Affiliation:
Institute of Science, Nirma University, Ahmedabad 382481, Gujarat, India
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6987-4724
Affiliation:
Institute of Science, Nirma University, Ahmedabad 382481, Gujarat, India
Email: sriram.seshadri@nirmauni.ac.in
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1547-2193
Explor Immunol. 2025;5:1003223 DOI: https://doi.org/10.37349/ei.2025.1003223
Received: May 26, 2025 Accepted: October 11, 2025 Published: October 24, 2025
Academic Editor: Jixin Zhong, Tongji Hospital, China
The human vaginal microbiome plays a pivotal role in maintaining female reproductive health through its Lactobacillus-dominated microbial ecology. These bacteria contribute to the acidic pH of the vagina by producing lactic acid, ultimately preventing the colonization of pathogens. Additionally, they produce bacteriocins and hydrogen peroxide, which are detrimental to other microorganisms. Human vaginal microbiota is subjected to alterations with advancement in age, hormonal status, puberty, menstruation cycle, pregnancy and gestation, vaginal tract diseases, exposure to antibiotics, etc. Diet, lifestyle factors, obesity, and gestational diabetes are also reported to cause a shift in vaginal microbiota. This review thoroughly illustrates the perpetually changing dynamics of vaginal microbiota throughout women’s lives, as well as focuses on the impact of dysbiosis in bacterial vaginosis. More emphasis is given on immunological changes observed during bacterial vaginosis, mainly IL-1β, and its involvement in the development of preeclampsia. Thereby, this review highlights a mechanistic link between lower genital tract disease, bacterial vaginosis, and a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, preeclampsia, via IL-1β–ROR-γt–Th17 axis, which is regulated by vitamin D, with a suggestion on how shifts in vaginal microbial community may pose a risk for preeclampsia.
Ravel et al. [1] demonstrated an exhaustive analysis of the diversity of the vaginal microbiome of women belonging to different ethnicities, such as White, Black, Asian, and Hispanic. Vaginal microbiome can be classified as five community state types (CSTs), i.e., CST-I to CST-V. Among these five, CST-I, -II, -III, and -V are dominated by L. crispatus, L. gasseri, L. iners, and L. jensenii, respectively. While CST-IV is the most diverse range of microbiome containing community, which is not usually rich in Lactobacillus species. CST-IV is a shelter for certain anaerobic bacterial populations, including Prevotella, Gardnerella, Atopobium, Megasphaera, Dialister, Eggerthella, Mobiluncus, Peptoniphilus, Finegoldia, and Sneathia [1]. Vaginal microflora dominated by Lactobacillus acquires natural protection against opportunistic pathogens. The details of how Lactobacillus are involved in protecting the vaginal environment are illustrated in Table 1.
Mode of action of Lactobacillus in protecting the vaginal environment.
| Mechanism | Description | Example | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen peroxide production | H2O2 is a potent antimicrobial oxidizing agent, toxic to catalase-negative microorganisms. It also promotes immune tolerance and prevents overgrowth of harmful bacteria, especially during pregnancy. | 94% of L. jensenii and 95% of L. crispatus produce H2O2. L. fermentum and L. acidophilus also produce H2O2 and protect against BV in pregnancy. | [2, 3] |
| Acidic pH | Lactobacillus spp., ferment glycogen, which is present in the vaginal epithelial cell, and produce D- and L-lactic acid, keeping the pH of the vaginal environment < 4.5, which is detrimental to certain pathogens. | L. crispatus, L. jensenii, L. gasseri | [2, 4–7] |
| Bacteriocin production | Bacteriocins are anti-microbial peptides produced by Lactobacillus that can hinder cell wall synthesis, nuclease activity, and inhibit spore formation, leading to the death of the pathogen. | L. salivarius CRL 1328 inhibits N. gonorrhoeae, Enterococcus faecalis.L. fermentum 123 against several Gram-positive, Gram-negative bacteria, and Candida spp. | [8–10] |
| Adherence & co-aggregation | Lactobacilli bind to epithelial cell surfaces and block receptor sites needed by pathogen colonization. They also co-aggregate with pathogens, depriving them of nutrition and forming an inhibitory barrier. | Co-aggregation is reported with G. vaginalis, Candida albicans, and E. coli. | [10–14] |
BV: bacterial vaginosis.
