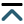

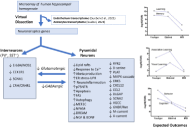


Diabetic wound healing presents a unique and complex challenge due to the impaired cellular and molecular functions associated with diabetes. Chronic wounds in diabetic patients are characterized by prolonged inflammation, reduced angiogenesis, and impaired collagen deposition, which significantly hinder the healing process. This comprehensive review focuses on the innovative applications of designer cytokines in precision therapy for diabetic wound healing, emphasizing the remarkable advancements made in overcoming the limitations of natural cytokines, such as their short half-life, potential cytotoxicity, and lack of specificity. We begin by detailing the intricate biological characteristics of diabetic wounds and the essential role that cytokines play in orchestrating the healing process. The review critically examines the constraints of natural cytokines and traces the evolution of synthetic alternatives, with a particular emphasis on peptide-based and nucleic acid-based artificial cytokines. Advanced strategies for designing these artificial cytokines are discussed, including molecular modifications, functional enhancements, and specificity improvements to better target pathological conditions in diabetic wounds. Furthermore, we explore the utilization of synthetic biology techniques to engineer effective cytokine-based therapies. The promising therapeutic potential of rationally designed cytokines is highlighted, showcasing their ability to modulate the wound microenvironment, enhance tissue regeneration, and reduce chronic inflammation. This review not only provides valuable perspectives on the future research directions but also offers insights into the potential clinical applications of these innovative therapies, aiming to significantly improve the outcomes for patients suffering from diabetic wounds.
Diabetic wound healing presents a unique and complex challenge due to the impaired cellular and molecular functions associated with diabetes. Chronic wounds in diabetic patients are characterized by prolonged inflammation, reduced angiogenesis, and impaired collagen deposition, which significantly hinder the healing process. This comprehensive review focuses on the innovative applications of designer cytokines in precision therapy for diabetic wound healing, emphasizing the remarkable advancements made in overcoming the limitations of natural cytokines, such as their short half-life, potential cytotoxicity, and lack of specificity. We begin by detailing the intricate biological characteristics of diabetic wounds and the essential role that cytokines play in orchestrating the healing process. The review critically examines the constraints of natural cytokines and traces the evolution of synthetic alternatives, with a particular emphasis on peptide-based and nucleic acid-based artificial cytokines. Advanced strategies for designing these artificial cytokines are discussed, including molecular modifications, functional enhancements, and specificity improvements to better target pathological conditions in diabetic wounds. Furthermore, we explore the utilization of synthetic biology techniques to engineer effective cytokine-based therapies. The promising therapeutic potential of rationally designed cytokines is highlighted, showcasing their ability to modulate the wound microenvironment, enhance tissue regeneration, and reduce chronic inflammation. This review not only provides valuable perspectives on the future research directions but also offers insights into the potential clinical applications of these innovative therapies, aiming to significantly improve the outcomes for patients suffering from diabetic wounds.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2024.00157

Aim:
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) became pandemic on 11th March 2020 and it deeply stressed the healthcare system. Cancer patients represent a vulnerable population, so many recommendations have been approved to ensure optimal management. Clinical research was notably impacted by COVID too. This review aims to analyze the challenges occurred during a pandemic for the management of enrolled patients (enrollment, use of telemedicine
Methods:
The studies included in the present review were selected from PubMed/Google Scholar/ScienceDirect databases.
Results:
During the first phase of pandemic many clinical trials were suspended in accrual and, as the pandemic progressed, recommendations were established to guarantee the safety and the continuity of care of enrolled patients. In addition, lot of new strategies was found during the pandemic to reduce the negative consequences on clinical trial performance and to guarantee new opportunities of care in the respect of good clinical practice (GCP) in a bad scenario.
Conclusions:
Among all modifiers, investigators would prefer to maintain the positive ones such as pragmatic and simplified trial designs and protocols, reducing in-person
Aim:
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) became pandemic on 11th March 2020 and it deeply stressed the healthcare system. Cancer patients represent a vulnerable population, so many recommendations have been approved to ensure optimal management. Clinical research was notably impacted by COVID too. This review aims to analyze the challenges occurred during a pandemic for the management of enrolled patients (enrollment, use of telemedicine
Methods:
The studies included in the present review were selected from PubMed/Google Scholar/ScienceDirect databases.
Results:
During the first phase of pandemic many clinical trials were suspended in accrual and, as the pandemic progressed, recommendations were established to guarantee the safety and the continuity of care of enrolled patients. In addition, lot of new strategies was found during the pandemic to reduce the negative consequences on clinical trial performance and to guarantee new opportunities of care in the respect of good clinical practice (GCP) in a bad scenario.
Conclusions:
Among all modifiers, investigators would prefer to maintain the positive ones such as pragmatic and simplified trial designs and protocols, reducing in-person
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00183
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer

