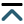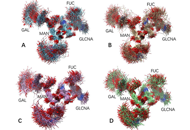



Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2021.00004

Aim:
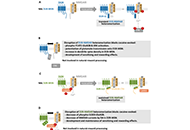
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
Aim:
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00188
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Strategies and Targets for Immunotherapy of Cancer

Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM is also the largest antibody structure among the five major human isotypes. Spontaneously formed pentamers and hexamers of IgM have avidity effects that could compensate for weaker interactions in monomeric Igs. However, this advantage is counterbalanced by potential steric clashes when binding to multiple large antigens. Recent findings have challenged the expected canonical independence of
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM is also the largest antibody structure among the five major human isotypes. Spontaneously formed pentamers and hexamers of IgM have avidity effects that could compensate for weaker interactions in monomeric Igs. However, this advantage is counterbalanced by potential steric clashes when binding to multiple large antigens. Recent findings have challenged the expected canonical independence of
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2022.00083

Age-related changes in the brain cause cognitive decline and dementia. In recent year’s researchers’ extensively stu
Age-related changes in the brain cause cognitive decline and dementia. In recent year’s researchers’ extensively stu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00256
This article belongs to the special issue Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia

Aim:
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the formation of neutralizing antibo
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted among mass vaccination attendees using inactivated CoronaVac. Collected the peripheral blood serum four weeks following the second vaccine dose. Forty-four adults aged 26–85 were split into two groups based on age (≤ 60 years and > 60 years) and BMI (non-obese ≤ 25 kg/m2 and obese > 25 kg/m2). Variables like age, gender, BMI, and the presence of comorbidities were recorded. CD4/CD8 ratio and vitamin D levels were examined for their influence on NAbs formation. NAbs were measured using ELISA, T-cells via flow cytometry, and vitamin D through radioimmunoassay. Descriptive data analysis was performed as mean ± standard deviation to show the characteristics of the sample. Students’ t-tests and multivariate and univariate regression analyses were used to evaluate the data.
Results:
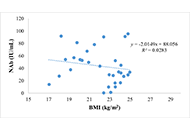
Significant variations in NAbs levels were observed with age (P = 0.013), BMI (P = 0.004), and comorbidities (P = 0.034). The elderly demonstrated higher NAb levels, potentially due to the high vitamin D levels compared to the adult group. The vitamin D levels strongly correlated with NAb titer (P < 0.001; R = 0.843). A collective correlation was found between NAb levels and the factors of age, BMI, and CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.033). A negative correlation existed between BMI and NAb levels (P = 0.018; R = –0.356) and between age and the CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.440; R = –0.119), but age alone did not correlate with NAb titer.
Conclusions:
Age, BMI, CD4/CD8 ratio, and comorbidities influence the production of post-vaccination NAbs. Sufficient vitamin D levels in the elderly significantly boost post-vaccination NAb levels. Maintaining a healthy body weight is also vital, as stu
Aim:
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the formation of neutralizing antibo
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted among mass vaccination attendees using inactivated CoronaVac. Collected the peripheral blood serum four weeks following the second vaccine dose. Forty-four adults aged 26–85 were split into two groups based on age (≤ 60 years and > 60 years) and BMI (non-obese ≤ 25 kg/m2 and obese > 25 kg/m2). Variables like age, gender, BMI, and the presence of comorbidities were recorded. CD4/CD8 ratio and vitamin D levels were examined for their influence on NAbs formation. NAbs were measured using ELISA, T-cells via flow cytometry, and vitamin D through radioimmunoassay. Descriptive data analysis was performed as mean ± standard deviation to show the characteristics of the sample. Students’ t-tests and multivariate and univariate regression analyses were used to evaluate the data.
Results:
Significant variations in NAbs levels were observed with age (P = 0.013), BMI (P = 0.004), and comorbidities (P = 0.034). The elderly demonstrated higher NAb levels, potentially due to the high vitamin D levels compared to the adult group. The vitamin D levels strongly correlated with NAb titer (P < 0.001; R = 0.843). A collective correlation was found between NAb levels and the factors of age, BMI, and CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.033). A negative correlation existed between BMI and NAb levels (P = 0.018; R = –0.356) and between age and the CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.440; R = –0.119), but age alone did not correlate with NAb titer.
Conclusions:
Age, BMI, CD4/CD8 ratio, and comorbidities influence the production of post-vaccination NAbs. Sufficient vitamin D levels in the elderly significantly boost post-vaccination NAb levels. Maintaining a healthy body weight is also vital, as stu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2025.1003180
This article belongs to the special issue Immunology, Immunopathology and Genomics of SARS-COV-2

