




Background:
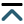
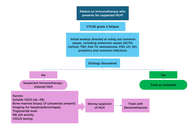
Docetaxel is a cornerstone chemotherapy for metastatic hormone-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Although the standard triweekly regimen is widely used, weekly and biweekly schedules are often employed to improve tolerability, particularly in elderly or frail patients. The comparative efficacy and safety of these dosing strategies remain unclear. This study aimed to systematically compare weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens using a network meta-analysis.
Methods:
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from inception to February 2025. Randomized controlled trials and observational retrospective studies comparing weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens were included. Outcomes assessed were prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate, time to treatment failure or progression, and adverse events. A frequentist random-effects network meta-analysis was conducted using R software.
Results:
Eleven studies involving 1,238 patients were included. PSA response rates did not differ significantly among regimens; triweekly docetaxel showed a numerically lower response compared with weekly dosing (RR = 0.79, 95% CI 0.52–1.22; I2 = 41.1%). Time to treatment failure was significantly longer with triweekly dosing compared with weekly dosing (mean difference = 10.91 months, 95% CI 6.94–14.87; I2 = 96.8%). Biweekly and triweekly regimens were associated with significantly higher hepatotoxicity compared with weekly dosing (RR = 3.71 and RR = 3.21, respectively; I2 = 0%). Vomiting was more frequent with triweekly docetaxel (RR = 2.47, 95% CI 1.31–4.63). No significant differences were observed for overall adverse events, hematologic toxicity, neuropathy, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, nausea, anorexia, or diarrhea.
Discussion:
Docetaxel dosing schedules show comparable PSA response rates. Triweekly dosing prolongs time to treatment failure but is associated with greater toxicity, whereas weekly dosing offers better tolerability. Treatment decisions should balance efficacy and safety based on individual patient characteristics.
Background:
Docetaxel is a cornerstone chemotherapy for metastatic hormone-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Although the standard triweekly regimen is widely used, weekly and biweekly schedules are often employed to improve tolerability, particularly in elderly or frail patients. The comparative efficacy and safety of these dosing strategies remain unclear. This study aimed to systematically compare weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens using a network meta-analysis.
Methods:
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched from inception to February 2025. Randomized controlled trials and observational retrospective studies comparing weekly, biweekly, and triweekly docetaxel regimens were included. Outcomes assessed were prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate, time to treatment failure or progression, and adverse events. A frequentist random-effects network meta-analysis was conducted using R software.
Results:
Eleven studies involving 1,238 patients were included. PSA response rates did not differ significantly among regimens; triweekly docetaxel showed a numerically lower response compared with weekly dosing (RR = 0.79, 95% CI 0.52–1.22; I2 = 41.1%). Time to treatment failure was significantly longer with triweekly dosing compared with weekly dosing (mean difference = 10.91 months, 95% CI 6.94–14.87; I2 = 96.8%). Biweekly and triweekly regimens were associated with significantly higher hepatotoxicity compared with weekly dosing (RR = 3.71 and RR = 3.21, respectively; I2 = 0%). Vomiting was more frequent with triweekly docetaxel (RR = 2.47, 95% CI 1.31–4.63). No significant differences were observed for overall adverse events, hematologic toxicity, neuropathy, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, nausea, anorexia, or diarrhea.
Discussion:
Docetaxel dosing schedules show comparable PSA response rates. Triweekly dosing prolongs time to treatment failure but is associated with greater toxicity, whereas weekly dosing offers better tolerability. Treatment decisions should balance efficacy and safety based on individual patient characteristics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002360

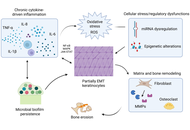
Acquired middle-ear cholesteatoma is a histologically benign keratinizing squamous epithelial lesion that paradoxically exhibits locally destructive, recurrent, and invasive behavior, often resulting in ossicular erosion, hearing loss, labyrinthine fistula, and, rarely, intracranial complications. Surgical excision remains the primary management strategy; however, recurrence is common due to persistent microenvironmental drivers. Recent mechanistic studies—including single-cell transcriptomics, spatial proteomics, and epigenetic profiling—reveal a multifactorial pathogenesis orchestrated by chronic inflammation, proteolytic extracellular-matrix remodeling, osteoclast activation via RANKL and activin A, epithelial plasticity with partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and a dysbiotic, biofilm-forming microbiome. Emerging evidence further implicates oxidative stress, RNA and epigenetic modifications, miRNA dysregulation, and immune cell infiltration as central modulators of lesion chronicity and bone resorption. Collectively, these processes establish a self-sustaining pro-osteolytic microenvironment that drives bone erosion and postoperative recurrence. Cholesteatoma recapitulates several features of malignant lesions—hyperproliferation, local invasion, and stromal/immune cell recruitment—yet remains fundamentally benign, lacking metastatic potential and genomic instability. Its aggression is ecological rather than genetic, highlighting the potential for microenvironment-directed, precision-based strategies. Adjunctive approaches may include local delivery of modulatory agents, targeted interference with inflammatory, proteolytic, osteoclastogenic, and microbial axes, and biomarker-guided patient stratification. Preclinical and early-phase experimental studies assessing target engagement, radiologic stabilization, and molecular surrogates of efficacy could inform safer, mechanism-driven interventions that complement surgery, reduce recurrence, and preserve hearing. Integrating molecular pathobiology with clinical strategy positions cholesteatoma as a model for benign yet locally aggressive, microenvironment-driven disease, providing a roadmap for translational therapies with direct relevance to surgical practice.
Acquired middle-ear cholesteatoma is a histologically benign keratinizing squamous epithelial lesion that paradoxically exhibits locally destructive, recurrent, and invasive behavior, often resulting in ossicular erosion, hearing loss, labyrinthine fistula, and, rarely, intracranial complications. Surgical excision remains the primary management strategy; however, recurrence is common due to persistent microenvironmental drivers. Recent mechanistic studies—including single-cell transcriptomics, spatial proteomics, and epigenetic profiling—reveal a multifactorial pathogenesis orchestrated by chronic inflammation, proteolytic extracellular-matrix remodeling, osteoclast activation via RANKL and activin A, epithelial plasticity with partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and a dysbiotic, biofilm-forming microbiome. Emerging evidence further implicates oxidative stress, RNA and epigenetic modifications, miRNA dysregulation, and immune cell infiltration as central modulators of lesion chronicity and bone resorption. Collectively, these processes establish a self-sustaining pro-osteolytic microenvironment that drives bone erosion and postoperative recurrence. Cholesteatoma recapitulates several features of malignant lesions—hyperproliferation, local invasion, and stromal/immune cell recruitment—yet remains fundamentally benign, lacking metastatic potential and genomic instability. Its aggression is ecological rather than genetic, highlighting the potential for microenvironment-directed, precision-based strategies. Adjunctive approaches may include local delivery of modulatory agents, targeted interference with inflammatory, proteolytic, osteoclastogenic, and microbial axes, and biomarker-guided patient stratification. Preclinical and early-phase experimental studies assessing target engagement, radiologic stabilization, and molecular surrogates of efficacy could inform safer, mechanism-driven interventions that complement surgery, reduce recurrence, and preserve hearing. Integrating molecular pathobiology with clinical strategy positions cholesteatoma as a model for benign yet locally aggressive, microenvironment-driven disease, providing a roadmap for translational therapies with direct relevance to surgical practice.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002359