Aim:
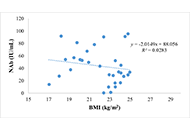
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the formation of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) in healthy adults four weeks post-COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted among mass vaccination attendees using inactivated CoronaVac. Collected the peripheral blood serum four weeks following the second vaccine dose. Forty-four adults aged 26–85 were split into two groups based on age (≤ 60 years and > 60 years) and BMI (non-obese ≤ 25 kg/m2 and obese > 25 kg/m2). Variables like age, gender, BMI, and the presence of comorbidities were recorded. CD4/CD8 ratio and vitamin D levels were examined for their influence on NAbs formation. NAbs were measured using ELISA, T-cells via flow cytometry, and vitamin D through radioimmunoassay. Descriptive data analysis was performed as mean ± standard deviation to show the characteristics of the sample. Students’ t-tests and multivariate and univariate regression analyses were used to evaluate the data.
Results:
Significant variations in NAbs levels were observed with age (P = 0.013), BMI (P = 0.004), and comorbidities (P = 0.034). The elderly demonstrated higher NAb levels, potentially due to the high vitamin D levels compared to the adult group. The vitamin D levels strongly correlated with NAb titer (P < 0.001; R = 0.843). A collective correlation was found between NAb levels and the factors of age, BMI, and CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.033). A negative correlation existed between BMI and NAb levels (P = 0.018; R = –0.356) and between age and the CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.440; R = –0.119), but age alone did not correlate with NAb titer.
Conclusions:
Age, BMI, CD4/CD8 ratio, and comorbidities influence the production of post-vaccination NAbs. Sufficient vitamin D levels in the elderly significantly boost post-vaccination NAb levels. Maintaining a healthy body weight is also vital, as studies have revealed a significant and negative correlation between BMI and the level of NAbs, suggesting a possible need for adjusted vaccine doses in obese individuals.
Aim:
This study aims to identify the factors affecting the formation of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) in healthy adults four weeks post-COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted among mass vaccination attendees using inactivated CoronaVac. Collected the peripheral blood serum four weeks following the second vaccine dose. Forty-four adults aged 26–85 were split into two groups based on age (≤ 60 years and > 60 years) and BMI (non-obese ≤ 25 kg/m2 and obese > 25 kg/m2). Variables like age, gender, BMI, and the presence of comorbidities were recorded. CD4/CD8 ratio and vitamin D levels were examined for their influence on NAbs formation. NAbs were measured using ELISA, T-cells via flow cytometry, and vitamin D through radioimmunoassay. Descriptive data analysis was performed as mean ± standard deviation to show the characteristics of the sample. Students’ t-tests and multivariate and univariate regression analyses were used to evaluate the data.
Results:
Significant variations in NAbs levels were observed with age (P = 0.013), BMI (P = 0.004), and comorbidities (P = 0.034). The elderly demonstrated higher NAb levels, potentially due to the high vitamin D levels compared to the adult group. The vitamin D levels strongly correlated with NAb titer (P < 0.001; R = 0.843). A collective correlation was found between NAb levels and the factors of age, BMI, and CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.033). A negative correlation existed between BMI and NAb levels (P = 0.018; R = –0.356) and between age and the CD4/CD8 ratio (P = 0.440; R = –0.119), but age alone did not correlate with NAb titer.
Conclusions:
Age, BMI, CD4/CD8 ratio, and comorbidities influence the production of post-vaccination NAbs. Sufficient vitamin D levels in the elderly significantly boost post-vaccination NAb levels. Maintaining a healthy body weight is also vital, as studies have revealed a significant and negative correlation between BMI and the level of NAbs, suggesting a possible need for adjusted vaccine doses in obese individuals.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2025.1003180
This article belongs to the special issue Immunology, Immunopathology and Genomics of SARS-COV-2

Aim:
The aim of this study was to validate a Chinese version of the painDETECT questionnaire (PD-Q) for the screening and assessment of neuropathic pain (NeP) in a Hong Kong Chinese population.
Methods:
The PD-Q was translated and cross-culturally adapted from the original German PD-Q, with forward and backward translation according to standard guidelines followed by cognitive debriefing, and finalized by an expert panel. A multicenter (6-site) observational study was conducted to evaluate the validity of the PD-Q. Patients aged 18 or above with medical conditions giving rise to either neuropathic or nociceptive pain (NoP) provided informed consent to participate in this study. Each patient was evaluated by at least two healthcare professionals for causes of pain, the visual analogue scale (VAS), numeric rating scale (NRS) and the PD-Q.
Results:
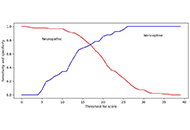
Hong Kong Chinese adults (n = 151) were given the clinical description of NeP (n = 93), NoP (n = 41), or mixed pain (n = 17). The mean age of study subjects was 58.5 years (age range: 26–90 years); 94 subjects (62.3%) were female. The mixed pain group was only analysed qualitatively, with validation based on the remaining 134 patients. Mean PD-Q scores for patients diagnosed with NeP and NoP were 19.9 [standard deviation (SD) = 6.4] and 12.5 (SD = 6.2) respectively. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted for the upper/lower boundaries. The upper boundary was calculated on the basis of a neuropathic diagnosis and a nociceptive diagnosis. The cut-off point was > 18 (80% sensitivity, 60% specificity), and area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.67 (P < 0.001). The lower boundary was calculated on the basis of a nociceptive and a neuropathic diagnosis. The cut-off point was < 13 (90% sensitivity, 50% specificity), and AUC was 0.79 (P < 0.001).
Conclusions:
The PD-Q is a reliable and valid scale to determine neuropathic components of chronic pain in the Hong Kong Chinese population. Validation in a larger Chinese-speaking population worldwide is necessary.
Aim:
The aim of this study was to validate a Chinese version of the painDETECT questionnaire (PD-Q) for the screening and assessment of neuropathic pain (NeP) in a Hong Kong Chinese population.
Methods:
The PD-Q was translated and cross-culturally adapted from the original German PD-Q, with forward and backward translation according to standard guidelines followed by cognitive debriefing, and finalized by an expert panel. A multicenter (6-site) observational study was conducted to evaluate the validity of the PD-Q. Patients aged 18 or above with medical conditions giving rise to either neuropathic or nociceptive pain (NoP) provided informed consent to participate in this study. Each patient was evaluated by at least two healthcare professionals for causes of pain, the visual analogue scale (VAS), numeric rating scale (NRS) and the PD-Q.
Results:
Hong Kong Chinese adults (n = 151) were given the clinical description of NeP (n = 93), NoP (n = 41), or mixed pain (n = 17). The mean age of study subjects was 58.5 years (age range: 26–90 years); 94 subjects (62.3%) were female. The mixed pain group was only analysed qualitatively, with validation based on the remaining 134 patients. Mean PD-Q scores for patients diagnosed with NeP and NoP were 19.9 [standard deviation (SD) = 6.4] and 12.5 (SD = 6.2) respectively. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted for the upper/lower boundaries. The upper boundary was calculated on the basis of a neuropathic diagnosis and a nociceptive diagnosis. The cut-off point was > 18 (80% sensitivity, 60% specificity), and area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.67 (P < 0.001). The lower boundary was calculated on the basis of a nociceptive and a neuropathic diagnosis. The cut-off point was < 13 (90% sensitivity, 50% specificity), and AUC was 0.79 (P < 0.001).
Conclusions:
The PD-Q is a reliable and valid scale to determine neuropathic components of chronic pain in the Hong Kong Chinese population. Validation in a larger Chinese-speaking population worldwide is necessary.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2024.00046
This article belongs to the special issue Neuropathic Pain