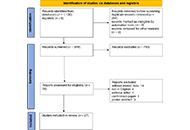
Brazil ranks second globally in absolute liver transplants and leads pediatric transplantation in Latin America. This scoping review aims to map the results and perspectives of pediatric liver transplantation in Brazil from 2000 to 2022. A scoping review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews Checklist (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines, using PubMed, Virtual Health Library (VHL), and ScienceDirect. From 293 records,
Brazil ranks second globally in absolute liver transplants and leads pediatric transplantation in Latin America. This scoping review aims to map the results and perspectives of pediatric liver transplantation in Brazil from 2000 to 2022. A scoping review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews Checklist (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines, using PubMed, Virtual Health Library (VHL), and ScienceDirect. From 293 records,
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edd.2025.100587

Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been stu
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
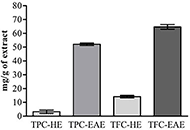
The higher T
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
Aim:
As far as is known, the pharmaceutical effects of neem on human B-lymphoblastoid (TK6) cells have not been stu
Methods:
Hexane extract (HE) was obtained in the first step. After that, the residual hexane was removed from the neem. The dried neem sample was used in a new extraction for obtaining the ethyl acetate extract (EAE). Total phenolic compounds (TPC) and total flavonoid contents (TFC) were determined by spectrophotometric methods. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) tests were used to evaluate the cytotoxicity in TK6 cells. The stop at G0/G1 cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in the TK6 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. For deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage evaluation, the alkaline comet test was used.
Results:
The higher T
Conclusions:
The extraction residue from neem leaf after hexane extraction is a source important of cytotoxic and genotoxic molecules against TK6 cells, the results also can suggest that the toxic effects in TK6 cells can be provided most likely due to the presence of high content of TPC from neem extracts.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00011

Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are aggressive tumors arising from different portions of the biliary tree and classified according to the anatomical location in intrahepatic (i) cholangiocarcinoma (CCA, iCCA), perihilar CCA (pCCA), and distal CCA (dCCA), gallbladder cancer (GBC), and ampulla of Vater cancer (AVC). Due to their silent behavior, BTCs are frequently diagnosed at advanced stages when the prognosis is poor. The available chemotherapeutic options are palliative and unfortunately, most patients will
Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) are aggressive tumors arising from different portions of the biliary tree and classified according to the anatomical location in intrahepatic (i) cholangiocarcinoma (CCA, iCCA), perihilar CCA (pCCA), and distal CCA (dCCA), gallbladder cancer (GBC), and ampulla of Vater cancer (AVC). Due to their silent behavior, BTCs are frequently diagnosed at advanced stages when the prognosis is poor. The available chemotherapeutic options are palliative and unfortunately, most patients will
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2021.00054
This article belongs to the special issue Precision Medicine for Cholangiocarcinoma

