per-patient AUC 0.80 vs. 0.78; per-vessel 0.76 vs. 0.73); explainable DL improves physician interpretation | Expert nuclear cardiology reading; TPD vs. standard software comparator | Not consistently reported; DL assistance can shorten review in practice | High | [32, 33] |
| Cardiac MRI | Automated cine/LGE/T1 analysis | Strong performance on cine/T1/LGE tasks; substantial workflow speed-up | Expert manual reading is the reference standard | AI saves ~ 10 min per patient; manual 30–90 min | Highest | [11, 34, 35] |
| FFR-CT (CT-derived FFR) | Lesion-specific ischemia vs. invasive FFR | AUC 0.84; accuracy 78% per-vessel & 85% per-patient; improves over visual CCTA (historical 58%/71%) | Visual CCTA accuracy 68–75% (historical) | AI processing ~ 60 min (historical); invasive FFR during procedure (per lesion) | Intermediate (lower than full invasive work-up) | [9, 36, 37] |
AI: artificial intelligence; AUROC: area under the ROC curve; CAC: coronary artery calcium; CAD: coronary artery disease; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; FFR: fractional flow reserve; CT: computed tomography; FFR-CT: FFR derived from CT; LGE: late gadolinium enhancement; MPI: myocardial perfusion imaging; SPECT: single-photon emission computed tomography; T1: T1 mapping; AUC: area under the curve; DL: deep learning; ECG: electrocardiogram; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
Precision medicine involves utilizing the capabilities of healthcare best practices to support individuals. AI-supported diagnostic systems will enable us to receive individually tailored medicine through accurate phenotyping and risk-stratification algorithms. Predictive and prescriptive modeling can identify subpopulations of patients with similar features or presentations; each may have an idiosyncratic pathophysiology or require patient-specific therapeutics. It is not unreasonable to expect that ML algorithms, when applied to integrated clinical data, will have the ability to predict treatment outcomes for individual patients based on a specific intervention, create a personalized list for drug selection, or identify those at the highest risk for an unwanted outcome. Personally tailored medicine is the future of cardiovascular medicine [38].
Regulatory status, validation evidence, and implementation notes for representative systems are summarized in Table 3. Table 3 lists platforms, methods, and deployment characteristics.
AI systems and platforms in clinical practice.
| System/Platform | Technology/Method | AI performance | Clinical validation | Implementation time | Regulatory status | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVVIGO+ | Automated HD-IVUS assessment with real-time lumen/vessel/plaque morphology analysis | Accuracy: 85% (lumen boundaries), 97% (stent area) | Validated against expert manual measurements in multicenter studies | Real-time (< 1 min per pullback) | FDA cleared, CE marked | [22] |
| Ultreon OCT | AI-powered lumen segmentation with automated stent sizing and landing zone recommendations | High concordance with expert analysis; automated workflow guidance | Clinical studies demonstrate improved procedural efficiency and standardization | Immediate (during procedure) | FDA cleared, CE marked | [39] |
| PROTEUS | AI-assisted stress echocardiography interpretation with automated wall motion scoring | Non-inferior to standard practice (primary endpoint met); AUC 0.87–0.91 | Randomized controlled trial; improved inter-reader consistency, especially for less-experienced operators | < 5 min additional analysis time | Under clinical investigation | [40] |
AI: artificial intelligence; AUC: area under the curve; CE: Conformité Européenne; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; HD-IVUS: high-definition intravascular ultrasound; iFR: instantaneous wave‑free ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography.
Progress in DL architecture, particularly transformer networks and attention-based architectures, is being applied to cardiovascular applications. These types of models have the potential to learn and generate sequential data, identify temporal dependencies, and incorporate multiscale information of unprecedented complexities [41].
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have been explored for generating synthetic data to support robust algorithms with limited data availability. This, along with other technologies, may help accelerate the algorithm development process and facilitate its application to other populations [42].