The composition of the vaginal microbiome changes throughout a woman’s lifespan, majorly affected by hormonal changes. In childhood, the vaginal environment is more alkaline and populated by anaerobic and skin-associated bacteria such as E. coli, Mycoplasma, and coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Puberty results in shoot in estrogenic levels, which is responsible for thickening of vaginal epithelium and an increase in glycogen availability, ultimately promoting the growth of Lactobacillus species, although some anaerobes like Prevotella and Atopobium may also be present [15, 16]. During reproductive years, women have a microbiome dominated by Lactobacillus, while others may have lower Lactobacillus levels. As women enter menopause, estrogenic levels drop, leading to reduced Lactobacillus abundance, increased vaginal pH, and a shift toward more diverse, Lactobacillus-depleted microbial communities [17, 18]. This shift is often associated with conditions such as vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA), where studies have shown a strong link between VVA and dominance of CST-IV-A microbiomes. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has been shown to partially reverse these changes, increasing glycogen levels and supporting Lactobacillus growth. Research indicates that women using HRT tend to have improved vaginal microbial profiles and reduced symptoms associated with estrogenic decline [19, 20].
Menstrual cycle causes alterations in the vaginal microbiota, particularly during menstruation, where an increase in microbial diversity and a decrease in Lactobacillus abundance has been observed [21, 22]. Studies have shown that during menses, G. vaginalis and L. iners tend to increase, while L. crispatus and L. jensenii decrease in relative abundance. These changes return to normal following menstruation [23, 24]. The luteal phase, with elevated estrogenic and progesterone levels, is associated with greater microbial stability and a return to Lactobacillus-dominant communities [17]. This pattern supports the notion that hormonal fluctuations, particularly the drop in estrogen during menses, contribute to microbiome fluctuation. However, findings are not entirely consistent. A study by Chaban et al. [21], which tracked women over a single menstrual cycle, reported minimal changes in microbial composition, though limited sample collection during menstruation may have influenced the results. Larger, longitudinal studies are needed to clarify the extent and patterns of menstrual cycle-related microbial shifts.
The pregnancy period has been reported to present a more stable and less diverse vaginal microbiome consortium, which is dominated by one or two species of Lactobacillus [25, 26]. Alhabardi et al. [27] explored vaginal CST in pregnant women. Pregnant women showed significantly lower abundance of CST-IV compared to non-pregnant women. The majority of pregnant women exhibited CST-I and -III [27]. Another study supporting these findings has been reported by MacIntyre et al. [28] in a British women’s cohort. It demonstrated that postpartum caused a diverse shift in vaginal microbiota with less abundance of Lactobacillus. A large population of African American women showed that postpartum-induced microbial alterations happen regardless of ethnicity [27]. Future insights with exhaustive research are required to understand the ethnically diverse population and their vaginal microbiome’s alterations during pregnancy.
Numerous studies have reported that the vaginal microbiome of North American, Chinese, Japanese, and European women is rich in Lactobacillus spp. [29–32]. While African American ethnicity presents vaginal microbiome with depleted abundance of Lactobacillus [29]. It has been reported that Black women harbour a vaginal microbiome of CST-IV four times than that seen in Caucasian women. Lactobacillus abundance is seen to be less common in Black women than their Caucasian counterparts [31]. As mentioned earlier, Lactobacillus dominant CST-I, -II, -III, and -V are seen in Asian and American women, while Hispanic and Black women reported to have CST-IV with higher levels of pathogenic bacteria [1].
One of the crucial factors affecting the population of the vaginal microbiome is diet. A diet rich in carbohydrates results in high levels of glycogen, which is a sole nutritional requirement of lactic acid bacteria. Thus, these carbohydrate-rich diets promote the growth of Lactobacillus [33]. Insufficient intake of vitamin A, C, D, E, and β-carotene, as well as calcium, has been reported to be associated with increased risk of bacterial vaginosis (BV) [34–36]. Fat rich diets are also linked with a higher risk of BV. On the other hand, vitamin E, folate, and calcium supplementation reduce the chances of BV infection [37, 38].
High-intensity workouts have been shown to affect the vaginal microbiota. It increases the alpha diversity and resembles the profiles of CST-IV [22]. Obese women with a high body mass index (BMI) ratio presented a lower abundance of Lactobacillus with elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines when compared to their healthy counterparts [39]. Lower BMI upon bariatric surgery resulted in a significant increase in Lactobacillus within six months of the surgery [40].