Aim:
Changes in strategies in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) crisis and the imposing of restrictions have isolated many vulnerable patients including those with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from routine medical care. This study investigated how the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Methods:
An extensive search was conducted in the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases by using the appropriate keywords: COVID-19, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatocellular cancer, and MeSH. Stu
Results:
The final qualitative analysis consisted of 27 articles. During the COVID-19 crisis, HCC diagnosis decreased from 20% to 34.13% compared to pre-crisis. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC treatment encompasses a wide range of aspects. Generally, delays in treatment for patients with HCC ranged from more than one month for 21.5% of patients in France, to two months for 26% of patients in Italy, up to 30% in Austria, and 66.7% in Asia-Pacific countries.
Conclusions:
According to the findings, developing and implementing appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies and developing low-cost and high-precision screening programs among high-risk populations seem to be effective in reducing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC management.
Aim:
Changes in strategies in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) crisis and the imposing of restrictions have isolated many vulnerable patients including those with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from routine medical care. This study investigated how the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Methods:
An extensive search was conducted in the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases by using the appropriate keywords: COVID-19, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatocellular cancer, and MeSH. Stu
Results:
The final qualitative analysis consisted of 27 articles. During the COVID-19 crisis, HCC diagnosis decreased from 20% to 34.13% compared to pre-crisis. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC treatment encompasses a wide range of aspects. Generally, delays in treatment for patients with HCC ranged from more than one month for 21.5% of patients in France, to two months for 26% of patients in Italy, up to 30% in Austria, and 66.7% in Asia-Pacific countries.
Conclusions:
According to the findings, developing and implementing appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies and developing low-cost and high-precision screening programs among high-risk populations seem to be effective in reducing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC management.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00179
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer

The tropics are abundant in both animals and plants, but also in pathogenic agents. There, the world’s greatest burden of diseases and mortality is concentrated. Co-infections are the rule, making laboratory diagnosis complex. Simultaneous multidiagnostic methods are desirable; however, they are mostly expensive and inaccessible to the populations of the region. The aim of our research was to produce synthetic peptides of the most important pathogens that can be used in a simultaneous multidiagnostic technique. Thus, we designed a low-cost method to detect antibo
The tropics are abundant in both animals and plants, but also in pathogenic agents. There, the world’s greatest burden of diseases and mortality is concentrated. Co-infections are the rule, making laboratory diagnosis complex. Simultaneous multidiagnostic methods are desirable; however, they are mostly expensive and inaccessible to the populations of the region. The aim of our research was to produce synthetic peptides of the most important pathogens that can be used in a simultaneous multidiagnostic technique. Thus, we designed a low-cost method to detect antibo
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2025.1008118
This article belongs to the special issue Bioactive Peptides discovery and development

Aim:
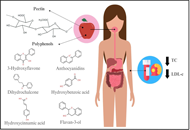
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) are among the main causes of death worldwide and dyslipidemias account for one of the risk factors for these diseases. Habitual apple consumption appears to be inversely associated with reduced cardiovascular risk. Then, this systematic review aims to investigate the effect of chronic apple consumption on the lipid profile of adults with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
A systematic search was performed in electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Scopus, without restriction of year of publication. Inclusion criteria were randomized clinical trials in humans that investigated the effect of chronic consumption of whole fresh or dried apple, for a period longer than two weeks of intervention on the lipid profile.
Results:
Based on the methodology used and following the pre-established search strategies, 4,468 articles were found. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, five articles were selected for qualitative evaluation, covering 522 adult participants of both sexes. Three randomized controlled trials included in this review demonstrated that there was a decrease in plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) concentrations, in addition to an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) concentration. Two other stu
Conclusions:
The analysis of the stu
Aim:
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) are among the main causes of death worldwide and dyslipidemias account for one of the risk factors for these diseases. Habitual apple consumption appears to be inversely associated with reduced cardiovascular risk. Then, this systematic review aims to investigate the effect of chronic apple consumption on the lipid profile of adults with dyslipidemia.
Methods:
A systematic search was performed in electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Scopus, without restriction of year of publication. Inclusion criteria were randomized clinical trials in humans that investigated the effect of chronic consumption of whole fresh or dried apple, for a period longer than two weeks of intervention on the lipid profile.
Results:
Based on the methodology used and following the pre-established search strategies, 4,468 articles were found. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, five articles were selected for qualitative evaluation, covering 522 adult participants of both sexes. Three randomized controlled trials included in this review demonstrated that there was a decrease in plasma total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) concentrations, in addition to an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) concentration. Two other stu
Conclusions:
The analysis of the stu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2023.00022