Aim:
From the start of the pandemic, several aspects of healthcare policies changed, not least the clinical trials management from recruiting capabilities to the protocol compliance in terms of schedule of procedures, follow-up
Methods:
Data from February to July of the years 2019, 2020 and 2021 were collected and three practical parameters of the trial unit were investigated: milestones, performance, and impact.
Results:
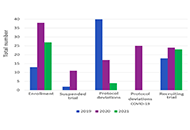
The trials mean numbers were 18, 24, and 23, in 2019, 2020, and 2021 respectively. The pre-Site Initiation
Conclusions:
The growing number of remote Site Initiation
Aim:
From the start of the pandemic, several aspects of healthcare policies changed, not least the clinical trials management from recruiting capabilities to the protocol compliance in terms of schedule of procedures, follow-up
Methods:
Data from February to July of the years 2019, 2020 and 2021 were collected and three practical parameters of the trial unit were investigated: milestones, performance, and impact.
Results:
The trials mean numbers were 18, 24, and 23, in 2019, 2020, and 2021 respectively. The pre-Site Initiation
Conclusions:
The growing number of remote Site Initiation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00168
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer

Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
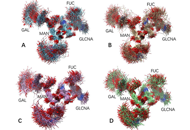
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
Aim:
Fragment crystallizable (Fc) glycans modulate
Methods:
Molecular dynamics simulations were used to generate conformation ensembles of free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-human Fc-gamma-receptor-I (hFcγRI) and antibody-antigen-hFcγRI, the hydrogen bonds and radial distance distribution involving N-glycans carbohydrate chains have been analyzed.
Results:
Two important interaction patterns have been observed. The first is the strong but non-specific interactions between two carbohydrate chains in free antibody. Secondly, it has been found that N-glycans carbohydrate chains can directly interact with CH3 domain in free antibody, and that the distance distribution between carbohydrate chains and CH3 domain clearly differentiate the free antibody, antibody-antigen complex, antibody-hFcγRI complex, and final antibody-antigen-hFcγRI complex.
Conclusions:
N-glycans partially acts as allosteric sensor and respond to antigen and hFcγRI binding.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2021.00004

Aim:
The unfermented pale-yellow exudates (“palm sap”) emerge from tapped unopened spathe of mostly oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) and raphia palm (Raphia hookeri). Besides, tiger nut milk (Kunuaya) is among the non-alcoholic refreshing drinks with dairy appearance. A sustainable alternative could therefore emerge from blends of tiger nut milk and sugar syrup to serve a resembling role as palm wine. In this context, therefore, palm wine analogue from different tiger nut milk and sugar syrup blends using palm wine dreg as inoculum was evaluated by proximate, physicochemical, microbial, and sensorial analyses at different time intervals.
Methods:
The materials were processed, analyzed, and packed using standard referenced procedures. This required freshly tapped palm sap juxtaposed with blends of tiger nut milk-sugar syrup beverage, and thereafter subjected to aerobic fermentation. Importantly, the tiger nut milk-sugar syrup medium has been pitched with palm wine dreg (inoculum source) between fermentation time 26–30 h, and temperature 29.8°–32°C.
Results:
Considering all the analytical outcomes, from proximate, microbiological, physicochemical, to sensory data, the control appeared to somewhat resemble those of the experimental samples of this study.
Conclusions:
Potentially, the (palm wine) analogue produced from tiger nut milk and sugar syrup blends using (palm wine) dreg as inoculum could be embraced by the market as natural palm wine. Indeed, the emergent product should serve as an alternative sustainable promise for palm wine, which could help fill the market supply gap, especially in the seasons of reduced supply/yield.
Aim:
The unfermented pale-yellow exudates (“palm sap”) emerge from tapped unopened spathe of mostly oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) and raphia palm (Raphia hookeri). Besides, tiger nut milk (Kunuaya) is among the non-alcoholic refreshing drinks with dairy appearance. A sustainable alternative could therefore emerge from blends of tiger nut milk and sugar syrup to serve a resembling role as palm wine. In this context, therefore, palm wine analogue from different tiger nut milk and sugar syrup blends using palm wine dreg as inoculum was evaluated by proximate, physicochemical, microbial, and sensorial analyses at different time intervals.
Methods:
The materials were processed, analyzed, and packed using standard referenced procedures. This required freshly tapped palm sap juxtaposed with blends of tiger nut milk-sugar syrup beverage, and thereafter subjected to aerobic fermentation. Importantly, the tiger nut milk-sugar syrup medium has been pitched with palm wine dreg (inoculum source) between fermentation time 26–30 h, and temperature 29.8°–32°C.
Results:
Considering all the analytical outcomes, from proximate, microbiological, physicochemical, to sensory data, the control appeared to somewhat resemble those of the experimental samples of this study.
Conclusions:
Potentially, the (palm wine) analogue produced from tiger nut milk and sugar syrup blends using (palm wine) dreg as inoculum could be embraced by the market as natural palm wine. Indeed, the emergent product should serve as an alternative sustainable promise for palm wine, which could help fill the market supply gap, especially in the seasons of reduced supply/yield.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101069
This article belongs to the special issue Food Authenticity and Emerging Challenges of Novel Food