Glioblastoma (GBM) is a complex condition with a poorly understood pathophysiology and no effective treatment to date. The present article highlights the role of canonical and non-canonical signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interactions with nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in the modulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in GBM microenvironment pathophysiology. The capacity of STAT3 and NF-κB to interact to upregulate the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway is suppressed systemically over the course of aging, thereby attenuating the capacity to achieve inflammation resolution. The suppressed capacity to induce the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway systemically is partly driven by the dramatic 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin over aging. The attenuation of pineal melatonin in the first half of sleep over aging and aging-accelerating conditions disinhibits the effects of cortisol in the second half of sleep. This decrease in the melatonin/cortisol ratio alters the nature of night-time dampening and resetting in preparation for the coming day by altering cellular and intercellular homeostatic interactions. Aging and aging-accelerating conditions, by impacting the night-time melatonin/cortisol ratio, also suppress the capacity of the vagal nerve to resolve inflammation. This further contributes to systemic changes that influence GBM pathoetiology and ongoing pathophysiology. Aging-associated changes in night-time dampening and resetting provide a novel framework on which many previously disparate bodies of data on GBM pathophysiology can be collated. This has numerous future research, prevention, and treatment implications.
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a complex condition with a poorly understood pathophysiology and no effective treatment to date. The present article highlights the role of canonical and non-canonical signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interactions with nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in the modulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in GBM microenvironment pathophysiology. The capacity of STAT3 and NF-κB to interact to upregulate the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway is suppressed systemically over the course of aging, thereby attenuating the capacity to achieve inflammation resolution. The suppressed capacity to induce the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway systemically is partly driven by the dramatic 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin over aging. The attenuation of pineal melatonin in the first half of sleep over aging and aging-accelerating conditions disinhibits the effects of cortisol in the second half of sleep. This decrease in the melatonin/cortisol ratio alters the nature of night-time dampening and resetting in preparation for the coming day by altering cellular and intercellular homeostatic interactions. Aging and aging-accelerating conditions, by impacting the night-time melatonin/cortisol ratio, also suppress the capacity of the vagal nerve to resolve inflammation. This further contributes to systemic changes that influence GBM pathoetiology and ongoing pathophysiology. Aging-associated changes in night-time dampening and resetting provide a novel framework on which many previously disparate bodies of data on GBM pathophysiology can be collated. This has numerous future research, prevention, and treatment implications.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002358

Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models applied to electronic health records (EHRs) have substantial potential to improve oncology care across diagnosis, prognosis, treatment selection, and trial recruitment. However, opacity of many high-performing models limits clinician trust, regulatory acceptance, and safe deployment. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) methods aim to make model behavior understandable and actionable in clinical contexts. The present perspective summarizes current XAI approaches applied to EHR-based oncology tasks, identifies key challenges in evaluation, reproducibility, clinical utility, and equity, and proposes pragmatic recommendations and research directions to accelerate safe adoption in oncology. Common XAI categories used with EHR data include feature importance/interaction methods, intrinsically interpretable models, attention mechanisms, dimensionality reduction, and knowledge distillation or rule extraction. Tree-based models with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) explanations dominate recent EHR studies. Other interpretable strategies, such as generalized additive models and rule sets, appear in settings where transparency is prioritized. Gaps include inconsistent reporting, scarce formal evaluation of explanations for clinical utility, limited reproducibility for data and code availability, inadequate external validation, and insufficient consideration of fairness and equity that these issues are particularly important in oncology, where heterogeneity and stakes are high. Overall, integrating XAI with EHR-driven oncology models is promising but underdeveloped, which requires further progress by multi-stakeholder evaluation frameworks, reproducible pipelines, prospective and multicenter validations, and equity-aware design. The field should prioritize clinically meaningful explanations beyond ranking features and study how explanations affect clinician decision-making and patient outcomes.
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models applied to electronic health records (EHRs) have substantial potential to improve oncology care across diagnosis, prognosis, treatment selection, and trial recruitment. However, opacity of many high-performing models limits clinician trust, regulatory acceptance, and safe deployment. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) methods aim to make model behavior understandable and actionable in clinical contexts. The present perspective summarizes current XAI approaches applied to EHR-based oncology tasks, identifies key challenges in evaluation, reproducibility, clinical utility, and equity, and proposes pragmatic recommendations and research directions to accelerate safe adoption in oncology. Common XAI categories used with EHR data include feature importance/interaction methods, intrinsically interpretable models, attention mechanisms, dimensionality reduction, and knowledge distillation or rule extraction. Tree-based models with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) explanations dominate recent EHR studies. Other interpretable strategies, such as generalized additive models and rule sets, appear in settings where transparency is prioritized. Gaps include inconsistent reporting, scarce formal evaluation of explanations for clinical utility, limited reproducibility for data and code availability, inadequate external validation, and insufficient consideration of fairness and equity that these issues are particularly important in oncology, where heterogeneity and stakes are high. Overall, integrating XAI with EHR-driven oncology models is promising but underdeveloped, which requires further progress by multi-stakeholder evaluation frameworks, reproducible pipelines, prospective and multicenter validations, and equity-aware design. The field should prioritize clinically meaningful explanations beyond ranking features and study how explanations affect clinician decision-making and patient outcomes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002357