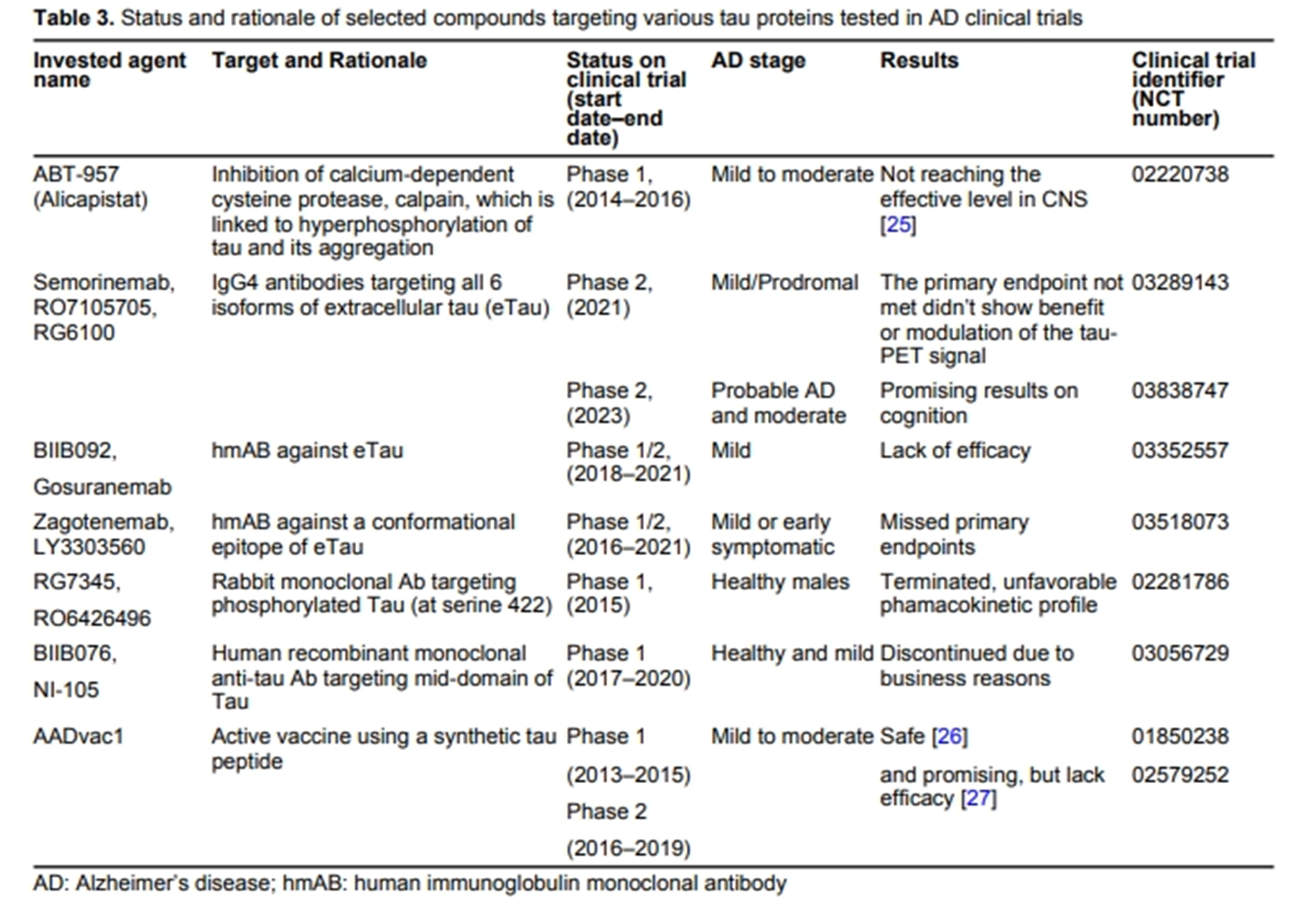
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a major type of dementia and neurodegenerative disease, characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline. Over decades, significant efforts have been dedicated to finding its cause, pathogenic mechanisms, biomarkers for early detection, and clinical trials for its treatment. Earlier approved drugs mainly ameliorated the symptoms of AD, until recent years when two drugs targeting amyloid-beta (Aβ) protein were approved to slow down the progression of the disease. This review article encompasses the history of drug development in treating AD and clinical trials that failed and succeeded. Clinicaltrials.org
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a major type of dementia and neurodegenerative disease, characterized by memory loss and cognitive decline. Over decades, significant efforts have been dedicated to finding its cause, pathogenic mechanisms, biomarkers for early detection, and clinical trials for its treatment. Earlier approved drugs mainly ameliorated the symptoms of AD, until recent years when two drugs targeting amyloid-beta (Aβ) protein were approved to slow down the progression of the disease. This review article encompasses the history of drug development in treating AD and clinical trials that failed and succeeded. Clinicaltrials.org
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2024.00048
This article belongs to the special issue Alzheimer’s Disease