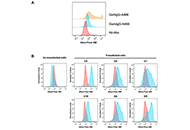
Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM is also the largest antibody structure among the five major human isotypes. Spontaneously formed pentamers and hexamers of IgM have avidity effects that could compensate for weaker interactions in monomeric Igs. However, this advantage is counterbalanced by potential steric clashes when binding to multiple large antigens. Recent findings have challenged the expected canonical independence of
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
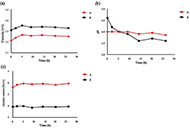
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
Aim:
As the primary response antibody with increasing use as a therapeutic immunoglobulin (Ig) format, IgM is also the largest antibody structure among the five major human isotypes. Spontaneously formed pentamers and hexamers of IgM have avidity effects that could compensate for weaker interactions in monomeric Igs. However, this advantage is counterbalanced by potential steric clashes when binding to multiple large antigens. Recent findings have challenged the expected canonical independence of
Methods:
Through a panel of 14 recombinant complementarity determining regions (CDRs)-grafted trastuzumab and pertuzumab VH1-7 IgMs subjected to bio-layer interferometry measurements, the interactions with the antigen human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), Fc-mu receptor (FcμR), and superantigen Protein L (PpL) were investigated.
Results:
Significant effects from the V-regions to mitigate FcμR binding and the IgM C-region bidirectional effect modulating Her2 antigen engagements at the V-regions were found. Additional modulatory effects from superantigen PpL binding on the V-region of the kappa chain (Vκ) mitigating antigen binding were also found, revealing possible novel mechanisms of antibody superantigens that can be moderated by the antibody VH frameworks.
Conclusions:
These findings show that the oligomerisation of IgMs plays a significant role in FcμR, antigen, and superantigen binding that made IgM distinct from the other antibody isotypes and how these features should be considered during further development and protein engineering of IgM therapeutics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2022.00083

Aim:
Amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) is a transitional stage toward Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For late-onset AD (95% of cases), aging is the main risk factor. Systematizing the transcriptome of hippocampal neurons under the native conditions of this disease is essential, as this information is scarce and the hippocampus is a highly vulnerable cerebral region.
Methods:
Public microarray data corresponding to homogenates of human hippocampus of Healthy-Younger, Healthy-Elder, and Elder-with-MCI individuals were re-analyzed herein. Through an optimized computational pipeline, those genes having splice forms and that belong to the neuronal type were identified. The differential genes arising from each group were then characterized by contrasting ontologies (functions, cellular components, and pathways). Additionally, the data were re-arranged factorially to determine the first- and second-order sex interactions.
Results:
Around 76% of the relevant changes actually occurred during the healthy-aging process, being further balanced or not during MCI. “Cognition”, “behavior”, “glutamatergic synaptic transmission”, “lipid rafts”, and “catecholamines” decreased across the three groups analyzed, whereas “associative/visual learning”, “gliogenesis”, “neuro-inflammation”, “corticosteroids”, “p75NTR”, “ER-stress” and “autophagy” peaked in Elders. On the contrary, “Learning/memory”, “GAP junctions”, “GABAergic transmission”, and “GNDF” showed a minimum in Elders. The “transcriptional regulators” (MeCP2, NPAS4, DREAM), “BNDF/NGFR”, “Ca2+ transport”, “CRHR1” and “CXCL12” were minimal in MCI. From Elder to MCI, “MAPKs”, “MEF2C”, “RGS7”, “CCKBR1”, “ErbB4”, “ERK5”, and “Ca2+-Na+-K+ channels” (RYR2, SCNA1/A8, KCNQ2/Q3, KCNN3, KCNIP2) appeared downregulated. “Long-term synaptic depression” (LTD) increased sharply in the MCI. Most of the findings detected were contrasted against 250 reports.
Conclusions:
The multiple alterations in the basic mechanisms—mainly in the CA3 dendrites of mossy fibers could be compatible with neuronal hyper-excitability, diminished synaptic transmission, and changes in the theta/gamma/SWR rhythms. Many functionalities appeared conditioned by sex-interactions. Particularly, women showed “pure” sex-effects and interactions with “cross-over” effects. Due to its consequences on the higher-order functions, all these predictions should be confirmed experimentally.
Aim:
Amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) is a transitional stage toward Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For late-onset AD (95% of cases), aging is the main risk factor. Systematizing the transcriptome of hippocampal neurons under the native conditions of this disease is essential, as this information is scarce and the hippocampus is a highly vulnerable cerebral region.
Methods:
Public microarray data corresponding to homogenates of human hippocampus of Healthy-Younger, Healthy-Elder, and Elder-with-MCI individuals were re-analyzed herein. Through an optimized computational pipeline, those genes having splice forms and that belong to the neuronal type were identified. The differential genes arising from each group were then characterized by contrasting ontologies (functions, cellular components, and pathways). Additionally, the data were re-arranged factorially to determine the first- and second-order sex interactions.
Results:
Around 76% of the relevant changes actually occurred during the healthy-aging process, being further balanced or not during MCI. “Cognition”, “behavior”, “glutamatergic synaptic transmission”, “lipid rafts”, and “catecholamines” decreased across the three groups analyzed, whereas “associative/visual learning”, “gliogenesis”, “neuro-inflammation”, “corticosteroids”, “p75NTR”, “ER-stress” and “autophagy” peaked in Elders. On the contrary, “Learning/memory”, “GAP junctions”, “GABAergic transmission”, and “GNDF” showed a minimum in Elders. The “transcriptional regulators” (MeCP2, NPAS4, DREAM), “BNDF/NGFR”, “Ca2+ transport”, “CRHR1” and “CXCL12” were minimal in MCI. From Elder to MCI, “MAPKs”, “MEF2C”, “RGS7”, “CCKBR1”, “ErbB4”, “ERK5”, and “Ca2+-Na+-K+ channels” (RYR2, SCNA1/A8, KCNQ2/Q3, KCNN3, KCNIP2) appeared downregulated. “Long-term synaptic depression” (LTD) increased sharply in the MCI. Most of the findings detected were contrasted against 250 reports.
Conclusions:
The multiple alterations in the basic mechanisms—mainly in the CA3 dendrites of mossy fibers could be compatible with neuronal hyper-excitability, diminished synaptic transmission, and changes in the theta/gamma/SWR rhythms. Many functionalities appeared conditioned by sex-interactions. Particularly, women showed “pure” sex-effects and interactions with “cross-over” effects. Due to its consequences on the higher-order functions, all these predictions should be confirmed experimentally.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001299
This article belongs to the special issue Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia

Aim:
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
Aim:
The present study aims to generate chimeric mouse single-chain variable fragment (scFv) and immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) crystallizable fragment (Fc) antibody against disialoganglioside (GD2) for the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB). The generated scFv-IgG
Methods:
Vector for scFv-IgG
Results:
Using plasmid fusion-human IgG1-Fc2 tag vector (pFUSE-hIgG1-Fc2), a plasmid vector encoding chimeric mouse scFv and hIgG1
Conclusions:
The results indicate that chimeric scFv-hIgG
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00188
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Strategies and Targets for Immunotherapy of Cancer

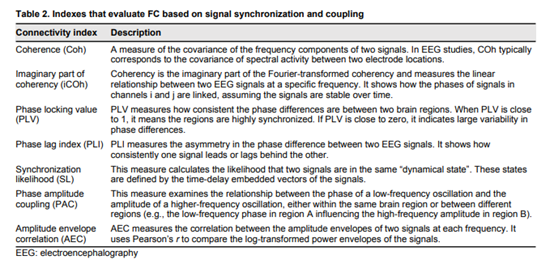
Age-related changes in the brain cause cognitive decline and dementia. In recent year’s researchers’ extensively studied the relationship between age related changes in functional connectivity (FC) in dementia. Those studies explore the alterations in
Age-related changes in the brain cause cognitive decline and dementia. In recent year’s researchers’ extensively studied the relationship between age related changes in functional connectivity (FC) in dementia. Those studies explore the alterations in
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00256
This article belongs to the special issue Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Aging and Dementia

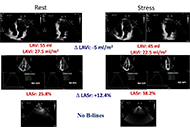
Aim:
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
Aim:
Left atrial volume index (LAVI), left atrial reservoir function through left atrial reservoir strain (LASr), and B-lines in lung ultrasound serve as supplementary indicators of left ventricular filling pressures. This study analyzes the interrelation between LAVI, LASr, and B-lines in both resting and peak vasodilator stress.
Methods:
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography (SE) was conducted on 252 individuals (180 males, 71%, age 65 years ± 10 years) with chronic coronary syndromes. LAVI was quantified using the biplane disk summation method; LASr was obtained using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography; B-lines were evaluated through a simplified 4-site scan in the third intercostal space during lung ultrasound.
Results:
During SE, a reduction in LAVI (
Conclusions:
Vasodilator SE with combined left atrial and volume assessment, related to pulmonary congestion, is feasible with a high success rate. Pulmonary congestion is more frequent with dilated left atrium with reduced atrial contractile reserve (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT030.49995; NCT050.81115).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2024.00018

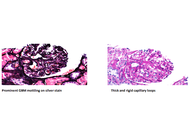
Patients who have lupus nephritis are usually asymptomatic. A few lupus nephritis patients may experience edema, hypertension, nocturia, polyuria, and foamy urine. Foamy urine or nocturia are early indicators of proteinuria, indicating tubular or glomerular dysfunction. Membranous-like glomerulopathy with masked IgG kappa deposits (MMMD) represents a form of immune complex deposition marked by concealed IgG kappa-restricted deposits, which are located in the subepithelial and mesangial areas as seen on electron microscopy. We report a rare case of a 26-year-old Hispanic woman with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) diagnosed in 2015, who was initially evaluated for proteinuria and underwent a renal biopsy in 2019. The biopsy demonstrated membranous glomerulonephritis consistent with class V lupus nephritis. The patient volunteered to participate in a clinical trial for lupus nephritis in mid-2023. The second renal biopsy done at this
Patients who have lupus nephritis are usually asymptomatic. A few lupus nephritis patients may experience edema, hypertension, nocturia, polyuria, and foamy urine. Foamy urine or nocturia are early indicators of proteinuria, indicating tubular or glomerular dysfunction. Membranous-like glomerulopathy with masked IgG kappa deposits (MMMD) represents a form of immune complex deposition marked by concealed IgG kappa-restricted deposits, which are located in the subepithelial and mesangial areas as seen on electron microscopy. We report a rare case of a 26-year-old Hispanic woman with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) diagnosed in 2015, who was initially evaluated for proteinuria and underwent a renal biopsy in 2019. The biopsy demonstrated membranous glomerulonephritis consistent with class V lupus nephritis. The patient volunteered to participate in a clinical trial for lupus nephritis in mid-2023. The second renal biopsy done at this
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001353

