The escalating prevalence of diabetes poses a significant health concern. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to a multitude of complications. A comprehensive management plan and continual adaptation of guidelines is needed. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) is a guiding force in this domain, providing diabetes care recommendations for clinicians, laboratorians, researchers, and policymakers since 1989. The latest ADA guidelines present both challenges and opportunities for laboratories. The increased emphasis on glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) testing for early diagnosis and personalized monitoring is expected to increase testing volumes, potentially leading to a rise in point-of-care testing. Ensuring standardized testing procedures becomes paramount to maintaining consistent and reliable results across laboratories. Moreover, laboratories may need to expand their test menus to accommodate the growing demand for personalized medicine approaches and collaborate closely with healthcare providers to support informed decision-making. This commentary provides a focused analysis of the 2024 ADA guidelines for the laboratory assessment of diabetes.
Read less.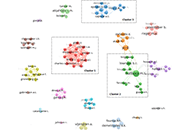
Surgeons are exposed to a high prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). The scientific issues surrounding this problem are generating a growing body of work. The aim of this study is to obtain quantitative and visual information from articles about WMSDs and surgeons through bibliometric analysis. The keywords “surgeon” and “work-related musculoskeletal disorders” were searched in the PubMed/Medline database until March 2024. Data extraction and visualization were performed using VOSviewer version 1.6.20. and Microsoft Excel on the overall distribution of publications by year, sources, articles, authors and keywords. A total of 173 English-language publications were extracted between 1982 and 2024. The number of publications has increased over the years. A significant increase was observed from 2016. America is the leader with 82/173 publications (47.4%) and 3,276 citations. Work [impact factor (IF): 2.3] is the first top source which has 7 articles followed by Surgical Endoscopy (IF: 3.1) with 5 publications. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation (IF: 3.3) is the top journal with 681 citations for 2 publications. Hallbeck MS, Yu D, and Vijendern A are the most productive authors with 23 publications. The analysis showed that the United States and the UK are the two most productive countries (journals, authors, citations). The most frequently used keywords were “ergonomics”, “musculoskeletal disorders”, “work-related musculoskeletal disorders”, and “surgeons”. Bibliometric analysis has shown that the prevalence of WMSDs in surgeons is a topic showing significant growth, particularly since 2016, dominated by American researchers. A synthesis of the WMSD prevalence by body area has been made based on the most cited articles. This field has evolved considerably. From a rather subjective analysis of prevalence based on questionnaires, work has moved towards a more ergonomic assessment using objective evaluation tools.
Read less.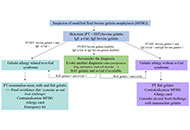
Gelatin is extracted from beef, pork, and fish tissues. An increasing number of cases of gelatin-induced anaphylaxis are associated with α-Gal syndrome (AGS). Only a few cases of anaphylaxis to bovine gelatin (BG) without AGS (BG-woAG) have been described. We report two new cases of anaphylaxis to BG-woAG, highlight the characteristics of this entity, and propose a procedure in cases of suspected anaphylaxis to BG. We selected articles on gelatin allergy between 1987 and 2024. Results: we report two new cases of severe anaphylaxis BG-woAG. Diagnosis was established using skin tests (ST), IgE, and basophil activation tests (BAT). We confirm the existence of allergies to BG-woAG. The main characteristic of these allergies seems to be the presence of BG IgE which differentiates them from AGS-related allergies. These initial data need to be confirmed by larger case series. We propose a diagnostic algorithm for better patient management. To confirm the diagnosis, ST and IgE to BG and α-Gal should be performed. The role of BAT to Gelofusine® in the diagnostic strategy remains to be defined.
Read less.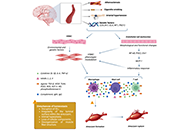
Intracranial artery dolichoectasia (IADE) is a vascular anomaly characterized by dilation and/or tortuosity of one or more intracranial arteries. While many cases are incidental findings on imaging, the associated ischemic neurological complications of IADE can be severe and must be promptly recognized. This study aims to increase awareness among general practitioners and neurologists regarding this rare and potentially life-threatening condition. We utilized reputable databases for this scoping review, including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, from database inception through September 2024, using a combination of terms such as “Dolichoectasia of Basilar Artery”, “Intracranial Dolichoectasia”, and “Ischemic Stroke”. Our scoping review revealed that IADE is a challenging and often underdiagnosed condition, with an estimated prevalence of less than 1% in the general population. Hypertension, atherosclerosis, and advanced age are well-documented risk factors. To minimize the risk of misdiagnosis, we briefly elucidated the pathophysiology of IADE, correlating it with clinical and radiological features. We discuss the diagnostic criteria for IADE based on radiological imaging, addressing the advantages and limitations of different techniques. Finally, we highlight the unmet clinical needs related to IADE management, which may involve pharmacological and surgical therapies tailored to individual cases, with careful consideration of safety and efficacy.
Read less.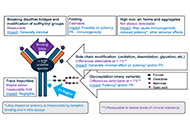
Routine regulatory requirements for large comparative efficacy trials (CETs) to support marketing approval of monoclonal antibody (mAb) biosimilars have been the focus of extensive debate in the last few years. This review examines the mounting evidence, accumulated over the past decade, focusing on relevant literature and data published in the European Product Assessment Reports (EPARs) for the fifteen anti-TNFα biosimilars approved to date. The potential for residual uncertainties that may require resolution through CETs following comparative physico-chemical, in-vitro potency, and single dose studies in healthy subjects is examined. It is noted that structural and physicochemical differences between biosimilars and reference products are detectable using modern analytical methods at levels well below those that could impact clinical outcomes, and that in vitro potency testing is fully capable of revealing clinically relevant differences. Additionally, comparative pharmacokinetic studies in healthy participants provide a sensitive assessment of potential differences in drug exposure and immunogenicity. The added value of CETs is further questioned in the light of the fact that anti-TNFα’s display a flat dose-response relationship, meaning that unlike cell-based assays, CETs have limited sensitivity to detect potency differences. Initial concerns about extrapolating data from rheumatoid arthritis studies to support marketing approval of other indications such as inflammatory bowel disease for which not all anti-TNFα’s are effective have been alleviated by post-approval studies. Additionally, as of the end of 2024, no cases where clinical efficacy data were necessary to resolve residual quality concerns have arisen following regulatory assessment of 56 mAb biosimilars and fusion proteins. CETs add significant cost and delay to the development of biosimilars and the time is now ripe to re-examine the need for these CET’s and for further evolution in regulatory thinking.
Read less.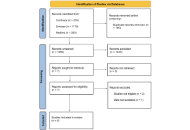
Background:
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematologic malignancy characterized by the clonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow, constituting approximately 13% of all hematologic malignancies. Isatuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the CD38 protein on myeloma cells, causing cell death through various immune-mediated mechanisms. Clinical trials have shown that adding isatuximab to standard regimens for MM significantly enhances efficacy but introduces some notable toxicities. The purpose of this study is to determine the risk of pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), and venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with MM treated with isatuximab.
Methods:
We conducted a comprehensive literature search using Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases from inception through July 22nd, 2024. Phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing isatuximab in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) reporting pneumonia, URTIs, and VTE as adverse events were included. Mantel-Haenszel (MH) method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-statistic. Random effects model was applied.
Results:
A total of 1,044 patients from three phase III RCTs (ICARIA-MM, IKEMA, IMROZ) were included for pneumonia and URTI analysis, while 1,403 patients from three trials (IKEMA, IMROZ, GMMG-HD7) were included for VTE evaluation. The incidence of any-grade pneumonia was higher in the isatuximab group (30.1% vs. 23.2%; RR, 1.31; 95% CI 1.06–1.61; P = 0.01), as was high-grade pneumonia (20.8% vs. 15.3%; RR, 1.38; 95% CI 1.06–1.81; P = 0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed between the isatuximab and control groups for any-grade URTIs, high-grade URTIs, or VTE.
Discussion:
This meta-analysis highlights a significant increase in the incidence of pneumonia with the addition of isatuximab to standard myeloma regimens, underscoring the need for routine antibiotic prophylaxis, thromboprophylaxis, vigilant monitoring and early intervention to mitigate these risks.
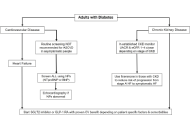
Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for both cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease (CKD) while CKD is also associated with cardiovascular morbidity. In fact, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mainly from heart failure or myocardial infarction. The newer therapeutic agents in diabetes have positive impact on both cardiovascular and renal outcomes. Thus, the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s annual update on the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes is an important resource for all caregivers involved in diabetes management as it incorporates the latest scientific research, clinical evidence, and emerging technologies in diabetes management. The 2025 guidelines present significant updates that reflect a deeper understanding of diabetes management, emphasizing expanded usage of technologies such as continuous glucose monitoring, personalized pharmacological approaches, and lifestyle interventions. This commentary provides an analysis of the key updates in the 2025 ADA guidelines exploring implications for clinical practice, laboratory assessments, and public health policy. Where relevant, comparisons to the 2024 version will be made.
Read less.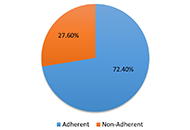
Aim:
Hypertension, a prevalent chronic condition, significantly contributes to cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Effective management of hypertension is highly dependent on patient adherence to prescribed medications, as the correct dose at the right time can lead to desirable therapeutic results. This study aims to analyze medication adherence among hypertensive patients in Islamabad and Rawalpindi through an open survey.
Methods:
A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted from 17th March 2024 to 30th May 2024, targeting hypertensive populations in Islamabad and Rawalpindi. 246 patients were recruited using a sample size formula, and a General Medication Adherence Scale (GMAS) questionnaire was used to collect data. All the tests were conducted as two-sided, with a significance level of P < 0.05 using Python.
Results:
Among 246 participants (mean age 57.1 years), most were married, literate, and living with families, 63% were from Islamabad, and 78.9% were employed. The study found high adherence in behavior-related areas but low adherence due to costs. Gender showed a statistically significant correlation (P = 0.03) by independent t-test. At the same time, ANOVA tests revealed that educational level (P = 0.02), monthly income (P = 0.001), family support (P = 0.04), and medication costs (P = 0.001) significantly impacted adherence, while factors like social status, employment status, and smoking did not have a considerable influence.
Conclusions:
72.4% of patients adhered to their prescribed therapy, and 27.6% did not highlight a critical issue that requires urgent intervention. Variables like gender, educational status, social status, occupation, and living with family are strongly associated with adherence. Common problems include taking multiple medications, lack of awareness about the importance of adherence, and financial constraints.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is characterized by its infiltrative growth pattern and high recurrence rate despite treatment. While local progression within the central nervous system (CNS) is the rule, manifestations outside the CNS, particularly skin and subcutaneous metastases, are very infrequent and seldom reported in the literature. The authors reviewed the current understanding of this rare condition, with the main purpose of giving visibility to its clinical presentation and prognostic implications, thus improving clinical management and encouraging research in this area. A PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE search from database inception through March 2024 was conducted. In this way, we compiled a total of thirty-five cases in our review. As far as we know, our work gathers the largest number of patients with this condition. Remarkably, we observed that the typical presentation of soft-tissue high-grade glioma metastases is the finding of subcutaneous erythematous nodules in patients previously operated on for a primary CNS tumor, within the craniotomy site and nearby, mostly in the first year after the initial surgery. It was also noted that there is a trend of developing a concomitant CNS recurrence and/or other metastases in different locations, either simultaneously or subsequently. From here, we propose some possible mechanisms that explain the extracranial spread of GBM. We concluded that a poor outcome is expected from the diagnosis of skin and subcutaneous metastases: the mean overall survival was 4.38 months. Yet, assessing individual characteristics is always mandatory; a palliative approach seems to be the best option for the majority of cases.
Read less.
Measles virus (Morbillivirus abbreviated as MV, but more recently MeV) is the causal agent of measles disease, thought to have existed at least 4,000 years ago, affecting predominantly infants, but also immunocompromised individuals remaining a public health issue today globally. In this review, we discuss the historical background about MeV infection to modern-day research on measles disease, current epidemiology, but also what is known about immunisation against it. We report what is known about the viral structure and the function of the viral proteins. This additionally covers the cellular structure of MeV, mechanisms, and clinical aspects of infection. Including a review of topics like cellular receptor-associated entry factors, to the immunology of MeV infection. In this review, the current knowledge of innate immune responses during infection is explained, which involves changes to chemokine and cytokine expression, finalised by the present understanding of adaptive immune responses to MeV. The genomic stability of the MeV proteins is explained and suggestive that it could be the third pathogen with eradication potential (after the variola and rinderpest viruses). Further biological and immunological clarification as to how this could occur is explained below.
Read less.
Sterigmatocystin (STE) is a possible human carcinogenic compound (2B) according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer classification. Structurally, STE is a precursor to aflatoxins, sharing a similar polyketide-derived biosynthetic pathway, which underscores its toxicological relevance. It has been reported to occur in a variety of foodstuffs including cereals and cereal-based products, spices, cheese, and nuts, among others. STE poses a substantial challenge to food safety and addressing this issue requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing prevention, monitoring, and regulation to protect both human and animal health from its harmful effects. The present paper presents the analytical methodologies for the determination of STE in foodstuffs and the reported levels of STE in food, based on a review of scientific publications from 2021 to 2024. Significative progress has been made in the development of analytical methodologies for STE determination in food; however, further advancements in analytical techniques, standardized protocols, and monitoring are essential to improve risk assessment and guide effective mitigation strategies.
Read less.
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a common skin infection caused by a poxvirus, primarily affecting children and immunocompromised adults. It manifests as single or multiple raised, pearl-like papules and is highly contagious, spreading through skin contact or contaminated objects. Traditional treatments include cryosurgery, curettage, and pulsed dye laser ablation. However, in early 2024, berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% (ZELSUVMITM), was approved as the first topical treatment for MC. This review explores the potential of Zelsuvmi gel as a significant advancement in treatment due to its nitric oxide (NO)-producing properties. NO is a naturally occurring molecule in the body with multiple roles, including immune defense, antimicrobial activity, and modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, and cytokine production. The novel mechanism of action of Zelsuvmi, utilizing NO’s antiviral properties, has demonstrated compelling efficacy in clinical settings. The article also considers the broader implications of this treatment, not only for current dermatological practice but also for future research into innovative therapies for viral skin infections. Through an evaluation of clinical data, this review highlights Zelsuvmi’s potential to transform treatment approaches for MC, offering a non-invasive, effective option that may influence both clinical management and future prevention strategies.
Read less.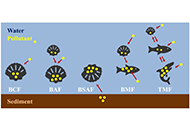
Seafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability to bioaccumulate pollutants. While not often linked to food poisoning, these molluscs can occasionally introduce health risks, highlighting the need for vigilant monitoring. This review provides a thorough analysis of pollutants—including persistent and emerging pollutants, as well as marine toxins—found in bivalve molluscs between 2019 and 2024. Among the studied pollutants, plasticizers and alkaloids are the most frequently analyzed, with liquid and gas chromatography (GC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS) the predominant methods, although novel approaches to determine these compounds, such as sensors, have also emerged in recent years. However, many studies are focused on establishing pollutant content without addressing bioaccumulation (BA) factors, and a lack of standardization in species and sampling locations complicates comparisons between the different published works. Despite some studies linking human activity and algal blooms to BA dynamics, more comprehensive research is needed. Additionally, limited data on the depuration capacity of molluscs underscores the need for further investigation. Although pollutant levels generally remain within legal limits, many substances remain unregulated. Environmental factors also play a critical role in influencing BA, emphasizing the need for future studies to focus on BA factors to better understand these complex dynamics.
Read less.
Depression is characterized by affective symptoms and neuropsychological deficits. After treatment, affective symptoms frequently remit, but cognitive alterations may remain affecting the lives of people and having an impact on health, economy, and societies. The present work describes the methods, procedures, and equipment for a randomized three-arm controlled experiment designed to measure the effects of exergames on executive functions (EFs) under depression. EFs are complex cognitive functions that are essential for organizing information, planning an action, reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving. Literature shows that EFs are compromised in depression, affecting daily-life activities and other cognitive domains. To conduct the experiment, depressed middle-aged adults will be randomly distributed into three experimental groups: an intervention group training with exergames, an active control group training only with cognitive video games, and a passive control group or wait-list. EFs are evaluated at three different time points: pre-post intervention, and three months follow-up, using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). Researchers will collect cognitive-behavioral and neural information [event-related potentials (ERPs)]. Results will be explored by performing analysis of variance to compare the outcomes of the diverse groups at the three different time points, understanding the benefits of exergames in terms of EFs under depression. The study of simultaneous multidomain interventions in depression holds promise for the development of novel approaches, to implementing psychological and neuropsychological health [this experiment is part of a registered clinical trial entitled “MUDgame” (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT06536530). Registered on August 2024, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06536530].
Read less.
Cardiovascular diseases, particularly ischemic heart disease (IHD), are the leading cause of mortality globally, accounting for 16% of deaths. Effective management of ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) is crucial, as outlined in the latest European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for chronic coronary syndrome (CCS). The guidelines emphasize a structured approach comprising four key steps: a general clinical evaluation to exclude non-cardiac causes, cardiac examination, and likelihood estimation using echocardiography, diagnostic testing such as stress echocardiography and coronary CT angiography, and treatment involving lifestyle changes and medication, alongside potential revascularization. The review underscores the importance of coronary angiography and functional assessments in diagnosing ischemic heart failure (IHF) and guiding treatment strategies. Non-invasive imaging techniques, including stress echocardiography and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, are valuable for assessing ischemia and myocardial viability while reducing unnecessary invasive procedures. Coronary CT angiography is also examined for its procedural advantages and risks. A comparative analysis of diagnostic modalities highlights the strengths and limitations of each technique, emphasizing the need for individualized approaches based on patient characteristics. The ESC 2024 guidelines advocate for a patient-centered imaging strategy based on the likelihood of coronary artery disease (CAD) while addressing the economic and environmental impacts of imaging practices. Overall, implementing these guidelines and leveraging diverse imaging modalities can optimize management strategies for IHD, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Read less.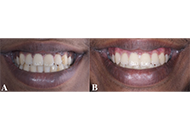
Aim:
The study aims to assess laypersons’ perceptions of smile aesthetics before and after gingival depigmentation and to correlate these perceptions with the degree of gingival pigmentation.
Methods:
The retrospective observational study examined individuals who received gingival depigmentation following orthodontic treatment between 2019 and 2024. Fifteen records were selected based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The pre- and post-depigmentation frontal smile photos were standardized, included into a Google Form, and distributed to 40 laypeople for the assessment of smile aesthetics. The laypeople evaluated the attractiveness of smiles using a 10-point Likert scale. Experienced periodontists classified the gingival pigmentation utilizing the oral pigmentation index (OPI). The differences between the pre- and post-treatment OPI scores and smile esthetic scores were assessed using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Spearman correlation was used to evaluate the association between smile scores and OPI scores. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was employed to evaluate the inter-rater reliability of the smile ratings and OPI scores. The statistical significance was established at p ≤ 0.05.
Results:
The average OPI scores before depigmentation were 2.67 ± 0.49; however, following depigmentation, the scores significantly declined to an average of 0.33 ± 0.5 (p < 0.001). The mean smile aesthetic score pre-depigmentation was 6.72 ± 0.32, whereas after depigmentation the scores significantly improved to 7.91 ± 0.18 (p = 0.001). Spearman correlation indicated a statistically significant negative association between smile aesthetics scores and OPI scores (r = –0.76). ICC indicated excellent inter-rater reliability for the OPI (0.923) and good reliability for smile esthetic scores (0.756).
Conclusions:
The study found that gingival de-pigmentation procedures improve the OPI scores and laypeople perceive gingival hyperpigmentation unattractive. While gingival depigmentation is not mandatory, it may be recommended for individuals seeking cosmetic smile enhancements post-orthodontic therapy to improve the overall patient satisfaction.
Migraine, a commonly occurring neurological disorder, disproportionately affects women during their reproductive years, and its symptoms are often intensified by hormonal fluctuations. This narrative review examines the impact of hormonal contraceptives, particularly combined oral contraceptives (COCs), on menstrual migraine (MM). This review assessed the impact of COCs on MM through a literature search in PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus using keywords like “menstrual migraine”, “hormone therapy”, and “COCs”. The selection criteria were peer-reviewed studies published between 2014 and 2024, written in English, and focused on MM treatment with COCs. Exclusion criteria were duplicates, editorials, irrelevant articles, and non-English studies. The literature reveals inconsistent results, with some studies reporting aggravation of migraine symptoms with COC use, whereas others indicate a decrease in the frequency and severity of attacks, especially with continuous use. Factors affecting these outcomes include patient age, menstrual cycle characteristics, and migraine type. It is crucial to choose contraceptives that suit individual patient profiles, considering the potential for increased migraine frequency or onset of migraine with aura in some women. Further studies are required to establish clear clinical guidelines. It is recommended to create personalized treatment plans that balance the effectiveness of migraine management with the overall health risks.
Read less.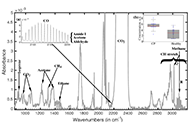
Breath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created internally by the body due to environmental interactions, gut and air passage bacteria, and metabolites of ingested precursors. Breath analysis may help diagnose disorders linked to changes in breath composition, according to several recent research. An analytical technique that shows promise for the metabolic examination of breath is infrared spectroscopy. Chemical substances found in exhaled human breath can be used to diagnose illnesses, determine physiological states, or evaluate environmental exposure. Exhaled breath (EB) is the perfect biological fluid because it is nearly limitless and causes little to no discomfort for the patient, which promotes collaboration. Furthermore, EB can be sampled without requiring medical professionals or privacy, and it usually doesn’t produce infectious waste (despite airborne infections), which makes breath analysis a desirable method for a variety of applications. Breath analysis is a non-invasive method that solely uses the volatile composition of the EB to characterize the bloodstream and airways’ volatile content, which indicates the state and condition of the entire body’s metabolism. The absorption strength of the metabolites is still very modest, though, because EB contains minimal amounts of them. Several of the most recent uses of infrared spectroscopy for breath analysis, published between 2020 and 2024, are presented in this study.
Read less.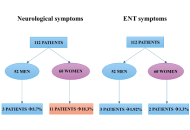
Aim:
COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological and otolaryngological symptoms in patients two years after acute infection, with a focus on gender differences and variant-specific effects.
Methods:
A retrospective follow-up was conducted in January 2024 on 112 patients who had been hospitalized for COVID-19. Patients completed a questionnaire assessing the persistence of neuropsychiatric, otolaryngological, and systemic symptoms.
Results:
Findings reveal that 18.3% of women reported persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as memory deficits, depression, and concentration issues, compared to 5.7% of men. Otolaryngological symptoms, including anosmia and ageusia, largely resolved, with only 4.5% reporting persistent issues. Symptom persistence was more common in older individuals, women, smokers, and those with severe acute-phase illness. Neuropsychiatric symptoms remain prominent, underscoring the need for targeted long-term care.
Conclusions:
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk and severity of long COVID, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms, emphasizing its role in mitigating the long-term burden of SARS-CoV-2. Future research should explore biomolecular markers and imaging techniques to better understand and address these long-term sequelae.
Aim:
This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic therapy. Additionally, the study sought to identify factors influencing 30-day all-cause mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Methods:
This was a retrospective study conducted at Jordan University Hospital from January 2018 to March 2024. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with confirmed Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections were included. Data were collected from medical records, focusing on demographics, infection characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and outcomes. The susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) or non-MDR. Logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with 30-day mortality.
Results:
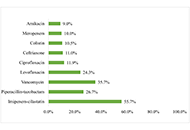
A total of 210 patients were included in the study, with 106 males (50.5%) and 104 females (49.5%). The majority of infections were community-acquired (n = 178, 84.8%), with the respiratory tract being the most common infection site (n = 81, 38.6%). Nearly half of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were MDR (n = 99, 47.1%). Empiric antibiotic therapy was administered to all patients, with imipenem-cilastatin (55.7%), vancomycin (35.7%), and piperacillin-tazobactam (26.7%) being the most commonly used antibiotics. Of the 210 patients, 32.4% (n = 68) received inappropriate empiric therapy. The 30-day all-cause mortality rate was 4.9% (n = 10). Multivariate analysis revealed that non-localized infections, such as bacteremia and sepsis, were strongly associated with increased mortality [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) = 17.455, P < 0.001].
Conclusions:
This study highlights the high prevalence of MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, especially in community-acquired cases, and emphasizes the need for improved antimicrobial stewardship. The significant proportion of patients (32.4%) receiving inappropriate empiric therapy calls for better guidance in antibiotic prescribing practices. The key predictor of mortality was infection localization, indicating the importance of early intervention for systemic infections to reduce mortality rates.