Federated learning methods enable the collaborative development of algorithms across multiple institutions while safeguarding the privacy of patient data. These methods support the development of robust diagnostic models using a variety of data sources while precluding the necessity for centralized data sharing, all while addressing privacy concerns and complying with all relevant regulations [43].
The advancement of edge computing solutions will allow for the deployment of AI algorithms in real-time within clinical contexts. These designs can provide instant feedback on diagnostic outcomes, procedural assistance, and risk evaluation, eliminating the need for cloud-based processing functions [44].
Emerging methods and their potential advantages are summarized in Table 4. The table outlines technical descriptions and development stages.
Emerging AI technologies in cardiac imaging.
| Technology | Technical description | Potential benefits | Development stage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer networks | Advanced deep learning architectures using self-attention mechanisms for sequence modeling and temporal pattern recognition | Sequential data analysis; modeling temporal dependencies in cardiac cycles; multi-scale context integration; improved long-range feature extraction | Research | [41] |
| GANs | Synthetic data generation and augmentation frameworks using a generator-discriminator architecture | Algorithm development with limited data; robustness via augmentation; domain adaptation between imaging vendors; privacy-preserving data synthesis | Experimental | [42] |
| Federated learning | Distributed training across institutions without centralizing patient data, using encrypted gradient updates | Privacy protection (HIPAA/GDPR compliance); multi-institutional collaboration; improved model generalizability; larger effective training datasets | Implementation | [43] |
| Edge computing | On-device/near-sensor computation for low-latency inference using optimized models (quantization, pruning) | Real-time processing (< 100 ms); instant feedback in clinical workflow; reduced cloud dependence; enhanced data security; offline capability | Development | [45] |
AI: artificial intelligence; GANs: generative adversarial networks; GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation; HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Meta-analyses indicate that AI-enhanced diagnostic systems can achieve diagnostic accuracies comparable to those of expert physicians in specific tasks. For example, pooled results for detecting CAD across various imaging modalities show sensitivities of ~ 85–95% and specificities of ~ 80–90%, which is on par with expert reader performance [46, 47].
The PROTEUS trial is the first prospective, randomized, controlled trial examining AI-assisted stress ECHO. This multicenter trial demonstrated the non-inferiority of AI-enhanced interpretation compared to standard clinical practice for coronary angiography referral decisions [40]. Notably, the PROTEUS results showed no significant difference in appropriate angiography referrals between AI-assisted and standard interpretations in the overall cohort, confirming non-inferiority. Significantly, AI support improved decision-making consistency among less-experienced clinicians and in complex cases, suggesting that AI can help level the field in diagnostic accuracy across operators [40].
While there is evidence of technical efficacy, several barriers hinder the implementation of AI diagnostic systems in clinical practice. These include approval processes for healthcare systems, acceptance by physician groups, reimbursement considerations, and integration with existing clinical workflows [48].
Another significant hurdle is standardizing AI algorithms across vendor platforms and clinical contexts. Comprehensive establishment of standardized protocols and comprehensive validation frameworks is necessary to facilitate widespread clinical adoption [47]. Another barrier is the lack of interpretability of many AI models—so-called “black box” algorithms—which can hinder trust among clinicians and patients. Ensuring transparency and explainability in AI decisions is increasingly seen as crucial for acceptance in practice. Data privacy and security also pose challenges; large datasets are needed to train robust algorithms, raising concerns about patient consent and data protection, especially when integrating AI tools across different hospital systems.
The regulatory landscape for AI medical devices is evolving as various government agencies with differing perspectives attempt to develop specific pathways for approving ML-based diagnostic tools. The FDA’s Software as Medical Device framework outlines the recommendations for algorithm validation and approval processes. As of 2023, the FDA has cleared or approved numerous AI-based medical devices, including several in cardiology, but the regulatory framework is still evolving to address ongoing algorithm updates and real-world performance monitoring [49].