Aim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses the effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the sensory, physical, nutritional, and antioxidant properties and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuits.
Methods:
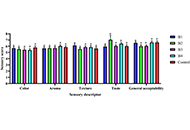
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3.
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
Aim:
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes has heightened the demand for low glycemic index food products, leading to the exploration of alternative baking ingredients. This study assesses the effects of bran-enriched flour blends on the sensory, physical, nutritional, and antioxidant properties and glycemic control of high-fiber biscuits.
Methods:
Wheat, corn, sorghum, and sweet potato were obtained from the market. Linear programming (LP) optimized fiber content to create four high-fiber flour blends assessed for functional properties [water absorption capacity (WAC), oil absorption capacity (OAC), foaming capacity (FC), and stability]. Four high-fiber biscuits were developed and evaluated for nutritional composition (ash, crude fibers, water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, Zn, Fe, Mg, Na, Ca, and P), sensory attributes (color, aroma, texture, and taste), physical properties (thickness, diameter, weight, spread ratio, browning index; L, a, and b), antioxidant properties (DPPH and FRAP activities), glycemic response, and in vitro glucose-binding capacity.
Results:
The formulated flours exhibited water and oil absorption capacities ranging from 1.95% to 2.70%, with the highest oil absorption in formulated flour 3.
Conclusions:
Incorporating diverse bran and flour types improves biscuit quality, particularly in blends like F2 (wheat flour, corn bran, and sorghum bran) and F3 (wheat flour, corn bran, sweet potato flour, and sorghum bran), offering beneficial options for diabetics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101076
This article belongs to the special issue The food (r)evolution towards food quality/security and human nutrition

Aim:
The social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, has emerged as a significant hub for healthcare-related conversations and sharing information. This study aims to investigate the impact and reach of the #physiotherapy hashtag on the X platform.
Methods:
We collected and analyzed tweets containing the hashtag #physiotherapy posted between September 1, 2022, and September 1, 2023. Data was retrieved from X using the Fedica analytics platform on October 26, 2023. The data were analyzed and expressed in number and percentage and categorical data were tested by chi-square test.
Results:
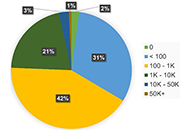
Over the course of one year, a total of 57,788 tweets were shared using #physiotherapy by 21,244 users, generating a remarkable 108,743,911 impressions. On average, there were 6 tweets posted per day (with a range from 3 to 9). Among the users, the majority (42%) had between 100 and 1000 followers, while 31.6% had fewer than 100 followers. The top three countries contributing to #physiotherapy tweets were the UK (29.9%), India (23.75%), and the USA (11.85%). An analysis of sentiment revealed that 84% of the tweets had a neutral tone, while 9% were positive and 7% were negative (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
The examination of tweets related to #physiotherapy unveiled a vibrant global dialogue, with active engagement from diverse backgrounds. Notably, contributions from the UK, India, and the USA were prominent.
Aim:
The social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, has emerged as a significant hub for healthcare-related conversations and sharing information. This study aims to investigate the impact and reach of the #physiotherapy hashtag on the X platform.
Methods:
We collected and analyzed tweets containing the hashtag #physiotherapy posted between September 1, 2022, and September 1, 2023. Data was retrieved from X using the Fedica analytics platform on October 26, 2023. The data were analyzed and expressed in number and percentage and categorical data were tested by chi-square test.
Results:
Over the course of one year, a total of 57,788 tweets were shared using #physiotherapy by 21,244 users, generating a remarkable 108,743,911 impressions. On average, there were 6 tweets posted per day (with a range from 3 to 9). Among the users, the majority (42%) had between 100 and 1000 followers, while 31.6% had fewer than 100 followers. The top three countries contributing to #physiotherapy tweets were the UK (29.9%), India (23.75%), and the USA (11.85%). An analysis of sentiment revealed that 84% of the tweets had a neutral tone, while 9% were positive and 7% were negative (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions:
The examination of tweets related to #physiotherapy unveiled a vibrant global dialogue, with active engagement from diverse backgrounds. Notably, contributions from the UK, India, and the USA were prominent.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/edht.2024.00016
This article belongs to the special issue Social Media Applications in Biomedical Research