The escalating prevalence of diabetes poses a significant health concern. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to a multitude of complications. A comprehensive management plan and continual adaptation of guidelines is needed. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) is a guiding force in this domain, providing diabetes care recommendations for clinicians, laboratorians, researchers, and policymakers since 1989. The latest ADA guidelines present both challenges and opportunities for laboratories. The increased emphasis on glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) testing for early diagnosis and personalized monitoring is expected to increase testing volumes, potentially leading to a rise in point-of-care testing. Ensuring standardized testing procedures becomes paramount to maintaining consistent and reliable results across laboratories. Moreover, laboratories may need to expand their test menus to accommodate the growing demand for personalized medicine approaches and collaborate closely with healthcare providers to support informed decision-making. This commentary provides a focused analysis of the 2024 ADA guidelines for the laboratory assessment of diabetes.
The escalating prevalence of diabetes poses a significant health concern. Uncontrolled diabetes leads to a multitude of complications. A comprehensive management plan and continual adaptation of guidelines is needed. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) is a guiding force in this domain, providing diabetes care recommendations for clinicians, laboratorians, researchers, and policymakers since 1989. The latest ADA guidelines present both challenges and opportunities for laboratories. The increased emphasis on glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) testing for early diagnosis and personalized monitoring is expected to increase testing volumes, potentially leading to a rise in point-of-care testing. Ensuring standardized testing procedures becomes paramount to maintaining consistent and reliable results across laboratories. Moreover, laboratories may need to expand their test menus to accommodate the growing demand for personalized medicine approaches and collaborate closely with healthcare providers to support informed decision-making. This commentary provides a focused analysis of the 2024 ADA guidelines for the laboratory assessment of diabetes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2024.00013