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2026.1002356

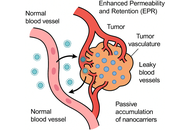
The evolution of nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems has transformed the paradigm of cancer therapeutics, advancing from conventional cytotoxic formulations to intelligent, adaptive nanosystems capable of precision targeting. Early-generation nanocarriers exploited the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect for passive tumor accumulation, yet their therapeutic efficiency remained constrained by tumor heterogeneity, limited penetration, and off-target toxicity. Emerging nanotechnologies now integrate active targeting, stimuli-responsive components, and biomimetic strategies to achieve spatiotemporal control over drug release and tumor-selective action. These “intelligent” nanocarriers are designed to recognize molecular signatures, respond dynamically to tumor microenvironmental cues such as pH, redox gradients, hypoxia, and enzymatic activity, and even engage in real-time feedback through imaging or biosensing modules. In addition, hybrid and multifunctional platforms—combining liposomes, micelles, dendrimers, polymeric nanoparticles, and inorganic systems—offer programmable functionality and synergistic delivery of chemotherapeutic, gene-editing, and immunomodulatory agents. This review delineates the mechanistic basis of passive and active targeting, highlights recent innovations in stimuli-responsive and biomimetic nanocarriers, and explores translational and regulatory perspectives shaping their clinical journey. By integrating nanotechnology with systems biology and artificial intelligence, next-generation nanocarriers promise to redefine the landscape of precision antitumor therapy.
The evolution of nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems has transformed the paradigm of cancer therapeutics, advancing from conventional cytotoxic formulations to intelligent, adaptive nanosystems capable of precision targeting. Early-generation nanocarriers exploited the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect for passive tumor accumulation, yet their therapeutic efficiency remained constrained by tumor heterogeneity, limited penetration, and off-target toxicity. Emerging nanotechnologies now integrate active targeting, stimuli-responsive components, and biomimetic strategies to achieve spatiotemporal control over drug release and tumor-selective action. These “intelligent” nanocarriers are designed to recognize molecular signatures, respond dynamically to tumor microenvironmental cues such as pH, redox gradients, hypoxia, and enzymatic activity, and even engage in real-time feedback through imaging or biosensing modules. In addition, hybrid and multifunctional platforms—combining liposomes, micelles, dendrimers, polymeric nanoparticles, and inorganic systems—offer programmable functionality and synergistic delivery of chemotherapeutic, gene-editing, and immunomodulatory agents. This review delineates the mechanistic basis of passive and active targeting, highlights recent innovations in stimuli-responsive and biomimetic nanocarriers, and explores translational and regulatory perspectives shaping their clinical journey. By integrating nanotechnology with systems biology and artificial intelligence, next-generation nanocarriers promise to redefine the landscape of precision antitumor therapy.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002355

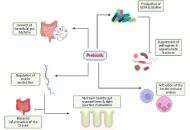
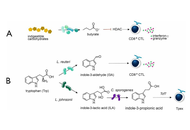
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy has revolutionized metastatic melanoma treatment, yet only a subset of patients respond effectively, and the treatment can induce a variety of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including colitis. The gut microbiome plays a critical role in determining patient responses to immunotherapy, prompting exploration of gut-modifying strategies such as prebiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) to overcome both primary and acquired resistance and improve treatment outcomes. Prebiotics, defined as dietary substrates that selectively support the growth and/or activity of beneficial gut microorganisms, represent a feasible and safe strategy for microbiome reshaping. Plant-derived prebiotics like castalagin, inulin, fructooligosaccharides, galactooligosaccharides, mushroom extract, kale extract, and konjac glucomannan offer unique advantages over synthetic or animal-derived alternatives due to their natural fiber content alongside their ability to enhance gut microbial diversity. Prebiotics are known to achieve health benefits by selectively stimulating beneficial gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that modulate the host immune system, suppressing pathogenic microbes, enhancing mucin production, and modulating systemic and gut-associated immune responses. SCFAs generated through prebiotic fermentation influence host innate and adaptive immunity and regulate metabolic activity via inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), influencing mTOR/MAPK signaling and cytokine production. They also act as ligands for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), altering intracellular calcium and cAMP to modulate immune cell gene expression. However, the specific mechanisms by which individual prebiotics interact with host genetics, beneficial gut bacteria, and their metabolites are not very well understood. This is crucial to optimize their therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy. This review synthesizes current evidence on plant-derived prebiotics, highlighting the impact of beneficial gut bacteria and their metabolites. Given their established safety for human consumption, prebiotics represent a promising, low-risk option to improve gut microbiome composition and potentially enhance immunotherapy and clinical outcomes in cancer.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy has revolutionized metastatic melanoma treatment, yet only a subset of patients respond effectively, and the treatment can induce a variety of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including colitis. The gut microbiome plays a critical role in determining patient responses to immunotherapy, prompting exploration of gut-modifying strategies such as prebiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) to overcome both primary and acquired resistance and improve treatment outcomes. Prebiotics, defined as dietary substrates that selectively support the growth and/or activity of beneficial gut microorganisms, represent a feasible and safe strategy for microbiome reshaping. Plant-derived prebiotics like castalagin, inulin, fructooligosaccharides, galactooligosaccharides, mushroom extract, kale extract, and konjac glucomannan offer unique advantages over synthetic or animal-derived alternatives due to their natural fiber content alongside their ability to enhance gut microbial diversity. Prebiotics are known to achieve health benefits by selectively stimulating beneficial gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that modulate the host immune system, suppressing pathogenic microbes, enhancing mucin production, and modulating systemic and gut-associated immune responses. SCFAs generated through prebiotic fermentation influence host innate and adaptive immunity and regulate metabolic activity via inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), influencing mTOR/MAPK signaling and cytokine production. They also act as ligands for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), altering intracellular calcium and cAMP to modulate immune cell gene expression. However, the specific mechanisms by which individual prebiotics interact with host genetics, beneficial gut bacteria, and their metabolites are not very well understood. This is crucial to optimize their therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy. This review synthesizes current evidence on plant-derived prebiotics, highlighting the impact of beneficial gut bacteria and their metabolites. Given their established safety for human consumption, prebiotics represent a promising, low-risk option to improve gut microbiome composition and potentially enhance immunotherapy and clinical outcomes in cancer.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002354

