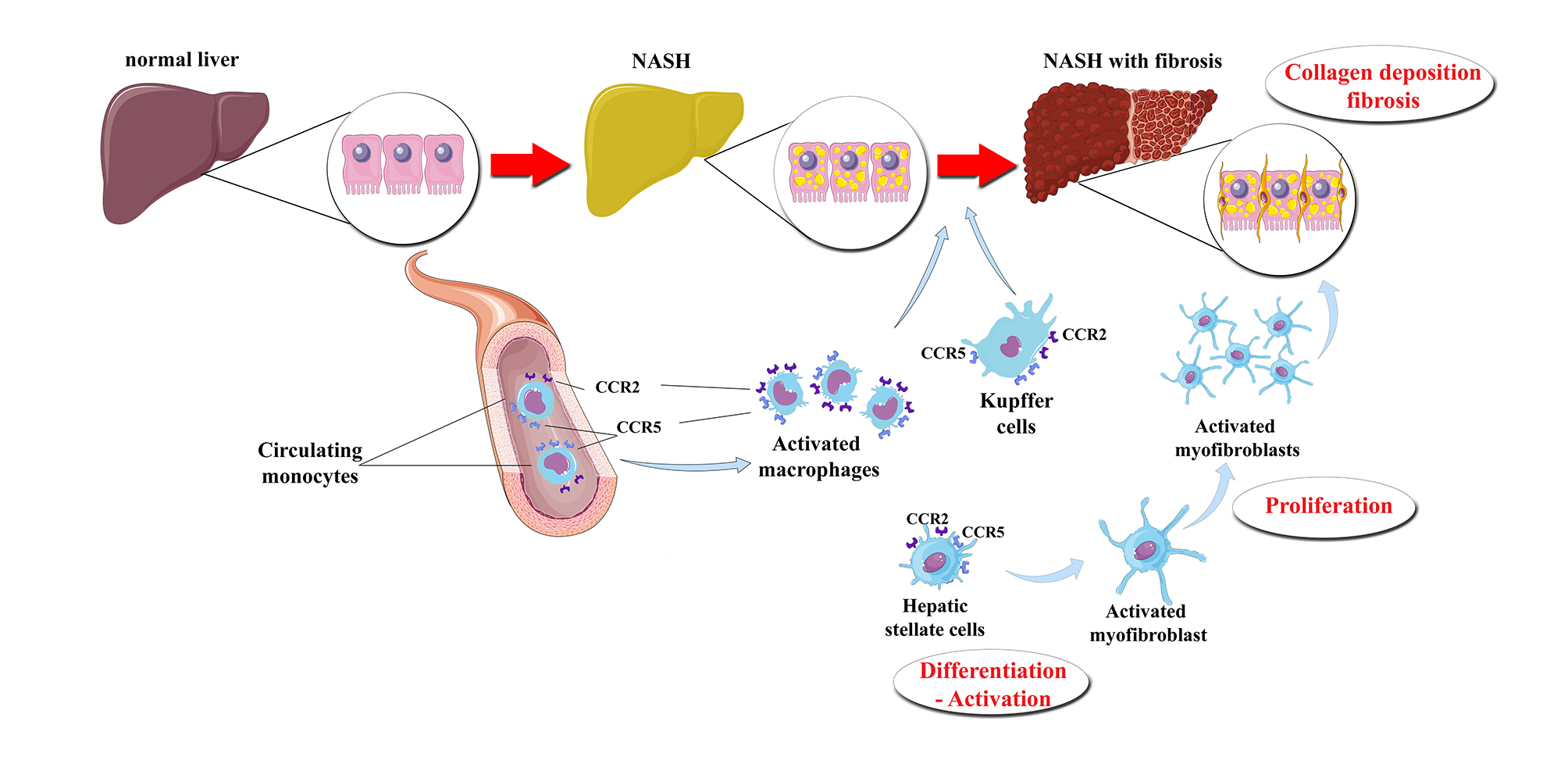
The presumptive effect of CVC on the liver of patients with NASH. Under certain pathogenetic factors (“hits”), a normal liver may subsequently progress to steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis. The activation of CCR2 and CCR5, which are possibly located on the Kupffer cells*, macrophages infiltrating the liver and HSCs, may result in their transformation and activation. Thus, hepatic inflammation and fibrosis are initiated and propagated. CVC is a dual CCR2 and CCR5 antagonist that seems to attenuate the activation of Kupffer cells, infiltrating macrophages, and HSCs, thus possibly mitigating hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. * CCR2 may be expressed in Kupffer cells of animal models, whereas CCR2 may not be expressed or may be not functional in human Kupffer cells