Surgeons are exposed to a high prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). The scientific issues surrounding this problem are generating a growing body of work. The aim of this study is to obtain quantitative and visual information from articles about WMSDs and surgeons through bibliometric analysis. The keywords “surgeon” and “work-related musculoskeletal disorders” were searched in the PubMed/Medline database until March 2024. Data extraction and visualization were performed using VOSviewer version 1.6.20. and Microsoft Excel on the overall distribution of publications by year, sources, articles, authors and keywords. A total of 173 English-language publications were extracted between 1982 and 2024. The number of publications has increased over the years. A significant increase was observed from 2016. America is the leader with 82/173 publications (47.4%) and 3,276 citations. Work [impact factor (IF): 2.3] is the first top source which has 7 articles followed by Surgical Endoscopy (IF: 3.1) with 5 publications. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation (IF: 3.3) is the top journal with 681 citations for 2 publications. Hallbeck MS, Yu D, and Vijendern A are the most productive authors with 23 publications. The analysis showed that the United States and the UK are the two most productive countries (journals, authors, citations). The most frequently used keywords were “ergonomics”, “musculoskeletal disorders”, “work-related musculoskeletal disorders”, and “surgeons”. Bibliometric analysis has shown that the prevalence of WMSDs in surgeons is a topic showing significant growth, particularly since 2016, dominated by American researchers. A synthesis of the WMSD prevalence by body area has been made based on the most cited articles. This field has evolved considerably. From a rather subjective analysis of prevalence based on questionnaires, work has moved towards a more ergonomic assessment using objective evaluation tools.
Surgeons are exposed to a high prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs). The scientific issues surrounding this problem are generating a growing body of work. The aim of this study is to obtain quantitative and visual information from articles about WMSDs and surgeons through bibliometric analysis. The keywords “surgeon” and “work-related musculoskeletal disorders” were searched in the PubMed/Medline database until March 2024. Data extraction and visualization were performed using VOSviewer version 1.6.20. and Microsoft Excel on the overall distribution of publications by year, sources, articles, authors and keywords. A total of 173 English-language publications were extracted between 1982 and 2024. The number of publications has increased over the years. A significant increase was observed from 2016. America is the leader with 82/173 publications (47.4%) and 3,276 citations. Work [impact factor (IF): 2.3] is the first top source which has 7 articles followed by Surgical Endoscopy (IF: 3.1) with 5 publications. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation (IF: 3.3) is the top journal with 681 citations for 2 publications. Hallbeck MS, Yu D, and Vijendern A are the most productive authors with 23 publications. The analysis showed that the United States and the UK are the two most productive countries (journals, authors, citations). The most frequently used keywords were “ergonomics”, “musculoskeletal disorders”, “work-related musculoskeletal disorders”, and “surgeons”. Bibliometric analysis has shown that the prevalence of WMSDs in surgeons is a topic showing significant growth, particularly since 2016, dominated by American researchers. A synthesis of the WMSD prevalence by body area has been made based on the most cited articles. This field has evolved considerably. From a rather subjective analysis of prevalence based on questionnaires, work has moved towards a more ergonomic assessment using objective evaluation tools.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2024.00059
This article belongs to the special issue Prevalence and Risk Factors of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders

Gelatin is extracted from beef, pork, and fish tissues. An increasing number of cases of gelatin-induced anaphylaxis are associated with α-Gal syndrome (AGS). Only a few cases of anaphylaxis to bovine gelatin (BG) without AGS (BG-woAG) have been described. We report two new cases of anaphylaxis to BG-woAG, highlight the characteristics of this entity, and propose a procedure in cases of suspected anaphylaxis to BG. We selected articles on gelatin allergy between 1987 and 2024. Results: we report two new cases of severe anaphylaxis BG-woAG. Diagnosis was established using skin tests (ST), IgE, and basophil activation tests (BAT). We confirm the existence of allergies to BG-woAG. The main characteristic of these allergies seems to be the presence of BG IgE which differentiates them from AGS-related allergies. These initial data need to be confirmed by larger case series. We propose a diagnostic algorithm for better patient management. To confirm the diagnosis, ST and IgE to BG and α-Gal should be performed. The role of BAT to Gelofusine® in the diagnostic strategy remains to be defined.
Gelatin is extracted from beef, pork, and fish tissues. An increasing number of cases of gelatin-induced anaphylaxis are associated with α-Gal syndrome (AGS). Only a few cases of anaphylaxis to bovine gelatin (BG) without AGS (BG-woAG) have been described. We report two new cases of anaphylaxis to BG-woAG, highlight the characteristics of this entity, and propose a procedure in cases of suspected anaphylaxis to BG. We selected articles on gelatin allergy between 1987 and 2024. Results: we report two new cases of severe anaphylaxis BG-woAG. Diagnosis was established using skin tests (ST), IgE, and basophil activation tests (BAT). We confirm the existence of allergies to BG-woAG. The main characteristic of these allergies seems to be the presence of BG IgE which differentiates them from AGS-related allergies. These initial data need to be confirmed by larger case series. We propose a diagnostic algorithm for better patient management. To confirm the diagnosis, ST and IgE to BG and α-Gal should be performed. The role of BAT to Gelofusine® in the diagnostic strategy remains to be defined.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eaa.2025.100970

Intracranial artery dolichoectasia (IADE) is a vascular anomaly characterized by dilation and/or tortuosity of one or more intracranial arteries. While many cases are incidental findings on imaging, the associated ischemic neurological complications of IADE can be severe and must be promptly recognized. This study aims to increase awareness among general practitioners and neurologists regarding this rare and potentially life-threatening condition. We utilized reputable databases for this scoping review, including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, from database inception through September 2024, using a combination of terms such as “Dolichoectasia of Basilar Artery”, “Intracranial Dolichoectasia”, and “Ischemic Stroke”. Our scoping review revealed that IADE is a challenging and often underdiagnosed condition, with an estimated prevalence of less than 1% in the general population. Hypertension, atherosclerosis, and advanced age are well-documented risk factors. To minimize the risk of misdiagnosis, we briefly elucidated the pathophysiology of IADE, correlating it with clinical and radiological features. We discuss the diagnostic criteria for IADE based on radiological imaging, addressing the advantages and limitations of different techniques. Finally, we highlight the unmet clinical needs related to IADE management, which may involve pharmacological and surgical therapies tailored to individual cases, with careful consideration of safety and efficacy.
Intracranial artery dolichoectasia (IADE) is a vascular anomaly characterized by dilation and/or tortuosity of one or more intracranial arteries. While many cases are incidental findings on imaging, the associated ischemic neurological complications of IADE can be severe and must be promptly recognized. This study aims to increase awareness among general practitioners and neurologists regarding this rare and potentially life-threatening condition. We utilized reputable databases for this scoping review, including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, from database inception through September 2024, using a combination of terms such as “Dolichoectasia of Basilar Artery”, “Intracranial Dolichoectasia”, and “Ischemic Stroke”. Our scoping review revealed that IADE is a challenging and often underdiagnosed condition, with an estimated prevalence of less than 1% in the general population. Hypertension, atherosclerosis, and advanced age are well-documented risk factors. To minimize the risk of misdiagnosis, we briefly elucidated the pathophysiology of IADE, correlating it with clinical and radiological features. We discuss the diagnostic criteria for IADE based on radiological imaging, addressing the advantages and limitations of different techniques. Finally, we highlight the unmet clinical needs related to IADE management, which may involve pharmacological and surgical therapies tailored to individual cases, with careful consideration of safety and efficacy.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2025.100671
This article belongs to the special issue Cerebral Ischemia, Genetics, Comorbidities, Risk Factors and New Therapeutic Options for Neurorestoration

Routine regulatory requirements for large comparative efficacy trials (CETs) to support marketing approval of monoclonal antibody (mAb) biosimilars have been the focus of extensive debate in the last few years. This review examines the mounting evidence, accumulated over the past decade, focusing on relevant literature and data published in the European Product Assessment Reports (EPARs) for the fifteen anti-TNFα biosimilars approved to date. The potential for residual uncertainties that may require resolution through CETs following comparative physico-chemical, in-vitro potency, and single dose studies in healthy subjects is examined. It is noted that structural and physicochemical differences between biosimilars and reference products are detectable using modern analytical methods at levels well below those that could impact clinical outcomes, and that in vitro potency testing is fully capable of revealing clinically relevant differences. Additionally, comparative pharmacokinetic studies in healthy participants provide a sensitive assessment of potential differences in drug exposure and immunogenicity. The added value of CETs is further questioned in the light of the fact that anti-TNFα’s display a flat dose-response relationship, meaning that unlike cell-based assays, CETs have limited sensitivity to detect potency differences. Initial concerns about extrapolating data from rheumatoid arthritis studies to support marketing approval of other indications such as inflammatory bowel disease for which not all anti-TNFα’s are effective have been alleviated by post-approval studies. Additionally, as of the end of 2024, no cases where clinical efficacy data were necessary to resolve residual quality concerns have arisen following regulatory assessment of 56 mAb biosimilars and fusion proteins. CETs add significant cost and delay to the development of biosimilars and the time is now ripe to re-examine the need for these CET’s and for further evolution in regulatory thinking.
Routine regulatory requirements for large comparative efficacy trials (CETs) to support marketing approval of monoclonal antibody (mAb) biosimilars have been the focus of extensive debate in the last few years. This review examines the mounting evidence, accumulated over the past decade, focusing on relevant literature and data published in the European Product Assessment Reports (EPARs) for the fifteen anti-TNFα biosimilars approved to date. The potential for residual uncertainties that may require resolution through CETs following comparative physico-chemical, in-vitro potency, and single dose studies in healthy subjects is examined. It is noted that structural and physicochemical differences between biosimilars and reference products are detectable using modern analytical methods at levels well below those that could impact clinical outcomes, and that in vitro potency testing is fully capable of revealing clinically relevant differences. Additionally, comparative pharmacokinetic studies in healthy participants provide a sensitive assessment of potential differences in drug exposure and immunogenicity. The added value of CETs is further questioned in the light of the fact that anti-TNFα’s display a flat dose-response relationship, meaning that unlike cell-based assays, CETs have limited sensitivity to detect potency differences. Initial concerns about extrapolating data from rheumatoid arthritis studies to support marketing approval of other indications such as inflammatory bowel disease for which not all anti-TNFα’s are effective have been alleviated by post-approval studies. Additionally, as of the end of 2024, no cases where clinical efficacy data were necessary to resolve residual quality concerns have arisen following regulatory assessment of 56 mAb biosimilars and fusion proteins. CETs add significant cost and delay to the development of biosimilars and the time is now ripe to re-examine the need for these CET’s and for further evolution in regulatory thinking.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emd.2025.100782
This article belongs to the special issue Biosimilars: State of the Art in the Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases

Background:
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematologic malignancy characterized by the clonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow, constituting approximately 13% of all hematologic malignancies. Isatuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the CD38 protein on myeloma cells, causing cell death through various immune-mediated mechanisms. Clinical trials have shown that adding isatuximab to standard regimens for MM significantly enhances efficacy but introduces some notable toxicities. The purpose of this study is to determine the risk of pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), and venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with MM treated with isatuximab.
Methods:
We conducted a comprehensive literature search using Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases from inception through July 22nd, 2024. Phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing isatuximab in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) reporting pneumonia, URTIs, and VTE as adverse events were included. Mantel-Haenszel (MH) method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-statistic. Random effects model was applied.
Results:
A total of 1,044 patients from three phase III RCTs (ICARIA-MM, IKEMA, IMROZ) were included for pneumonia and URTI analysis, while 1,403 patients from three trials (IKEMA, IMROZ, GMMG-HD7) were included for VTE evaluation. The incidence of any-grade pneumonia was higher in the isatuximab group (30.1% vs. 23.2%; RR, 1.31; 95% CI 1.06–1.61; P = 0.01), as was high-grade pneumonia (20.8% vs. 15.3%; RR, 1.38; 95% CI 1.06–1.81; P = 0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed between the isatuximab and control groups for any-grade URTIs, high-grade URTIs, or VTE.
Discussion:
This meta-analysis highlights a significant increase in the incidence of pneumonia with the addition of isatuximab to standard myeloma regimens, underscoring the need for routine antibiotic prophylaxis, thromboprophylaxis, vigilant monitoring and early intervention to mitigate these risks.
Background:
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematologic malignancy characterized by the clonal proliferation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow, constituting approximately 13% of all hematologic malignancies. Isatuximab is a monoclonal antibody targeting the CD38 protein on myeloma cells, causing cell death through various immune-mediated mechanisms. Clinical trials have shown that adding isatuximab to standard regimens for MM significantly enhances efficacy but introduces some notable toxicities. The purpose of this study is to determine the risk of pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), and venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with MM treated with isatuximab.
Methods:
We conducted a comprehensive literature search using Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases from inception through July 22nd, 2024. Phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing isatuximab in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) reporting pneumonia, URTIs, and VTE as adverse events were included. Mantel-Haenszel (MH) method was used to calculate the estimated pooled risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-statistic. Random effects model was applied.
Results:
A total of 1,044 patients from three phase III RCTs (ICARIA-MM, IKEMA, IMROZ) were included for pneumonia and URTI analysis, while 1,403 patients from three trials (IKEMA, IMROZ, GMMG-HD7) were included for VTE evaluation. The incidence of any-grade pneumonia was higher in the isatuximab group (30.1% vs. 23.2%; RR, 1.31; 95% CI 1.06–1.61; P = 0.01), as was high-grade pneumonia (20.8% vs. 15.3%; RR, 1.38; 95% CI 1.06–1.81; P = 0.02). No statistically significant differences were observed between the isatuximab and control groups for any-grade URTIs, high-grade URTIs, or VTE.
Discussion:
This meta-analysis highlights a significant increase in the incidence of pneumonia with the addition of isatuximab to standard myeloma regimens, underscoring the need for routine antibiotic prophylaxis, thromboprophylaxis, vigilant monitoring and early intervention to mitigate these risks.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/etat.2025.1002300

Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for both cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease (CKD) while CKD is also associated with cardiovascular morbidity. In fact, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mainly from heart failure or myocardial infarction. The newer therapeutic agents in diabetes have positive impact on both cardiovascular and renal outcomes. Thus, the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s annual update on the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes is an important resource for all caregivers involved in diabetes management as it incorporates the latest scientific research, clinical evidence, and emerging technologies in diabetes management. The 2025 guidelines present significant updates that reflect a deeper understanding of diabetes management, emphasizing expanded usage of technologies such as continuous glucose monitoring, personalized pharmacological approaches, and lifestyle interventions. This commentary provides an analysis of the key updates in the 2025 ADA guidelines exploring implications for clinical practice, laboratory assessments, and public health policy. Where relevant, comparisons to the 2024 version will be made.
Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for both cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease (CKD) while CKD is also associated with cardiovascular morbidity. In fact, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mainly from heart failure or myocardial infarction. The newer therapeutic agents in diabetes have positive impact on both cardiovascular and renal outcomes. Thus, the American Diabetes Association (ADA)’s annual update on the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes is an important resource for all caregivers involved in diabetes management as it incorporates the latest scientific research, clinical evidence, and emerging technologies in diabetes management. The 2025 guidelines present significant updates that reflect a deeper understanding of diabetes management, emphasizing expanded usage of technologies such as continuous glucose monitoring, personalized pharmacological approaches, and lifestyle interventions. This commentary provides an analysis of the key updates in the 2025 ADA guidelines exploring implications for clinical practice, laboratory assessments, and public health policy. Where relevant, comparisons to the 2024 version will be made.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eemd.2025.101428

Aim:
Hypertension, a prevalent chronic condition, significantly contributes to cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Effective management of hypertension is highly dependent on patient adherence to prescribed medications, as the correct dose at the right time can lead to desirable therapeutic results. This study aims to analyze medication adherence among hypertensive patients in Islamabad and Rawalpindi through an open survey.
Methods:
A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted from 17th March 2024 to 30th May 2024, targeting hypertensive populations in Islamabad and Rawalpindi. 246 patients were recruited using a sample size formula, and a General Medication Adherence Scale (GMAS) questionnaire was used to collect data. All the tests were conducted as two-sided, with a significance level of P < 0.05 using Python.
Results:
Among 246 participants (mean age 57.1 years), most were married, literate, and living with families, 63% were from Islamabad, and 78.9% were employed. The study found high adherence in behavior-related areas but low adherence due to costs. Gender showed a statistically significant correlation (P = 0.03) by independent t-test. At the same time, ANOVA tests revealed that educational level (P = 0.02), monthly income (P = 0.001), family support (P = 0.04), and medication costs (P = 0.001) significantly impacted adherence, while factors like social status, employment status, and smoking did not have a considerable influence.
Conclusions:
72.4% of patients adhered to their prescribed therapy, and 27.6% did not highlight a critical issue that requires urgent intervention. Variables like gender, educational status, social status, occupation, and living with family are strongly associated with adherence. Common problems include taking multiple medications, lack of awareness about the importance of adherence, and financial constraints.
Aim:
Hypertension, a prevalent chronic condition, significantly contributes to cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Effective management of hypertension is highly dependent on patient adherence to prescribed medications, as the correct dose at the right time can lead to desirable therapeutic results. This study aims to analyze medication adherence among hypertensive patients in Islamabad and Rawalpindi through an open survey.
Methods:
A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted from 17th March 2024 to 30th May 2024, targeting hypertensive populations in Islamabad and Rawalpindi. 246 patients were recruited using a sample size formula, and a General Medication Adherence Scale (GMAS) questionnaire was used to collect data. All the tests were conducted as two-sided, with a significance level of P < 0.05 using Python.
Results:
Among 246 participants (mean age 57.1 years), most were married, literate, and living with families, 63% were from Islamabad, and 78.9% were employed. The study found high adherence in behavior-related areas but low adherence due to costs. Gender showed a statistically significant correlation (P = 0.03) by independent t-test. At the same time, ANOVA tests revealed that educational level (P = 0.02), monthly income (P = 0.001), family support (P = 0.04), and medication costs (P = 0.001) significantly impacted adherence, while factors like social status, employment status, and smoking did not have a considerable influence.
Conclusions:
72.4% of patients adhered to their prescribed therapy, and 27.6% did not highlight a critical issue that requires urgent intervention. Variables like gender, educational status, social status, occupation, and living with family are strongly associated with adherence. Common problems include taking multiple medications, lack of awareness about the importance of adherence, and financial constraints.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00248
This article belongs to the special issue Drug Adherence in Hypertension