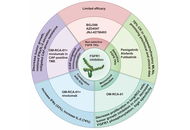
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) is crucial in the progression of various cancers, participating in the processes of cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. FGFR1 plays a role in the resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab. Therefore, using monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors to target FGFR1 and enhancing ICIs by modifying the tumor microenvironment and combating immune suppression represents a potential therapeutic strategy. Based on the FGFR1-related research and the active targeting strategy, we believe that modifying the surface of nanomedicines with anti-FGFR1 antibodies (such as OM-RCA-01) is an effective targeted treatment method for tumors with high expression of FGFR1. Although there have been relevant studies confirming the feasibility of this approach, there are challenges in clinical application, especially in terms of maintaining uniform quality during large-scale production. Therefore, we suggest conducting further optimization studies in the future to accelerate the clinical application of such drug delivery systems and provide more efficient and cost-effective options for tumor treatment.
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) is crucial in the progression of various cancers, participating in the processes of cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. FGFR1 plays a role in the resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab. Therefore, using monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors to target FGFR1 and enhancing ICIs by modifying the tumor microenvironment and combating immune suppression represents a potential therapeutic strategy. Based on the FGFR1-related research and the active targeting strategy, we believe that modifying the surface of nanomedicines with anti-FGFR1 antibodies (such as OM-RCA-01) is an effective targeted treatment method for tumors with high expression of FGFR1. Although there have been relevant studies confirming the feasibility of this approach, there are challenges in clinical application, especially in terms of maintaining uniform quality during large-scale production. Therefore, we suggest conducting further optimization studies in the future to accelerate the clinical application of such drug delivery systems and provide more efficient and cost-effective options for tumor treatment.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002353

Radiation exposure to the eye during cancer treatment can lead to ocular radiation injury (ORI), a devastating condition that can have a profound and permanent impact on vision-related quality of life. Rodent models do not have adequate ocular anatomy to accurately simulate human ORI, and modeling in non-human primates is limited by logistical and ethical concerns. To improve future translational research investigating ways to treat or prevent ORI, we developed protocols for a tree shrew model of ORI. Northern tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri) were obtained by our laboratory. Custom housing and handling methods were developed, including custom body suits to maintain the tree shrew’s body temperature during procedures. Radiation delivery was optimized to accurately deliver radiation, and imaging was performed to observe fundus changes from ORI. Optimization of tree shrew handling, housing, anesthesia approaches, radiation delivery, and clinically-relevant ocular imaging permitted successful induction and assessment of ORI in tree shrews. With these protocols, tree shrews can be used as a highly relevant model organism with key anatomic features similar to humans to study ORI.
Radiation exposure to the eye during cancer treatment can lead to ocular radiation injury (ORI), a devastating condition that can have a profound and permanent impact on vision-related quality of life. Rodent models do not have adequate ocular anatomy to accurately simulate human ORI, and modeling in non-human primates is limited by logistical and ethical concerns. To improve future translational research investigating ways to treat or prevent ORI, we developed protocols for a tree shrew model of ORI. Northern tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri) were obtained by our laboratory. Custom housing and handling methods were developed, including custom body suits to maintain the tree shrew’s body temperature during procedures. Radiation delivery was optimized to accurately deliver radiation, and imaging was performed to observe fundus changes from ORI. Optimization of tree shrew handling, housing, anesthesia approaches, radiation delivery, and clinically-relevant ocular imaging permitted successful induction and assessment of ORI in tree shrews. With these protocols, tree shrews can be used as a highly relevant model organism with key anatomic features similar to humans to study ORI.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002352

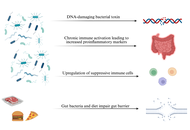
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a significant global health problem, ranking as the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. The highest incidence of CRC is found in developed regions, thus underlining its characterization as a Western disease. Major risk factors for CRC include an unhealthy diet, lack of physical exercise, and cigarette smoking. The gut microbiota refers to the complex community of microorganisms inhabiting the digestive tract and plays a crucial role in the maintenance of host health and modulation of immune responses. Gut dysbiosis can be caused by poor diet and alcohol consumption, increasing CRC risk. Specific bacteria, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum and Escherichia coli, may have a close relationship with CRC development, while the beneficial bacteria are frequently depleted in CRC patients. This paper will discuss the mechanisms of colorectal carcinogenesis, focusing on the effects of bacterial genotoxins, immune evasion, inflammation, and diet. Additionally, it reviews preventative strategies including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotic supplements, and the method of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), showing their potential to improve overall gut health and reduce the risk for CRC. Understanding these mechanisms and implementing specific preventative strategies could significantly enhance clinical interventions and reduce the global burden of CRC.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a significant global health problem, ranking as the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the world. The highest incidence of CRC is found in developed regions, thus underlining its characterization as a Western disease. Major risk factors for CRC include an unhealthy diet, lack of physical exercise, and cigarette smoking. The gut microbiota refers to the complex community of microorganisms inhabiting the digestive tract and plays a crucial role in the maintenance of host health and modulation of immune responses. Gut dysbiosis can be caused by poor diet and alcohol consumption, increasing CRC risk. Specific bacteria, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum and Escherichia coli, may have a close relationship with CRC development, while the beneficial bacteria are frequently depleted in CRC patients. This paper will discuss the mechanisms of colorectal carcinogenesis, focusing on the effects of bacterial genotoxins, immune evasion, inflammation, and diet. Additionally, it reviews preventative strategies including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotic supplements, and the method of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), showing their potential to improve overall gut health and reduce the risk for CRC. Understanding these mechanisms and implementing specific preventative strategies could significantly enhance clinical interventions and reduce the global burden of CRC.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002351