Aim:
BRCA1/2-associated breast and ovarian carcinomas are often regarded as a single entity, assuming that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are almost equivalent with regard to their clinical significance. However, BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes differ in their function; therefore, a comparison of treatment outcomes in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 carriers is warranted.
Methods:
This study focused on consecutive patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), given that these subjects are treatment-naive and accessible for immediate assessment of pathological and clinical outcomes.
Results:
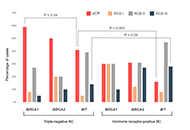
BRCA2-associated high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas (HGSOCs) demonstrated significantly higher rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) as compared to BRCA1-related cancers [8/15 (53%) vs. 7/48 (15%), P = 0.004]. In contrast, HER2-negative breast cancer (BC) patients showed a numerically higher rate of pCR in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 mutation carriers [38/69 (55%) vs. 13/36 (36%), P = 0.1]. However, the comparison with BRCA-wild-type (WT) tumors revealed that this tendency was mainly attributed to the increased prevalence of hormone receptor (HR)-negative disease in the former group. When BC patients were stratified according to the tumor receptor status, the response rates in triple-negative patients were consistently higher than in HR+/HER2– patients across all analyzed subgroups [BRCA1: 35/59 (59%) vs. 3/10 (30%); BRCA2: 5/10 (50%) vs. 8/
Conclusions:
Hereditary ovarian carcinomas demonstrate better NACT outcomes in BRCA2 vs. BRCA1 mutation carriers. The opposite trend is observed in BC, which is likely to be attributed to a high frequency of triple-negative disease in BRCA1- but not BRCA2-associated BCs. Triple-negative receptor status rather than BRCA1/2 status is the strongest predictor of response to NACT in BC.
Aim:
BRCA1/2-associated breast and ovarian carcinomas are often regarded as a single entity, assuming that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are almost equivalent with regard to their clinical significance. However, BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes differ in their function; therefore, a comparison of treatment outcomes in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 carriers is warranted.
Methods:
This study focused on consecutive patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), given that these subjects are treatment-naive and accessible for immediate assessment of pathological and clinical outcomes.
Results:
BRCA2-associated high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas (HGSOCs) demonstrated significantly higher rates of pathologic complete response (pCR) as compared to BRCA1-related cancers [8/15 (53%) vs. 7/48 (15%), P = 0.004]. In contrast, HER2-negative breast cancer (BC) patients showed a numerically higher rate of pCR in BRCA1 vs. BRCA2 mutation carriers [38/69 (55%) vs. 13/36 (36%), P = 0.1]. However, the comparison with BRCA-wild-type (WT) tumors revealed that this tendency was mainly attributed to the increased prevalence of hormone receptor (HR)-negative disease in the former group. When BC patients were stratified according to the tumor receptor status, the response rates in triple-negative patients were consistently higher than in HR+/HER2– patients across all analyzed subgroups [BRCA1: 35/59 (59%) vs. 3/10 (30%); BRCA2: 5/10 (50%) vs. 8/
Conclusions:
Hereditary ovarian carcinomas demonstrate better NACT outcomes in BRCA2 vs. BRCA1 mutation carriers. The opposite trend is observed in BC, which is likely to be attributed to a high frequency of triple-negative disease in BRCA1- but not BRCA2-associated BCs. Triple-negative receptor status rather than BRCA1/2 status is the strongest predictor of response to NACT in BC.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002325

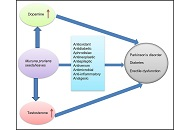
Among the most common medical problems experienced by older adults (over 60 years) are diabetes, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and erectile dysfunction (ED). The potential use of Mucu
Among the most common medical problems experienced by older adults (over 60 years) are diabetes, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and erectile dysfunction (ED). The potential use of Mucu
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2025.101083
This article belongs to the special issue Natural Products in Health and Disease

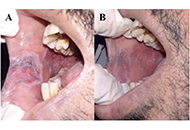
Aim:
The present study was designed to assess the effectiveness of topical application of sulfasalazine in combination with topically applied corticosteroids versus using topical steroids alone as the standard control in management of symptomatic oral lichen planus (OLP).
Methods:
The trial involved 46 participants having symptomatic OLP. Subjects included were divided into two equal groups at random. Group C (control group), in this group patients were treated with topically applied corticosteroids only as the standard treatment of OLP. In Group T (test group) topical sulfasalazine was used in combination with topical corticosteroids in management of the OLP cases. The patients used the topical applications four times per day in an alternate sequence (in Group T). The treatment schedule was continuous for 4 weeks with one
Results:
The results of all patients reported no unwanted reactions or complications using both treatment strategies. Both study groups reported a significant decrease in the pain scale and sign score recordings over time as shown within the intragroup findings. Group T experienced a significantly higher reduction in pain scale (starting at two weeks) and sign score results (starting at three weeks) as compared to Group C.
Conclusions:
Based on the data presented in this study, combination of topical sulfasalazine with topical corticosteroids is an efficient treatment in management of OLP in terms of decreasing pain scale and sign score values (Clinical Trials.gov with registration number NCT06060301).
Aim:
The present study was designed to assess the effectiveness of topical application of sulfasalazine in combination with topically applied corticosteroids versus using topical steroids alone as the standard control in management of symptomatic oral lichen planus (OLP).
Methods:
The trial involved 46 participants having symptomatic OLP. Subjects included were divided into two equal groups at random. Group C (control group), in this group patients were treated with topically applied corticosteroids only as the standard treatment of OLP. In Group T (test group) topical sulfasalazine was used in combination with topical corticosteroids in management of the OLP cases. The patients used the topical applications four times per day in an alternate sequence (in Group T). The treatment schedule was continuous for 4 weeks with one
Results:
The results of all patients reported no unwanted reactions or complications using both treatment strategies. Both study groups reported a significant decrease in the pain scale and sign score recordings over time as shown within the intragroup findings. Group T experienced a significantly higher reduction in pain scale (starting at two weeks) and sign score results (starting at three weeks) as compared to Group C.
Conclusions:
Based on the data presented in this study, combination of topical sulfasalazine with topical corticosteroids is an efficient treatment in management of OLP in terms of decreasing pain scale and sign score values (Clinical Trials.gov with registration number NCT06060301).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001283