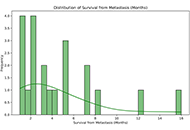
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is characterized by its infiltrative growth pattern and high recurrence rate despite treatment. While local progression within the central nervous system (CNS) is the rule, manifestations outside the CNS, particularly skin and subcutaneous metastases, are very infrequent and seldom reported in the literature. The authors reviewed the current understanding of this rare condition, with the main purpose of giving visibility to its clinical presentation and prognostic implications, thus improving clinical management and encouraging research in this area. A PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE search from database inception through March 2024 was conducted. In this way, we compiled a total of thirty-five cases in our review. As far as we know, our work gathers the largest number of patients with this condition. Remarkably, we observed that the typical presentation of soft-tissue high-grade glioma metastases is the finding of subcutaneous erythematous nodules in patients previously operated on for a primary CNS tumor, within the craniotomy site and nearby, mostly in the first year after the initial surgery. It was also noted that there is a trend of developing a concomitant CNS recurrence and/or other metastases in different locations, either simultaneously or subsequently. From here, we propose some possible mechanisms that explain the extracranial spread of GBM. We concluded that a poor outcome is expected from the diagnosis of skin and subcutaneous metastases: the mean overall survival was 4.38 months. Yet, assessing individual characteristics is always mandatory; a palliative approach seems to be the best option for the majority of cases.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is characterized by its infiltrative growth pattern and high recurrence rate despite treatment. While local progression within the central nervous system (CNS) is the rule, manifestations outside the CNS, particularly skin and subcutaneous metastases, are very infrequent and seldom reported in the literature. The authors reviewed the current understanding of this rare condition, with the main purpose of giving visibility to its clinical presentation and prognostic implications, thus improving clinical management and encouraging research in this area. A PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE search from database inception through March 2024 was conducted. In this way, we compiled a total of thirty-five cases in our review. As far as we know, our work gathers the largest number of patients with this condition. Remarkably, we observed that the typical presentation of soft-tissue high-grade glioma metastases is the finding of subcutaneous erythematous nodules in patients previously operated on for a primary CNS tumor, within the craniotomy site and nearby, mostly in the first year after the initial surgery. It was also noted that there is a trend of developing a concomitant CNS recurrence and/or other metastases in different locations, either simultaneously or subsequently. From here, we propose some possible mechanisms that explain the extracranial spread of GBM. We concluded that a poor outcome is expected from the diagnosis of skin and subcutaneous metastases: the mean overall survival was 4.38 months. Yet, assessing individual characteristics is always mandatory; a palliative approach seems to be the best option for the majority of cases.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2024.00065
This article belongs to the special issue Current Approaches to Malignant Tumors of the Nervous System

Measles virus (Morbillivirus abbreviated as MV, but more recently MeV) is the causal agent of measles disease, thought to have existed at least 4,000 years ago, affecting predominantly infants, but also immunocompromised individuals remaining a public health issue today globally. In this review, we discuss the historical background about MeV infection to modern-day research on measles disease, current epidemiology, but also what is known about immunisation against it. We report what is known about the viral structure and the function of the viral proteins. This additionally covers the cellular structure of MeV, mechanisms, and clinical aspects of infection. Including a review of topics like cellular receptor-associated entry factors, to the immunology of MeV infection. In this review, the current knowledge of innate immune responses during infection is explained, which involves changes to chemokine and cytokine expression, finalised by the present understanding of adaptive immune responses to MeV. The genomic stability of the MeV proteins is explained and suggestive that it could be the third pathogen with eradication potential (after the variola and rinderpest viruses). Further biological and immunological clarification as to how this could occur is explained below.
Measles virus (Morbillivirus abbreviated as MV, but more recently MeV) is the causal agent of measles disease, thought to have existed at least 4,000 years ago, affecting predominantly infants, but also immunocompromised individuals remaining a public health issue today globally. In this review, we discuss the historical background about MeV infection to modern-day research on measles disease, current epidemiology, but also what is known about immunisation against it. We report what is known about the viral structure and the function of the viral proteins. This additionally covers the cellular structure of MeV, mechanisms, and clinical aspects of infection. Including a review of topics like cellular receptor-associated entry factors, to the immunology of MeV infection. In this review, the current knowledge of innate immune responses during infection is explained, which involves changes to chemokine and cytokine expression, finalised by the present understanding of adaptive immune responses to MeV. The genomic stability of the MeV proteins is explained and suggestive that it could be the third pathogen with eradication potential (after the variola and rinderpest viruses). Further biological and immunological clarification as to how this could occur is explained below.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2024.00167

Sterigmatocystin (STE) is a possible human carcinogenic compound (2B) according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer classification. Structurally, STE is a precursor to aflatoxins, sharing a similar polyketide-derived biosynthetic pathway, which underscores its toxicological relevance. It has been reported to occur in a variety of foodstuffs including cereals and cereal-based products, spices, cheese, and nuts, among others. STE poses a substantial challenge to food safety and addressing this issue requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing prevention, monitoring, and regulation to protect both human and animal health from its harmful effects. The present paper presents the analytical methodologies for the determination of STE in foodstuffs and the reported levels of STE in food, based on a review of scientific publications from 2021 to 2024. Significative progress has been made in the development of analytical methodologies for STE determination in food; however, further advancements in analytical techniques, standardized protocols, and monitoring are essential to improve risk assessment and guide effective mitigation strategies.
Sterigmatocystin (STE) is a possible human carcinogenic compound (2B) according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer classification. Structurally, STE is a precursor to aflatoxins, sharing a similar polyketide-derived biosynthetic pathway, which underscores its toxicological relevance. It has been reported to occur in a variety of foodstuffs including cereals and cereal-based products, spices, cheese, and nuts, among others. STE poses a substantial challenge to food safety and addressing this issue requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing prevention, monitoring, and regulation to protect both human and animal health from its harmful effects. The present paper presents the analytical methodologies for the determination of STE in foodstuffs and the reported levels of STE in food, based on a review of scientific publications from 2021 to 2024. Significative progress has been made in the development of analytical methodologies for STE determination in food; however, further advancements in analytical techniques, standardized protocols, and monitoring are essential to improve risk assessment and guide effective mitigation strategies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00059
This article belongs to the special issue Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment

Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a common skin infection caused by a poxvirus, primarily affecting children and immunocompromised adults. It manifests as single or multiple raised, pearl-like papules and is highly contagious, spreading through skin contact or contaminated objects. Traditional treatments include cryosurgery, curettage, and pulsed dye laser ablation. However, in early 2024, berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% (ZELSUVMITM), was approved as the first topical treatment for MC. This review explores the potential of Zelsuvmi gel as a significant advancement in treatment due to its nitric oxide (NO)-producing properties. NO is a naturally occurring molecule in the body with multiple roles, including immune defense, antimicrobial activity, and modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, and cytokine production. The novel mechanism of action of Zelsuvmi, utilizing NO’s antiviral properties, has demonstrated compelling efficacy in clinical settings. The article also considers the broader implications of this treatment, not only for current dermatological practice but also for future research into innovative therapies for viral skin infections. Through an evaluation of clinical data, this review highlights Zelsuvmi’s potential to transform treatment approaches for MC, offering a non-invasive, effective option that may influence both clinical management and future prevention strategies.
Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a common skin infection caused by a poxvirus, primarily affecting children and immunocompromised adults. It manifests as single or multiple raised, pearl-like papules and is highly contagious, spreading through skin contact or contaminated objects. Traditional treatments include cryosurgery, curettage, and pulsed dye laser ablation. However, in early 2024, berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% (ZELSUVMITM), was approved as the first topical treatment for MC. This review explores the potential of Zelsuvmi gel as a significant advancement in treatment due to its nitric oxide (NO)-producing properties. NO is a naturally occurring molecule in the body with multiple roles, including immune defense, antimicrobial activity, and modulation of apoptosis, inflammation, and cytokine production. The novel mechanism of action of Zelsuvmi, utilizing NO’s antiviral properties, has demonstrated compelling efficacy in clinical settings. The article also considers the broader implications of this treatment, not only for current dermatological practice but also for future research into innovative therapies for viral skin infections. Through an evaluation of clinical data, this review highlights Zelsuvmi’s potential to transform treatment approaches for MC, offering a non-invasive, effective option that may influence both clinical management and future prevention strategies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2024.00266

Seafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability to bioaccumulate pollutants. While not often linked to food poisoning, these molluscs can occasionally introduce health risks, highlighting the need for vigilant monitoring. This review provides a thorough analysis of pollutants—including persistent and emerging pollutants, as well as marine toxins—found in bivalve molluscs between 2019 and 2024. Among the studied pollutants, plasticizers and alkaloids are the most frequently analyzed, with liquid and gas chromatography (GC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS) the predominant methods, although novel approaches to determine these compounds, such as sensors, have also emerged in recent years. However, many studies are focused on establishing pollutant content without addressing bioaccumulation (BA) factors, and a lack of standardization in species and sampling locations complicates comparisons between the different published works. Despite some studies linking human activity and algal blooms to BA dynamics, more comprehensive research is needed. Additionally, limited data on the depuration capacity of molluscs underscores the need for further investigation. Although pollutant levels generally remain within legal limits, many substances remain unregulated. Environmental factors also play a critical role in influencing BA, emphasizing the need for future studies to focus on BA factors to better understand these complex dynamics.
Seafood is both nutritionally and economically significant, with bivalve molluscs being particularly valuable for monitoring environmental pollutants due to their filter-feeding nature and ability to bioaccumulate pollutants. While not often linked to food poisoning, these molluscs can occasionally introduce health risks, highlighting the need for vigilant monitoring. This review provides a thorough analysis of pollutants—including persistent and emerging pollutants, as well as marine toxins—found in bivalve molluscs between 2019 and 2024. Among the studied pollutants, plasticizers and alkaloids are the most frequently analyzed, with liquid and gas chromatography (GC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS) the predominant methods, although novel approaches to determine these compounds, such as sensors, have also emerged in recent years. However, many studies are focused on establishing pollutant content without addressing bioaccumulation (BA) factors, and a lack of standardization in species and sampling locations complicates comparisons between the different published works. Despite some studies linking human activity and algal blooms to BA dynamics, more comprehensive research is needed. Additionally, limited data on the depuration capacity of molluscs underscores the need for further investigation. Although pollutant levels generally remain within legal limits, many substances remain unregulated. Environmental factors also play a critical role in influencing BA, emphasizing the need for future studies to focus on BA factors to better understand these complex dynamics.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eff.2024.00062
This article belongs to the special issue Food Contaminants: Analysis, Occurrence and Risk Assessment