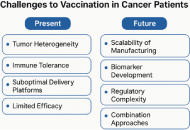
Therapeutic cancer vaccines harness the adaptive immune system to eradicate malignancies by targeting tumor-specific antigens. This review charts the evolution of cancer vaccine platforms—from shared tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and dendritic cell (DC) vaccines to next-generation neoantigen-messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccines—highlighting advances in vaccine delivery, antigen discovery, computational prediction, and translational efficacy. We explore cutting-edge clinical data, including long-lived T-cell memory and promising outcomes in various cancer types, including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), melanoma, head and neck cancers, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and others. We address critical challenges, including tumor heterogeneity, manufacturing scalability, biomarker development, and regulatory frameworks, and propose an integrated translational ecosystem to accelerate the adoption of personalized cancer vaccines.
Therapeutic cancer vaccines harness the adaptive immune system to eradicate malignancies by targeting tumor-specific antigens. This review charts the evolution of cancer vaccine platforms—from shared tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and dendritic cell (DC) vaccines to next-generation neoantigen-messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccines—highlighting advances in vaccine delivery, antigen discovery, computational prediction, and translational efficacy. We explore cutting-edge clinical data, including long-lived T-cell memory and promising outcomes in various cancer types, including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), melanoma, head and neck cancers, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and others. We address critical challenges, including tumor heterogeneity, manufacturing scalability, biomarker development, and regulatory frameworks, and propose an integrated translational ecosystem to accelerate the adoption of personalized cancer vaccines.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002350
This article belongs to the special issue Cancer Vaccines: From Basic Innovations to Clinical Translation

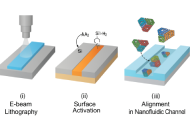
The convergence of DNA nanotechnology with nanofluidics has catalyzed a transformative shift in precision drug delivery. DNA origami, a self-assembled nanoscale architecture constructed via programmable base pairing, offers atomically precise control over size, shape, and function—making it an ideal scaffold for site-specific therapeutic cargo loading and release. When integrated into nanofluidic systems, these origami nanostructures form intelligent platforms capable of navigating biological barriers, sensing intracellular cues, and delivering payloads in a spatially and temporally controlled manner. This review explores the fabrication principles, design strategies, and intracellular trafficking mechanisms that underpin the efficacy of these smart nanofluidic DNA origami systems. We highlight key stimuli-responsive features such as pH-triggered unfolding, enzyme-cleavable hinges, redox-sensitive disassembly, and light-mediated gate release. Case studies from preclinical models demonstrate their superiority in overcoming drug resistance, enhancing tumor selectivity, and minimizing systemic toxicity compared to conventional nanocarriers. We also evaluate methods for surface modification, channel integration, and stimulus modulation using electron-beam lithography and soft lithography techniques. Additional biosafety and scalability challenges are discussed, alongside regulatory and immunogenicity considerations. The review concludes by outlining future directions involving AI-assisted DNA origami design, microfluidic diagnostics, and digital therapeutics. The synthesis of programmable nanocarriers with smart fluidic control represents a new frontier in targeted therapy, combining modularity, precision, and adaptability. As such, nanofluidic DNA origami systems hold immense promise for next-generation therapeutics in oncology, gene therapy, and personalized medicine, paving the way for dynamic and autonomous intracellular delivery platforms with real-world translational potential.
The convergence of DNA nanotechnology with nanofluidics has catalyzed a transformative shift in precision drug delivery. DNA origami, a self-assembled nanoscale architecture constructed via programmable base pairing, offers atomically precise control over size, shape, and function—making it an ideal scaffold for site-specific therapeutic cargo loading and release. When integrated into nanofluidic systems, these origami nanostructures form intelligent platforms capable of navigating biological barriers, sensing intracellular cues, and delivering payloads in a spatially and temporally controlled manner. This review explores the fabrication principles, design strategies, and intracellular trafficking mechanisms that underpin the efficacy of these smart nanofluidic DNA origami systems. We highlight key stimuli-responsive features such as pH-triggered unfolding, enzyme-cleavable hinges, redox-sensitive disassembly, and light-mediated gate release. Case studies from preclinical models demonstrate their superiority in overcoming drug resistance, enhancing tumor selectivity, and minimizing systemic toxicity compared to conventional nanocarriers. We also evaluate methods for surface modification, channel integration, and stimulus modulation using electron-beam lithography and soft lithography techniques. Additional biosafety and scalability challenges are discussed, alongside regulatory and immunogenicity considerations. The review concludes by outlining future directions involving AI-assisted DNA origami design, microfluidic diagnostics, and digital therapeutics. The synthesis of programmable nanocarriers with smart fluidic control represents a new frontier in targeted therapy, combining modularity, precision, and adaptability. As such, nanofluidic DNA origami systems hold immense promise for next-generation therapeutics in oncology, gene therapy, and personalized medicine, paving the way for dynamic and autonomous intracellular delivery platforms with real-world translational potential.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002349

The realization that the composition and functionality of gut microbiota have an impact on the outcome of immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) therapy of cancer has initiated research into the potential of microbiota management as adjunctive therapy. Fecal microbiota transplantation can improve the outcome of ICI, but for optimal donor selection, safety, and large-scale implementation, there remain bottlenecks. Alternative strategies, such as the use of selected bacterial species, require fundamental knowledge of the underlying mechanisms governing the interaction between (intestinal) microbiota and the immune system. Gut microbiota also appears to be able to colonize the tumor microenvironment. Some bacterial species directly or indirectly promote tumor growth. Other defined species have tumoricidal properties. These findings and insights are now being used to further optimize the functionality of the immune system and shape the tumor microenvironment in order to improve the outcome of ICI.
The realization that the composition and functionality of gut microbiota have an impact on the outcome of immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) therapy of cancer has initiated research into the potential of microbiota management as adjunctive therapy. Fecal microbiota transplantation can improve the outcome of ICI, but for optimal donor selection, safety, and large-scale implementation, there remain bottlenecks. Alternative strategies, such as the use of selected bacterial species, require fundamental knowledge of the underlying mechanisms governing the interaction between (intestinal) microbiota and the immune system. Gut microbiota also appears to be able to colonize the tumor microenvironment. Some bacterial species directly or indirectly promote tumor growth. Other defined species have tumoricidal properties. These findings and insights are now being used to further optimize the functionality of the immune system and shape the tumor microenvironment in order to improve the outcome of ICI.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002348

Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are established treatments for various malignancies, including lung, kidney, and colorectal cancers. However, their broad use has led to an increase in immune-related adverse events (irAEs), with thyroiditis, colitis, and pneumonitis being the most common. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare but severe irAE characterized by excessive immune activation, leading to systemic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction. We present three cases of ICI-induced HLH in patients with lung cancer who were treated with ICIs. All patients showed elevated inflammatory markers and responded to high-dose corticosteroids without the addition of etoposide. These cases underscore the importance of early recognition and treatment of HLH in patients receiving ICIs to mitigate morbidity and mortality. Large-scale studies are needed to establish standardized guidelines for diagnosing and managing ICI-induced HLH.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are established treatments for various malignancies, including lung, kidney, and colorectal cancers. However, their broad use has led to an increase in immune-related adverse events (irAEs), with thyroiditis, colitis, and pneumonitis being the most common. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare but severe irAE characterized by excessive immune activation, leading to systemic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction. We present three cases of ICI-induced HLH in patients with lung cancer who were treated with ICIs. All patients showed elevated inflammatory markers and responded to high-dose corticosteroids without the addition of etoposide. These cases underscore the importance of early recognition and treatment of HLH in patients receiving ICIs to mitigate morbidity and mortality. Large-scale studies are needed to establish standardized guidelines for diagnosing and managing ICI-induced HLH.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002347

Cancer is one of the leading global causes of mortality and morbidity, so it needs early diagnosis and therapies. Traditional diagnostic and therapeutic strategies are inadequate due to several limitations, such as poor specificity, systemic toxicity, and delays, while metal-grafted Gr nanostructures have emerged as promising theranostic platforms due to their unique electronic, optical, and structural properties. Metals such as Fe3O4, Au, Ag, TiO2, Pd, Pt, Bi, ZnO, and Cu grafted onto the Gr surface impart electronic modulation, enhance surface area, flexibility, conductivity, reactivity, biomolecular interactions, and biosensing, thereby enabling precise biomarker detection, targeted drug delivery, imaging, and photothermal/photodynamic therapy (PTT/PDT). Eco-friendly synthesis using plant extracts and microbes offers a sustainable and biocompatible alternative to conventional chemical synthesis. However, challenges remain, such as homogenous doping, synthetic complexity, long-term safety, and clinical scalability. Innovations such as scalable, cost-effective, biocompatible nanofibers, nanopapers, microfluidic, and wearable biosensors are being explored by incorporating AI and advanced diagnostic tools for advanced biomedical devices. In vitro, half maximum inhibitory concentrations (IC50) studies show that size- and dose-dependent nanohybrids such as Fe3O4-Gr, γ-Fe2O3-Gr, Au-Gr, and Bi-Gr exhibited safer responses at lower concentrations 10–200 µg/mL across HBE, MCF-7, HeLa B, and LNCaP cell lines. Bi-Gr was tested on human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line, which exhibits higher reactivity despite a safer profile of Bi at ~53–88 µg/mL. Pd-Gr and Pt-Gr significantly reduced viability in prostate and ovarian cancer cells at 10–50 µg/mL, while ZnO-Gr, Ag-Gr, and Cu-Gr showed safer activity at lower concentrations on MCF-7. In vivo studies remain limited; median lethal dose (LD50) values for Fe3O4-Gr and γ-Fe2O3-Gr were determined to be associated with rapid lethal biodistribution observed in the liver, lungs, and spleen. Metal-grafted Gr nanohybrids demonstrate immense potential for multifunctional cancer theranostics, though systematic in vivo toxicity studies still need to be explored by the intravenously administered route to lower the LD50 of nanohybrids for their clinical translation.
Cancer is one of the leading global causes of mortality and morbidity, so it needs early diagnosis and therapies. Traditional diagnostic and therapeutic strategies are inadequate due to several limitations, such as poor specificity, systemic toxicity, and delays, while metal-grafted Gr nanostructures have emerged as promising theranostic platforms due to their unique electronic, optical, and structural properties. Metals such as Fe3O4, Au, Ag, TiO2, Pd, Pt, Bi, ZnO, and Cu grafted onto the Gr surface impart electronic modulation, enhance surface area, flexibility, conductivity, reactivity, biomolecular interactions, and biosensing, thereby enabling precise biomarker detection, targeted drug delivery, imaging, and photothermal/photodynamic therapy (PTT/PDT). Eco-friendly synthesis using plant extracts and microbes offers a sustainable and biocompatible alternative to conventional chemical synthesis. However, challenges remain, such as homogenous doping, synthetic complexity, long-term safety, and clinical scalability. Innovations such as scalable, cost-effective, biocompatible nanofibers, nanopapers, microfluidic, and wearable biosensors are being explored by incorporating AI and advanced diagnostic tools for advanced biomedical devices. In vitro, half maximum inhibitory concentrations (IC50) studies show that size- and dose-dependent nanohybrids such as Fe3O4-Gr, γ-Fe2O3-Gr, Au-Gr, and Bi-Gr exhibited safer responses at lower concentrations 10–200 µg/mL across HBE, MCF-7, HeLa B, and LNCaP cell lines. Bi-Gr was tested on human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line, which exhibits higher reactivity despite a safer profile of Bi at ~53–88 µg/mL. Pd-Gr and Pt-Gr significantly reduced viability in prostate and ovarian cancer cells at 10–50 µg/mL, while ZnO-Gr, Ag-Gr, and Cu-Gr showed safer activity at lower concentrations on MCF-7. In vivo studies remain limited; median lethal dose (LD50) values for Fe3O4-Gr and γ-Fe2O3-Gr were determined to be associated with rapid lethal biodistribution observed in the liver, lungs, and spleen. Metal-grafted Gr nanohybrids demonstrate immense potential for multifunctional cancer theranostics, though systematic in vivo toxicity studies still need to be explored by the intravenously administered route to lower the LD50 of nanohybrids for their clinical translation.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002346
This article belongs to the special issue Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in Cancer