Aim:
Changes in strategies in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) crisis and the imposing of restrictions have isolated many vulnerable patients including those with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from routine medical care. This study investigated how the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Methods:
An extensive search was conducted in the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases by using the appropriate keywords: COVID-19, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatocellular cancer, and MeSH. Studies in English related to the purpose of the study were included in the analysis, and review studies, case reports, letters to editors, comments, and reports were excluded. The quality of the studies was assessed by the “Adapted Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scales” checklist. The Endnote X7 software has been used for managing items.
Results:
The final qualitative analysis consisted of 27 articles. During the COVID-19 crisis, HCC diagnosis decreased from 20% to 34.13% compared to pre-crisis. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC treatment encompasses a wide range of aspects. Generally, delays in treatment for patients with HCC ranged from more than one month for 21.5% of patients in France, to two months for 26% of patients in Italy, up to 30% in Austria, and 66.7% in Asia-Pacific countries.
Conclusions:
According to the findings, developing and implementing appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies and developing low-cost and high-precision screening programs among high-risk populations seem to be effective in reducing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC management.
Aim:
Changes in strategies in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) crisis and the imposing of restrictions have isolated many vulnerable patients including those with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from routine medical care. This study investigated how the COVID-19 pandemic is affecting the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Methods:
An extensive search was conducted in the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases by using the appropriate keywords: COVID-19, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatocellular cancer, and MeSH. Studies in English related to the purpose of the study were included in the analysis, and review studies, case reports, letters to editors, comments, and reports were excluded. The quality of the studies was assessed by the “Adapted Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scales” checklist. The Endnote X7 software has been used for managing items.
Results:
The final qualitative analysis consisted of 27 articles. During the COVID-19 crisis, HCC diagnosis decreased from 20% to 34.13% compared to pre-crisis. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC treatment encompasses a wide range of aspects. Generally, delays in treatment for patients with HCC ranged from more than one month for 21.5% of patients in France, to two months for 26% of patients in Italy, up to 30% in Austria, and 66.7% in Asia-Pacific countries.
Conclusions:
According to the findings, developing and implementing appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies and developing low-cost and high-precision screening programs among high-risk populations seem to be effective in reducing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HCC management.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2023.00179
This article belongs to the special issue COVID-19 and Cancer

Aim:
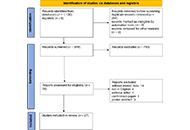
This study aims to investigate the impact of asthma on quality of life, explore its associations with anxiety and depression, and identify the key determining factors.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted in the pulmonology department of Hassan II University Hospital in Fez in 2021. Data were collected using an anonymous questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and therapeutic information. The Moroccan versions of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and the Short-Form-12 (SF-12) scale were used to assess anxiety, depression, and quality of life. Descriptive analysis was performed, followed by univariate analysis to examine the associations between quality of life, anxiety, depression, and other factors, using statistical tests appropriate for the types of variables studied. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data entry was performed using Excel 2013, and statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26.
Results:
Among the 67 patients included (77.6% women, 61.2% aged ≥ 50 years), wheezing (44.8%) and dyspnoea (26.9%) were the most frequent symptoms. Depression was significantly associated with pain (p = 0.020), and frequent hospitalizations (p = 0.021), while anxiety was more common among women (p = 0.034). For quality of life, patients with depression had lower physical component summary (PCS) scores (p = 0.008). Patients over 50 years old had significantly lower PCS and mental component summary (MCS) scores (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). Illiterate patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.022), hypertensive patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.032), and a nearly significant difference for the MCS (p = 0.053). Diabetic patients had lower MCS scores (p = 0.034). Finally, a positive correlation was observed between respiratory function forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and both PCS scores (p = 0.025) and MCS scores (p = 0.018).
Conclusions:
This study underscores the importance of an integrated approach to enhancing the quality of life of asthmatic patients, taking into account respiratory, psychological, and social factors.
Aim:
This study aims to investigate the impact of asthma on quality of life, explore its associations with anxiety and depression, and identify the key determining factors.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted in the pulmonology department of Hassan II University Hospital in Fez in 2021. Data were collected using an anonymous questionnaire that included sociodemographic, clinical, and therapeutic information. The Moroccan versions of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and the Short-Form-12 (SF-12) scale were used to assess anxiety, depression, and quality of life. Descriptive analysis was performed, followed by univariate analysis to examine the associations between quality of life, anxiety, depression, and other factors, using statistical tests appropriate for the types of variables studied. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data entry was performed using Excel 2013, and statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26.
Results:
Among the 67 patients included (77.6% women, 61.2% aged ≥ 50 years), wheezing (44.8%) and dyspnoea (26.9%) were the most frequent symptoms. Depression was significantly associated with pain (p = 0.020), and frequent hospitalizations (p = 0.021), while anxiety was more common among women (p = 0.034). For quality of life, patients with depression had lower physical component summary (PCS) scores (p = 0.008). Patients over 50 years old had significantly lower PCS and mental component summary (MCS) scores (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). Illiterate patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.022), hypertensive patients had lower PCS scores (p = 0.032), and a nearly significant difference for the MCS (p = 0.053). Diabetic patients had lower MCS scores (p = 0.034). Finally, a positive correlation was observed between respiratory function forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and both PCS scores (p = 0.025) and MCS scores (p = 0.018).
Conclusions:
This study underscores the importance of an integrated approach to enhancing the quality of life of asthmatic patients, taking into account respiratory, psychological, and social factors.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2025.100976
This article belongs to the special issue Asthma and its Relationship with Psychological and Psychopathological Factors
 Previous
Previous