Depression is characterized by affective symptoms and neuropsychological deficits. After treatment, affective symptoms frequently remit, but cognitive alterations may remain affecting the lives of people and having an impact on health, economy, and societies. The present work describes the methods, procedures, and equipment for a randomized three-arm controlled experiment designed to measure the effects of exergames on executive functions (EFs) under depression. EFs are complex cognitive functions that are essential for organizing information, planning an action, reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving. Literature shows that EFs are compromised in depression, affecting daily-life activities and other cognitive domains. To conduct the experiment, depressed middle-aged adults will be randomly distributed into three experimental groups: an intervention group training with exergames, an active control group training only with cognitive video games, and a passive control group or wait-list. EFs are evaluated at three different time points: pre-post intervention, and three months follow-up, using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). Researchers will collect cognitive-behavioral and neural information [event-related potentials (ERPs)]. Results will be explored by performing analysis of variance to compare the outcomes of the diverse groups at the three different time points, understanding the benefits of exergames in terms of EFs under depression. The study of simultaneous multidomain interventions in depression holds promise for the development of novel approaches, to implementing psychological and neuropsychological health [this experiment is part of a registered clinical trial entitled “MUDgame” (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT06536530). Registered on August 2024, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06536530].
Depression is characterized by affective symptoms and neuropsychological deficits. After treatment, affective symptoms frequently remit, but cognitive alterations may remain affecting the lives of people and having an impact on health, economy, and societies. The present work describes the methods, procedures, and equipment for a randomized three-arm controlled experiment designed to measure the effects of exergames on executive functions (EFs) under depression. EFs are complex cognitive functions that are essential for organizing information, planning an action, reasoning, decision-making, and problem-solving. Literature shows that EFs are compromised in depression, affecting daily-life activities and other cognitive domains. To conduct the experiment, depressed middle-aged adults will be randomly distributed into three experimental groups: an intervention group training with exergames, an active control group training only with cognitive video games, and a passive control group or wait-list. EFs are evaluated at three different time points: pre-post intervention, and three months follow-up, using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). Researchers will collect cognitive-behavioral and neural information [event-related potentials (ERPs)]. Results will be explored by performing analysis of variance to compare the outcomes of the diverse groups at the three different time points, understanding the benefits of exergames in terms of EFs under depression. The study of simultaneous multidomain interventions in depression holds promise for the development of novel approaches, to implementing psychological and neuropsychological health [this experiment is part of a registered clinical trial entitled “MUDgame” (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT06536530). Registered on August 2024, https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06536530].
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/en.2024.00068
This article belongs to the special issue Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Depression

Cardiovascular diseases, particularly ischemic heart disease (IHD), are the leading cause of mortality globally, accounting for 16% of deaths. Effective management of ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) is crucial, as outlined in the latest European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for chronic coronary syndrome (CCS). The guidelines emphasize a structured approach comprising four key steps: a general clinical evaluation to exclude non-cardiac causes, cardiac examination, and likelihood estimation using echocardiography, diagnostic testing such as stress echocardiography and coronary CT angiography, and treatment involving lifestyle changes and medication, alongside potential revascularization. The review underscores the importance of coronary angiography and functional assessments in diagnosing ischemic heart failure (IHF) and guiding treatment strategies. Non-invasive imaging techniques, including stress echocardiography and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, are valuable for assessing ischemia and myocardial viability while reducing unnecessary invasive procedures. Coronary CT angiography is also examined for its procedural advantages and risks. A comparative analysis of diagnostic modalities highlights the strengths and limitations of each technique, emphasizing the need for individualized approaches based on patient characteristics. The ESC 2024 guidelines advocate for a patient-centered imaging strategy based on the likelihood of coronary artery disease (CAD) while addressing the economic and environmental impacts of imaging practices. Overall, implementing these guidelines and leveraging diverse imaging modalities can optimize management strategies for IHD, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Cardiovascular diseases, particularly ischemic heart disease (IHD), are the leading cause of mortality globally, accounting for 16% of deaths. Effective management of ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) is crucial, as outlined in the latest European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for chronic coronary syndrome (CCS). The guidelines emphasize a structured approach comprising four key steps: a general clinical evaluation to exclude non-cardiac causes, cardiac examination, and likelihood estimation using echocardiography, diagnostic testing such as stress echocardiography and coronary CT angiography, and treatment involving lifestyle changes and medication, alongside potential revascularization. The review underscores the importance of coronary angiography and functional assessments in diagnosing ischemic heart failure (IHF) and guiding treatment strategies. Non-invasive imaging techniques, including stress echocardiography and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy, are valuable for assessing ischemia and myocardial viability while reducing unnecessary invasive procedures. Coronary CT angiography is also examined for its procedural advantages and risks. A comparative analysis of diagnostic modalities highlights the strengths and limitations of each technique, emphasizing the need for individualized approaches based on patient characteristics. The ESC 2024 guidelines advocate for a patient-centered imaging strategy based on the likelihood of coronary artery disease (CAD) while addressing the economic and environmental impacts of imaging practices. Overall, implementing these guidelines and leveraging diverse imaging modalities can optimize management strategies for IHD, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ec.2025.101243
This article belongs to the special issue Multimodality Imaging in Ischemic Heart Disease

Aim:
The study aims to assess laypersons’ perceptions of smile aesthetics before and after gingival depigmentation and to correlate these perceptions with the degree of gingival pigmentation.
Methods:
The retrospective observational study examined individuals who received gingival depigmentation following orthodontic treatment between 2019 and 2024. Fifteen records were selected based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The pre- and post-depigmentation frontal smile photos were standardized, included into a Google Form, and distributed to 40 laypeople for the assessment of smile aesthetics. The laypeople evaluated the attractiveness of smiles using a 10-point Likert scale. Experienced periodontists classified the gingival pigmentation utilizing the oral pigmentation index (OPI). The differences between the pre- and post-treatment OPI scores and smile esthetic scores were assessed using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Spearman correlation was used to evaluate the association between smile scores and OPI scores. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was employed to evaluate the inter-rater reliability of the smile ratings and OPI scores. The statistical significance was established at p ≤ 0.05.
Results:
The average OPI scores before depigmentation were 2.67 ± 0.49; however, following depigmentation, the scores significantly declined to an average of 0.33 ± 0.5 (p < 0.001). The mean smile aesthetic score pre-depigmentation was 6.72 ± 0.32, whereas after depigmentation the scores significantly improved to 7.91 ± 0.18 (p = 0.001). Spearman correlation indicated a statistically significant negative association between smile aesthetics scores and OPI scores (r = –0.76). ICC indicated excellent inter-rater reliability for the OPI (0.923) and good reliability for smile esthetic scores (0.756).
Conclusions:
The study found that gingival de-pigmentation procedures improve the OPI scores and laypeople perceive gingival hyperpigmentation unattractive. While gingival depigmentation is not mandatory, it may be recommended for individuals seeking cosmetic smile enhancements post-orthodontic therapy to improve the overall patient satisfaction.
Aim:
The study aims to assess laypersons’ perceptions of smile aesthetics before and after gingival depigmentation and to correlate these perceptions with the degree of gingival pigmentation.
Methods:
The retrospective observational study examined individuals who received gingival depigmentation following orthodontic treatment between 2019 and 2024. Fifteen records were selected based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The pre- and post-depigmentation frontal smile photos were standardized, included into a Google Form, and distributed to 40 laypeople for the assessment of smile aesthetics. The laypeople evaluated the attractiveness of smiles using a 10-point Likert scale. Experienced periodontists classified the gingival pigmentation utilizing the oral pigmentation index (OPI). The differences between the pre- and post-treatment OPI scores and smile esthetic scores were assessed using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Spearman correlation was used to evaluate the association between smile scores and OPI scores. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was employed to evaluate the inter-rater reliability of the smile ratings and OPI scores. The statistical significance was established at p ≤ 0.05.
Results:
The average OPI scores before depigmentation were 2.67 ± 0.49; however, following depigmentation, the scores significantly declined to an average of 0.33 ± 0.5 (p < 0.001). The mean smile aesthetic score pre-depigmentation was 6.72 ± 0.32, whereas after depigmentation the scores significantly improved to 7.91 ± 0.18 (p = 0.001). Spearman correlation indicated a statistically significant negative association between smile aesthetics scores and OPI scores (r = –0.76). ICC indicated excellent inter-rater reliability for the OPI (0.923) and good reliability for smile esthetic scores (0.756).
Conclusions:
The study found that gingival de-pigmentation procedures improve the OPI scores and laypeople perceive gingival hyperpigmentation unattractive. While gingival depigmentation is not mandatory, it may be recommended for individuals seeking cosmetic smile enhancements post-orthodontic therapy to improve the overall patient satisfaction.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001274