Chronic stress can activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to elevated levels of cortisol that can suppress immune function and disrupt vaginal microbial homeostasis by reducing Lactobacillus abundance [41]. This stress-induced dysbiosis has been linked with increased risk of BV and preterm birth. Multiple studies have demonstrated that stress is an independent risk factor for BV. Culhane et al. [42] found that pregnant women experiencing moderate to high stress measured using the Cohen Perceived Stress Scale were over twice as likely to have BV compared to those with low stress levels. Furthermore, racial differences in BV prevalence have been associated with differential exposure to chronic stress, with Black women reporting higher stress levels and significantly increased rates of BV compared to White women [43].
The factors influencing the vaginal microbiota diversity, such as age, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, ethnicity, diet, BMI and exercise, and stress, are illustrated in Figure 1.
Alteration in the diversity of normal vaginal ecology is termed “vaginal dysbiosis”, which can result in adverse outcomes. Dysbiotic state exhibits a reduction in the CST-I, -II, -III, and -V, which are dominated by Lactobacillus and show an increase in bacterial population belonging to CST-IV, which contains Prevotella, Gardnerella, Atopobium, Mobiluncus, etc. These bacteria can further initiate a cascade of inflammatory reactions, inducing local and systemic inflammation [1].
BV is a polymicrobial disease seen in women of childbearing age. It can either be symptomatic or asymptomatic, and women with BV experience discomfort, itching, vaginal discharge, malodour from the vagina, burning sensation, and an increased pH of the vaginal environment. BV is characterised by the shift of vaginal microbiome from Lactobacillus-dominated CST to the CST-IV with reduced count of Lactobacillus along with the presence of opportunistic anaerobic pathogens [44]. The most prevalent bacterial species associated with BV are G. vaginalis, Prevotella, Mobiluncus, Sneathia, Atopobium, Peptostreptococcus, and Bacteroidetes. Previously, BV was referred to as Haemophilus vaginalis, but it was later found that this bacterium did not belong to the genus Haemophilus and was then renamed as G. vaginalis.
Clinically, BV is diagnosed based on Amsel’s criteria. According to this method, there should at least be three of the following symptoms in the sample: vaginal discharge with basic pH, i.e., pH > 4.5, discharge, release of fishy smell upon addition of potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution to vaginal discharge, and presence of squamous epithelial cells coated with bacterial cells [45]. Another method for BV diagnosis is based on the Nugent score system. This method implies microscopical examination of vaginal discharge for the presence of Gram-negative bacteria. Nugent scores 0–3 are considered normal samples, scores 4–6 are intermediate, while scores 7–10 are considered as BV [46]. One of the most widely reported bacteria causing BV is G. vaginalis, which plays a crucial pathogenic role in the pathogenesis of BV via contributing to pro-inflammatory characteristics, biofilm formation, competition with other host microbiota, and virulence factors. It belongs to the genus Gardnerella of the family Bifidobacteriaceae. They are rod-shaped, non-motile, and are Gram-variable [47]. G. vaginalis has virulence factors like vaginolysin and adhesins. Vaginolysin shows cytolytic activities on red blood cells and then thrives on them for nutrition [48]. G. vaginalis also forms biofilms that provide a favourable environment for other pathogens and lead to antibiotic resistance with persistent infections [48].
Vaginal swabs of BV patients have shown an increased level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, IL-1β, and IL-1α [49]. The mechanistic link between G. vaginalis and immune activation has been studied. In THP-1 monocytes and human macrophages, exposure to G. vaginalis showed a significant upregulation of nucleotide-binding domain, leucin-rich containing family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3). This NLRP3 inflammasome further cleaves pro-IL-1β into IL-1β, which is an indicator of pro-inflammatory cascade initiation. Another study has also reported the significantly elevated levels of IL-1β correlated with higher neutrophil count in BV patients when compared to their healthy counterparts [50]. The molBV, a diagnostic tool that uses 16s rRNA gene sequencing for BV diagnosis, showed increased levels of IL-1β, and an increased ratio of IL-1β/IP-10 cytokine is associated with clearance of high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV). This study proved that L. iners is associated with pro-inflammatory characteristics related to BV [51]. Women with BV are also reported to have significantly higher amounts of not just IL-1β but also of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and IL-6 [52, 53]. Conclusively, it can be said that the BV condition leads to an inflammatory milieu with an elevation in the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 via the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Impact and association of fluctuations in vaginal ecology have been studied in various complications related to pregnancy, such as miscarriage, recurrent miscarriage, premature birth, gestational diabetes, preterm premature rupture of membrane, and preeclampsia (PE). Table 2 describes vaginal microflora diversity associated with these diseases.