Recent approvals of AI-enhanced cardiovascular diagnostic tools, including automated ECG interpretation systems and imaging analysis systems, have laid the groundwork for regulatory considerations and evaluation of this technology [50].
Ethical questions surrounding the implementation of AI in cardiovascular medicine include algorithmic bias, transparency requirements, and physician liability. To ensure equitable healthcare delivery, training datasets must be diverse and representative. Moreover, mechanisms for algorithmic accountability should be in place—including providing at least partial explanations for AI decisions and continuous monitoring of performance across different patient populations—so that biases can be detected and corrected [51].
Early economic analyses suggest that AI-assisted diagnostic systems could lower healthcare expenditures through more efficient diagnosis, avoidance of unnecessary procedures, and improved resource utilization. There are reports of cost savings from 20–40% in health systems that incorporate an AI system into their daily clinical workflows [52]. However, these projections assume optimal implementation; real-world cost savings will depend on integration costs, staff training, and the extent to which such systems are adopted.
The improved time to interpretation, better consistency of diagnoses, and reduced repeat examinations offer significant economic benefits for health systems adopting AI diagnostics, resulting in a decrease in non-value-added time across the clinical workflow [53].
AI-assisted systems now save seconds on image assessment for each imaging study, rather than minutes, which does offer an improvement to workflow. Still, the actual impact on overall clinical workflow depends on factors such as system interoperability and the need for manual review of AI outputs—gains in speed must be weighed against time for validation of AI findings by clinicians. Automated preliminary reads have previously opened up the ideals of prioritizing urgent cases, reducing turnaround times, and optimizing resources [54].
Clinical and economic outcomes related to AI-assisted diagnostics are summarized in Table 5. Table 5 presents diagnostic accuracy ranges, projected cost savings, and time benefits.
Clinical and economic outcomes.
| Aspect | Value | Details | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic accuracy | Sensitivity 85–95%; Specificity 80–92% | Meta-analyses of ML for CAD detection across imaging modalities; AI performance comparable to expert readers | [9, 47] |
| Cost savings | 20–40% (projected) | Early economic analyses of health systems implementing AI diagnostics; the magnitude depends on integration, training, and adoption | [36] |
| Time savings | Seconds vs. minutes per imaging study | Automated preliminary reads shorten per-study assessment; potential gains in triage and turnaround times | [35, 55] |
| Expert agreement | ≥ 85% (task-specific) | HD-IVUS agreement with experts: lumen 85% and stent area 97%; AI-assisted stress ECHO non-inferior, with improved consistency for less-experienced readers | [22, 40] |
AI: artificial intelligence; CAD: coronary artery disease; HD-IVUS: high-definition intravascular ultrasound; ML: machine learning; ECHO: echocardiography.
A summary of performance across key applications is shown in Figure 6, which displays pooled estimates of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy across different modalities and tasks.