Gynecological cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Recent advances in genomic and molecular sequencing have significantly enhanced our understanding of the biological pathways that drive tumor progression and resistance to therapy. Targeted therapies, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), have revolutionized cancer treatment by selectively interfering with oncogenic proteins expressed on cancer cells. However, the long-term clinical benefit is often limited due to the emergence of drug resistance, frequently mediated by compensatory signaling pathways or immune escape mechanisms. To overcome these limitations, bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) represent an innovative class of therapeutic agents that have shown promising results across various medical fields. They have been developed to engage two distinct targets simultaneously, such as tumor antigens, immune effectors, or immunomodulatory checkpoints, thereby enhancing anti-tumor activity and reducing the risk of resistance. There are 17 bsAbs approved for clinical use in various countries, with numerous others currently in active development and over 600 bsAbs undergoing clinical trials worldwide. Among these, 11 have received FDA approval for the treatment of hematologic malignancies as well as solid tumors, including uveal melanoma, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and biliary tract cancers. Although some studies have explored bsAbs in gynecological cancers, this area remains underdeveloped compared to other oncology fields. Most ongoing studies in this area are still in their early phases (phase I or phase II), and there is a need for optimization in terms of antibody design, efficacy, and safety profiles. Therefore, the purpose of this review is to present a comprehensive summary of the current research on bsAbs in gynecological cancers, with a focus on endometrial, cervical, and ovarian cancers. We will highlight ongoing clinical trials, discuss the mechanisms of action of these agents, and explore their potential benefits in enhancing treatment outcomes.
Gynecological cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Recent advances in genomic and molecular sequencing have significantly enhanced our understanding of the biological pathways that drive tumor progression and resistance to therapy. Targeted therapies, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), have revolutionized cancer treatment by selectively interfering with oncogenic proteins expressed on cancer cells. However, the long-term clinical benefit is often limited due to the emergence of drug resistance, frequently mediated by compensatory signaling pathways or immune escape mechanisms. To overcome these limitations, bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) represent an innovative class of therapeutic agents that have shown promising results across various medical fields. They have been developed to engage two distinct targets simultaneously, such as tumor antigens, immune effectors, or immunomodulatory checkpoints, thereby enhancing anti-tumor activity and reducing the risk of resistance. There are 17 bsAbs approved for clinical use in various countries, with numerous others currently in active development and over 600 bsAbs undergoing clinical trials worldwide. Among these, 11 have received FDA approval for the treatment of hematologic malignancies as well as solid tumors, including uveal melanoma, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and biliary tract cancers. Although some studies have explored bsAbs in gynecological cancers, this area remains underdeveloped compared to other oncology fields. Most ongoing studies in this area are still in their early phases (phase I or phase II), and there is a need for optimization in terms of antibody design, efficacy, and safety profiles. Therefore, the purpose of this review is to present a comprehensive summary of the current research on bsAbs in gynecological cancers, with a focus on endometrial, cervical, and ovarian cancers. We will highlight ongoing clinical trials, discuss the mechanisms of action of these agents, and explore their potential benefits in enhancing treatment outcomes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002345

Aim:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) displays both shared and ethnicity-specific molecular characteristics. Using transcriptomic data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we compared gene expression profiles between Asian and Caucasian HCC patients.
Methods:
Gene expression profiles were analyzed using the PyDESeq2 implementation of DESeq2, applying size factor normalization and dispersion estimation. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified with thresholds of false discovery rate (FDR) of < 0.05 and |log2FC| ≥ 1.0. Gene annotation, visualization, and pathway enrichment were conducted using Sanbomics, seaborn, and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) via the GSEApy package.
Results:
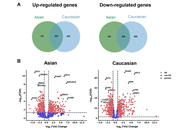
A total of 387 and 250 genes were commonly upregulated and downregulated, respectively, in both populations, including the upregulations of GPC3 and PLVAP and the downregulations of FCN3 and OIT3, indicating their potential as universal HCC markers. Conversely, 16 genes were upregulated in Asians but downregulated in Caucasians, and 25 showed the reverse pattern. Asian-specific upregulation of AKR1B10, UBE2C, and S100P suggests links to viral etiology and immune modulation, while MDK, LCN2, and NQO1 were upregulated in Caucasians, implicating proliferative and metabolic roles. Functional enrichment analysis revealed distinct immune and metabolic pathways. Asians showed elevated ubiquitin ligase activity and suppressed inflammatory responses, while Caucasians exhibited enhanced cytokine signaling, complement activation, and xenobiotic metabolism.
Conclusions:
These findings highlight key molecular differences in HCC across ethnicities and emphasize the value of TCGA data for identifying both shared targets and population-specific therapeutic strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for advancing precision oncology and developing tailored interventions.
Aim:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) displays both shared and ethnicity-specific molecular characteristics. Using transcriptomic data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we compared gene expression profiles between Asian and Caucasian HCC patients.
Methods:
Gene expression profiles were analyzed using the PyDESeq2 implementation of DESeq2, applying size factor normalization and dispersion estimation. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified with thresholds of false discovery rate (FDR) of < 0.05 and |log2FC| ≥ 1.0. Gene annotation, visualization, and pathway enrichment were conducted using Sanbomics, seaborn, and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) via the GSEApy package.
Results:
A total of 387 and 250 genes were commonly upregulated and downregulated, respectively, in both populations, including the upregulations of GPC3 and PLVAP and the downregulations of FCN3 and OIT3, indicating their potential as universal HCC markers. Conversely, 16 genes were upregulated in Asians but downregulated in Caucasians, and 25 showed the reverse pattern. Asian-specific upregulation of AKR1B10, UBE2C, and S100P suggests links to viral etiology and immune modulation, while MDK, LCN2, and NQO1 were upregulated in Caucasians, implicating proliferative and metabolic roles. Functional enrichment analysis revealed distinct immune and metabolic pathways. Asians showed elevated ubiquitin ligase activity and suppressed inflammatory responses, while Caucasians exhibited enhanced cytokine signaling, complement activation, and xenobiotic metabolism.
Conclusions:
These findings highlight key molecular differences in HCC across ethnicities and emphasize the value of TCGA data for identifying both shared targets and population-specific therapeutic strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for advancing precision oncology and developing tailored interventions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002344