Vaginal microflora dysbiosis in various pregnancy complications.
| Pregnancy complications | Vaginal microflora dysbiosis | References |
|---|---|---|
| Miscarriage | Low abundance of Lactobacillus but elevation in L. iners, high levels of B. plebeius, G. vaginalis, M. girerdii, and increased diversity of CST-IV | [54–57] |
| Recurrent miscarriage | Decreased abundance of Lactobacillus, high abundance of Prevotella, Gardnerella, Pseudomonas, family Ruminococcaceae, Anaerococcus | [58–60] |
| Preterm birth | Low abundance of Lactobacillus, high abundance of G. vaginalis, increased diversity of CST-IV with L. iners dominance, high levels of S. amnii, Prevotella, Atopobium vaginane, Megasphaera | [61–64] |
| Gestational diabetes | Higher abundance of Bacteroidetes, Veillonella, Klebsiella, Escherichia-Shigella, Enterobacter, Enterococcus, high levels of fungal flora like Candida and Saccharomyces | [65, 66] |
| Preterm premature rupture of membrane | L. iners, U. parvum, P. bivia, P. timonensis, G. vaginalis positively associated | [67] |
| Preeclampsia | High abundance of Prevotella bivia | [68] |
CST: community state type.
This review discusses one of the pregnancy complications, PE, and its correlation with BV. The review describes how BV and its immune consequences affect an individual during pregnancy, eventually setting an alarm for early development and/or aggravation of PE (Table 2).
PE is considered a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy that is one of the most common gynaecological disorders. Globally, PE negatively impacts approximately 2–8% of pregnancies, leading to fetal and maternal morbidity as well as mortality. This disorder is usually seen after 20 weeks of gestation and is characterised by hypertension (> 140/90 mmHg) and the presence of proteins in urine referred to as proteinuria (> 300 mg/24 h) [45, 69]. There are numerous risk factors for the development of PE, including pregnancy at an advanced age, renal diseases, obesity, gestational diabetes, and chronic hypertension. Most importantly, a previous pregnancy with PE possesses a significant risk for the development of PE in the following subsequent pregnancies [69]. These days, genetic predisposition and its association with PE have also come to the surface. Chromosome 13 with a single nucleotide polymorphism proximate to the FLT-1 locus is associated with an increased risk of developing PE [70].
Pathologically, PE is characterised by impaired and defective placentation, spiral arteries leading to hypoxia, oxidative stress, and placental ischemia. Hypertension and proteinuria are seen due to enhanced endothelial dysfunction. One of the placental antiangiogenic factors, i.e., soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, antagonises the placental and vascular endothelial growth factors, and this results in impaired functionality of endothelial growth factors. This ultimately leads to venous congestion, contributing to reduced blood flow to various organs, including the heart [71].
During PE, the immune tolerance shifts from normal to pro-inflammatory phenotype with an imbalance in the population of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) and a subset of helper T cells (Th cells), which is Th17. PE is associated with pro-inflammatory immune markers in peripheral blood, which are known to induce oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and local as well as systemic inflammation, leading to fetal mortality. PE is not only a multi-factorial disorder, but it is also an “immunovascular” complication, pertaining to severe damage at the maternal-fetal axis, and may lead to systemic immune dysfunction. This section of the review explains the role of Th17/Treg cell profiling in PE.
Treg cell population is a crucial factor involved in the maintenance of tolerance against the fetus during pregnancy, and a high abundance of these immune cells is seen under normal pregnancy cases. They are the subpopulations of CD4+CD25+ lymphocytes. Treg cells differentiation and functionality require expression of a transcription factor, forkhead box protein 3 (Foxp3) [72, 73]. On the other hand, another independent subset of CD4+ T cells, Th17 cells, possesses pro-inflammatory characteristics. Th17 requires retinoic acid-related orphan receptors-γt (ROR-γt) for its differentiation and functions.