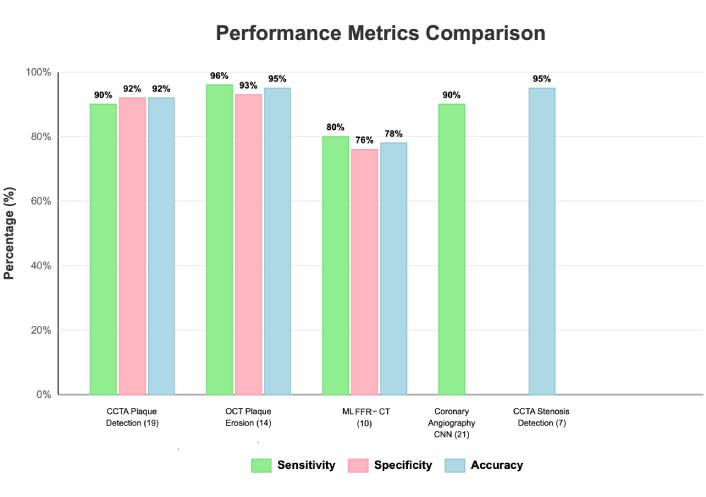
Performance metrics and clinical validation of AI applications in cardiovascular diagnostics. Descriptive comparison of the study-reported diagnostic performance by modality and task. Bars display the median of study-level sensitivity, specificity, and—where available—accuracy within each category; parentheses indicate the number of contributing studies: CCTA plaque detection (N = 19), OCT plaque erosion (N = 14), ML FFR-CT (N = 10), coronary angiography CNN models (N = 21), and CCTA stenosis detection (N = 7). Due to heterogeneous thresholds and reference standards, no formal meta-analysis was performed; values are descriptive and not pooled estimates. Where only one bar appears for a method, the other metrics were not consistently reported in the source literature. Key findings. OCT-based plaque-erosion detection showed the highest sensitivity (~ 96%) with strong overall balance across metrics; CCTA plaque and stenosis detection demonstrated consistently high accuracy across studies; ML FFR-CT achieved moderate performance (~ 76–80%) with variability by lesion complexity and image quality; CNN-based analysis of coronary angiography yielded high sensitivity (~ 90%). Overall variability across tasks underscores the need for application-specific validation and ongoing algorithm refinement before broad clinical deployment. CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CNN: convolutional neural network; FFR-CT: fractional flow reserve derived from CT; OCT: optical coherence tomography; AI: artificial intelligence; CT: computed tomography.
A comprehensive analysis of AI performance across 12 key cardiovascular applications reveals notable differences in diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, depending on the specific clinical task. The top-performing applications include ECG arrhythmia detection (with 97.8% accuracy), heart disease prediction (with 97.6% accuracy), and cardiac MRI segmentation (with 95.2% accuracy). More difficult applications, such as FFR estimation, achieve lower but still clinically relevant performance levels of 84%. Implementation barriers and practical solutions across regulatory, ethical, clinical, and economic areas are outlined in Table 6. Table 6 offers a brief checklist for deployment planning.
Implementation challenges.
| Category | Challenges | Solutions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory | FDA/CE approval pathways; validation standards; lifecycle oversight of adaptive algorithms | Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) frameworks; dedicated guidance; post-market performance monitoring | [49, 50, 56] |
| Ethical | Algorithmic bias; transparency/interpretability; liability; data privacy | Diverse and representative datasets; bias auditing; explainable AI; accountability mechanisms | [48, 51, 56] |
| Clinical | Workflow integration; physician acceptance; standardization; prospective validation | Training and protocols; vendor-agnostic standards; multi-center trials to demonstrate efficacy (e.g., PROTEUS) | [34–36, 40, 52] |
| Economic | Implementation costs, reimbursement models, and uncertain ROI | Cost-benefit analyses; value-based payment models; phased deployment; workflow efficiency gains | [36, 57] |
AI: artificial intelligence; CE: Conformité Européenne; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; ROI: return on investment.
The increasing use of algorithms in diagnosing IHD marks a significant change in cardiovascular medicine, with the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, improve workflow efficiency, and enable more personalized patient care. Current applications of AI and ML for data collection demonstrate diagnostic accuracy that is equal to or superior to that of human experts for specific imaging methods and clinical scenarios.
The links between algorithms and multimodal imaging platform environments facilitate a holistic approach to cardiovascular assessment, revealing methodologically significant physiological and prognostic findings within a lucid and coherent diagnostic framework. AI-enhanced HD-IVUS and OCT imaging are showing great promise for both more detailed plaque characterization and procedural quality that was previously not possible.
Future directions include DL architectures for AI systems and ML, as well as federated learning and opportunities for real-time implementation of systems, which will further enhance the potential for diagnostics and clinical adoption. However, for widespread integration to be practical, fundamental issues of regulation, ethically responsible utilization, and clear and explicit clinical and economic value need to be overcome.
