4 results in Exploration of Digestive Diseases
Latest
Sort by :
- Latest
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
Open Access
Original Article
Familial achalasia isolated or syndromic: about 18 families
Amar Tebaibia ... Nadia Oumnia
Published: October 26, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:276–281
This article belongs to the special issue Advances in Hepato-gastroenterology: Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Disease Stratification

Open Access
Review
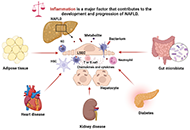
Molecular mechanisms of metabolic disease-associated hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Chunye Zhang ... Ming Yang
Published: October 25, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:246–275
This article belongs to the special issue Cellular and Molecular Targets for NAFLD or MAFLD Treatments and Their Functions in Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, and Cancer
Open Access
Review
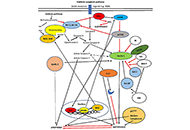
Interplay of autophagy, apoptosis, and senescence in primary biliary cholangitis
Elias Kouroumalis ... Argyro Voumvouraki
Published: October 16, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:223–245
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Open Access
Review
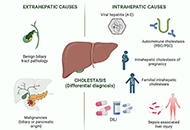
Drug-induced cholestasis: causative agents and challenges in diagnosis and management
Jose M. Pinazo-Bandera ... Miren García-Cortés
Published: September 18, 2023 Explor Dig Dis. 2023;2:202–222
This article belongs to the special issue CHOLESTASIS
Journal Information