Aim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingre
Methods:
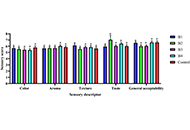
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3.
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
Aim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingre
Methods:
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3.
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101076
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Similar to other psychiatric disorders, drug addiction is linked to changes in neuronal activity within the mesolimbic system, which consists of dopamine (DA) neurons of the ventral tegmental area projecting to the ventral part of the striatum, the nucleus accumbens (NAc). All drugs of abuse indeed artificially increase DA concentration in the NAc, which hijacks the reward system and triggers lasting behavioral alterations, including compulsive drug-seeking and drug-taking behavior despite negative consequences and a high rate of relapse after abstinence. DA chiefly signals through DA receptor (DAR) type 1 (D1R) and type 2 (D2R), which are G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that are positively and negatively coupled to adenyl cyclase, respectively. Multiple evidence indicates that the potent modulatory roles of DA on other neurotransmitters and neuromodulator systems implicate the direct physical interactions (i.e., heteromerization) of DAR with other receptors. DAR heteromerization, which is increased in several preclinical models of psychiatric disorders, leads to a reciprocal and fine-tuned modulation of DAR and partner receptors, therefore suggesting that targeting DAR heteromerization may contribute to the development of clinically relevant strategies. Herein, we provide an overview of current methodologies used for detecting receptor heteromers both in heterologous systems and in situ in the brain and discuss their respective advantages and limitations. We also argue that D1R and D2R have been shown to form heteromers with multiple partner receptors in heterologous systems but only few stu
Similar to other psychiatric disorders, drug addiction is linked to changes in neuronal activity within the mesolimbic system, which consists of dopamine (DA) neurons of the ventral tegmental area projecting to the ventral part of the striatum, the nucleus accumbens (NAc). All drugs of abuse indeed artificially increase DA concentration in the NAc, which hijacks the reward system and triggers lasting behavioral alterations, including compulsive drug-seeking and drug-taking behavior despite negative consequences and a high rate of relapse after abstinence. DA chiefly signals through DA receptor (DAR) type 1 (D1R) and type 2 (D2R), which are G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that are positively and negatively coupled to adenyl cyclase, respectively. Multiple evidence indicates that the potent modulatory roles of DA on other neurotransmitters and neuromodulator systems implicate the direct physical interactions (i.e., heteromerization) of DAR with other receptors. DAR heteromerization, which is increased in several preclinical models of psychiatric disorders, leads to a reciprocal and fine-tuned modulation of DAR and partner receptors, therefore suggesting that targeting DAR heteromerization may contribute to the development of clinically relevant strategies. Herein, we provide an overview of current methodologies used for detecting receptor heteromers both in heterologous systems and in situ in the brain and discuss their respective advantages and limitations. We also argue that D1R and D2R have been shown to form heteromers with multiple partner receptors in heterologous systems but only few stu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ent.2025.1004100
This article belongs to the special issue GPCR Heteroreceptor Complexes as Key Players in Neuroprotection