The evidence indicates that algorithmic methods are not just complementary to traditional evaluation; they are already altering how IHD is diagnosed, risk-stratified, and managed. They are poised to become ubiquitous in cardiovascular medicine, but realizing their full benefits will require ongoing evaluation of their impact on patient outcomes and addressing the remaining challenges in regulation, integration, and trust.
A stage-wise mapping of AI tools across the IHD diagnostic pathway is presented in Table 7. Table 7 aligns tools with clinical intent and expected benefits.
Applications by diagnostic stage.
| Stage | AI tools | Main benefits | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screening | AI-ECG | Early detection of latent disease and population-level risk prediction/triage | [6, 17] |
| Anatomical diagnosis | AI-CCTA; AI-CMR | Accurate plaque quantification and characterization (CCTA); quantitative myocardial tissue characterization, including LGE/T1 mapping (CMR) | [7, 10, 11, 21] |
| Functional assessment | AI-FFR (FFR-CT); AI-perfusion (stress imaging: echocardiography/nuclear) | Non-invasive hemodynamic evaluation; lesion-specific ischemia assessment; potential improvement of reader performance in stress imaging | [9, 32, 33, 36, 40] |
| Intervention planning | AI-IVUS; AI-OCT | Procedure optimization (e.g., stent sizing and landing zone selection), outcome prediction, and intraprocedural decision support | [13, 22, 39] |
| Monitoring | Integrated CDSS (with imaging and ECG data) | Personalized risk stratification, longitudinal follow-up, and event prediction with integration of multimodal data into clinical workflows | [16, 18, 52] |
AI: artificial intelligence; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CDSS: clinical decision support systems; CMR: cardiovascular magnetic resonance; CT: computed tomography; FFR: fractional flow reserve; FFR-CT: FFR derived from CT; ECG: electrocardiogram; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; LGE: late gadolinium enhancement; OCT: optical coherence tomography.
3D: three-dimensional
AI: artificial intelligence
AUC: area under the curve
AUROC: area under the ROC curve
CAC: coronary artery calcium
CAD: coronary artery disease
CAD-RADS: Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System
CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography
CDSS: clinical decision support systems
CE: Conformité Européenne
CMR: cardiovascular magnetic resonance
CNNs: convolutional neural networks
CT: computed tomography
DICOM: Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
DL: deep learning
ECG: electrocardiogram
ECHO: echocardiography
EMR: electronic medical record
ESC: European Society of Cardiology
FDA: Food and Drug Administration
FFR: fractional flow reserve
FFR-CT: fractional flow reserve derived from computed tomography
FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources
GANs: generative adversarial networks
GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation
HD-IVUS: high-definition intravascular ultrasound
HIPAA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
HL7: Health Level Seven
iFR: instantaneous wave‑free ratio
IHD: ischemic heart disease
IVUS: intravascular ultrasound
LGE: late gadolinium enhancement
LV/RV: left/right ventricle
LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction
MACE: major adverse cardiac events
ML: machine learning
MPI: myocardial perfusion imaging
MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
NPV: negative predictive value
OCT: optical coherence tomography
PACS: picture archiving and communication system
PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
PPV: positive predictive value
QFR: quantitative flow ratio
ROI: return on investment
SaMD: Software as a Medical Device
SPECT: single‑photon emission computed tomography
TCFAs: thin-cap fibroatheromas
TPD: total perfusion deficit
MT: Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. The author read and approved the submitted version.
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Open Exploration maintains a neutral stance on jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliations and maps. All opinions expressed in this article are the personal views of the author(s) and do not represent the stance of the editorial team or the publisher.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2025. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
View: 2686
Download: 170
Times Cited: 0
Marco Fabio Costantino ... Luisiana Stolfi
Cristhian Espinoza Romero ... Tatiana Torres Leal
Marco Antonio Rodrigues Torres, Natália Moraes de Quevedo
Praveen Kumar Chandra Sekar, Ramakrishnan Veerabathiran
Emma Cerracchio ... Quirino Ciampi