Numerous studies have reported the role of imbalance in Th17/Treg cells in PE. Eghbal-Fard et al. [74] showed that PE patients’ peripheral blood samples exhibited significantly elevated levels of Th17 cells and upregulation of ROR-γt with significant downregulation of Foxp3 and IL-10 mRNA. These were indications of an altered ratio of Th17/Treg cells with a predominance of Th17 cells. PE samples also showed upregulation of microRNAs like miR-106b and miR-326, which suggests the differentiation of Th17 cells. Higher expression of CD81 in trophoblasts, which is ultimately responsible for Th17 cell differentiation over Treg cells, was also seen in PE [74]. Comparative analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from PE and normal pregnant women showed a significant decrease in Foxp3 expression with a significant decrease in the Treg cell population. This was accompanied by a significant elevation in the expression of ROR-γt in PE patients, suggesting a higher population of Th17 cells in PE [75]. Zhang et al. [76] studied the immunological differences associated with severe PE (sPE). They analysed peripheral blood samples of sPE and healthy pregnant women, and it showed that sPE patients had significantly higher percentages of Th17 and Th22 cells in PBMC when compared to their normal counterparts. sPE patients also had decreased concentration of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in plasma, with a notable reduction in the Treg cells. They also established a positive correlation between Th17 and Th22, leading to pro-inflammatory characteristics. Thus, it can be said that sPE may have a Th17 and Th22-dominated immunological profile with reduced abundance of Treg cells [76].
Furthermore, the frequencies of CD4+ T cells expressing Foxp3 as an indication of Treg cells and IL-17 as an indicator of Th17 cells have also been reported. Researchers compared the peripheral blood samples of healthy pregnant women and PE patients during the third trimester to check Treg cell markers such as CD4+CD25high, CD4+CD127lowCD25+, and CD4+Foxp3+, as well as Th17 cell marker CD4+IL-17+ T cells. Healthy pregnant women had significantly higher frequencies of CD4+CD25high, CD4+CD127lowCD25+, and CD4+Foxp3+ compared to PE patients and nonpregnant controls. PE samples showed a significant elevation in the percentage of CD4+IL-17+ T cells. PE patients exhibited a decreased ratio of CD4+Foxp3+ and CD4+IL-17+ T cells, suggesting a higher abundance of Th17 cells, resulting in a pro-inflammatory phenotype [77]. This finding was in alignment with another paper that reported similar results. PE patients showed significantly higher percentage of CD3⁺CD4⁺ T lymphocytes that produce IL-17A, compared to healthy pregnant individuals. CD4⁺CD25⁺Foxp3⁺ Treg cell markers were notably downregulated in PE than in controls. Whether the Treg cells show proliferative responses as well as suppressive capability was also studied as an index of stimulation (SI). In PE samples, the addition of autologous Treg cells to CD3⁺CD4⁺CD25⁻ T lymphocytes did not make a difference in SI, which highlights the fact that it has lost its suppressive characteristic. While it showed a significant reduction in SI in healthy pregnant women, suggesting its immunosuppressive function [78].
Vitamin D is a diverse, multifaceted master regulator of the extracellular system, possessing several antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties. Vitamin D induces the transcription of genes encoding antimicrobial peptides like cathelicidin (LL-37) and β-defensin 2, which can disrupt the bacterial cell membrane [79]. It promotes cell death via inducing autophagy or lysosomal disruption and inhibits the viral replication and invasion, exerting antiviral properties [80]. Vitamin D inhibits NF-κB, leading to downregulation of IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-12, and TNF-α [81]. More importantly, vitamin D also maintains the ratio of Th17/Treg cells. It can suppress ROR-γt, thereby inhibiting the differentiation of Th17 cells [82] and promoting the transcription of Foxp3, in turn promoting the differentiation of Treg cells [83]. It also promotes the growth of Lactobacillus in the vagina via promoting insulin secretion. This insulin secretion can result in glycogen synthesis and its deposition. Increased glycogen in the vaginal microenvironment lowers the vaginal pH, providing suitable conditions for the colonisation of Lactobacillus, simultaneously inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms [84]. Vitamin D maintains vaginal epithelial barrier integrity via promoting vaginal epithelial cell growth, increasing the thickness of the barrier, and restricting the invasion of pathogens [85].