Aim:
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising targeted anti-cancer agent for several types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib can further potentiate rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC cells. Here, the mechanisms underlying this sensitization were examined in TRAIL-sensitive H460 and TRAIL-resistant A549 and SW1573 NSCLC cells.
Methods:
NSCLC cell lines were treated with rhTRAIL and bortezomib, and apoptosis was assessed through caspase activation assays, western blotting, and gene silencing of key apoptotic regulators, including Bid, XIAP, and cFLIP. Clonogenic assays were performed to evaluate long-term tumor growth suppression.
Results:
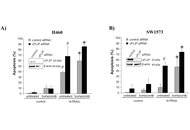
Bortezomib sensitization mechanisms varied across NSCLC cell lines. Combined rhTRAIL/bortezomib treatment enhanced apoptosis across all cell lines. In TRAIL-sensitive H460 cells, rapid caspase activation was observed, with both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways contributing to cell death. Sensitization in H460 cells was predominantly mediated via the caspase-8/Bid amplification loop. In A549 cells, the bortezomib sensitizing effect also relied on the caspase-8/Bid amplification loop. Additionally, the inhibition of Bid and XIAP emphasized the critical role of mitochondrial pathways in apoptosis. In SW1573 cells, limited caspase cleavage was detected, with distinct cleavage patterns suggesting cell-specific apoptotic mechanisms. In this cell line, bortezomib primarily enhanced the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, with XIAP depression further increasing apoptosis. Silencing cFLIP, a caspase-8 inhibitor, significantly improved rhTRAIL sensitivity, emphasizing the critical role of caspase-8 activation in overcoming resistance in SW1573. The clonogenic assay demonstrated that bortezomib combined with rhTRAIL significantly suppressed tumor growth, especially in resistant cell lines.
Conclusions:
This study underscores bortezomib’s ability to differentially enhance rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis by targeting multiple apoptotic regulators. The variety of effects that bortezomib can exert to enhance rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis makes it a very powerful combination for the treatment of NSCLC and various other types of cancer cells.
Aim:
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising targeted anti-cancer agent for several types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib can further potentiate rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC cells. Here, the mechanisms underlying this sensitization were examined in TRAIL-sensitive H460 and TRAIL-resistant A549 and SW1573 NSCLC cells.
Methods:
NSCLC cell lines were treated with rhTRAIL and bortezomib, and apoptosis was assessed through caspase activation assays, western blotting, and gene silencing of key apoptotic regulators, including Bid, XIAP, and cFLIP. Clonogenic assays were performed to evaluate long-term tumor growth suppression.
Results:
Bortezomib sensitization mechanisms varied across NSCLC cell lines. Combined rhTRAIL/bortezomib treatment enhanced apoptosis across all cell lines. In TRAIL-sensitive H460 cells, rapid caspase activation was observed, with both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways contributing to cell death. Sensitization in H460 cells was predominantly mediated via the caspase-8/Bid amplification loop. In A549 cells, the bortezomib sensitizing effect also relied on the caspase-8/Bid amplification loop. Additionally, the inhibition of Bid and XIAP emphasized the critical role of mitochondrial pathways in apoptosis. In SW1573 cells, limited caspase cleavage was detected, with distinct cleavage patterns suggesting cell-specific apoptotic mechanisms. In this cell line, bortezomib primarily enhanced the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, with XIAP depression further increasing apoptosis. Silencing cFLIP, a caspase-8 inhibitor, significantly improved rhTRAIL sensitivity, emphasizing the critical role of caspase-8 activation in overcoming resistance in SW1573. The clonogenic assay demonstrated that bortezomib combined with rhTRAIL significantly suppressed tumor growth, especially in resistant cell lines.
Conclusions:
This study underscores bortezomib’s ability to differentially enhance rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis by targeting multiple apoptotic regulators. The variety of effects that bortezomib can exert to enhance rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis makes it a very powerful combination for the treatment of NSCLC and various other types of cancer cells.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002342

DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002343

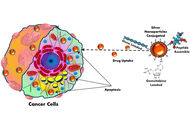
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has recently gained prominence as a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional physical and chemical methods. Utilizing biological entities such as plant extracts, bacteria, fungi, and biomolecules, the method acts by both reducing and stabilizing mechanisms. It does not use any harmful chemical substances, thus proving to be eco-friendly. Green-synthesized AgNPs exhibit enhanced biocompatibility, stability, and targeted delivery of the drug due to the use of naturally derived surface capping agents. These unique characteristics allow selective interference with cancer cells. The mechanism involved is the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), the induction of apoptosis, DNA damage, and cell cycle arrest. Green AgNPs also possess broad-spectrum antimicrobial, catalytic, antiparasitic, and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting the fact that they can be utilised in biomedical fields such as drug delivery, bioimaging, biosensing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine. Recent advancements have focused on controlling NP size, shape, and surface functionality to maximize efficacy while simultaneously minimizing cytotoxicity. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the latest green synthesis strategies, their characterizations, and the molecular mechanisms by which they exert anticancer effects. Recent patents highlight the clinical potential of AgNPs in cancer therapy. US Patent 12201650 (2025) describes green synthesis using Caralluma sinaica, while other patents (WO2007001453, US7462753) outline adaptable biomedical formulations. Studies on biogenic AgNPs also show significant tumor inhibition and selective cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Furthermore, the article discusses current biomedical applications and critically evaluates the limitations, such as reproducibility, toxicity concerns, and scalability for clinical translation. Addressing these challenges is essential for the integration of green AgNPs into mainstream cancer therapeutics. The convergence of nanotechnology and biologically derived synthesis opens promising avenues for the development of safe, effective, and environmentally sustainable medical innovations.
The green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has recently gained prominence as a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional physical and chemical methods. Utilizing biological entities such as plant extracts, bacteria, fungi, and biomolecules, the method acts by both reducing and stabilizing mechanisms. It does not use any harmful chemical substances, thus proving to be eco-friendly. Green-synthesized AgNPs exhibit enhanced biocompatibility, stability, and targeted delivery of the drug due to the use of naturally derived surface capping agents. These unique characteristics allow selective interference with cancer cells. The mechanism involved is the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), the induction of apoptosis, DNA damage, and cell cycle arrest. Green AgNPs also possess broad-spectrum antimicrobial, catalytic, antiparasitic, and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting the fact that they can be utilised in biomedical fields such as drug delivery, bioimaging, biosensing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine. Recent advancements have focused on controlling NP size, shape, and surface functionality to maximize efficacy while simultaneously minimizing cytotoxicity. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the latest green synthesis strategies, their characterizations, and the molecular mechanisms by which they exert anticancer effects. Recent patents highlight the clinical potential of AgNPs in cancer therapy. US Patent 12201650 (2025) describes green synthesis using Caralluma sinaica, while other patents (WO2007001453, US7462753) outline adaptable biomedical formulations. Studies on biogenic AgNPs also show significant tumor inhibition and selective cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Furthermore, the article discusses current biomedical applications and critically evaluates the limitations, such as reproducibility, toxicity concerns, and scalability for clinical translation. Addressing these challenges is essential for the integration of green AgNPs into mainstream cancer therapeutics. The convergence of nanotechnology and biologically derived synthesis opens promising avenues for the development of safe, effective, and environmentally sustainable medical innovations.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002341
This article belongs to the special issue Potential Clinical Applications of Inorganic Nanomaterials in Cancer
 Previous
Previous