Aim:
This study aims to investigate the impact of asthma on quality of life, explore its associations with anxiety and depression, and identify the key determining factors.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted in the pulmonology department of Hassan II University Hospital in Fez in 2021. Data were collected using an anonymous questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and therapeutic information. The Moroccan versions of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and the Short-Form-12 (SF-12) scale were used to assess anxiety, depression, and quality of life. Descriptive analysis was performed, followed by univariate analysis to examine the associations between quality of life, anxiety, depression, and other factors, using statistical tests appropriate for the types of variables stu
Results:
Among the 67 patients included (77.6% women, 61.2% aged ≥ 50 years), wheezing (44.8%) and dyspnoea (26.9%) were the most frequent symptoms. Depression was significantly associated with pain (p = 0.020), and frequent hospitalizations (p = 0.021), while anxiety was more common among women (p = 0.034). For quality of life, patients with depression had lower physical component summary (PCS) scores (p = 0.008). Patients over 50 years old had significantly lower PCS and mental component summary (MCS) scores (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). Illiterate patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.022), hypertensive patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.032), and a nearly significant difference for the MCS (p = 0.053). Diabetic patients had lower MCS scores (p = 0.034). Finally, a positive correlation was observed between respiratory function forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and both PCS scores (p = 0.025) and MCS scores (p = 0.018).
Conclusions:
This study underscores the importance of an integrated approach to enhancing the quality of life of asthmatic patients, taking into account respiratory, psychological, and social factors.
Aim:
This study aims to investigate the impact of asthma on quality of life, explore its associations with anxiety and depression, and identify the key determining factors.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted in the pulmonology department of Hassan II University Hospital in Fez in 2021. Data were collected using an anonymous questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and therapeutic information. The Moroccan versions of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and the Short-Form-12 (SF-12) scale were used to assess anxiety, depression, and quality of life. Descriptive analysis was performed, followed by univariate analysis to examine the associations between quality of life, anxiety, depression, and other factors, using statistical tests appropriate for the types of variables stu
Results:
Among the 67 patients included (77.6% women, 61.2% aged ≥ 50 years), wheezing (44.8%) and dyspnoea (26.9%) were the most frequent symptoms. Depression was significantly associated with pain (p = 0.020), and frequent hospitalizations (p = 0.021), while anxiety was more common among women (p = 0.034). For quality of life, patients with depression had lower physical component summary (PCS) scores (p = 0.008). Patients over 50 years old had significantly lower PCS and mental component summary (MCS) scores (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). Illiterate patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.022), hypertensive patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.032), and a nearly significant difference for the MCS (p = 0.053). Diabetic patients had lower MCS scores (p = 0.034). Finally, a positive correlation was observed between respiratory function forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and both PCS scores (p = 0.025) and MCS scores (p = 0.018).
Conclusions:
This study underscores the importance of an integrated approach to enhancing the quality of life of asthmatic patients, taking into account respiratory, psychological, and social factors.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2025.100976
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors

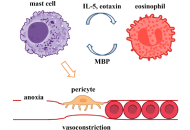
Activation of eosinophils and mast cells in dysregulated type 2 immunity may play key roles in allergic diseases. Eosinophils are linked to the pathobiology of multiple human diseases, including eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs), functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), Kimura’s disease, hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES), rheumatoid lesions, allergy, asthma, and some forms of heart disease etc. Eosinophils are part of the innate immune response involved in combating multicellular parasites and some infections. Mast cells play a key role in allergies, allergic conjunctivitis, allergic dermatitis (eczema), allergic rhinitis (hay fever), anaphylaxis, asthma, and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS). Mast cells can also play a key role in eosinophilic diseases. Eosinophils respond to interleukin 5 (IL-5) and chemotactic chemokine eosinophil chemotactic factor (eotaxin) released from activated mast cells. Mast cells can be activated by fragment crystallizable (Fc) receptor bound immunoglobulin E (IgE) and G (IgG) antibo
Activation of eosinophils and mast cells in dysregulated type 2 immunity may play key roles in allergic diseases. Eosinophils are linked to the pathobiology of multiple human diseases, including eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs), functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), Kimura’s disease, hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES), rheumatoid lesions, allergy, asthma, and some forms of heart disease etc. Eosinophils are part of the innate immune response involved in combating multicellular parasites and some infections. Mast cells play a key role in allergies, allergic conjunctivitis, allergic dermatitis (eczema), allergic rhinitis (hay fever), anaphylaxis, asthma, and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS). Mast cells can also play a key role in eosinophilic diseases. Eosinophils respond to interleukin 5 (IL-5) and chemotactic chemokine eosinophil chemotactic factor (eotaxin) released from activated mast cells. Mast cells can be activated by fragment crystallizable (Fc) receptor bound immunoglobulin E (IgE) and G (IgG) antibo
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2025.100983
This article belongs to the special issue Innate Immune Mechanisms in Allergic Diseases

Aim:
BRCA1/2-associated breast and ovarian carcinomas are often regarded as a single entity, assuming that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are almost equivalent with regard to their clinical significance. However, BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes differ in their function; therefore, a comparison of treatment outcomes in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 carriers is warranted.
Methods:
This study focused on consecutive patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), given that these subjects are treatment-naive and accessible for immediate assessment of pathological and clinical outcomes.
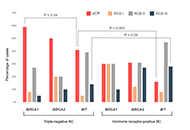
Results:
BRCA2-associated high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas (HGSOCs) demonstrated significantly higher rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) as compared to BRCA1-related cancers [8/15 (53%) vs. 7/48 (15%), P = 0.004]. In contrast, HER2-negative breast cancer (BC) patients showed a numerically higher rate of pCR in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 mutation carriers [38/69 (55%) vs. 13/36 (36%), P = 0.1]. However, the comparison with BRCA-wild-type (WT) tumors revealed that this tendency was mainly attributed to the increased prevalence of hormone receptor (HR)-negative disease in the former group. When BC patients were stratified according to the tumor receptor status, the response rates in triple-negative patients were consistently higher than in HR+/HER2– patients across all analyzed subgroups [BRCA1: 35/59 (59%) vs. 3/10 (30%); BRCA2: 5/10 (50%) vs. 8/
Conclusions:
Hereditary ovarian carcinomas demonstrate better NACT outcomes in BRCA2 vs. BRCA1 mutation carriers. The opposite trend is observed in BC, which is likely to be attributed to a high frequency of triple-negative disease in BRCA1- but not BRCA2-associated BCs. Triple-negative receptor status rather than BRCA1/2 status is the strongest predictor of response to NACT in BC.
Aim:
BRCA1/2-associated breast and ovarian carcinomas are often regarded as a single entity, assuming that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are almost equivalent with regard to their clinical significance. However, BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes differ in their function; therefore, a comparison of treatment outcomes in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 carriers is warranted.
Methods:
This study focused on consecutive patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), given that these subjects are treatment-naive and accessible for immediate assessment of pathological and clinical outcomes.
Results:
BRCA2-associated high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas (HGSOCs) demonstrated significantly higher rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) as compared to BRCA1-related cancers [8/15 (53%) vs. 7/48 (15%), P = 0.004]. In contrast, HER2-negative breast cancer (BC) patients showed a numerically higher rate of pCR in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 mutation carriers [38/69 (55%) vs. 13/36 (36%), P = 0.1]. However, the comparison with BRCA-wild-type (WT) tumors revealed that this tendency was mainly attributed to the increased prevalence of hormone receptor (HR)-negative disease in the former group. When BC patients were stratified according to the tumor receptor status, the response rates in triple-negative patients were consistently higher than in HR+/HER2– patients across all analyzed subgroups [BRCA1: 35/59 (59%) vs. 3/10 (30%); BRCA2: 5/10 (50%) vs. 8/
Conclusions:
Hereditary ovarian carcinomas demonstrate better NACT outcomes in BRCA2 vs. BRCA1 mutation carriers. The opposite trend is observed in BC, which is likely to be attributed to a high frequency of triple-negative disease in BRCA1- but not BRCA2-associated BCs. Triple-negative receptor status rather than BRCA1/2 status is the strongest predictor of response to NACT in BC.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002325