Numerous studies have shown that a deficiency of vitamin D can have an adverse effect on vaginal health and pregnancy outcomes. This section of the review illustrates how vitamin D deficiency (VDD) can increase the risk of developing BV and PE.
In non-pregnant women, lower levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) have been reported to be significantly associated with increased risk of symptomatic and asymptomatic BV [86, 87]. A meta-analysis revealed that VDD during pregnancy can increase the risk of BV by 54% and it is associated with ethnicity and gestational age. Up to 56% and 122% increased prevalence of BV due to VDD is seen in the case of African women and the first trimester, respectively [88]. A dose-dependent relationship between BV and maternal vitamin D levels has also been studied. Pregnant women with severe VDD, i.e., < 20 nmol/L, had a 57% prevalence of BV. VDD increased the risk of developing BV by 1.26 to 1.56-fold [35]. A National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-based meta-analysis showed a significantly increased odds of developing BV in pregnant women with VDD, wherein non-Hispanic Black women had increased prevalence of BV as well as VDD [36]. Additionally, Liu et al. [89] reported that VDD acts as an independent risk factor for BV, and the risk increases as the vitamin D levels drop. However, this association can only be seen up to vitamin D levels of ≥ 63.1 nmol/L. This was considered a plateau, above which the vitamin D supplementation did not reduce the risk of BV [89].
Significant association between VDD and PE has also been reported. Women in their 22 weeks or fewer gestational weeks with VDD had developed PE in the later stages of their pregnancies. It was observed that a 50 nmol/L decrease in the levels of vitamin D resulted in almost twice times higher risk of developing PE [90]. A meta-analysis revealed that VDD with levels < 20 ng/mL was associated with a significant risk of PE [91]. In an Indian cohort-based study, PE showed a significant 11-fold increased odds due to VDD [92]. Another Indian cross-sectional study reported that 82.8% of preeclamptic women had VDD. It was seen that sPE was associated with severely low levels of vitamin D, indicating a dose-dependent association [93]. In Arab-American cohorts, pregnant women with VDD showed a 3-fold increased risk of developing PE [94]. These clinical findings indicate that vitamin D acts as a unifying factor that bridges the gap between BV and PE through the IL-1β–ROR-γt–Th17 axis.
BV and PE are two clinically distinct disorders. However, they share a common factor in their underlying pro-inflammatory milieu. In case of BV, the disruption of the Lactobacillus-dominated vaginal microbiota leads to an overgrowth of opportunistic pathogens such as G. vaginalis, which provokes local inflammation via activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and elevated levels of cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. IL-1β is a known inducer of Th17 cells. As mentioned earlier, Foxp3 is a key transcriptional factor required for differentiation and the functions of Treg cells. IL-1β can induce the alternative splicing of Foxp3 at exon 7, leading to Foxp3 isoform Foxp3Δ7. This isoform induces differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into the inflammatory Th17 subtype [95]. IL-1β, along with IL-6 and IL-23, has been reported to activate ROR-γt, which is a Th17 lineage-specific transcription factor, leading to differentiation of Th17 cells from naïve CD4+ T cells [96]. Parallelly, VDD also fails to inhibit IL-1β, thereby aggravating Th17 predominance. PE, on the other hand, is characterised by systemic immune dysregulation, specifically the imbalance between pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and immunosuppressive Treg cells, which leads to elevated IL-17, decreased IL-10, and increased oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. These immune responses reflect a shift from immune tolerance to a pro-inflammatory state in both conditions. BV and PE both present an increased ratio of Th17/Treg cells.
Therefore, it can be hypothesised that microbial dysbiosis in the vaginal ecosystem, i.e., vaginal dysbiosis in case of BV, can contribute to pro-inflammatory characteristics with an elevation in IL-1β, a potent inducer of Th17 cells. IL-1β, via upregulating the ROR-γt, VDD, or alternative splicing of Foxp3, can induce the differentiation of Th17 cells, which are the immunological players responsible for local inflammation. The lower genital tract disorder BV, which has already provoked local inflammation in vaginal mucosa, can lead to systemic inflammation via favouring the differentiation of Th17 cells, which may go up to the upper genital tract, where it can induce systemic inflammation with endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress and high systolic as well as diastolic blood pressure, all of which are symptoms of PE. Thus, when an individual with vaginal microbiota dysbiosis due to BV conceives, she will be at higher risk for developing PE in later stages of her pregnancy. Figure 2 displays the vitamin D-regulated IL-1β–ROR-γt–Th17 axis responsible for a dynamic interaction between BV and PE.