Migraine, a commonly occurring neurological disorder, disproportionately affects women during their reproductive years, and its symptoms are often intensified by hormonal fluctuations. This narrative review examines the impact of hormonal contraceptives, particularly combined oral contraceptives (COCs), on menstrual migraine (MM). This review assessed the impact of COCs on MM through a literature search in PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus using keywords like “menstrual migraine”, “hormone therapy”, and “COCs”. The selection criteria were peer-reviewed studies published between 2014 and 2024, written in English, and focused on MM treatment with COCs. Exclusion criteria were duplicates, editorials, irrelevant articles, and non-English studies. The literature reveals inconsistent results, with some studies reporting aggravation of migraine symptoms with COC use, whereas others indicate a decrease in the frequency and severity of attacks, especially with continuous use. Factors affecting these outcomes include patient age, menstrual cycle characteristics, and migraine type. It is crucial to choose contraceptives that suit individual patient profiles, considering the potential for increased migraine frequency or onset of migraine with aura in some women. Further studies are required to establish clear clinical guidelines. It is recommended to create personalized treatment plans that balance the effectiveness of migraine management with the overall health risks.
Migraine, a commonly occurring neurological disorder, disproportionately affects women during their reproductive years, and its symptoms are often intensified by hormonal fluctuations. This narrative review examines the impact of hormonal contraceptives, particularly combined oral contraceptives (COCs), on menstrual migraine (MM). This review assessed the impact of COCs on MM through a literature search in PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus using keywords like “menstrual migraine”, “hormone therapy”, and “COCs”. The selection criteria were peer-reviewed studies published between 2014 and 2024, written in English, and focused on MM treatment with COCs. Exclusion criteria were duplicates, editorials, irrelevant articles, and non-English studies. The literature reveals inconsistent results, with some studies reporting aggravation of migraine symptoms with COC use, whereas others indicate a decrease in the frequency and severity of attacks, especially with continuous use. Factors affecting these outcomes include patient age, menstrual cycle characteristics, and migraine type. It is crucial to choose contraceptives that suit individual patient profiles, considering the potential for increased migraine frequency or onset of migraine with aura in some women. Further studies are required to establish clear clinical guidelines. It is recommended to create personalized treatment plans that balance the effectiveness of migraine management with the overall health risks.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/eds.2024.00067

Breath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created internally by the body due to environmental interactions, gut and air passage bacteria, and metabolites of ingested precursors. Breath analysis may help diagnose disorders linked to changes in breath composition, according to several recent research. An analytical technique that shows promise for the metabolic examination of breath is infrared spectroscopy. Chemical substances found in exhaled human breath can be used to diagnose illnesses, determine physiological states, or evaluate environmental exposure. Exhaled breath (EB) is the perfect biological fluid because it is nearly limitless and causes little to no discomfort for the patient, which promotes collaboration. Furthermore, EB can be sampled without requiring medical professionals or privacy, and it usually doesn’t produce infectious waste (despite airborne infections), which makes breath analysis a desirable method for a variety of applications. Breath analysis is a non-invasive method that solely uses the volatile composition of the EB to characterize the bloodstream and airways’ volatile content, which indicates the state and condition of the entire body’s metabolism. The absorption strength of the metabolites is still very modest, though, because EB contains minimal amounts of them. Several of the most recent uses of infrared spectroscopy for breath analysis, published between 2020 and 2024, are presented in this study.
Breath analysis is a relatively new topic of study that has a lot of potential for both therapeutic and scientific applications. The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in breath are created internally by the body due to environmental interactions, gut and air passage bacteria, and metabolites of ingested precursors. Breath analysis may help diagnose disorders linked to changes in breath composition, according to several recent research. An analytical technique that shows promise for the metabolic examination of breath is infrared spectroscopy. Chemical substances found in exhaled human breath can be used to diagnose illnesses, determine physiological states, or evaluate environmental exposure. Exhaled breath (EB) is the perfect biological fluid because it is nearly limitless and causes little to no discomfort for the patient, which promotes collaboration. Furthermore, EB can be sampled without requiring medical professionals or privacy, and it usually doesn’t produce infectious waste (despite airborne infections), which makes breath analysis a desirable method for a variety of applications. Breath analysis is a non-invasive method that solely uses the volatile composition of the EB to characterize the bloodstream and airways’ volatile content, which indicates the state and condition of the entire body’s metabolism. The absorption strength of the metabolites is still very modest, though, because EB contains minimal amounts of them. Several of the most recent uses of infrared spectroscopy for breath analysis, published between 2020 and 2024, are presented in this study.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001308

Aim:
COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological and otolaryngological symptoms in patients two years after acute infection, with a focus on gender differences and variant-specific effects.
Methods:
A retrospective follow-up was conducted in January 2024 on 112 patients who had been hospitalized for COVID-19. Patients completed a questionnaire assessing the persistence of neuropsychiatric, otolaryngological, and systemic symptoms.
Results:
Findings reveal that 18.3% of women reported persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as memory deficits, depression, and concentration issues, compared to 5.7% of men. Otolaryngological symptoms, including anosmia and ageusia, largely resolved, with only 4.5% reporting persistent issues. Symptom persistence was more common in older individuals, women, smokers, and those with severe acute-phase illness. Neuropsychiatric symptoms remain prominent, underscoring the need for targeted long-term care.
Conclusions:
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk and severity of long COVID, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms, emphasizing its role in mitigating the long-term burden of SARS-CoV-2. Future research should explore biomolecular markers and imaging techniques to better understand and address these long-term sequelae.
Aim:
COVID-19, a multisystemic syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2, often results in long-term complications collectively referred to as long COVID. This study explores the persistence of neurological and otolaryngological symptoms in patients two years after acute infection, with a focus on gender differences and variant-specific effects.
Methods:
A retrospective follow-up was conducted in January 2024 on 112 patients who had been hospitalized for COVID-19. Patients completed a questionnaire assessing the persistence of neuropsychiatric, otolaryngological, and systemic symptoms.
Results:
Findings reveal that 18.3% of women reported persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as memory deficits, depression, and concentration issues, compared to 5.7% of men. Otolaryngological symptoms, including anosmia and ageusia, largely resolved, with only 4.5% reporting persistent issues. Symptom persistence was more common in older individuals, women, smokers, and those with severe acute-phase illness. Neuropsychiatric symptoms remain prominent, underscoring the need for targeted long-term care.
Conclusions:
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk and severity of long COVID, particularly neuropsychiatric symptoms, emphasizing its role in mitigating the long-term burden of SARS-CoV-2. Future research should explore biomolecular markers and imaging techniques to better understand and address these long-term sequelae.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001310
This article belongs to the special issue Emerging Infectious Diseases

Aim:
This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic therapy. Additionally, the study sought to identify factors influencing 30-day all-cause mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Methods:
This was a retrospective study conducted at Jordan University Hospital from January 2018 to March 2024. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with confirmed Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections were included. Data were collected from medical records, focusing on demographics, infection characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and outcomes. The susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) or non-MDR. Logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with 30-day mortality.
Results:
A total of 210 patients were included in the study, with 106 males (50.5%) and 104 females (49.5%). The majority of infections were community-acquired (n = 178, 84.8%), with the respiratory tract being the most common infection site (n = 81, 38.6%). Nearly half of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were MDR (n = 99, 47.1%). Empiric antibiotic therapy was administered to all patients, with imipenem-cilastatin (55.7%), vancomycin (35.7%), and piperacillin-tazobactam (26.7%) being the most commonly used antibiotics. Of the 210 patients, 32.4% (n = 68) received inappropriate empiric therapy. The 30-day all-cause mortality rate was 4.9% (n = 10). Multivariate analysis revealed that non-localized infections, such as bacteremia and sepsis, were strongly associated with increased mortality [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) = 17.455, P < 0.001].
Conclusions:
This study highlights the high prevalence of MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, especially in community-acquired cases, and emphasizes the need for improved antimicrobial stewardship. The significant proportion of patients (32.4%) receiving inappropriate empiric therapy calls for better guidance in antibiotic prescribing practices. The key predictor of mortality was infection localization, indicating the importance of early intervention for systemic infections to reduce mortality rates.
Aim:
This study aimed to investigate the susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, examine infection characteristics, and evaluate the appropriateness of empiric antibiotic therapy. Additionally, the study sought to identify factors influencing 30-day all-cause mortality in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Methods:
This was a retrospective study conducted at Jordan University Hospital from January 2018 to March 2024. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with confirmed Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections were included. Data were collected from medical records, focusing on demographics, infection characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and outcomes. The susceptibility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were classified as multidrug-resistant (MDR) or non-MDR. Logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with 30-day mortality.
Results:
A total of 210 patients were included in the study, with 106 males (50.5%) and 104 females (49.5%). The majority of infections were community-acquired (n = 178, 84.8%), with the respiratory tract being the most common infection site (n = 81, 38.6%). Nearly half of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates were MDR (n = 99, 47.1%). Empiric antibiotic therapy was administered to all patients, with imipenem-cilastatin (55.7%), vancomycin (35.7%), and piperacillin-tazobactam (26.7%) being the most commonly used antibiotics. Of the 210 patients, 32.4% (n = 68) received inappropriate empiric therapy. The 30-day all-cause mortality rate was 4.9% (n = 10). Multivariate analysis revealed that non-localized infections, such as bacteremia and sepsis, were strongly associated with increased mortality [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) = 17.455, P < 0.001].
Conclusions:
This study highlights the high prevalence of MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, especially in community-acquired cases, and emphasizes the need for improved antimicrobial stewardship. The significant proportion of patients (32.4%) receiving inappropriate empiric therapy calls for better guidance in antibiotic prescribing practices. The key predictor of mortality was infection localization, indicating the importance of early intervention for systemic infections to reduce mortality rates.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/emed.2025.1001312