Cancer serum biomarkers are valuable or even indispensable for cancer diagnostics and/or monitoring and, currently, many cancer serum markers are routinely used in the clinic. Most of those markers are glycoproteins, carrying cancer-specific glycan structures that can provide extra-information for cancer monitoring. Nonetheless, in the majority of cases, this differential feature is not exploited and the corresponding analytical assays detect only the protein amount, disregarding the analysis of the aberrant glycoform. Two exceptions to this trend are the biomarkers α-fetoprotein (AFP) and cancer antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), which are clinically monitored for their cancer-related glycan changes, and only the AFP assay includes quantification of both the protein amount and the altered glycoform. This narrative review demonstrates, through several examples, the advantages of the combined quantification of protein cancer biomarkers and the respective glycoform analysis, which enable to yield the maximum information and overcome the weaknesses of each individual analysis. This strategy allows to achieve higher sensitivity and specificity in the detection of cancer, enhancing the diagnostic power of biomarker-based cancer detection tests.
Cancer serum biomarkers are valuable or even indispensable for cancer diagnostics and/or monitoring and, currently, many cancer serum markers are routinely used in the clinic. Most of those markers are glycoproteins, carrying cancer-specific glycan structures that can provide extra-information for cancer monitoring. Nonetheless, in the majority of cases, this differential feature is not exploited and the corresponding analytical assays detect only the protein amount, disregarding the analysis of the aberrant glycoform. Two exceptions to this trend are the biomarkers α-fetoprotein (AFP) and cancer antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), which are clinically monitored for their cancer-related glycan changes, and only the AFP assay includes quantification of both the protein amount and the altered glycoform. This narrative review demonstrates, through several examples, the advantages of the combined quantification of protein cancer biomarkers and the respective glycoform analysis, which enable to yield the maximum information and overcome the weaknesses of each individual analysis. This strategy allows to achieve higher sensitivity and specificity in the detection of cancer, enhancing the diagnostic power of biomarker-based cancer detection tests.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00140
This article belongs to the special issue Biomarkers for Personalized and Precise Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment

Aim:
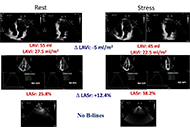
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
Aim:
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00018

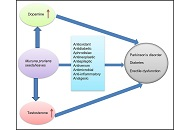
Among the most common medical problems experienced by older adults (over 60 years) are diabetes, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and erectile dysfunction (ED). The potential use of Mucuna pruriens in treating type 2 diabetes (T2D), PD, and ED is being investigated. Literature searches were conducted using the PubMed, MEDLINE, and Mendeley databases (1990–2023). Key words related to Mucuna pruriens, PD, diabetes, and EDs were used. An analysis of
Among the most common medical problems experienced by older adults (over 60 years) are diabetes, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and erectile dysfunction (ED). The potential use of Mucuna pruriens in treating type 2 diabetes (T2D), PD, and ED is being investigated. Literature searches were conducted using the PubMed, MEDLINE, and Mendeley databases (1990–2023). Key words related to Mucuna pruriens, PD, diabetes, and EDs were used. An analysis of
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101083
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease
 Previous
Previous