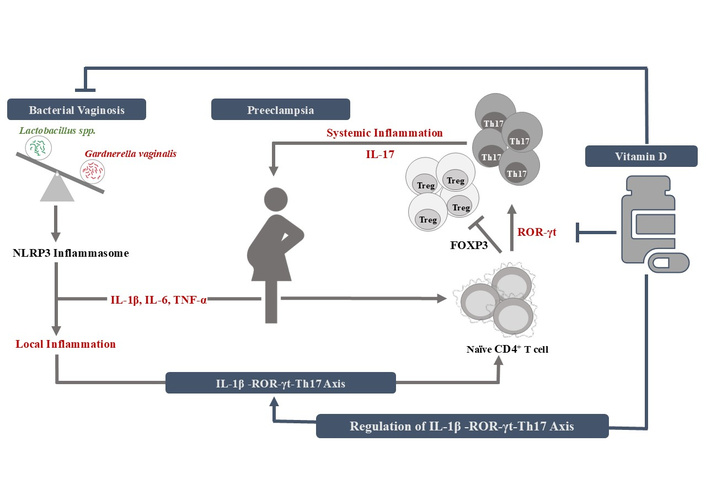
Crosstalk between bacterial vaginosis and preeclampsia via vitamin D-regulated IL-1β–ROR-γt–Th17 axis. FOXP3: forkhead box protein 3; ROR-γt: retinoic acid-related orphan receptors-γt; Th17: helper T cells 17; Treg: regulatory T cells.
Vaginal microbiome is a vital player in women’s reproductive health, and a healthy Lactobacillus-dominant vaginal microbial environment provides protective benefits to the host. However, any factors causing changes in this microbial community can provoke a local or system-wide inflammation with adverse consequences. This review illustrates a probable interplay between dysbiosis in vaginal microbiota and its immunological consequences, which might be an alarming factor for pregnancy-related complications. BV with a highly diverse vaginal microbial community CST-IV, high abundance of G. vaginalis, and the following shift in immunophenotype from normal to pro-inflammatory, ultimately possesses a major risk for the development of PE, via IL-1β–ROR-γt–Th17 axis. Vitamin D is also emerging as a master regulator of this axis, as its deficiency can aggravate IL-1β-mediated inflammation along with impairment of the vaginal epithelial barrier. The reversal of this diseased inflammatory state can be achieved by addressing the vaginal dysbiosis first, followed by already available marketed drugs and vitamin D supplementation. This way, it not only ensures symptom management but also restores a balance in the vaginal microbial community, which reduces the chances of recurrent infection as well as decreases the chances of complications in future pregnancies of an individual. The newly emerging association between vaginal health and hypertensive disorder of pregnancy calls for speculative and exhaustive future research. Screening for any changes in vaginal ecology and vitamin D check-ups during early gestation periods can aid in understanding this complicated vaginal microbial-immuno-obstetric axis, which can open the doors for new diagnostic methods and microbiota-targeted therapies. Understanding and employing this axis can improve maternal and fetal health during complicated pregnancies.
BMI: body mass index
BV: bacterial vaginosis
CSTs: community state types
Foxp3: forkhead box protein 3
HRT: hormone replacement therapy
IL: interleukin
NLRP3: nucleotide-binding domain, leucin-rich containing family, pyrin domain containing 3
PBMCs: peripheral blood mononuclear cells
PE: preeclampsia
ROR-γt: retinoic acid-related orphan receptors-γt
SI: index of stimulation
sPE: severe preeclampsia
Th cells: helper T cells
TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α
Treg cells: regulatory T cells
VDD: vitamin D deficiency
VVA: vulvovaginal atrophy
The authors would like to thank Nirma University, Ahmedabad-Gujarat, for providing the NU-fellowship to Ms. Devanshi Gajjar.
DG: Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing, Validation. SS: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing—review & editing, Supervision. Both authors read and approved the submitted version.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Open Exploration maintains a neutral stance on jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliations and maps. All opinions expressed in this article are the personal views of the author(s) and do not represent the stance of the editorial team or the publisher.
Copyright: © The Author(s) 2025. This is an Open Access article licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
View: 2474
Download: 37
Times Cited: 0